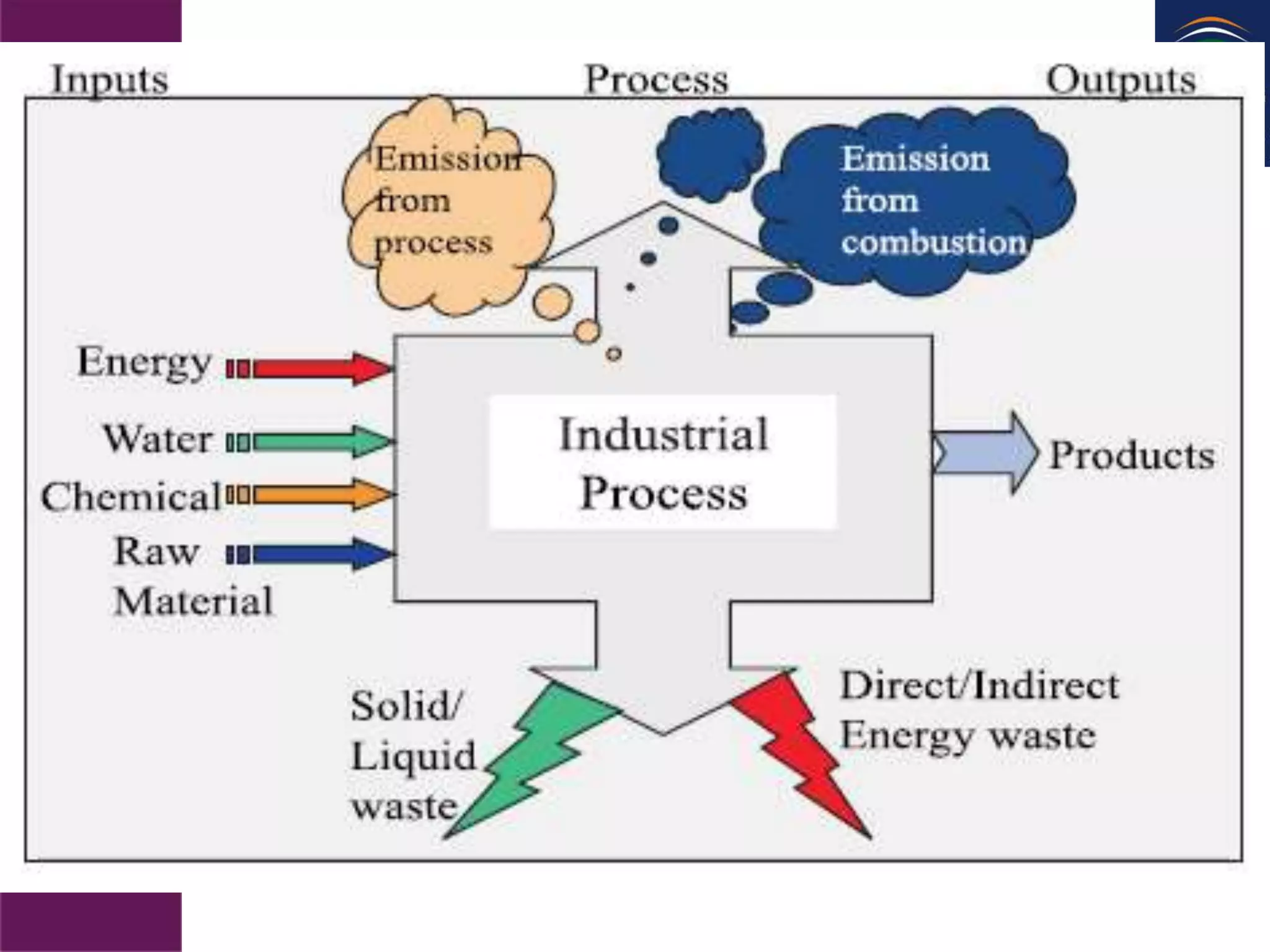
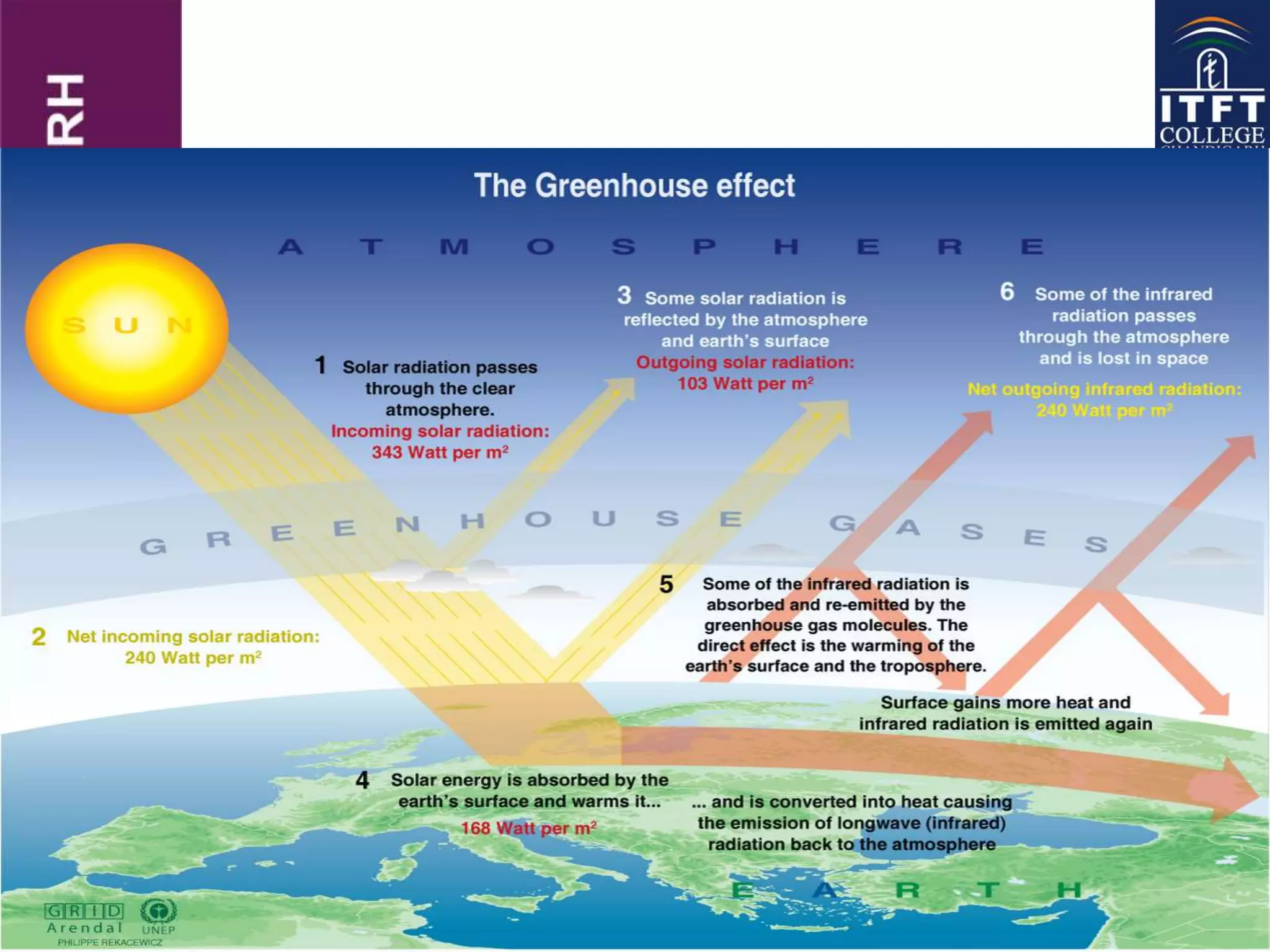
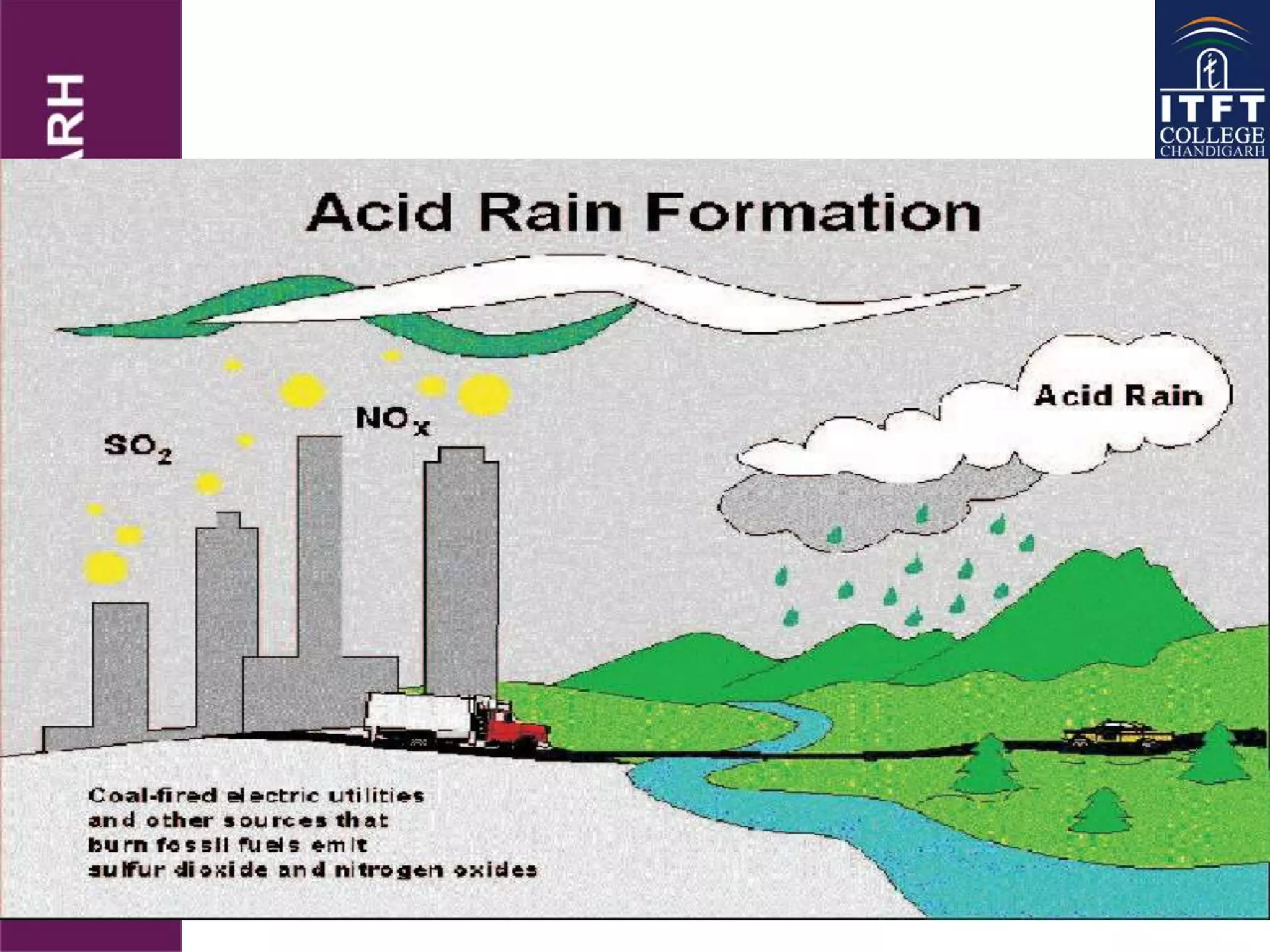
Usage of fossil fuels for energy and transportation leads to various air pollutants like SO2, NOX, particulate matter, and greenhouse gases that cause environmental damage. This includes health problems, effects on climate and aquatic life, acid rain, smog, and global warming. Human activities that release these pollutants, especially the combustion of coal, oil, and gas, have increased the greenhouse effect and threaten to disrupt the climate through higher temperatures, rising sea levels, and more extreme weather.