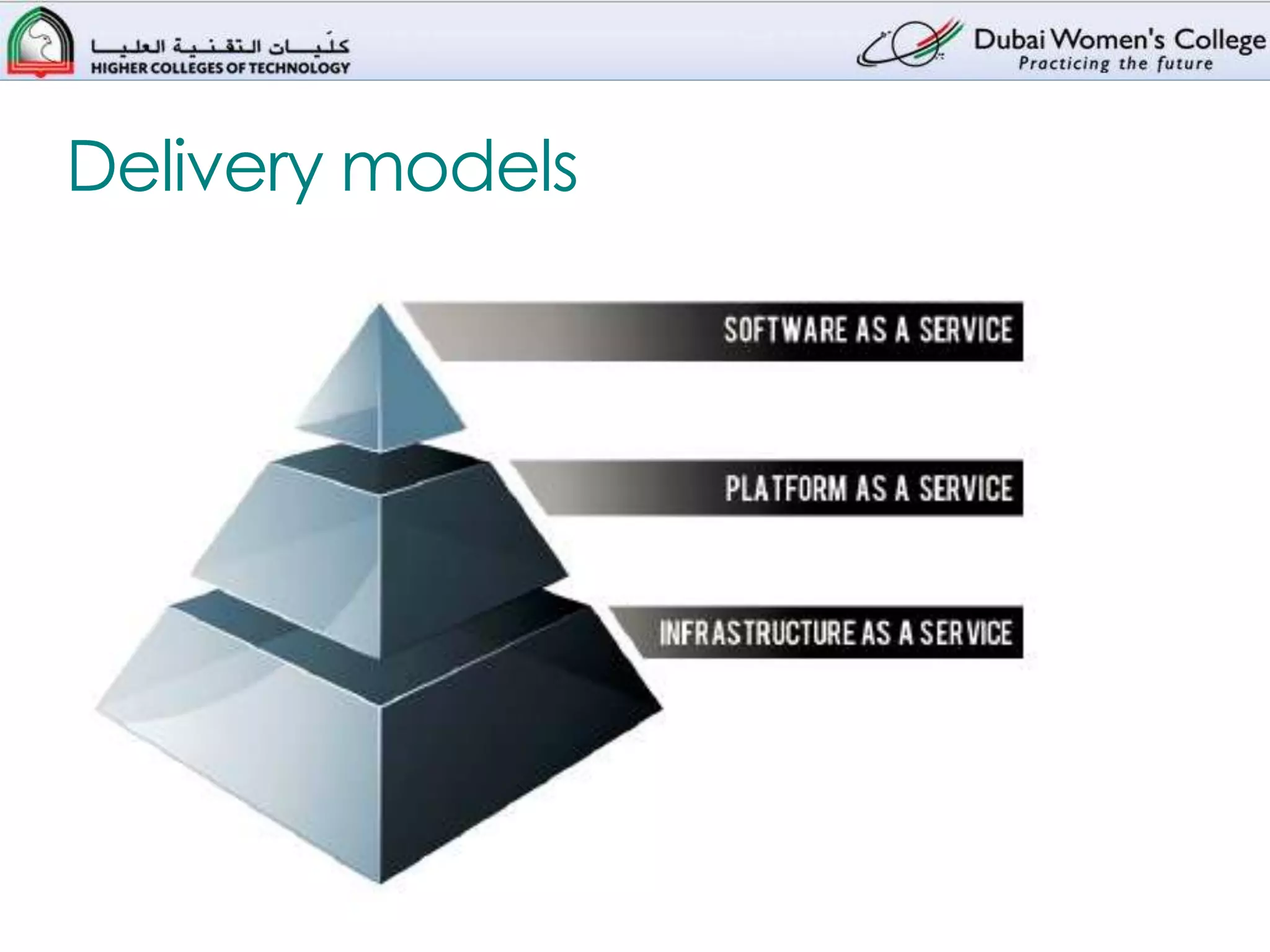
This document provides an overview of cloud computing. It defines cloud computing as using computing resources over the Internet rather than owning local hardware and software. The key benefits are lower costs through economies of scale and flexibility to scale resources up or down as needed. There are three main delivery models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides basic storage and computing resources, PaaS provides development environments, and SaaS provides complete applications. Cloud services can be public, private, or hybrid combinations of both.



![Emerging Technology: Cloud Computing
What is Cloud computing?
• “A model of computing where firms and individuals
obtain computing power and software applications over
the Internet, rather than purchasing their own hardware
and software.” [1, P.196]
• According to Wikipedia
• Cloud computing is Internet-based computing, whereby shared
resources, software and information are provided to computers and
other devices on-demand, like a public utility.
[1] Laudon, K. Laudon, J. “Management Information Systems” 2010, 11/e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itecn453cloudcomputing-130317043250-phpapp01/75/Itecn453-cloud-computing-4-2048.jpg)
![Emerging Technology: Cloud Computing
• “The cloud in cloud computing provides the means
through which everything — from computing power to
computing infrastructure, applications, business processes
to personal collaboration — can be delivered to you as a
service wherever and whenever you need.” [3]
• Elastic: cloud can easily expand and contract.
• This elasticity means that users can request additional
resources on demand and just as easily de-provision (or
release) those resources when they’re no longer needed.
[3] Cloud Computing for Dummies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itecn453cloudcomputing-130317043250-phpapp01/75/Itecn453-cloud-computing-5-2048.jpg)


![Facts & Statistics
• Fastest growing form of computing
• Estimated market size in 2009 of $8 billion
• Projected size of $160 billion in 2012 [1, P.196]
• Hardware
• Firms IBM, HP, and Dell are building huge, scalable cloud
computing centers which provide computing power, data storage,
and high speed Internet connections to firms who rely on the
Internet for business software applications. [1, P.196]
• Software
• Software firms such as Google, Microsoft, SAP, Oracle and
Salesforce.com sell software applications as services delivered over
the Internet. [1, P.196]
[1] Laudon, K. Laudon, J. “Management Information Systems” 2010, 11/e](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itecn453cloudcomputing-130317043250-phpapp01/75/Itecn453-cloud-computing-9-2048.jpg)






![References
• [1] Laudon, K. Laudon, J. “Management Information
Systems” 2010, 11/e
• [2] <csrc.nist.gov/groups/SNS/cloud-computing/cloud-
def-v15.doc> Oct, 06 2010.
• [3] Cloud Computing for Dummies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/itecn453cloudcomputing-130317043250-phpapp01/75/Itecn453-cloud-computing-19-2048.jpg)