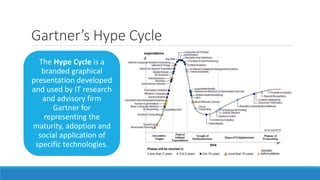
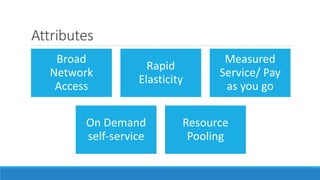
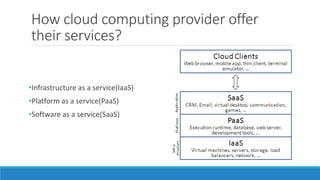
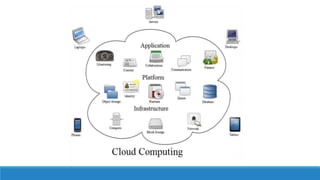
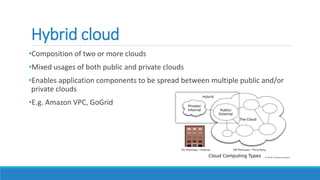
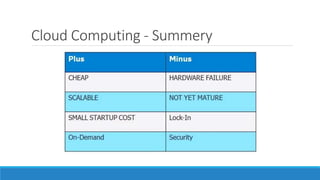
This document discusses cloud computing. It defines cloud computing as utilizing remote servers and networks to allow centralized data storage and online access to computer resources. Cloud computing delivers IT services over the internet. It discusses the key attributes of cloud computing including broad network access, rapid elasticity, and pay-as-you-go pricing. It also outlines the main service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), deployment models (private, public, hybrid clouds), and some security concerns regarding cloud computing such as sharing infrastructure with other tenants.