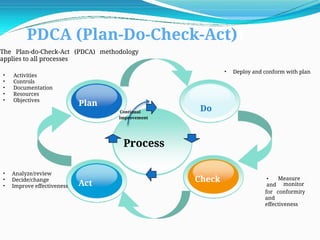
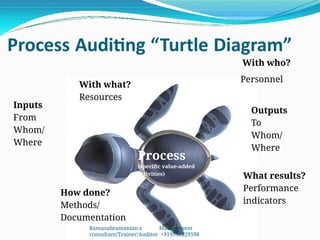
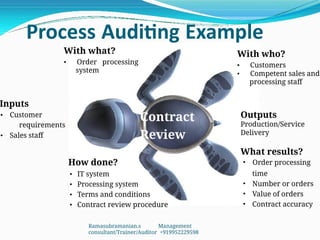
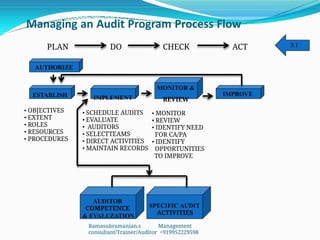
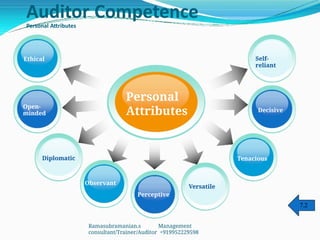
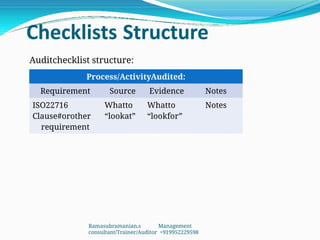
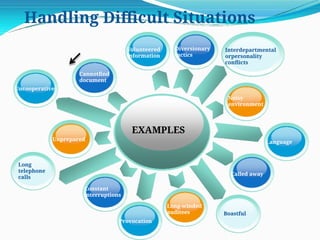
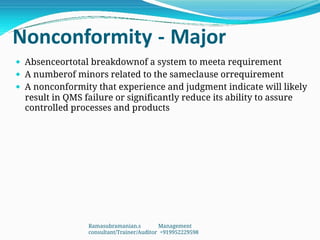
The document outlines the principles and processes involved in auditing, emphasizing the importance of systematic evaluations to ensure compliance with standards such as ISO 9001:2008. It covers various aspects including auditor responsibilities, types of audits, the process approach, and management of audit programs. Additionally, the document discusses techniques for conducting audits, handling nonconformities, and the significance of continuous improvement within management systems.