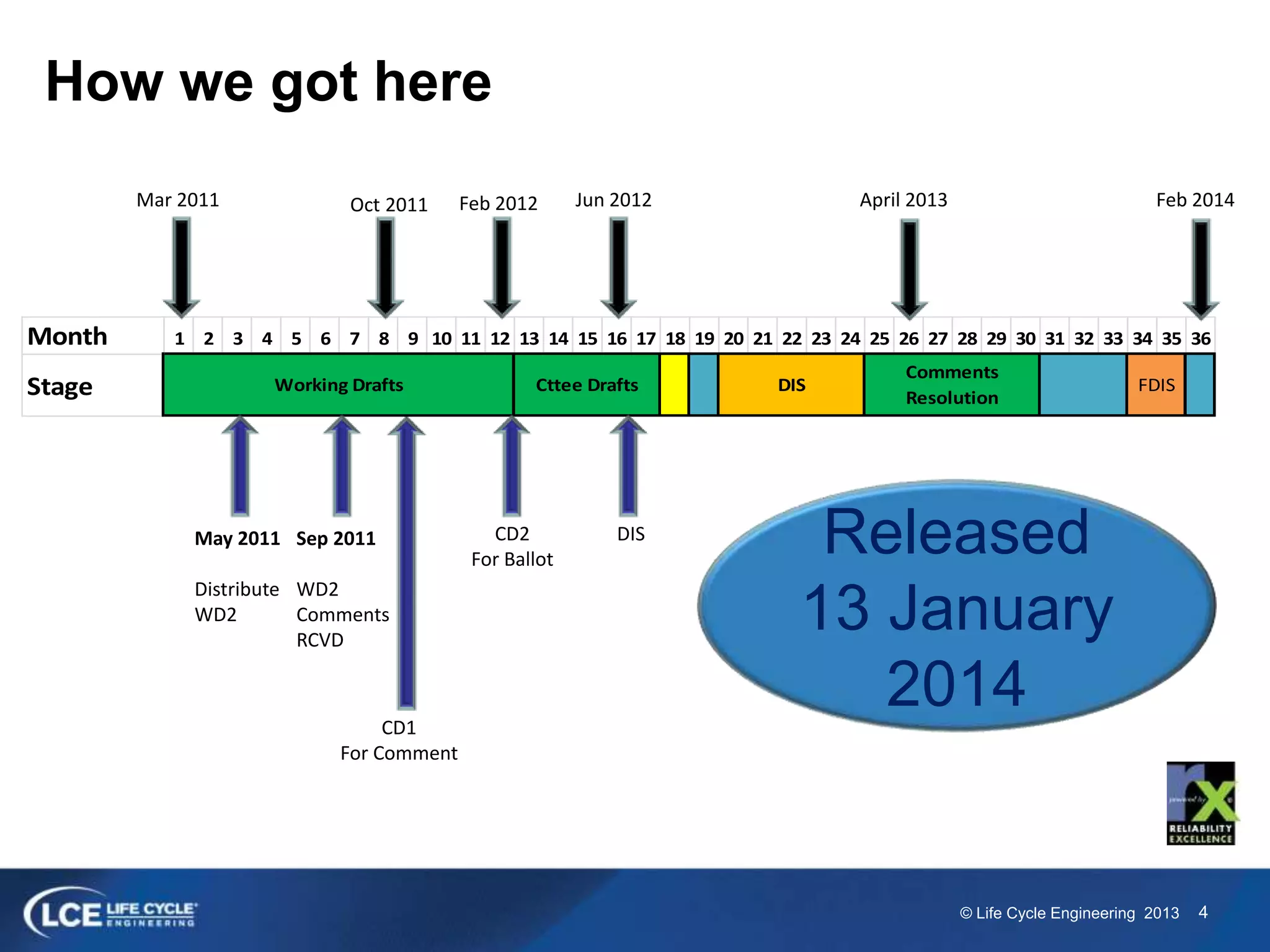
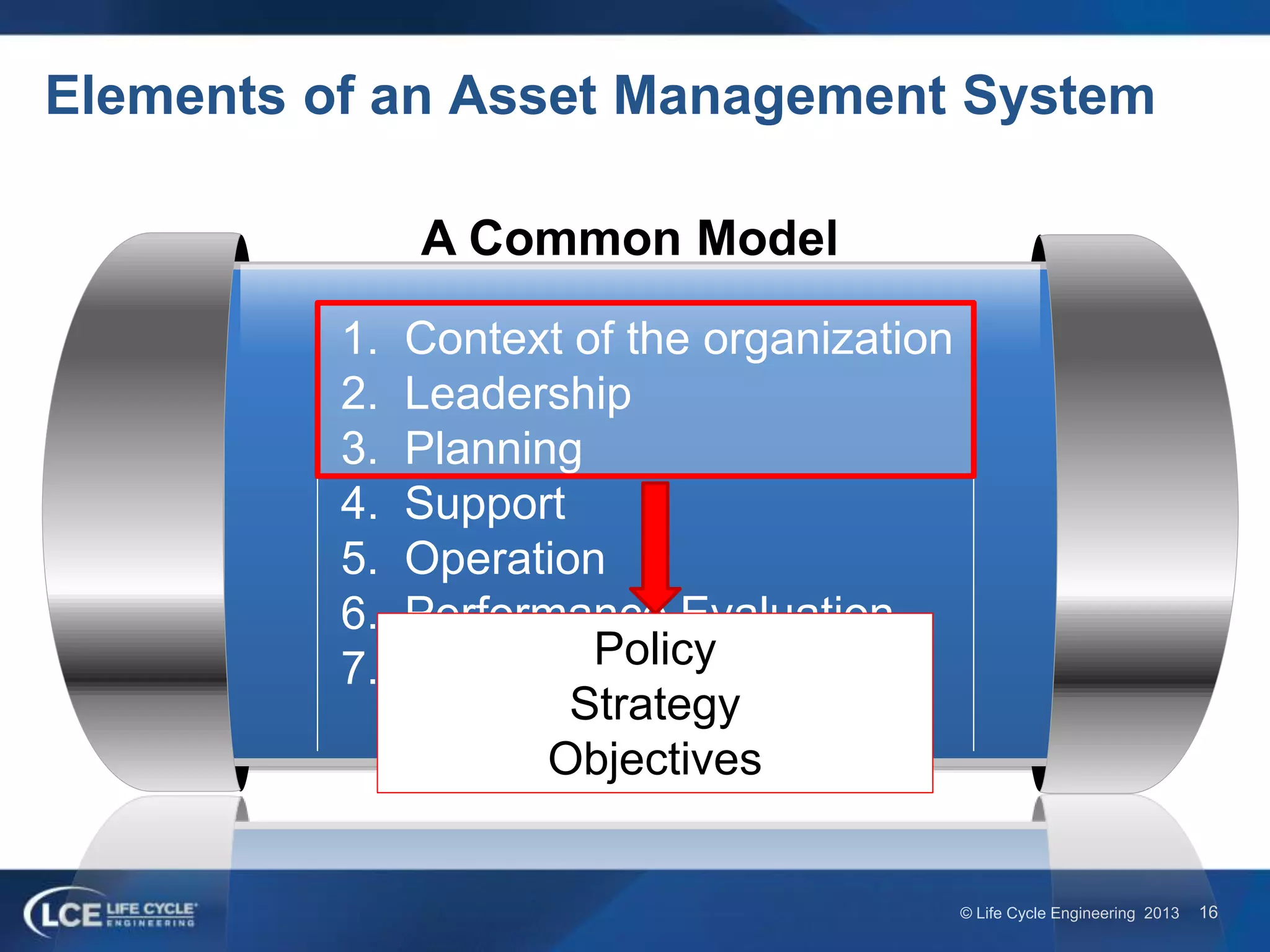
The document discusses the ISO 55000 standard for asset management, which includes guidelines on terminology, requirements, and guidance. It emphasizes the importance of effective asset management in realizing value and mitigating risk through structured policies and strategies. Additionally, the document outlines the roles of leadership and organizational alignment in achieving asset management objectives.