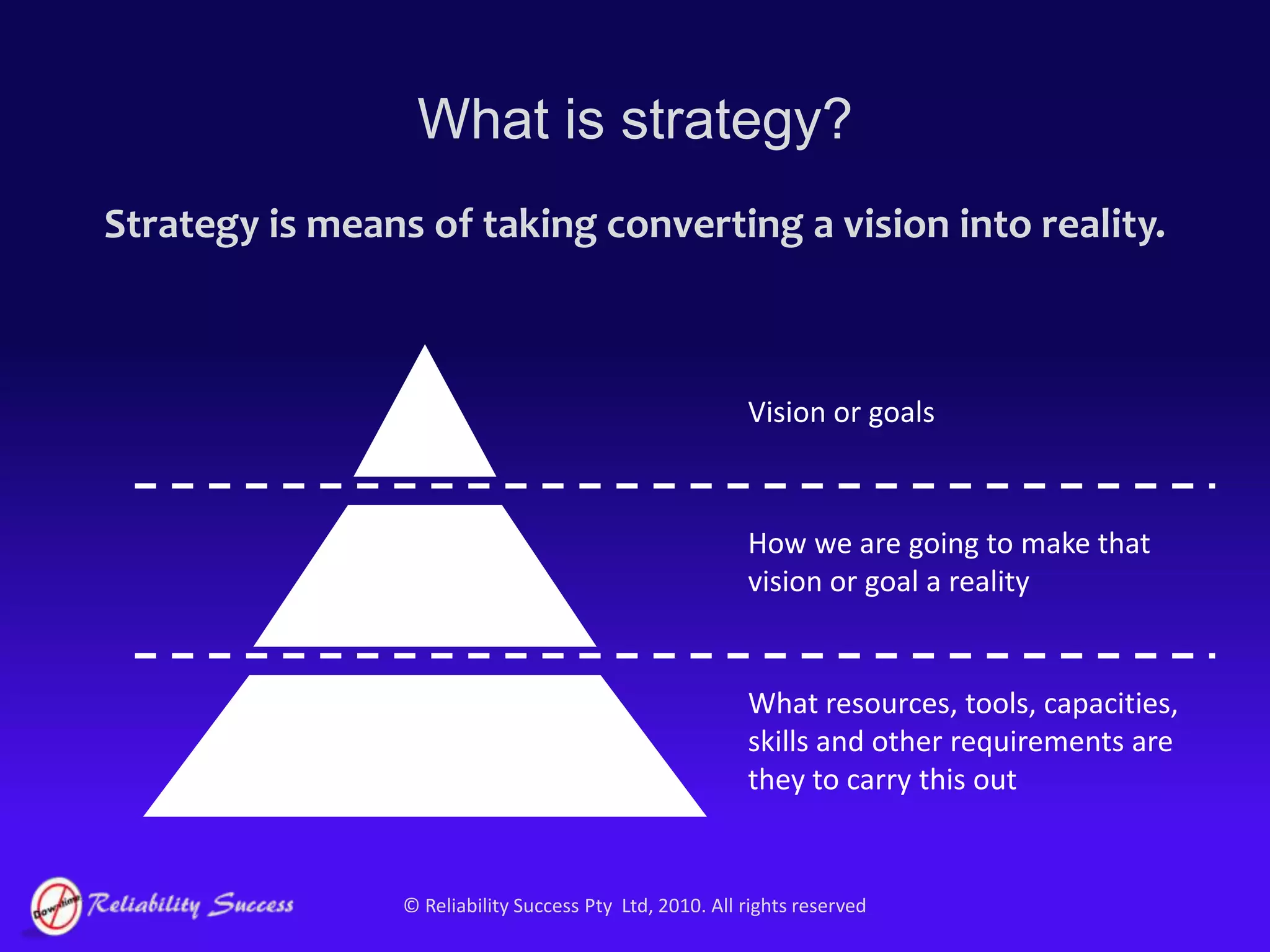
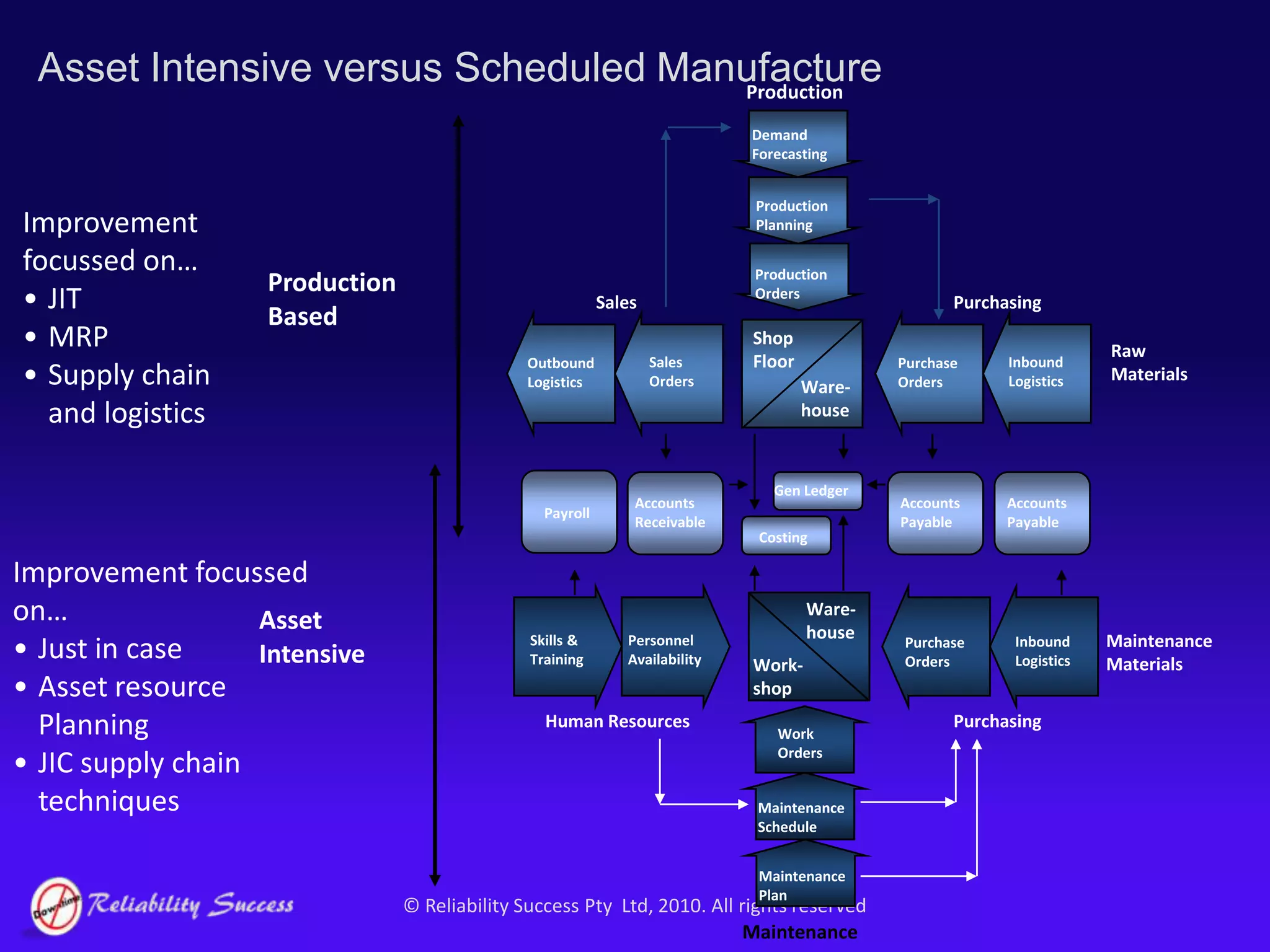
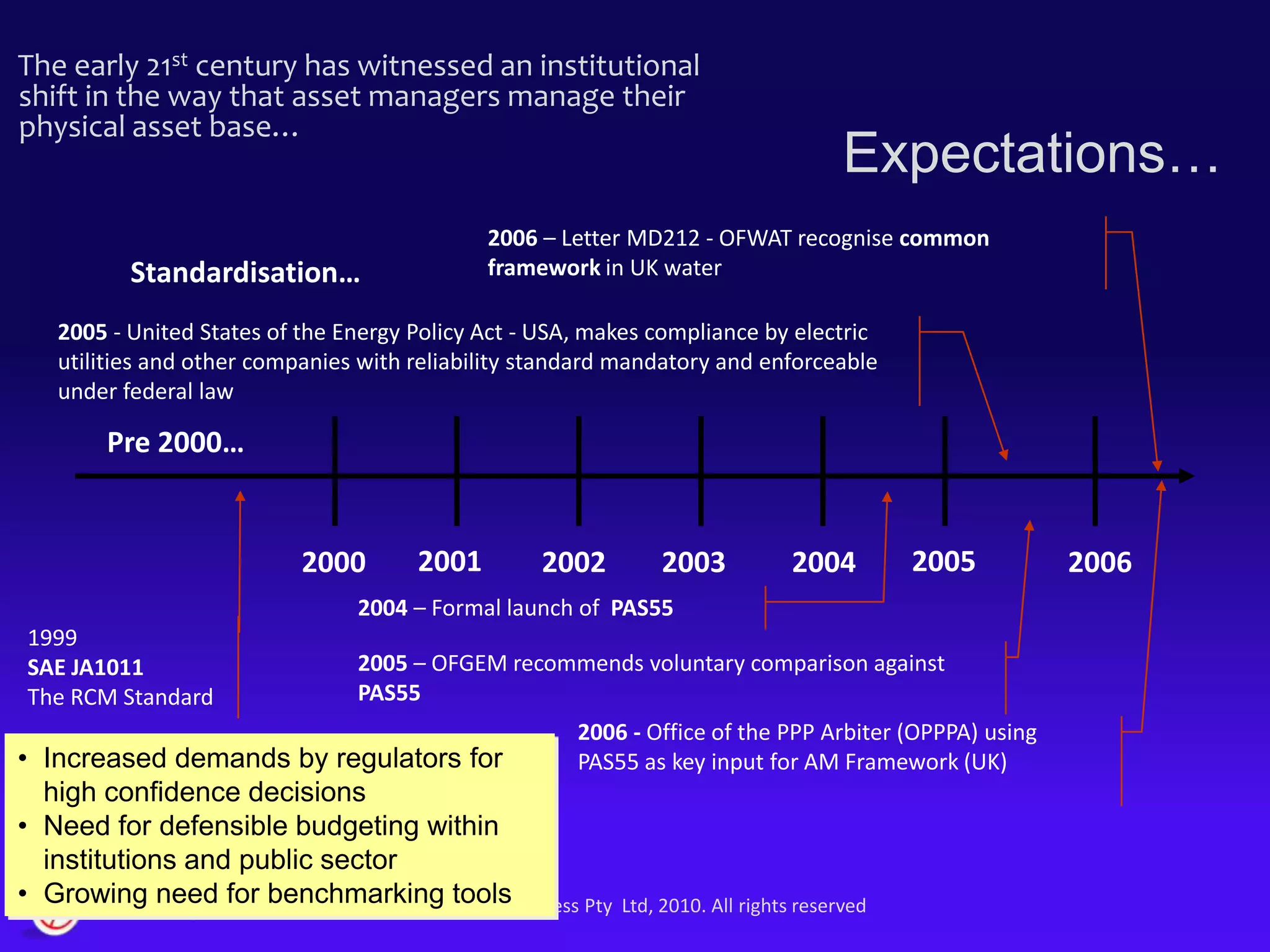
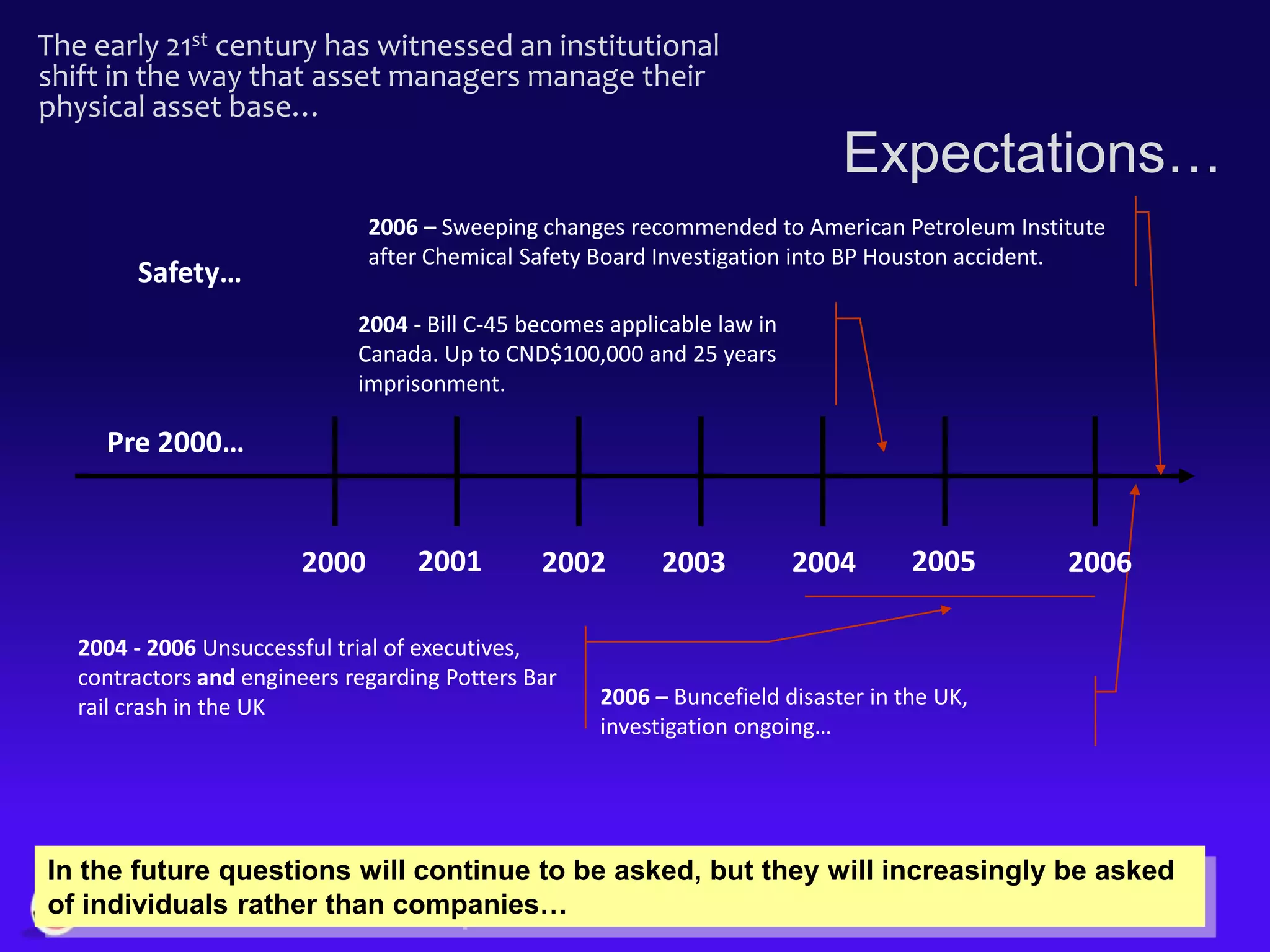
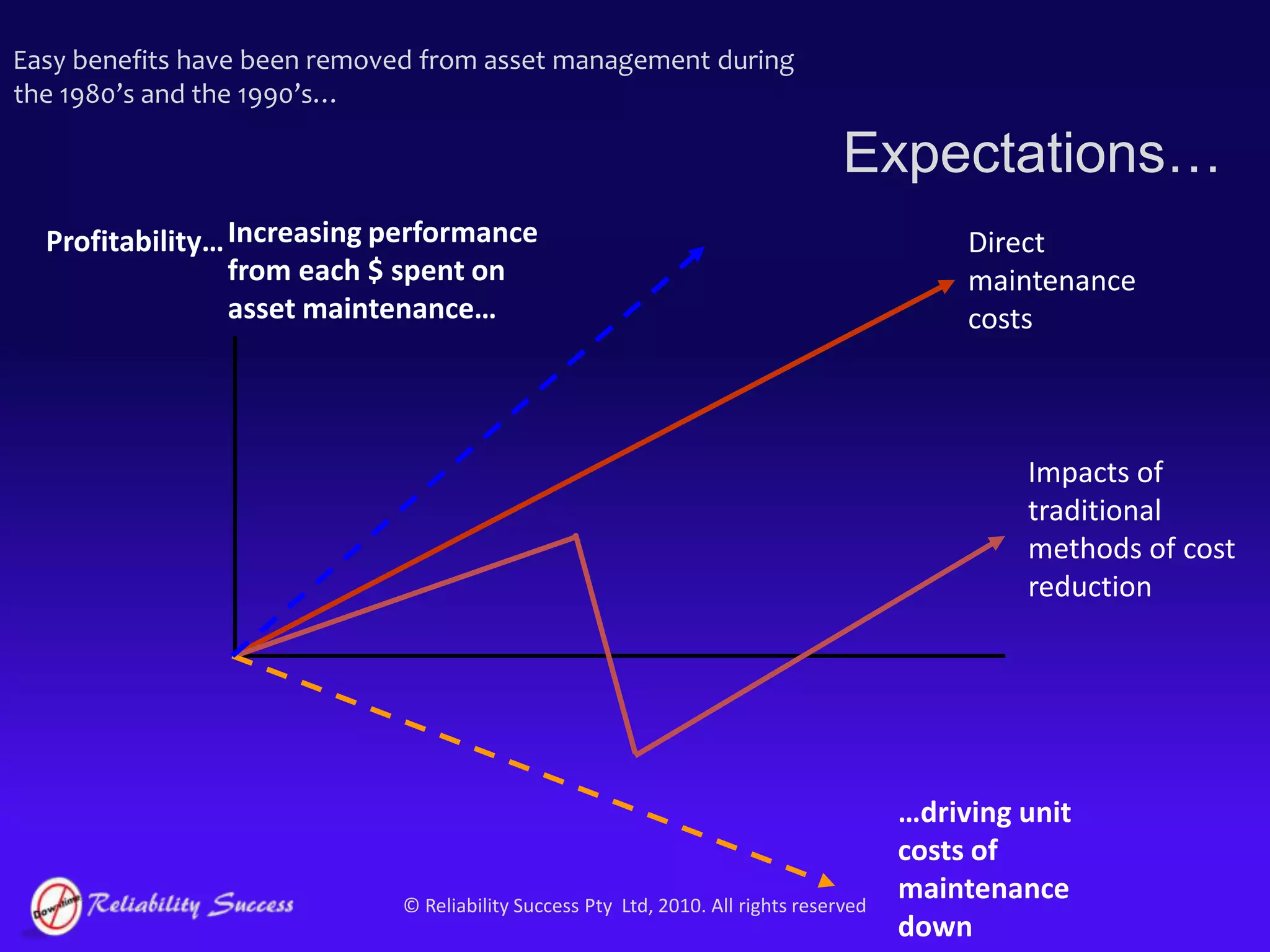
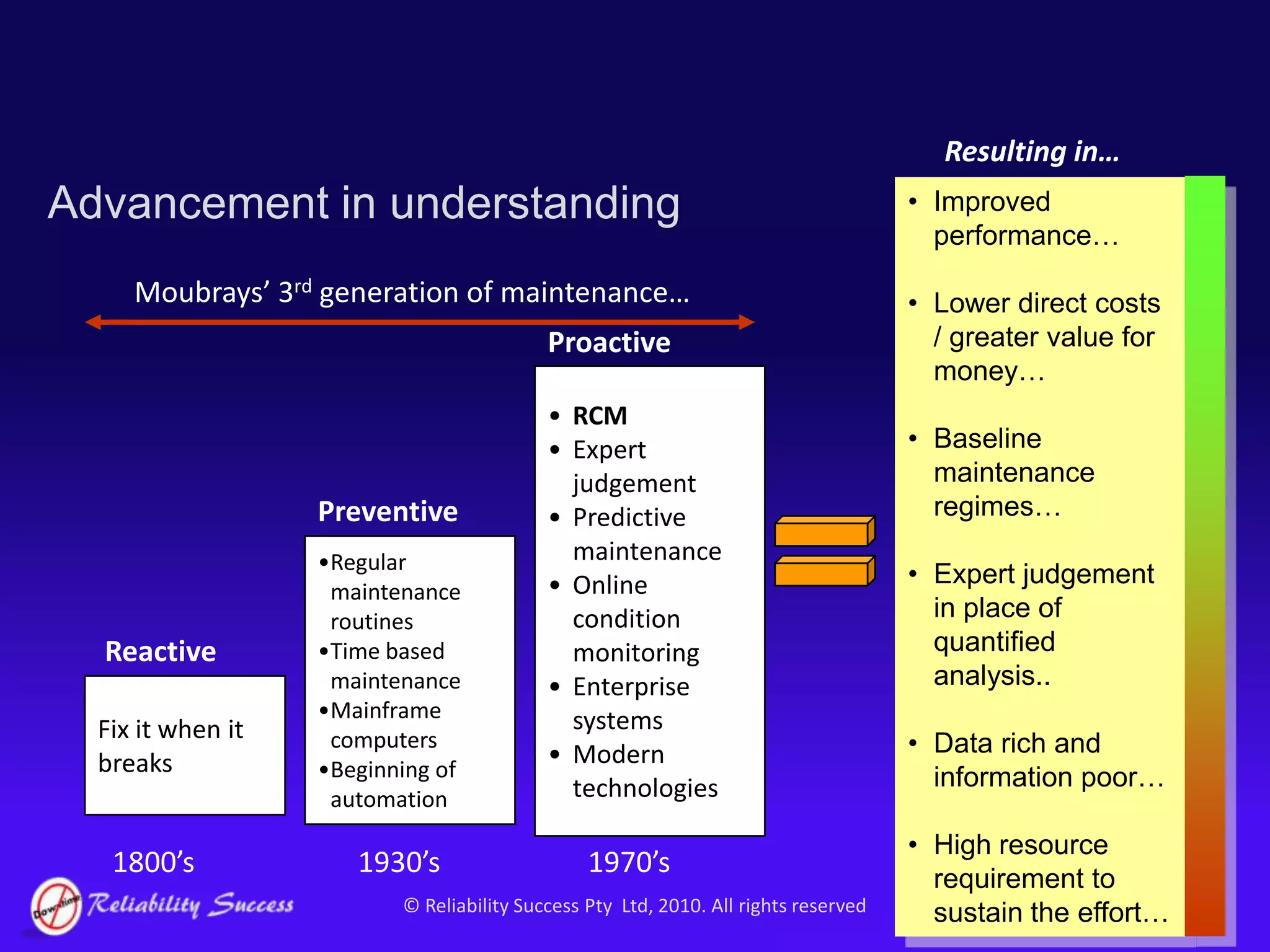
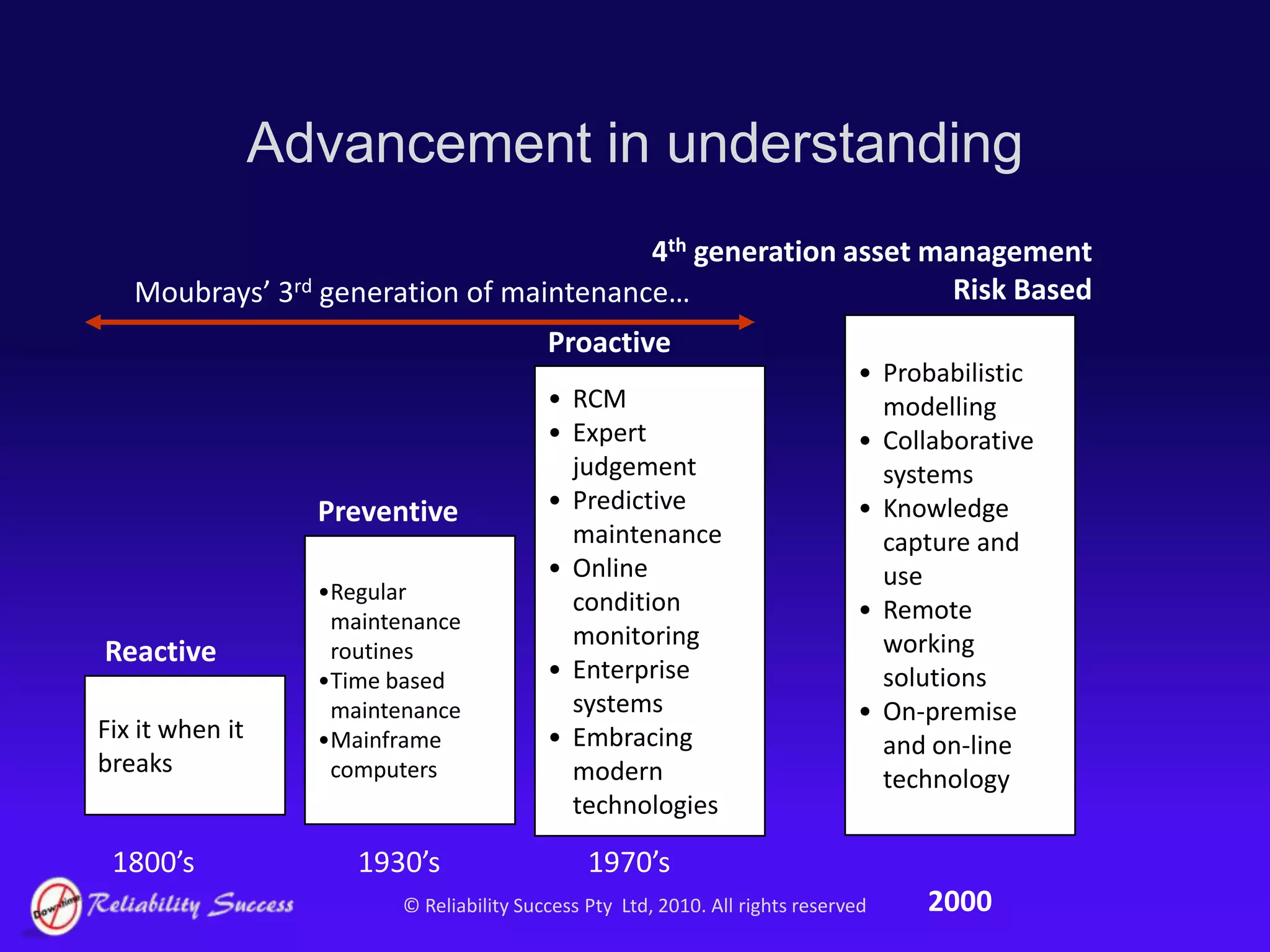
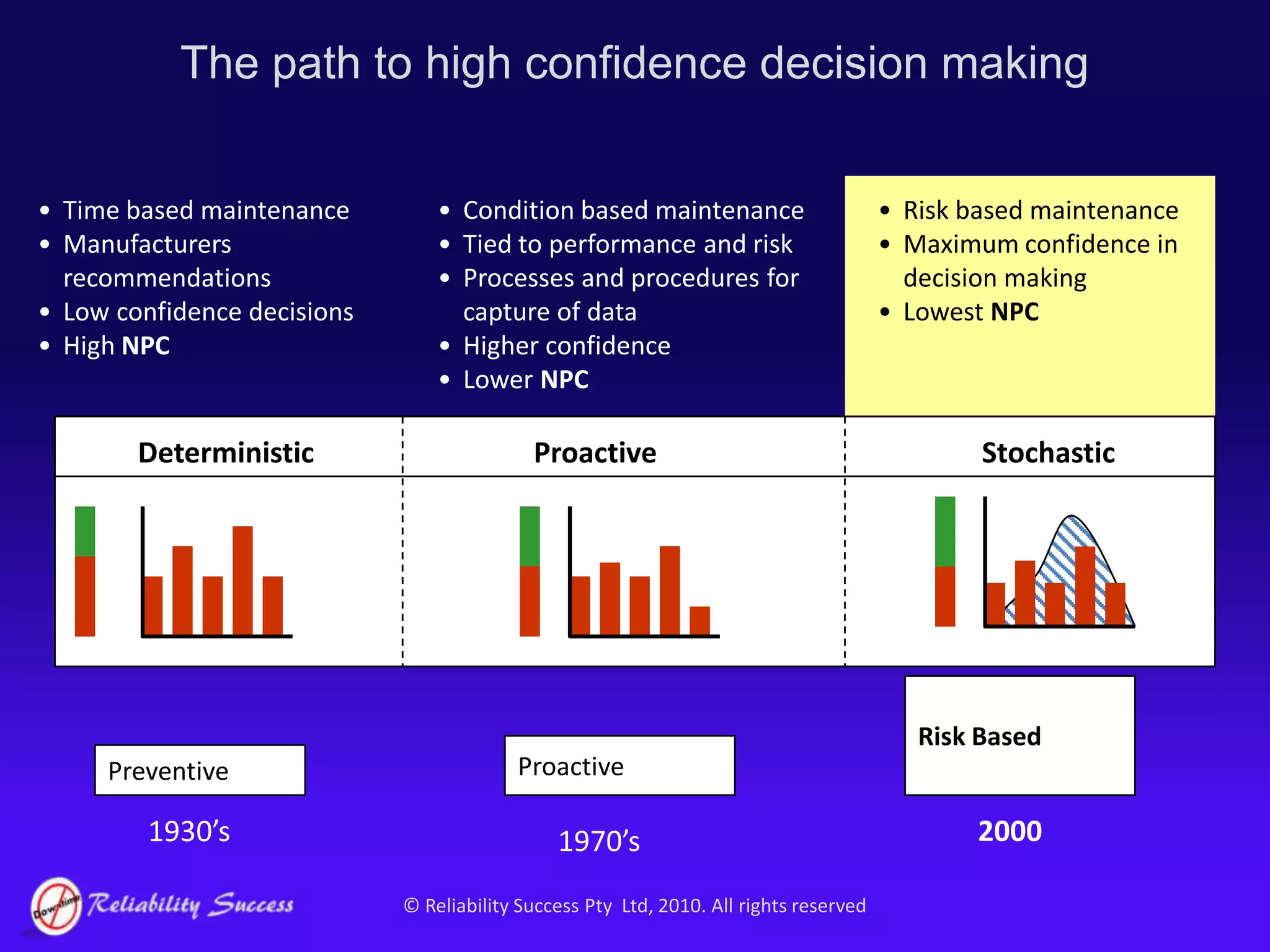
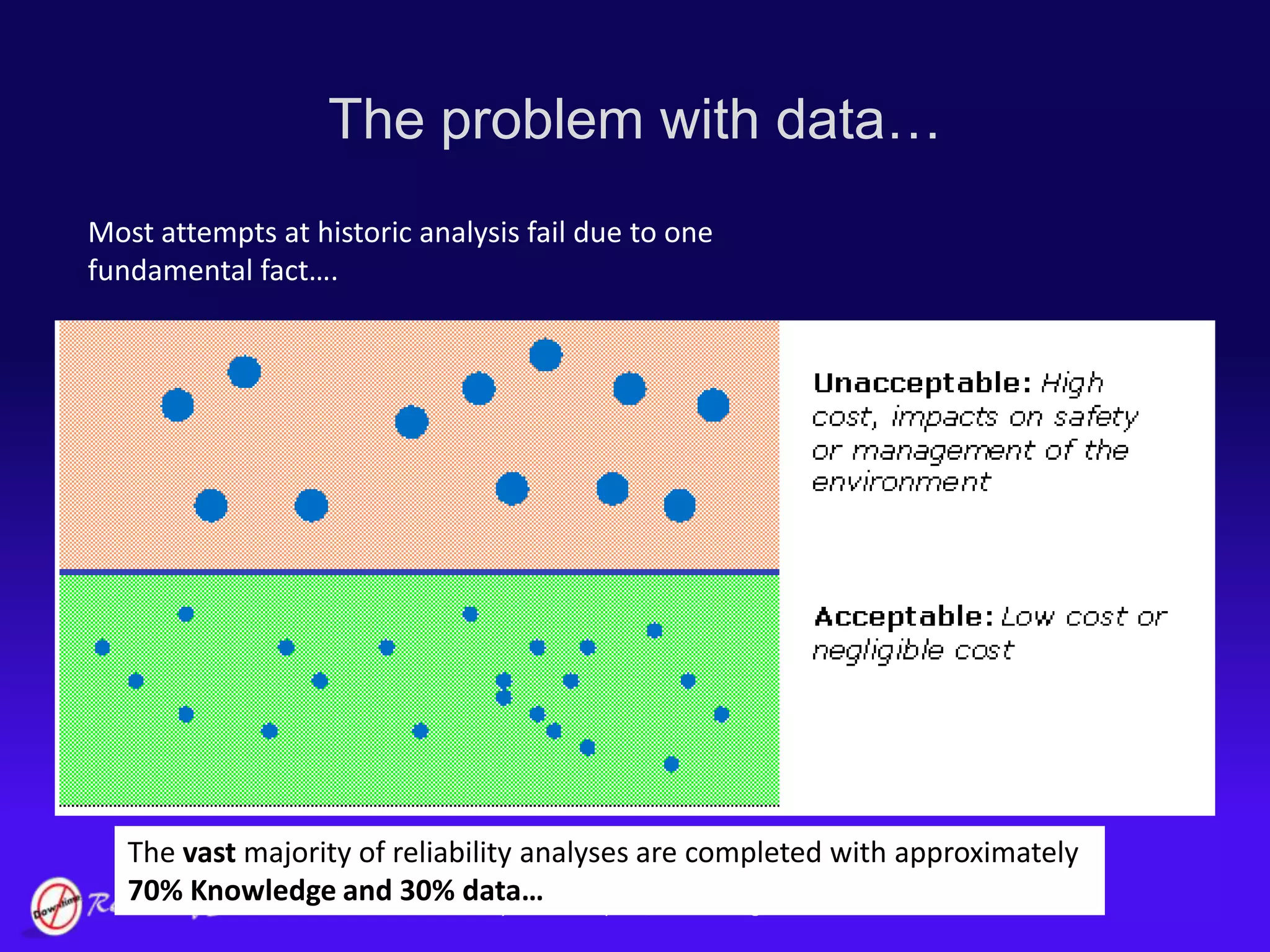
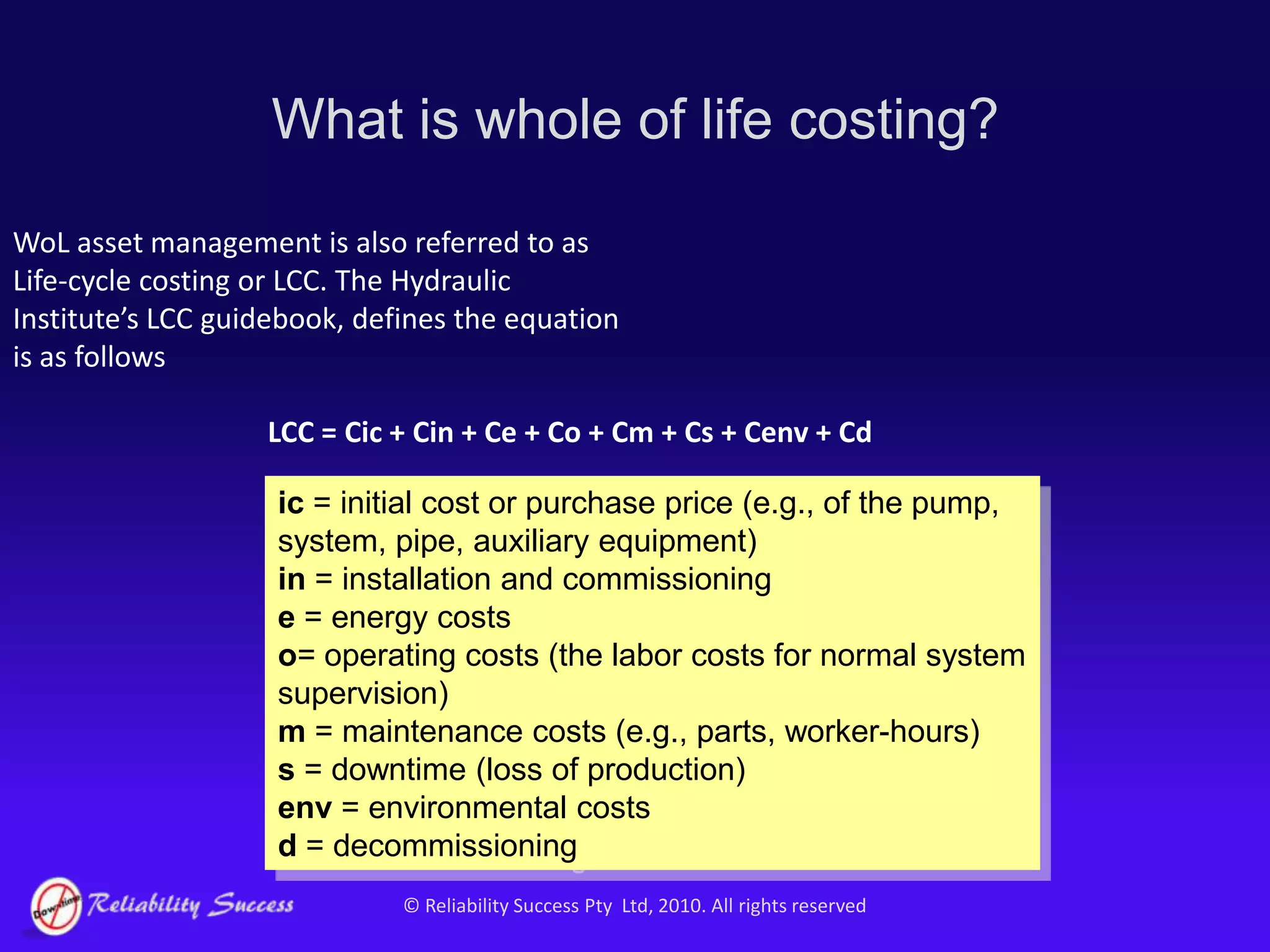
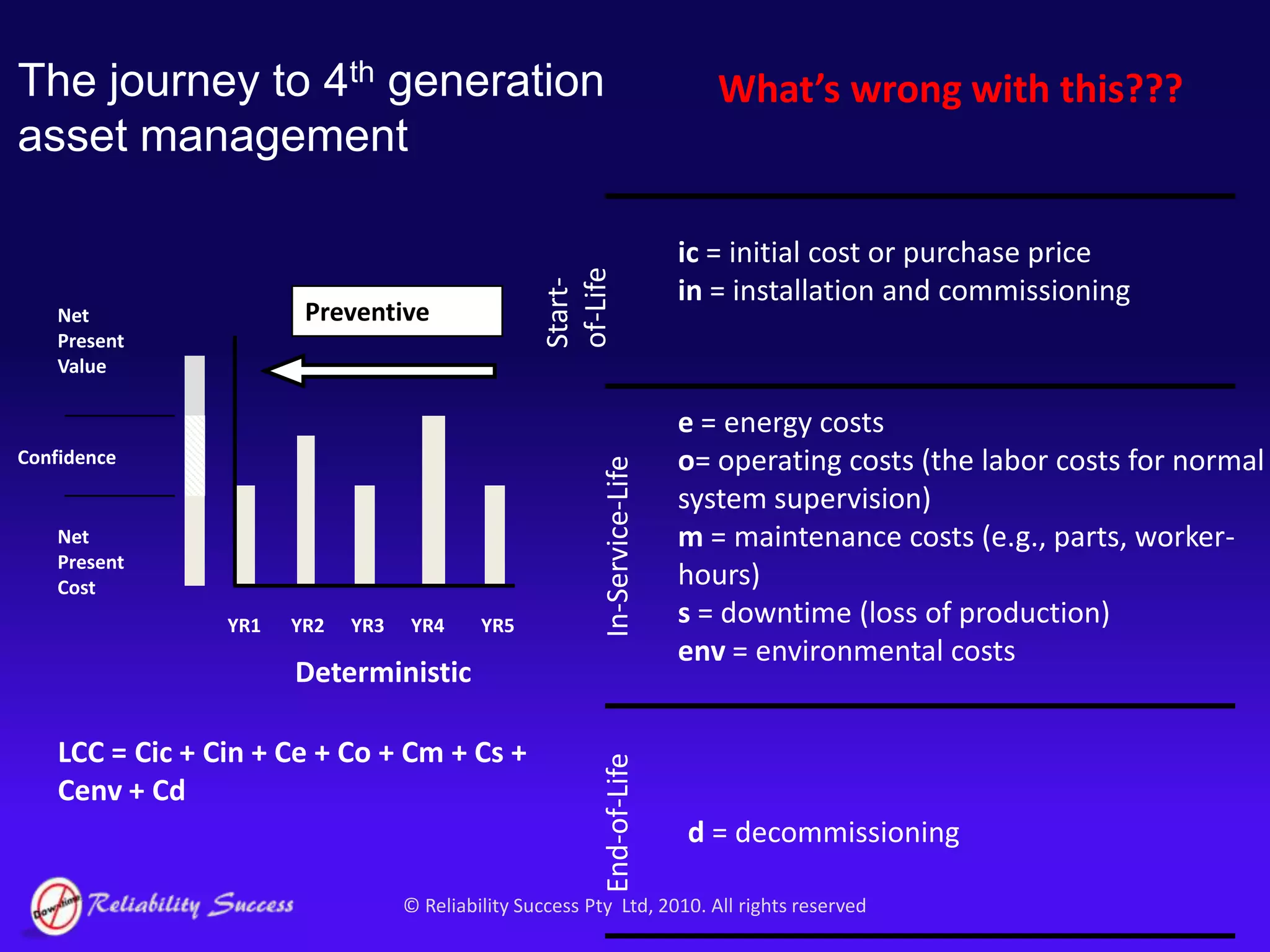
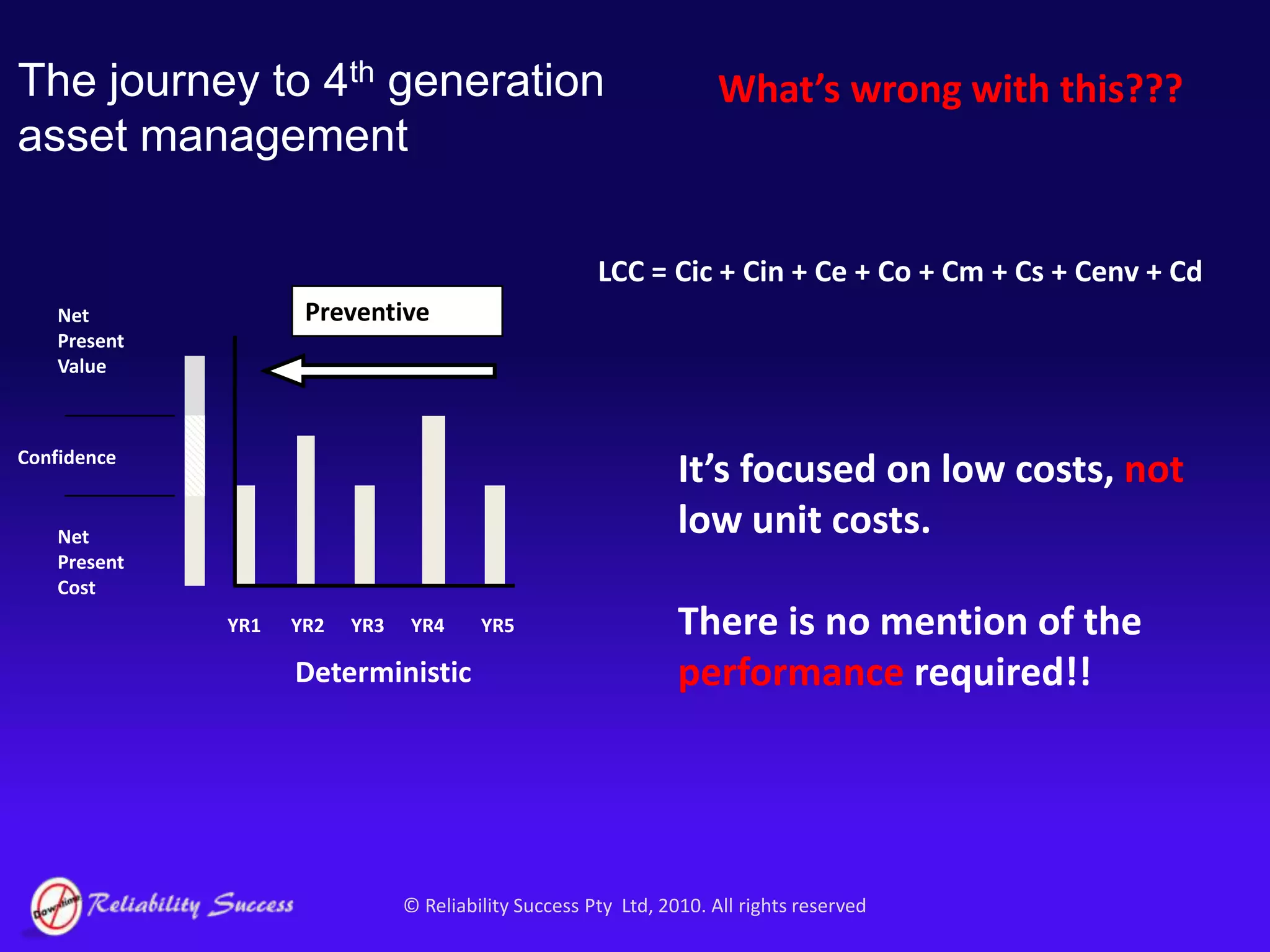
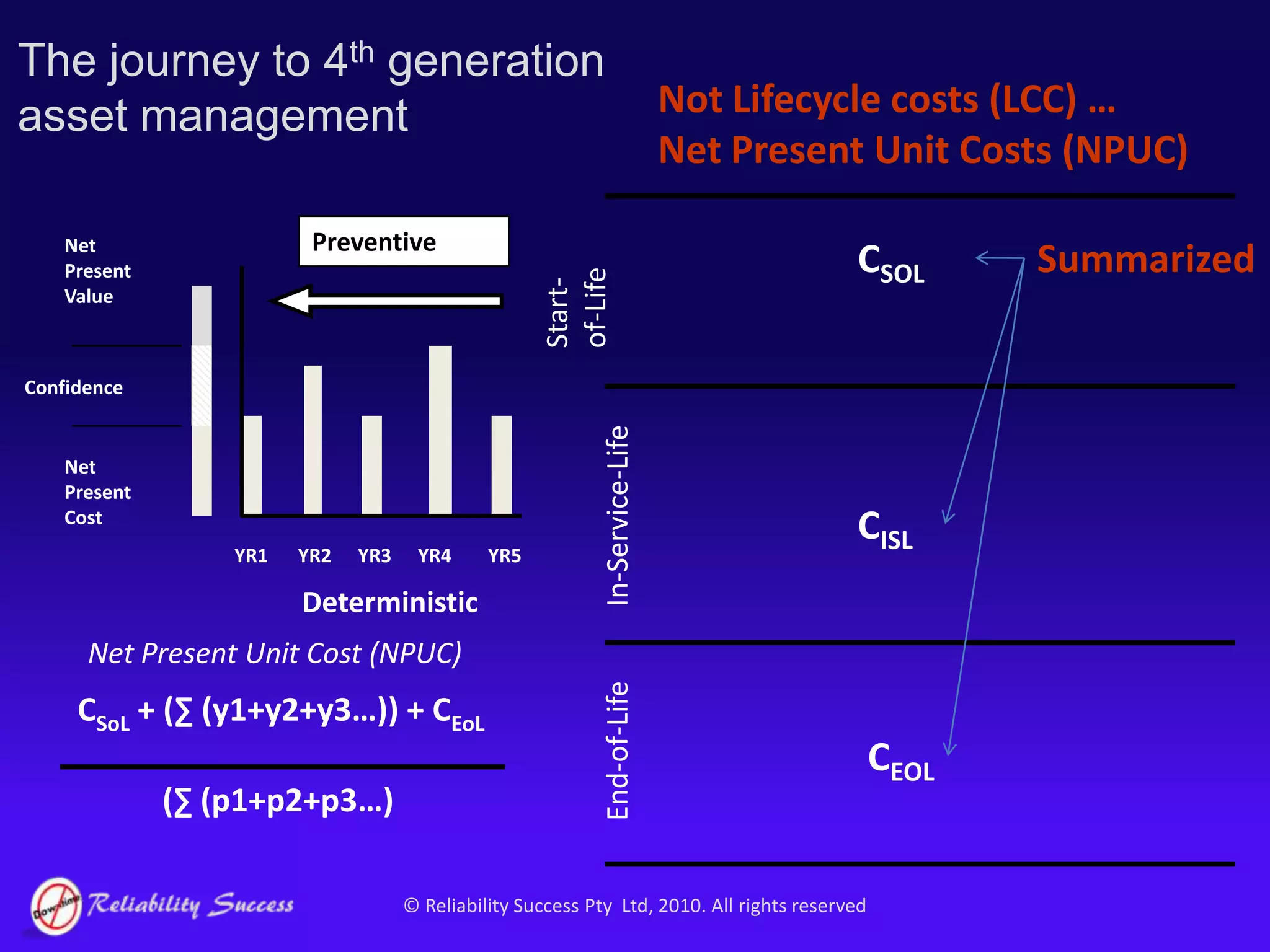
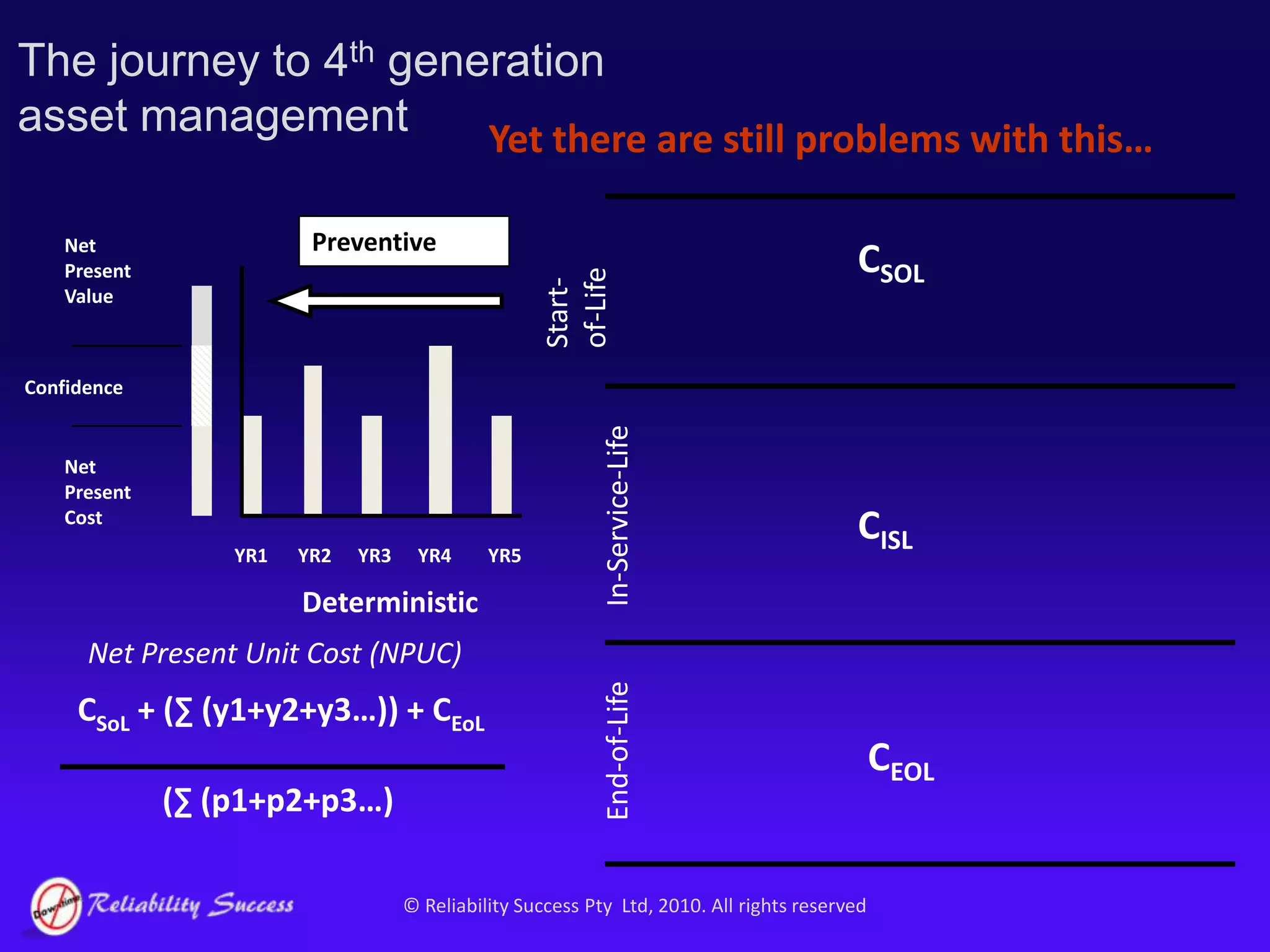
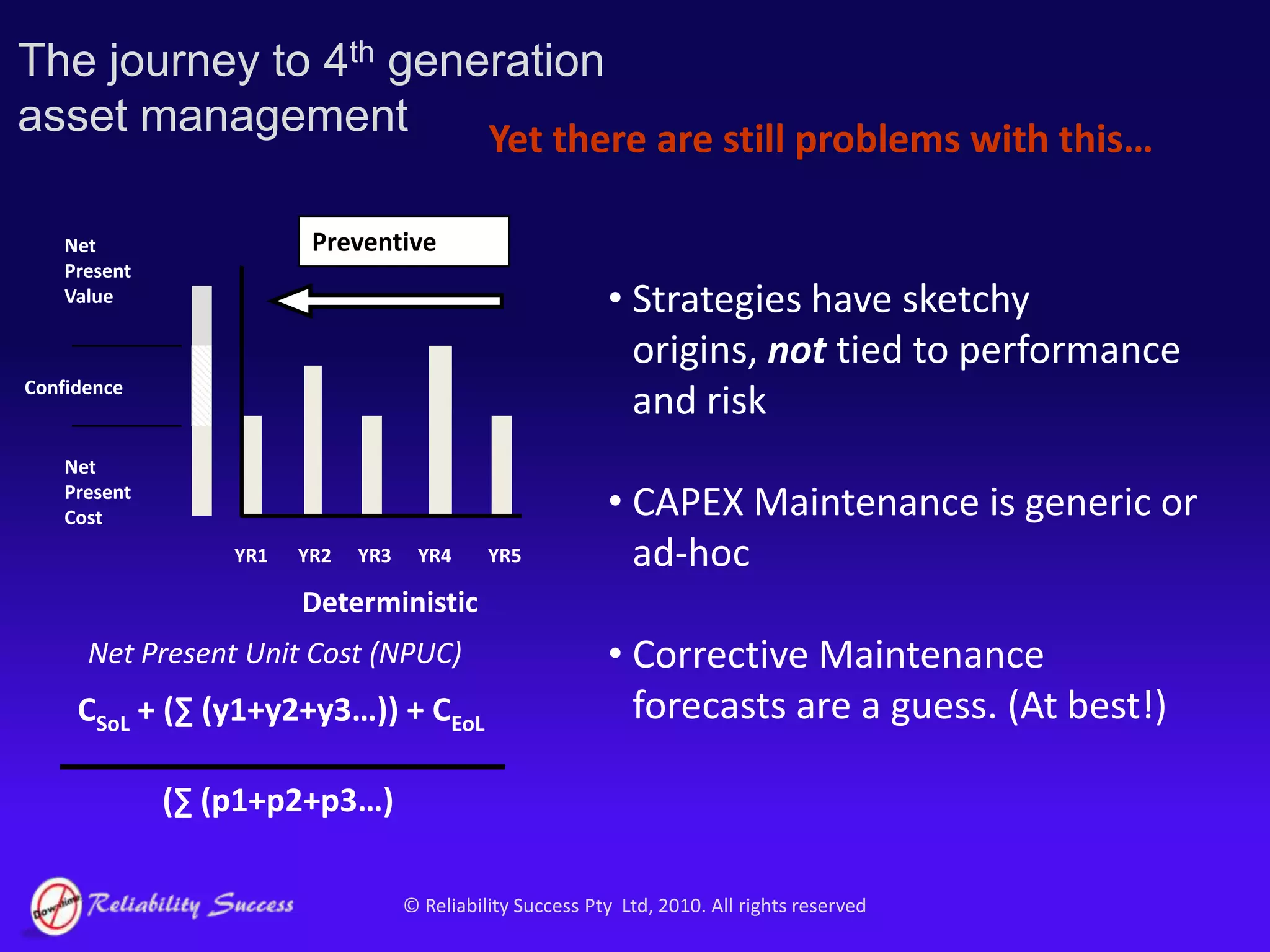
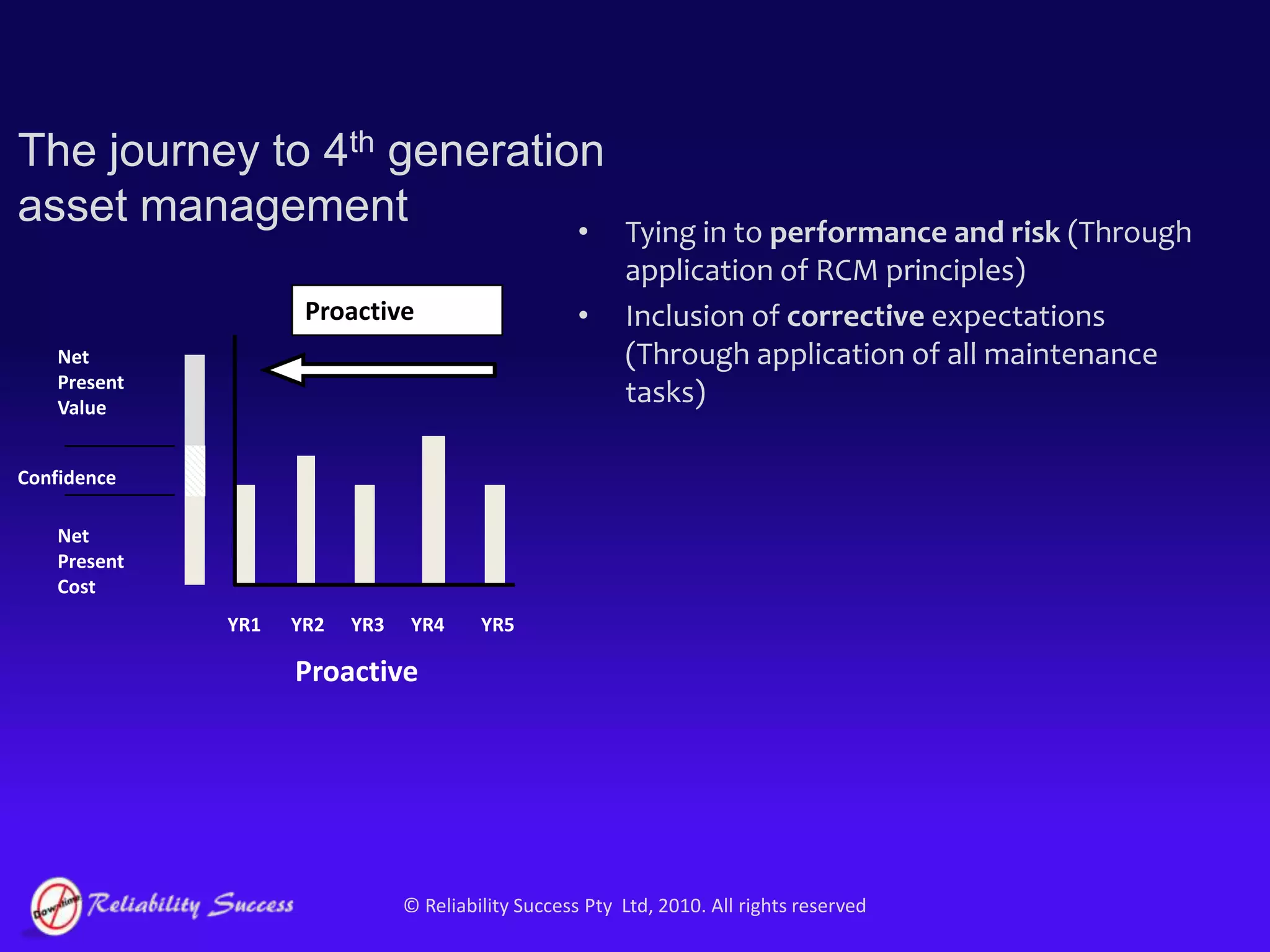
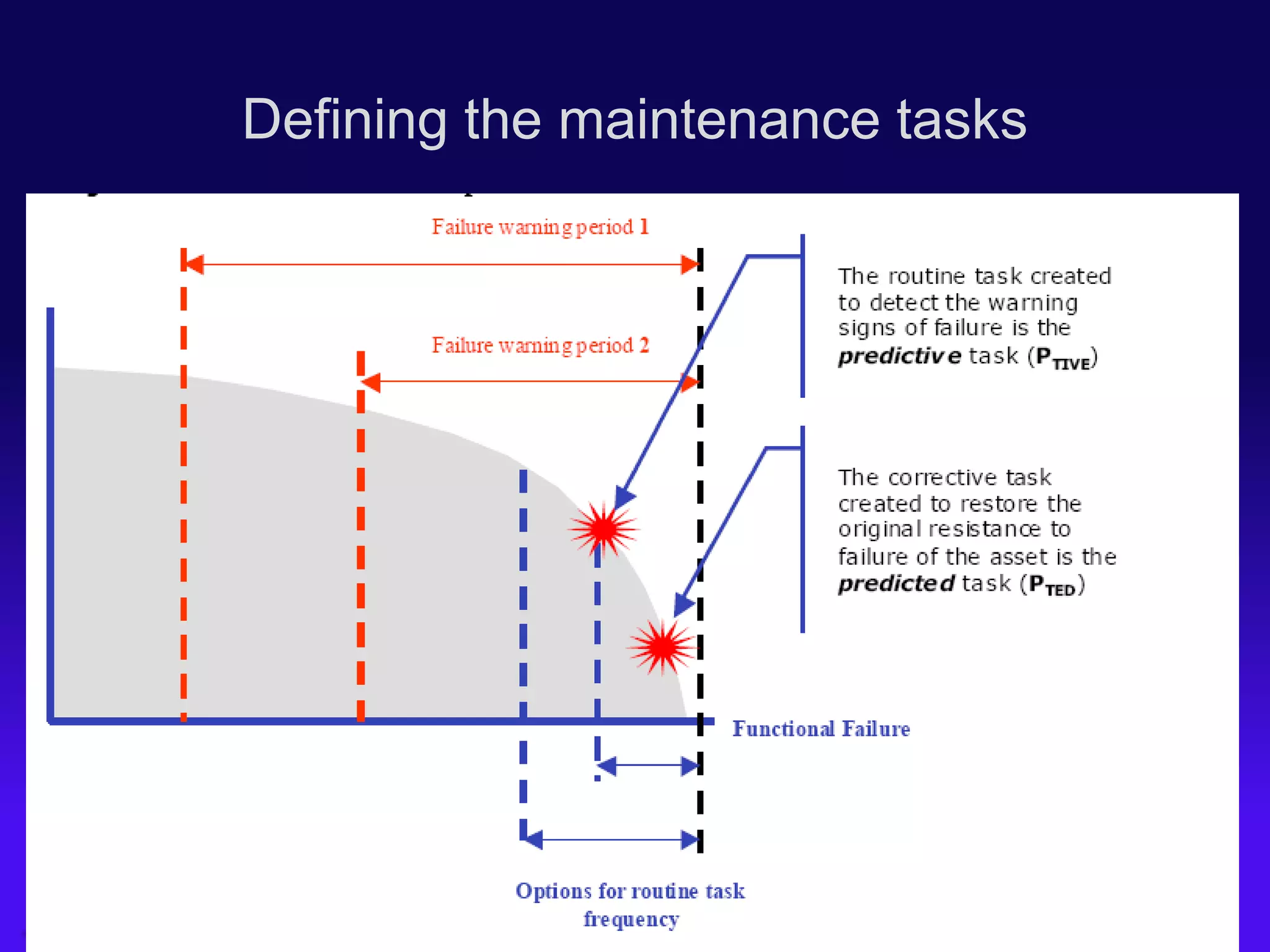
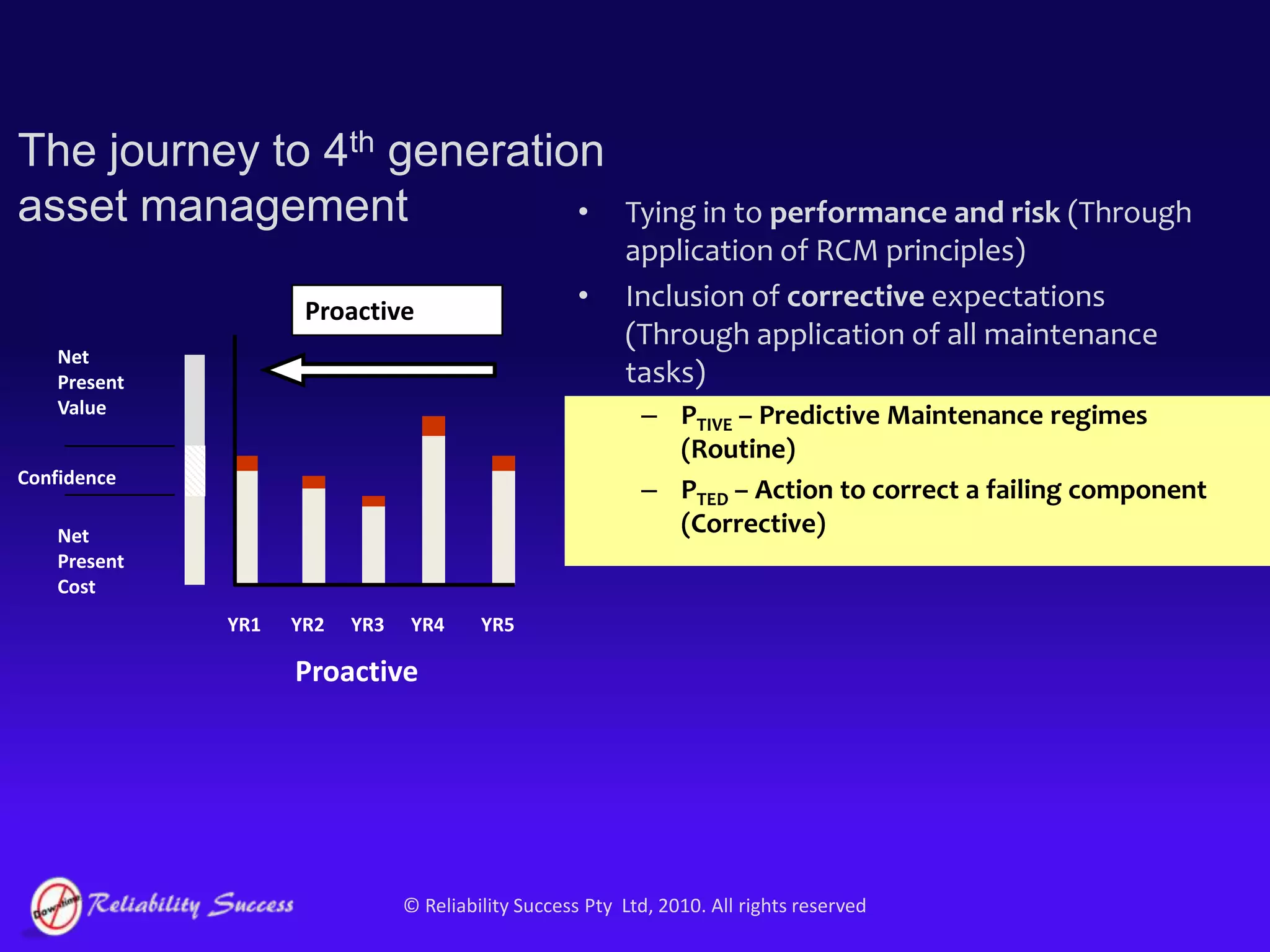
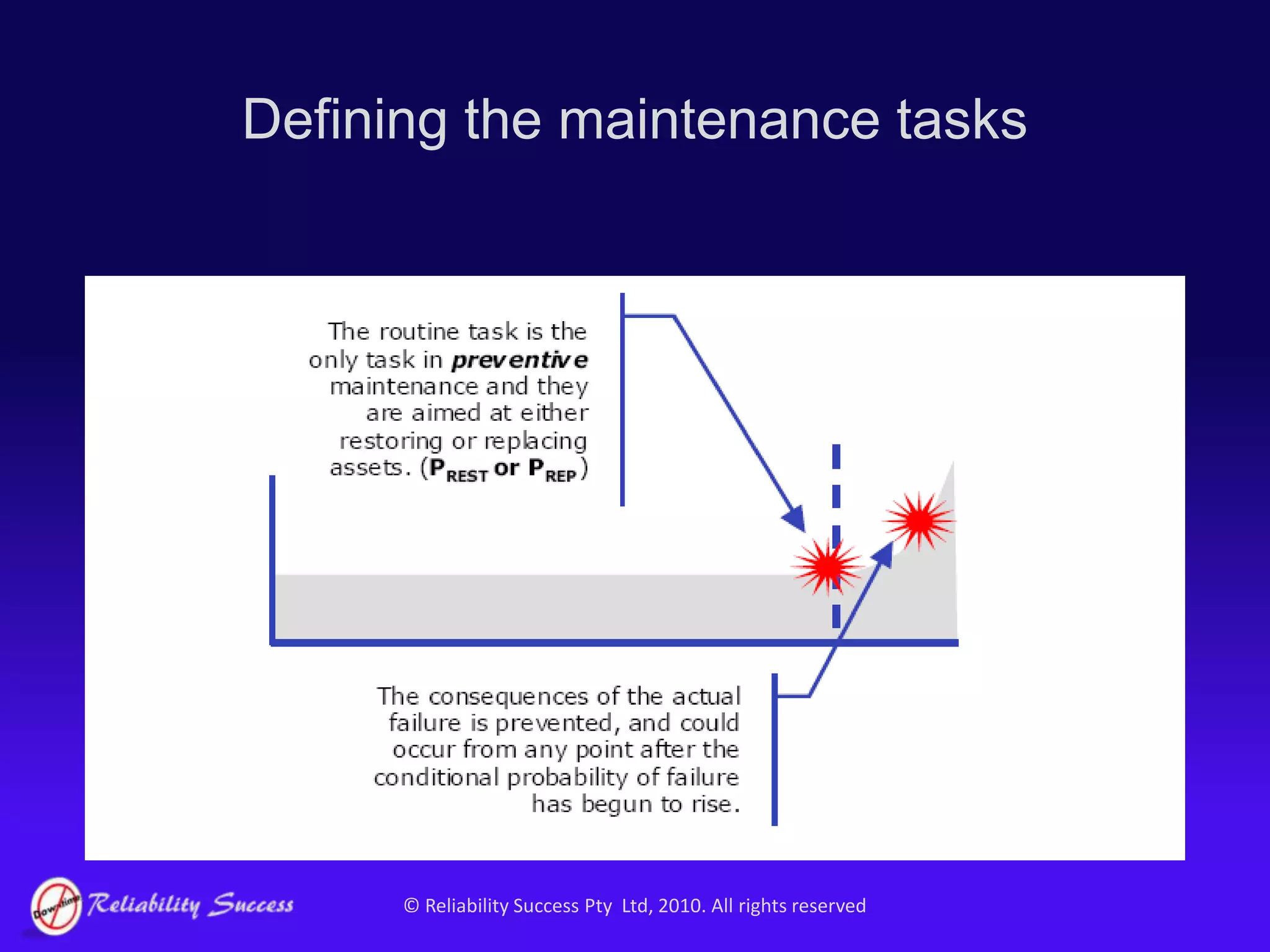
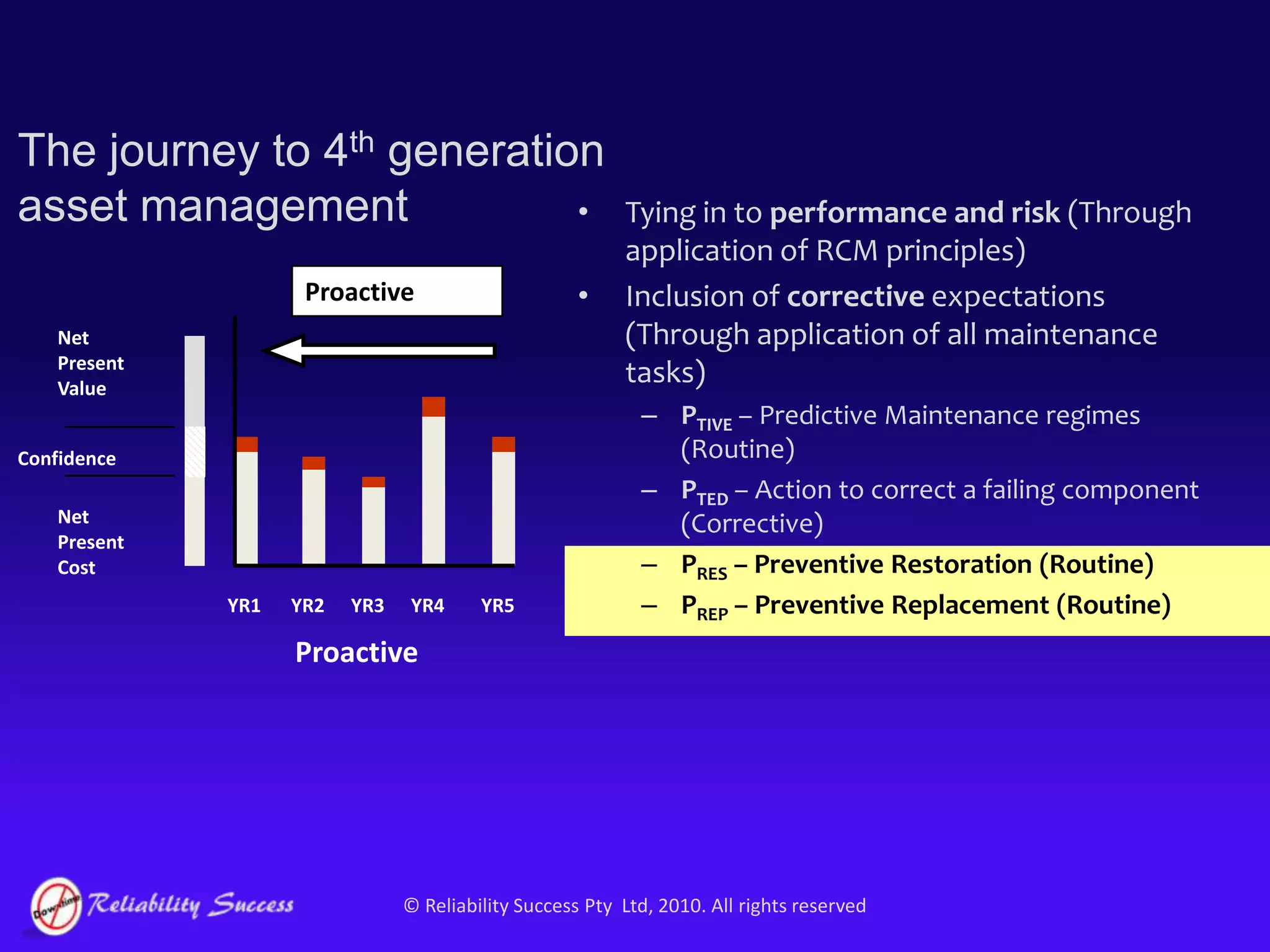
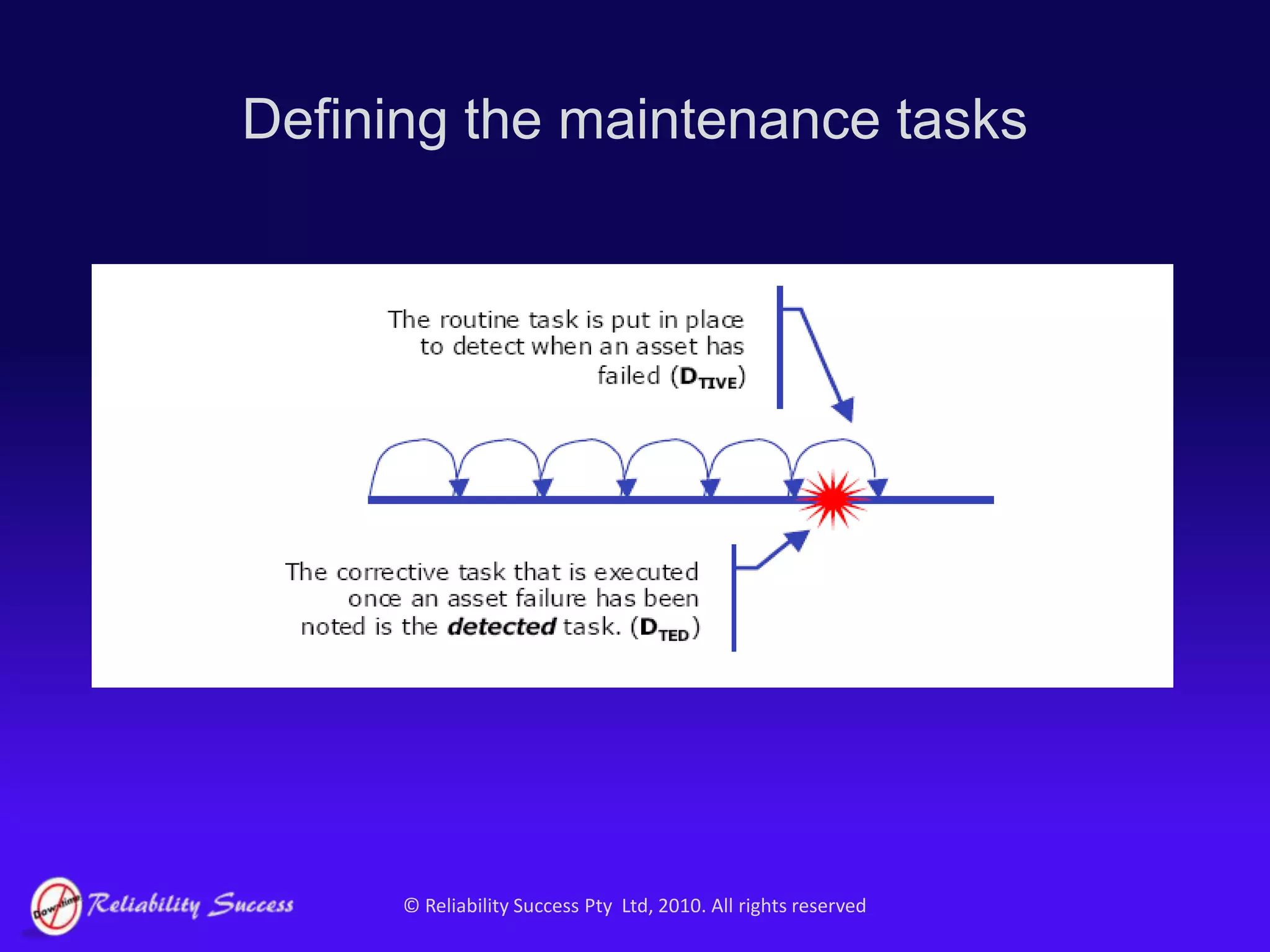
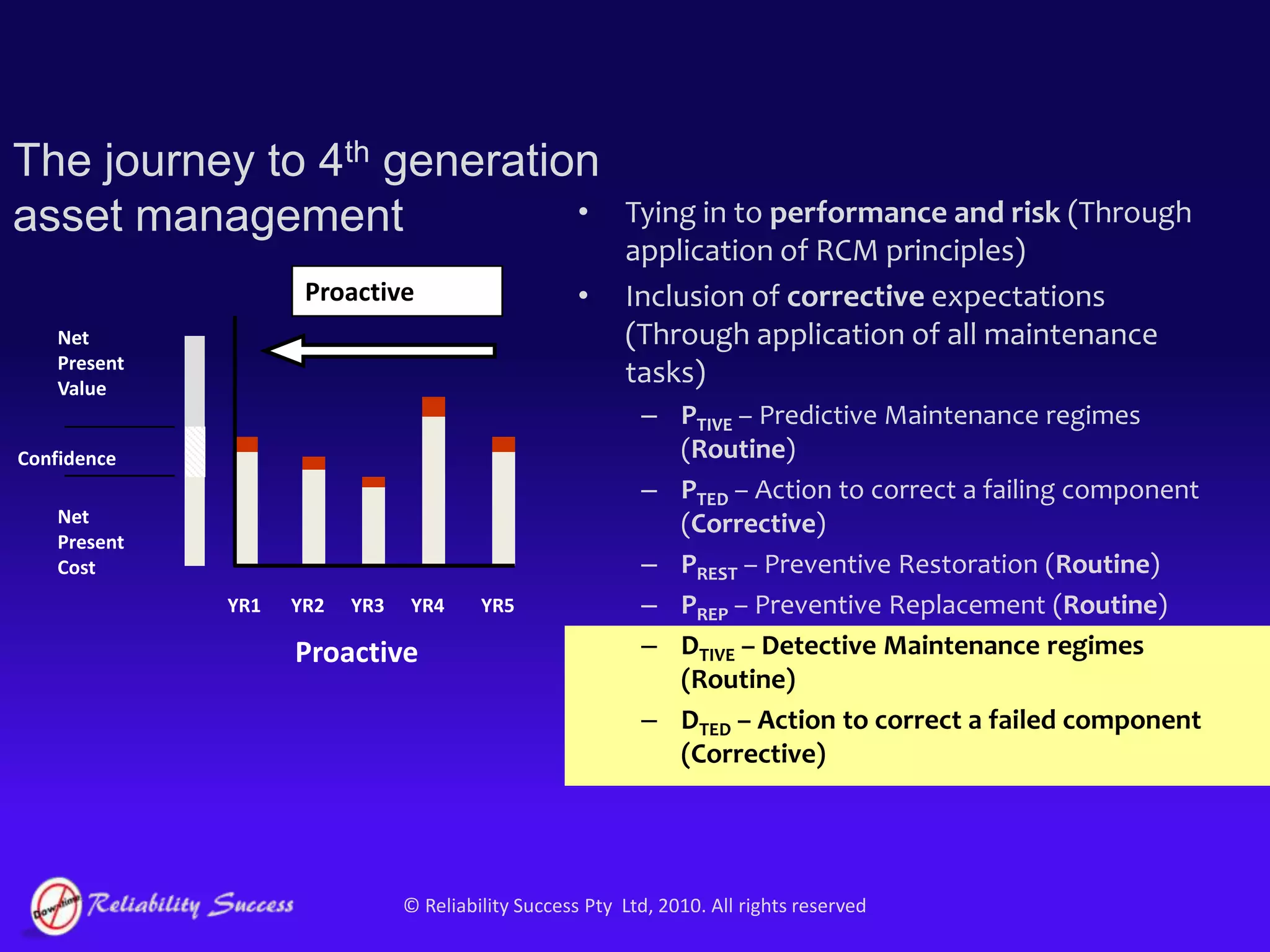
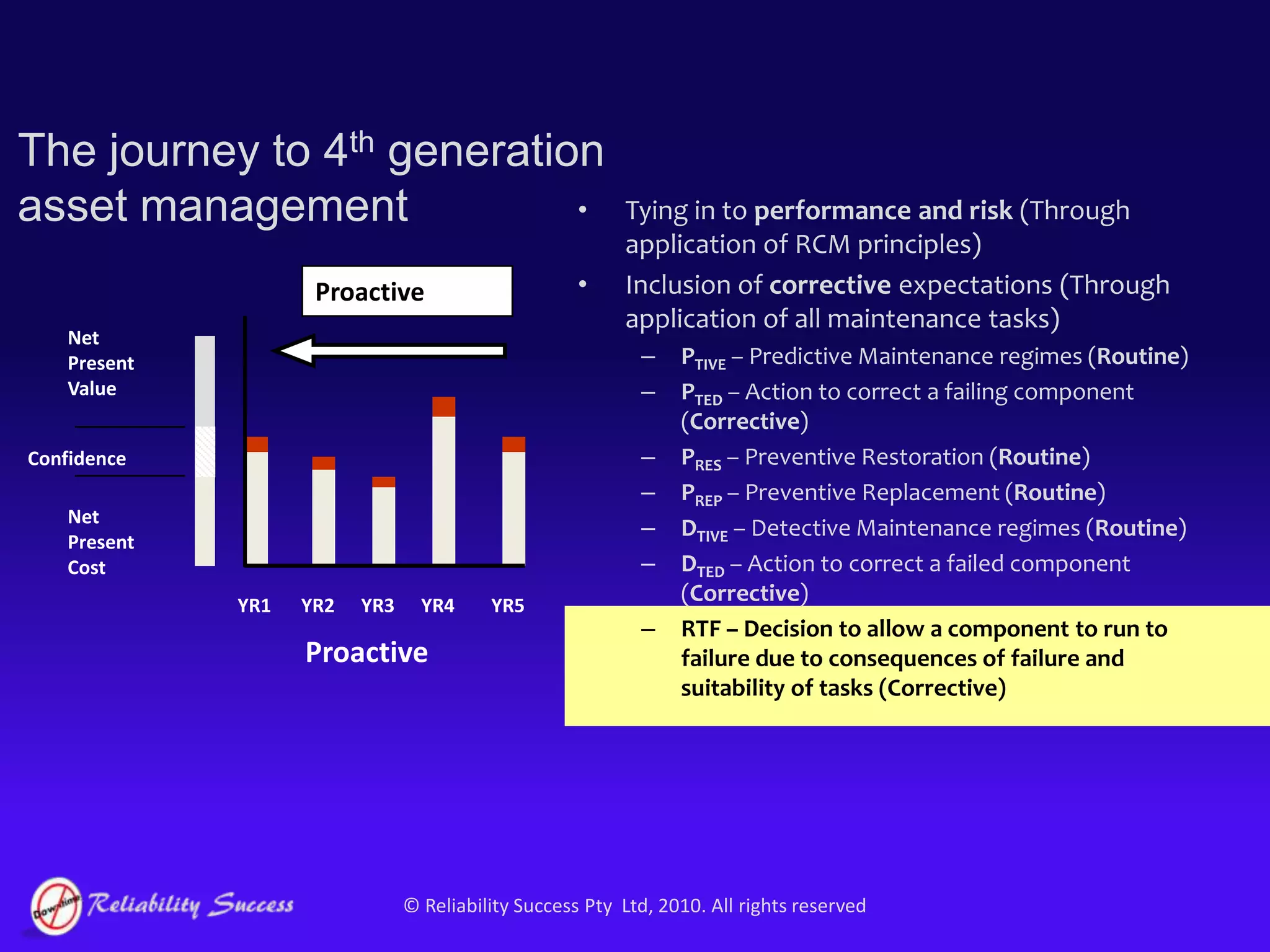
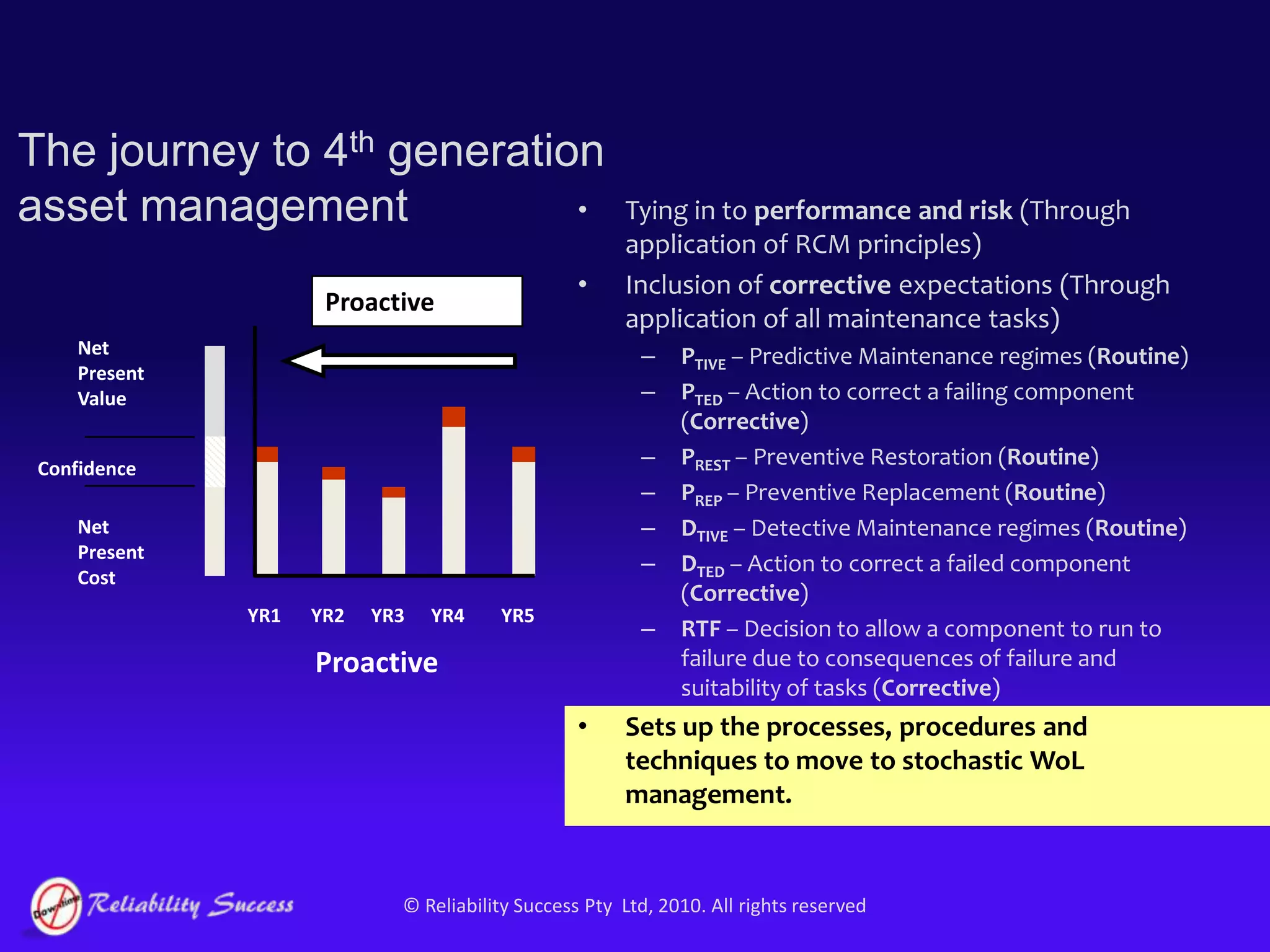
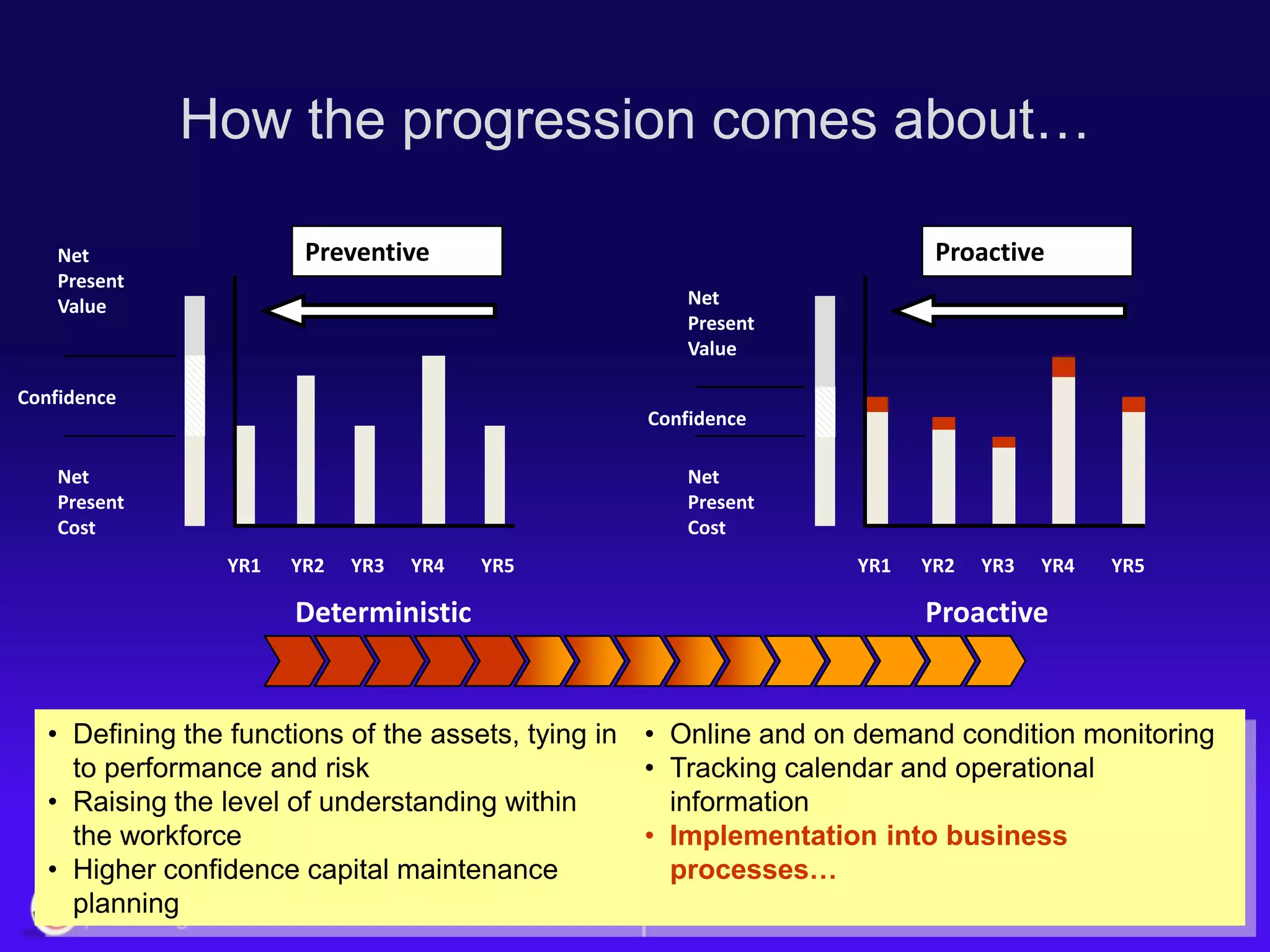
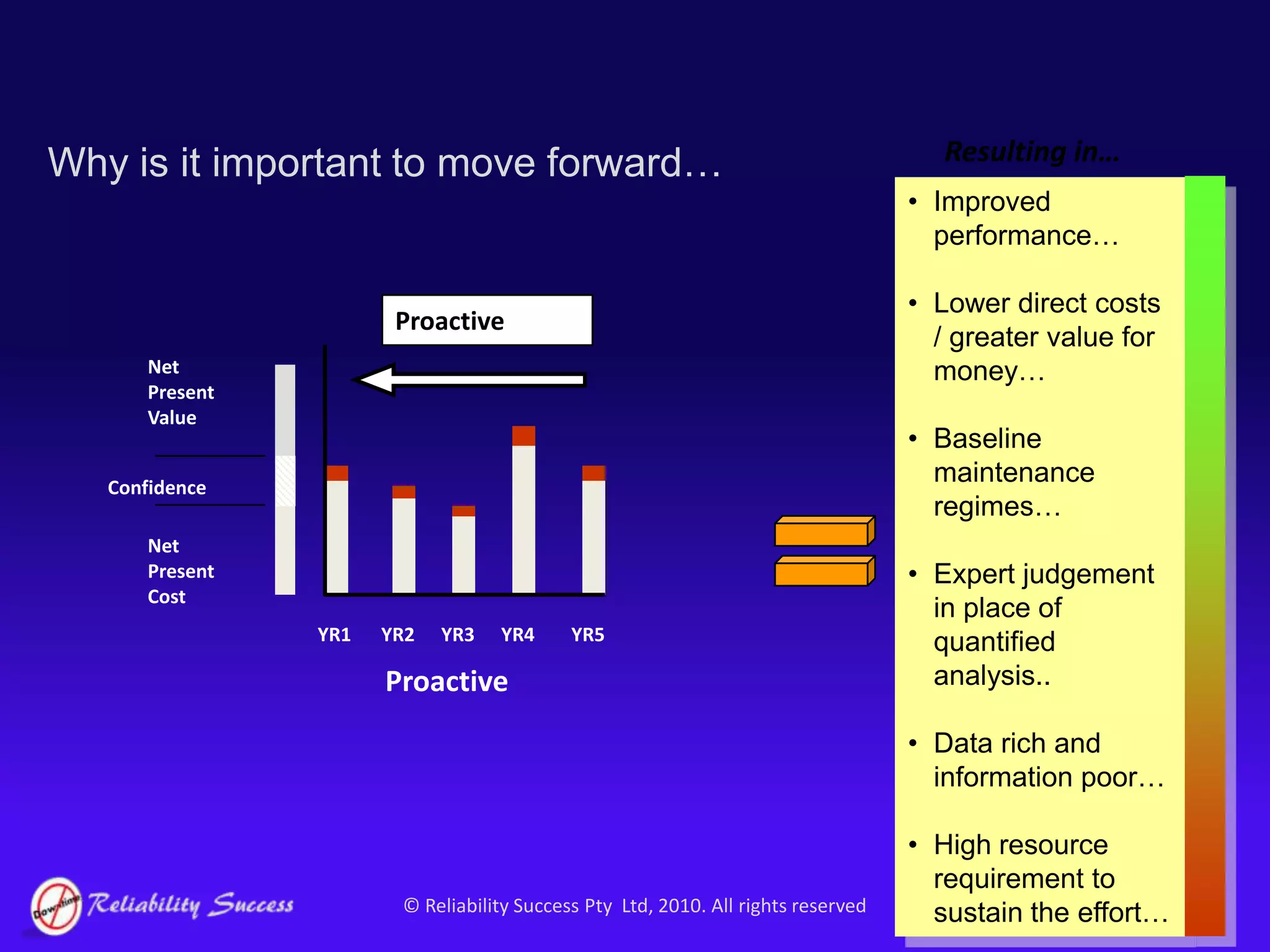
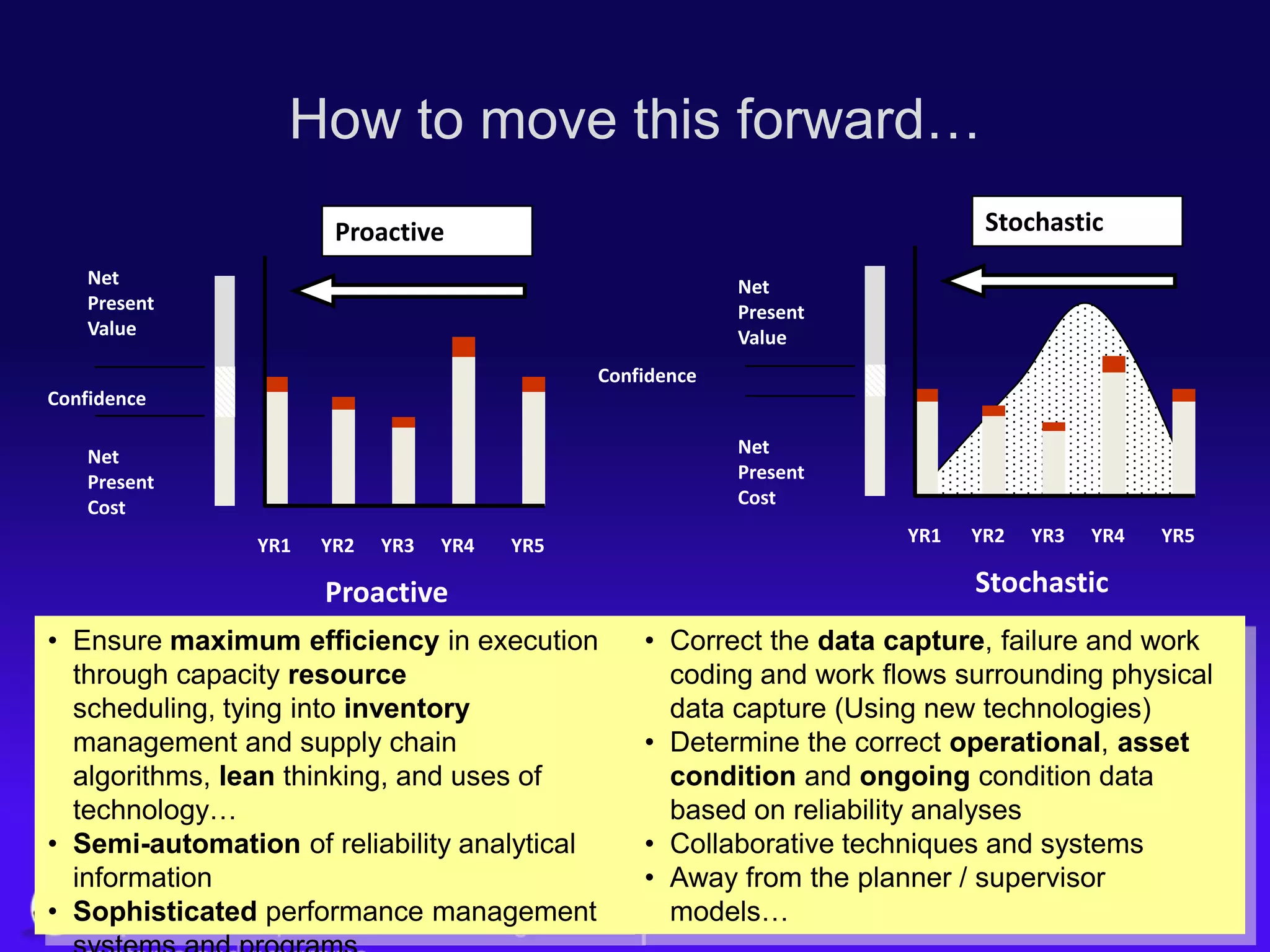
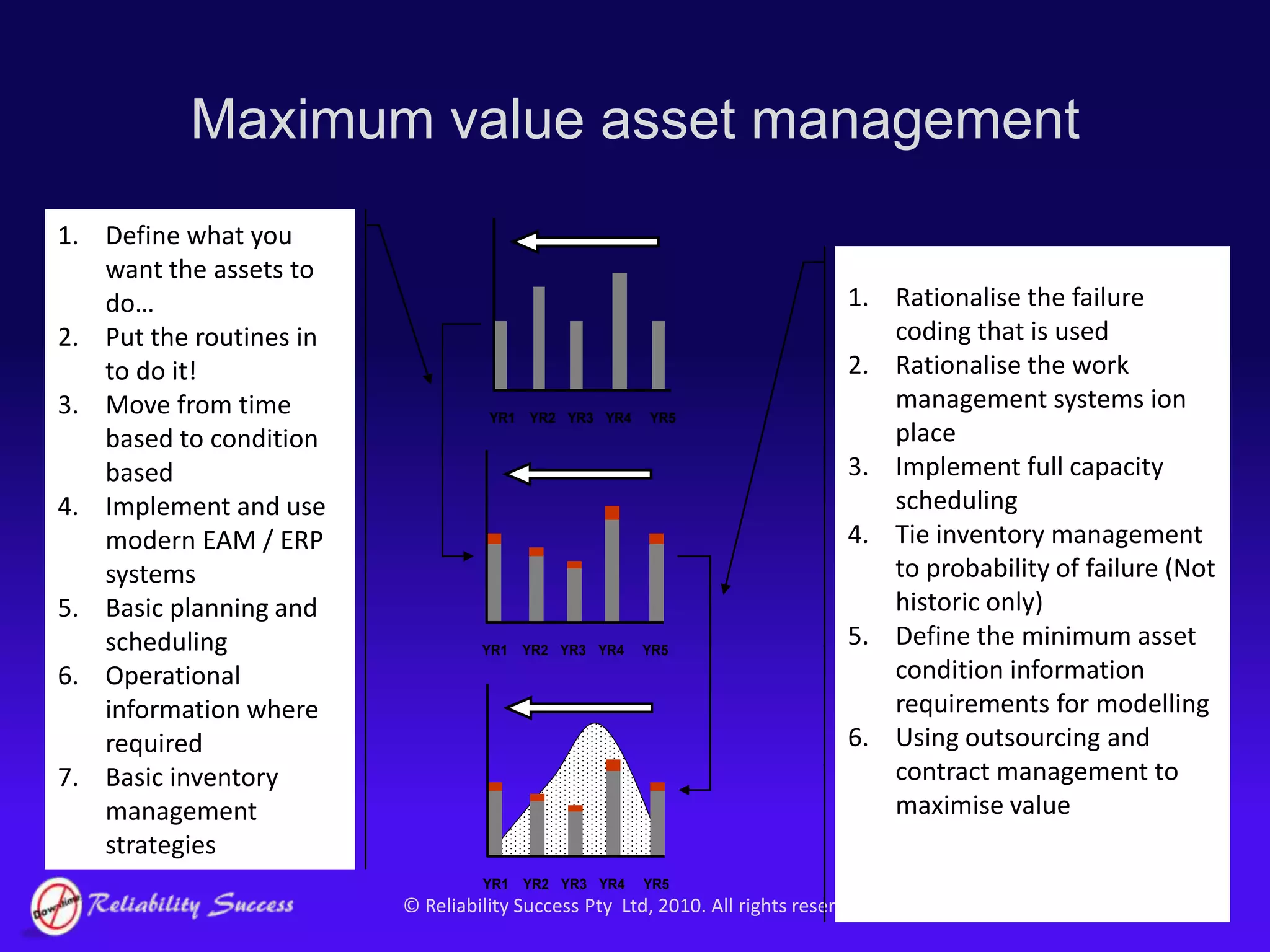
The document discusses the evolution of asset management practices, emphasizing the transition from traditional methods to a fourth generation focused on performance, risk, and comprehensive management strategies. It highlights the importance of strategies in achieving corporate visions, detailing various maintenance approaches and the need for modern technologies and data-driven decision-making. The need for improved performance and reduced costs is underscored, alongside the critical role of reliable information and proactive management in achieving organizational goals.