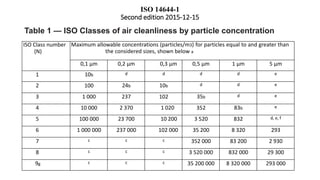
The document outlines ISO 14644-1:2015, which specifies standards for cleanrooms, including classifications of air cleanliness by particle concentration across various industries such as pharmaceuticals and aerospace. It details methods for monitoring, test procedures, and definitions related to cleanroom performance, focusing on airborne particles ranging from 0.1 μm to 5 μm. Additionally, it highlights the importance of maintaining specific air cleanliness classes based on defined thresholds and occupancy states.









![ISO 14644-1
Second edition 2015-12-15
3.4 Testing instrumentation
3.4.1 resolution
• smallest change in a quantity being measured that causes a perceptible
change in the corresponding indication
• [SOURCE: ISO/IEC Guide 99:2007, 4.14]
3.4.2 maximum permissible measurement error
• extreme value of measurement error, with respect to a known reference
quantity value, permitted by specifications or regulations for a given
measurement, measuring instrument, or measuring system
• [SOURCE: ISO/IEC Guide 99:2007, 4.26]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iso14644-1-240211053039-0ce67d38/85/ISO-14644-1-pptx-Cleanrooms-and-associated-controlled-environments-10-320.jpg)