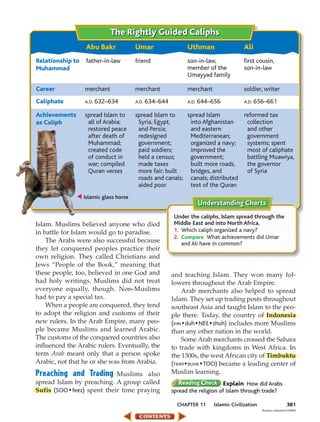
1. Muhammad experienced a difficult childhood, being orphaned at a young age and raised by relatives.
2. As an adult, he became a successful merchant in Makkah but was troubled by the inequality he saw.
3. In A.D. 610, while meditating in a cave, Muhammad received his first revelation from God and began preaching the message of Islam.













![Struggles Within Islam to the present day. Today most Muslims are
Sunnis. Iran and Iraq have the largest pop-
While Muslims split into two groups, ulations of Shiites.
the Arab Empire reached new heights.
Reading Focus Have you ever belonged to a club How Did Islam Split? Shiites (SHEE • eyets)
whose members could not agree on a leader? Read to believed that Ali, Muhammad’s son-in-law,
find out what happened when Muslims disagreed about should succeed him and that all future
who should lead them. caliphs should be Ali’s descendants.
According to the Shiites, the Umayyad
From the moment Muhammad died, caliphs in Damascus had no right to rule.
Muslims began arguing about who had Sunnis (SU • nees), who outnumbered
the right to be caliph. The quarrel over Shiites, accepted the Umayyad dynasty as
who should succeed Muhammad split the rightful caliphs, though they did not always
Muslim world into two groups, the Sunnis agree with their policies. Over time, the
and the Shiites. This division has remained Shiites and Sunnis developed different reli-
gious practices and customs.
Who Were the Abbasids? The Abbasids
(uh • BA • suhds) were the dynasty that came
Royal Caliphs after the Umayyads. The Umayyads lost
Ibn Khaldun recorded historical events and power in A.D. 750 because they angered
his interpretation of them. many Muslims, especially in Persia. Persian
“When one considers Muslims felt that Arab Muslims got
what God meant the special treatment. They got the best
caliphate to be, nothing jobs and paid fewer taxes.
more needs [to be said]
When these Muslims rebelled,
about it. God made the
caliph his substitute to people all over the empire joined
handle the affairs of His them. They overthrew the Umayyads,
servants. He is to make and a new dynasty began. The
them do the things that new caliph was a descendant of
are good for them and Muhammad’s uncle. His name was
forbid them to do those Abu al-Abbas. The new Abbasid
that are harmful. He has
been directly told so.
dynasty lasted until 1258.
A person who lacks the The Great Mosque The Abbasids devoted their energies to
power to do a thing is of Damascus trade, scholarship, and the arts. They also
never told to do it.” built by the built a new capital, Baghdad (BAG • dad).
Umayyad caliphs.
—Ibn Khaldun, Baghdad prospered because it was
“The Muqaddimah”
beside the Tigris River and near the
Euphrates River. It was a good location to
trade since many people used the rivers to
According to Khaldun, what is the ship goods north and south. As a result, the
relationship between God and the caliph? Arab Empire grew even wealthier.
The Abbasid dynasty is also known for
bringing Persian influence into the empire.
382 CHAPTER 11 Islamic Civilization
Alison Wright/CORBIS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap11r-121114122341-phpapp02/85/islamic-civilization-15-320.jpg)




![Muslim
Ways of Life
What’s the Connection? Meeting People
In Section 2, you learned that Mamun (mah • MOON)
many Muslim rulers brought peace al-Razi (ahl • RAH • zee)
and order to their empires. Peace and Ibn Sina (IH • buhn SEE • nuh)
order helped trade to increase. Trade, Omar Khayyam
in turn, brought great wealth to the (OH • MAHR KY • YAHM)
Muslim empires. Ibn Khaldun (IH • buhn KAL • DOON)
Focus on the Building Your Vocabulary
• While Muslim traders enjoyed great mosque (MAHSK)
success and cities grew, most
bazaar (buh • ZAHR)
Muslims lived in villages in the
country. (page 388) minaret (MIH • nuh • REHT]
crier (KRY • uhr)
• Muslims made valuable contributions
in math, science, and the arts.
(page 390)
Reading Strategy
Organizing Information Create a
pyramid to show the social classes
Locating Places in the early Muslim world.
Granada (gruh • NAH • duh)
Agra (AH • gruh)
A.D. 800 1100 1400
c. A.D. 900 c. 1100 c. 1375
Al-Razi writes Omar Khayyam Ibn Khaldun
medical texts writes the writes
Rubaiyat histories
CHAPTER 11 Islamic Civilization 387
(l)Mary Evans Picture Library, (c)Bettmann/CORBIS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap11r-121114122341-phpapp02/85/islamic-civilization-20-320.jpg)



![founded the House of Wisdom in Baghdad.
Mamun staffed his center with Christian, The Mystery
Jewish, and Muslim scholars. These scholars of Smallpox
exchanged ideas and rewrote Greek, Persian, The Muslim scientist al-Razi urged scientists
and Indian works in Arabic. and doctors to search for the causes of
Scholars in Muslim lands saved much of disease, rather than just treatments.
the learning of the ancient world. “Although [scholars] have certainly
Europeans in the West had made some mention of the
lost this knowledge after the treatment of the Small-Pox . . .
there is not one of them who
Western Roman Empire fell.
has mentioned the cause of the
Through Muslim scholars, existence of the disease, and how
western Europeans found it comes to pass that hardly any
out about Aristotle and other one escapes it . . .”
ancient Greek thinkers. —Al-Razi, “On the Causes
of Small-Pox”
Mathematics and Science Al-Razi’s own theory about the
Muslims made important cause of smallpox was incorrect.
advances in mathematics. His efforts to find the cause,
Later, they passed on these however, helped change how
discoveries to Europeans. doctors and scientists investi-
For example, Muslims gated diseases.
Muslim
invented algebra, a type of medical
mathematics still taught in drawing
schools today. The Arabs also
Why was al-Razi concerned about previous
borrowed the symbols 0 through 9 from scholars’ studies of smallpox?
Hindu scholars in India. These numbers
were later used by Europeans. Today, they
are known as “Arabic numerals.”
Muslims also made progress in science. Other Muslim scientists experimented
Muslim scientists who studied the heavens with metals and kept records of their work.
perfected the Greek astrolabe. Sailors used As a result, the Arabs are considered the
this tool to study the stars and then deter- founders of chemistry. One of the best-
mine their location at known Muslim chemists was al-Razi (ahl •
sea. Muslim scientists RAH • zee), who lived from A.D. 865 to A.D. 925.
used the astrolabe to Al-Razi developed a system for categoriz-
measure the size and ing substances as animal, mineral, or veg-
distance around the etable. He also wrote books for doctors that
earth. Based on their helped them to identify diseases.
measurements, they Arab doctors were the first to discover
realized that the earth that blood circulates, or moves to and from
is round. the heart. The Persian doctor Ibn Sina (IH •
buhn SEE • nuh) showed how diseases spread
from person to person. As they worked,
Muslim astrolabe Muslim doctors published their findings.
CHAPTER 11 Islamic Civilization 391
(t)R & S Michaud/Woodfin Camp & Assoc., (b)Paul Dupuy Museum, Toulouse, France/Lauros-Giraudon, Paris/SuperStock](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap11r-121114122341-phpapp02/85/islamic-civilization-24-320.jpg)
![Bettmann/CORBIS
OMAR KHAYYAM
1048–1131
and IBN KHALDUN
1332–1406
Persia—was a
Omar Khayyam—who was born in
losopher, but he is
mathematician, astronomer, and phi
that Khayyam
best known as a poet. Scholars believe
poem, the Rubaiyat,
wrote only parts of his most famous
verses and the
but they are certain that at least 120
ds:
main concepts are his. Stanza XII rea
gh,
“ A Book of Verses underneath the Bou
Thou
A Jug of Wine, a Loaf of Bread—and
Beside me singing the Wilderness— Omar Khayyam
Oh, Wilderness were Paradise enow
[enough]! ”
—Omar Khayyam, Rubaiyat
music before he
Khayyam wrote books on algebra and
ry for 18 years and
was 25 years old. He led an observato
r.
developed a more accurate calenda
Arab scholars.
Ibn Khaldun is one of the most famous
gist, and politician.
He was a historian, geographer, sociolo
the rulers of Tunis
He was born in Tunisia and worked for
sador to one of the
and Morocco. He also served as ambas
Cairo, Egypt. He wrote
Spanish kingdoms and as a judge in
. His best-known
much about social and political change
written in 1375. It is
work is Muqaddimah (Introduction),
bar (universal history).
the first volume of his book Kitab al-I
ntific way to analyze
In this book, he tried to develop a scie
t historians who studied
historical events. He is one of the firs
ure affect history.
how geography, economics, and cult
verses
The Rubaiyat is a collection of 4-line
m that is
called quatrains. Find a modern poe
made up of quatrains.
Ibn Khaldun
392](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap11r-121114122341-phpapp02/85/islamic-civilization-25-320.jpg)




![Self-Check Quiz To help you prepare for
Geography Skills the Chapter Test, visit jat.glencoe.com
Study the map below and answer the follow-
ing questions.
20. Movement Why was the Abbasid empire Using Technology
unable to expand to the Black Sea? 25. Exploring Language Use the Internet and
21. Region What bodies of water could your local library to find English words that
Abbasid merchants use to trade with have their origins in the Arabic language.
the outside world? Create a chart using your computer show-
ing English words and their Arabic roots.
22. Place You learned that the Abbasids
changed the capital city from Damascus
to Baghdad. Look at the locations of those
Linking Past and Present
cities. Which do you think would have been 26. Evaluating Impact Which Islamic inven-
the best location for a capital city? Why? tion or development do you think has the
greatest effect on the world today? Explain
your choice.
Abbasid Empire
Building Citizenship Skills
40°E
N
Aral 60°E
27. Analyzing Documents Do research to
Da
Ca
nu b
e R. W E
Sea find out how the United States Constitution
sp
Black Sea 40°N protects religious freedoms. Do you think
ian
S
BYZANTINE the way Muslim empires treated religion
Se
EMPIRE would be allowed under the U.S.
a
Ti
Constitution? Explain.
gri
PERSIA
sR
SYRIA
.
Baghdad
Mediterranean Damascus
Eu
ph
Sea r
Jerusalem ates R.
Pe
EGYPT
PALESTINE r si a
nG
ulf
Analyze
Re
Madinah 0 500 mi. In the first stanza of the Rubaiyat, Omar
dS
0 500 km Khayyam welcomes the morning.
20°N
ea
.
R Makkah Lambert Azimuthal
le
Equal-Area projection
(Mecca) “Wake! for the sun, the shepherd of
Ni
the sky,
KEY Has penned [confined] the stars within
Abbasid empire during reign Abbasid capital their fold on high,
of Harun al-Rashid, A.D. 800 Former Umayyad
capital And, shaking darkness from his mighty
limbs,
Scatters the daylight from his burning eye.”
Read to Write —Rubáiyát of Omar Khayyám:
A Paraphrase From
23. Descriptive Writing Suppose you are Several Literal Translations,
an Arab merchant traveling in the desert by Richard Le Gallienne
with a caravan. Write three diary entries,
each describing the events of your day.
Each day you choose to describe should
focus on a different aspect of the life 28. What has been penned up by the sun?
of a merchant. Share your entries with 29. Personification is when a writer gives
the class. human qualities to something that
is not human. How does Khayyam
24. Using Your Write a poem or personify the sun in this stanza?
short story using the facts from your
completed foldable.
CHAPTER 11 Islamic Civilization 397](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap11r-121114122341-phpapp02/85/islamic-civilization-30-320.jpg)

