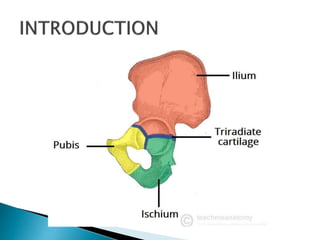
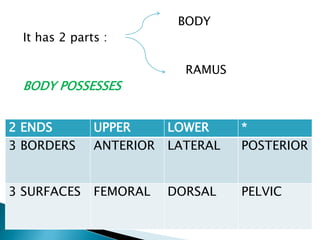
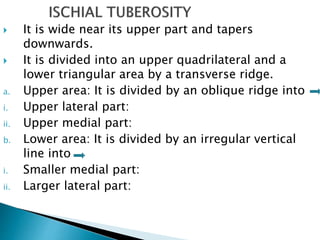
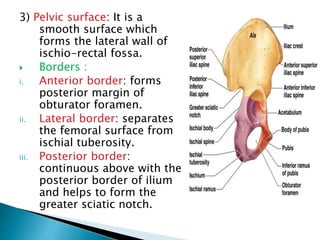
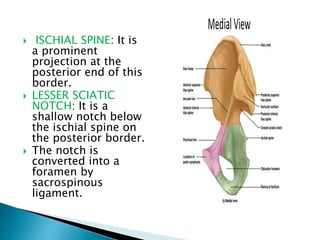
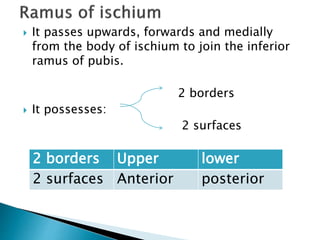
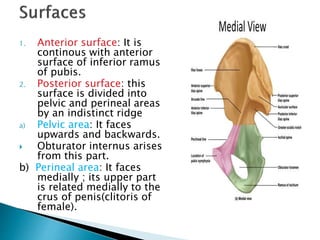
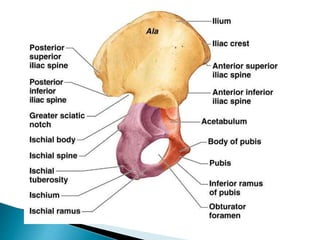
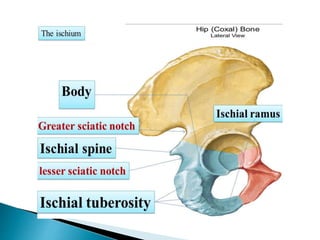
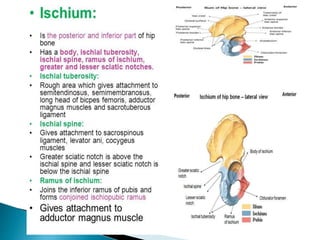
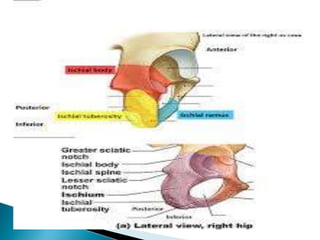
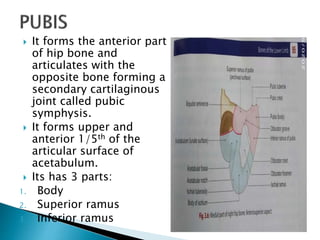
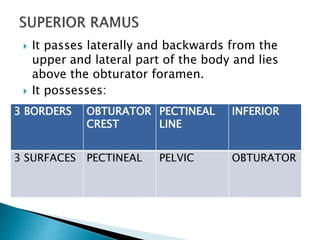
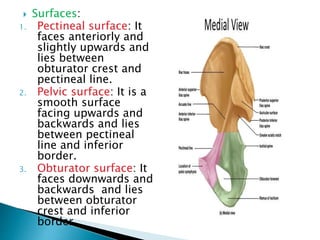
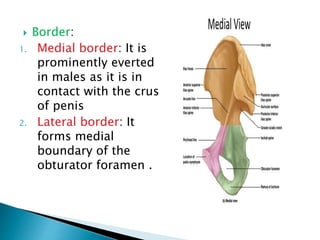
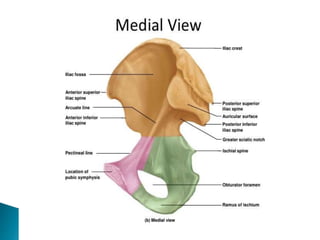
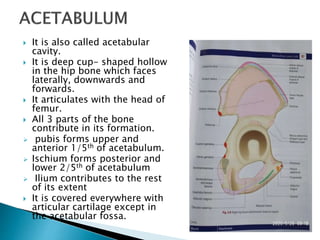
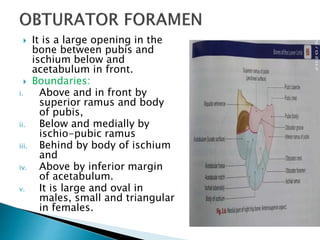
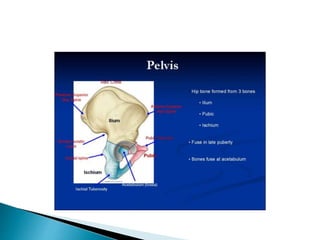
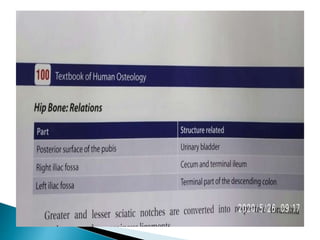
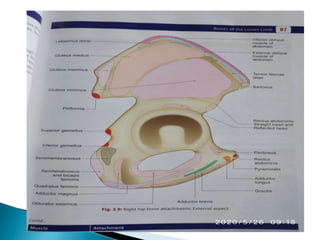
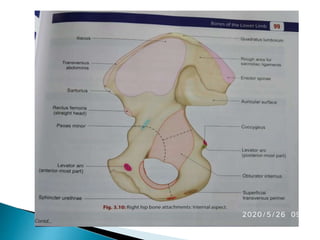
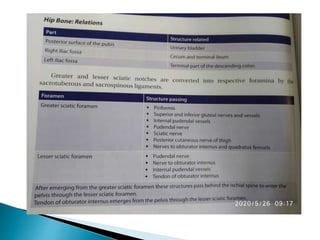
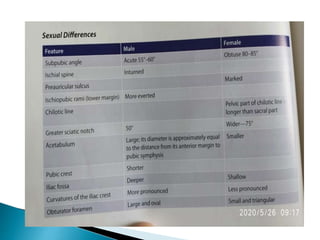
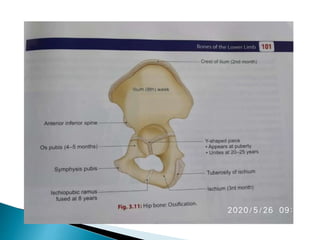
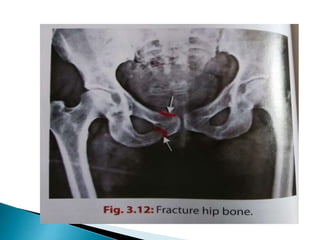
The document provides details on the anatomy of the hip bone, including its key parts and features. It describes the three parts that make up the hip bone - the ilium, ischium, and pubis. It outlines the structures and surfaces of each part, including the acetabulum, ischial tuberosity, obturator foramen, and pubic crest. Sex differences in anatomy are also briefly mentioned.