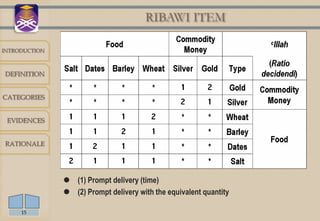
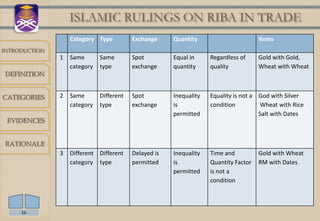
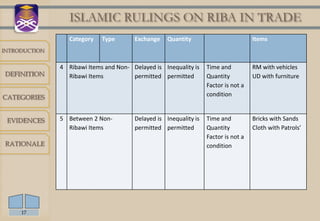
Riba refers to usury or interest charged on loans. It is prohibited in Islam based on evidence from the Quran and hadith. There are two main categories of riba - debt riba, which includes interest on loans, and trade riba, which involves unequal exchange of goods. Certain goods like gold, silver, wheat and barley are considered ribawi items where rules on quantity and time of exchange must be followed to avoid riba. The prohibition aims to prevent injustice and burden on borrowers that can destabilize societies.