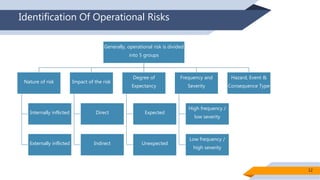
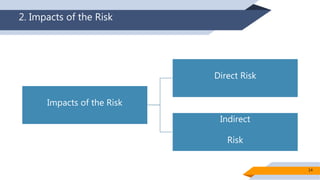
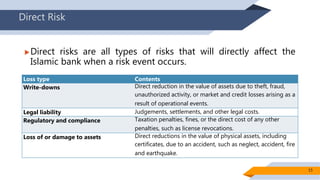
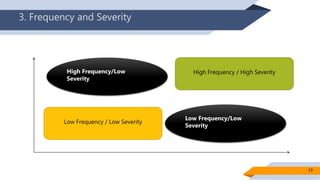
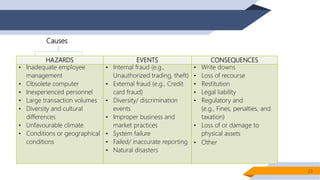
Operational risk in Islamic finance can arise from a variety of sources. The document identifies six main categories of operational risk: 1) Shariah non-compliance risk, 2) people risk, 3) technology risk, 4) fiduciary risk, 5) legal risk, and 6) reputational risk. It also discusses the nature of operational risks as either internally or externally inflicted, the impacts as direct or indirect, and the degree of expectancy as expected or unexpected losses. Proper identification and management of operational risks are important for Islamic financial institutions.