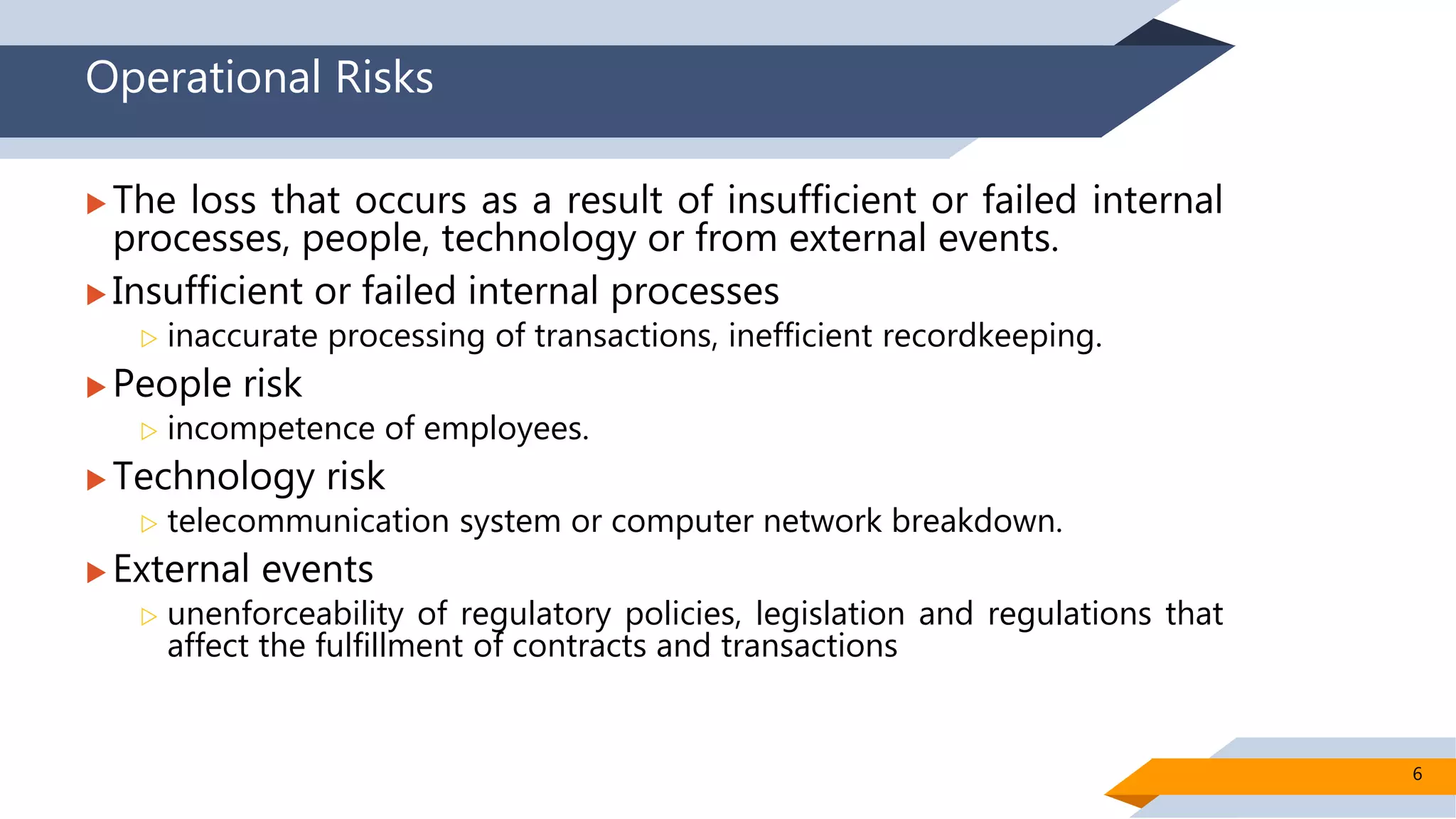
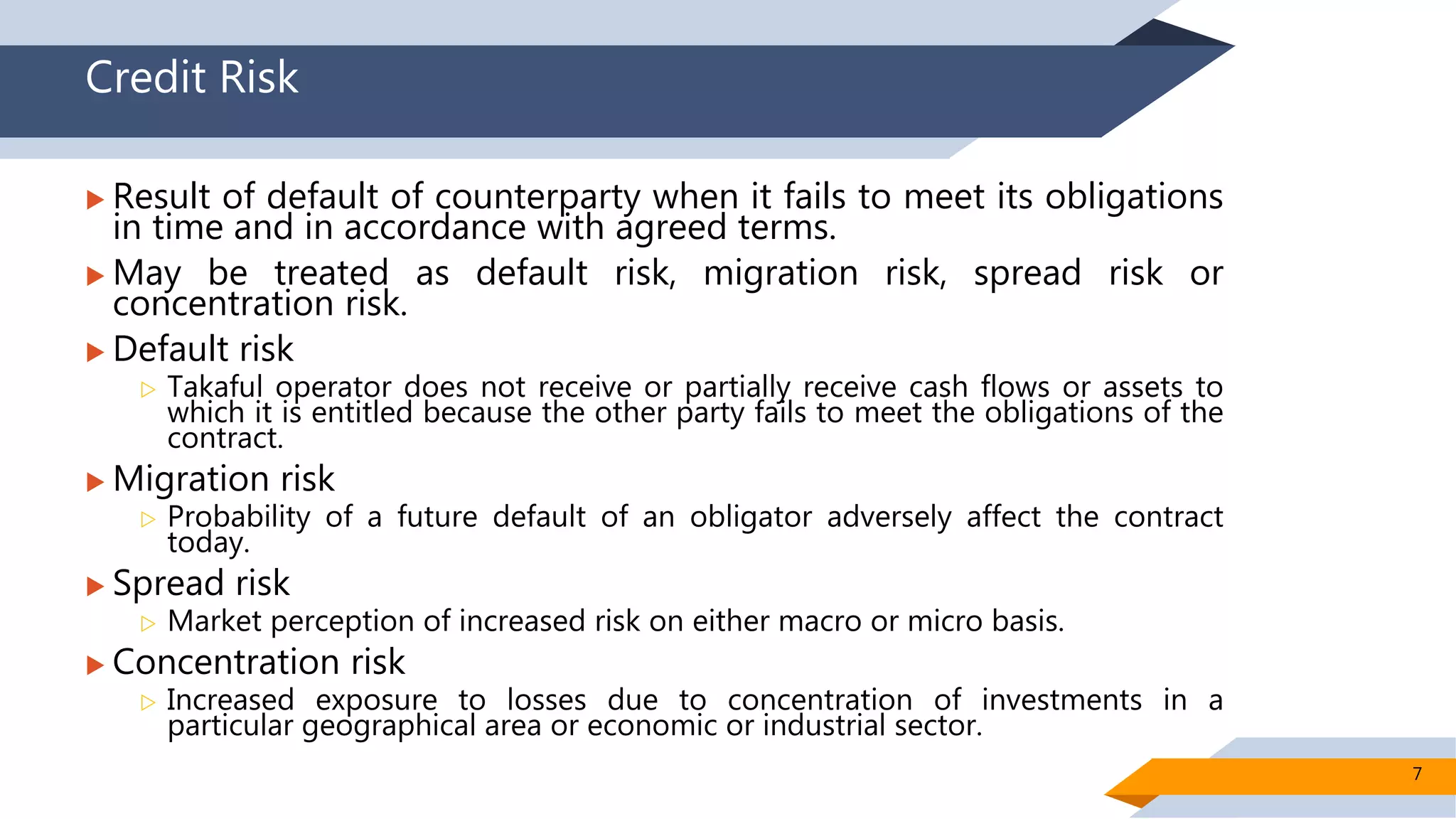
This document discusses risk management in Islamic finance, specifically for Takaful (Islamic insurance) operations. It identifies five main types of risk for Takaful operators: underwriting risks, operational risks, credit risks, liquidity risks, and market risks. For each risk, it provides examples of how the risk can occur in a Takaful context. It then outlines several ways Takaful operators can manage each of these risks, such as establishing standard underwriting procedures, recruiting skilled IT professionals, implementing liquidity ratios, and exploring Shariah-compliant hedging instruments. The document emphasizes that effective risk management is important for Takaful operators to provide protection in accordance with Islamic principles.