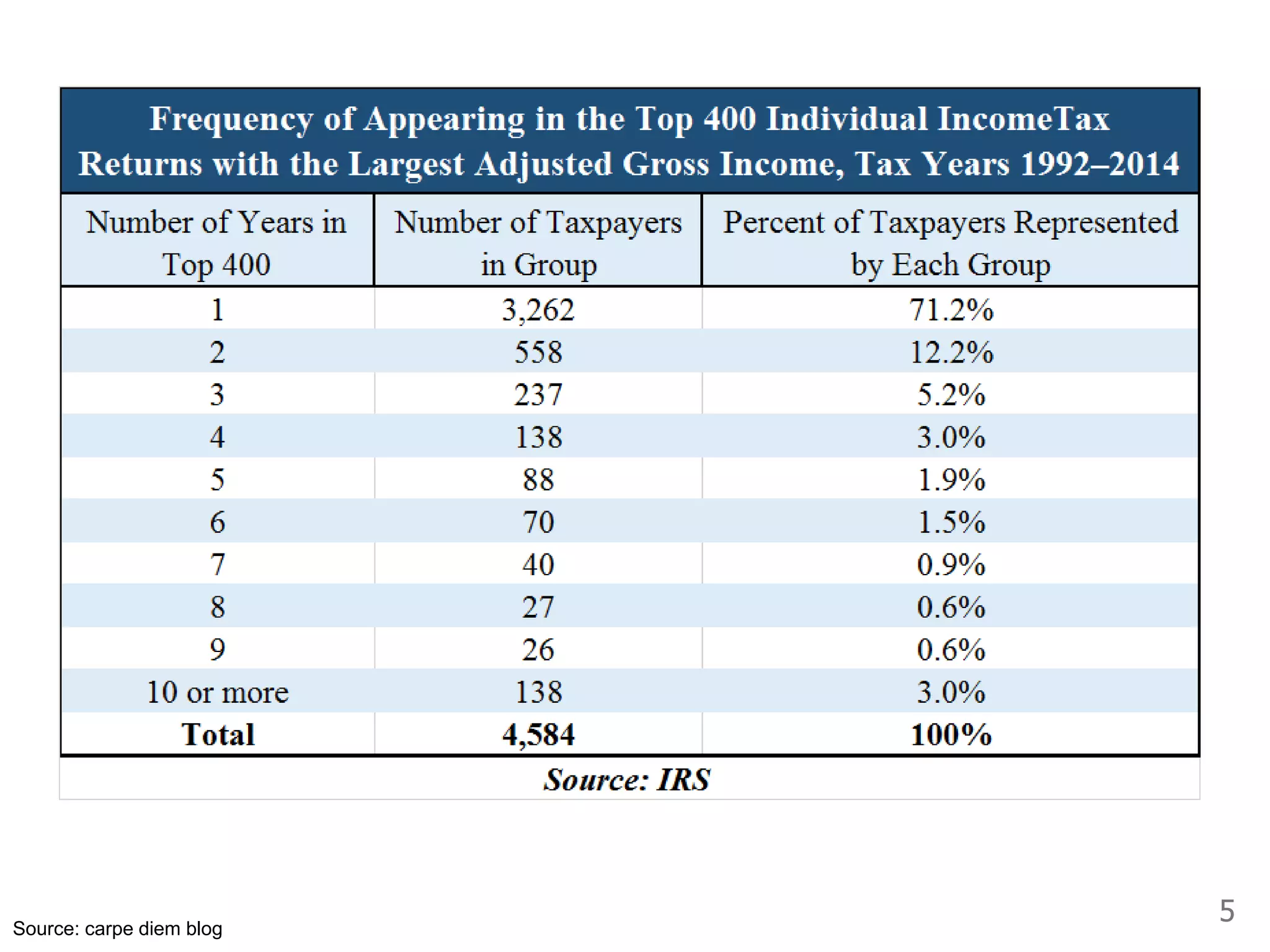
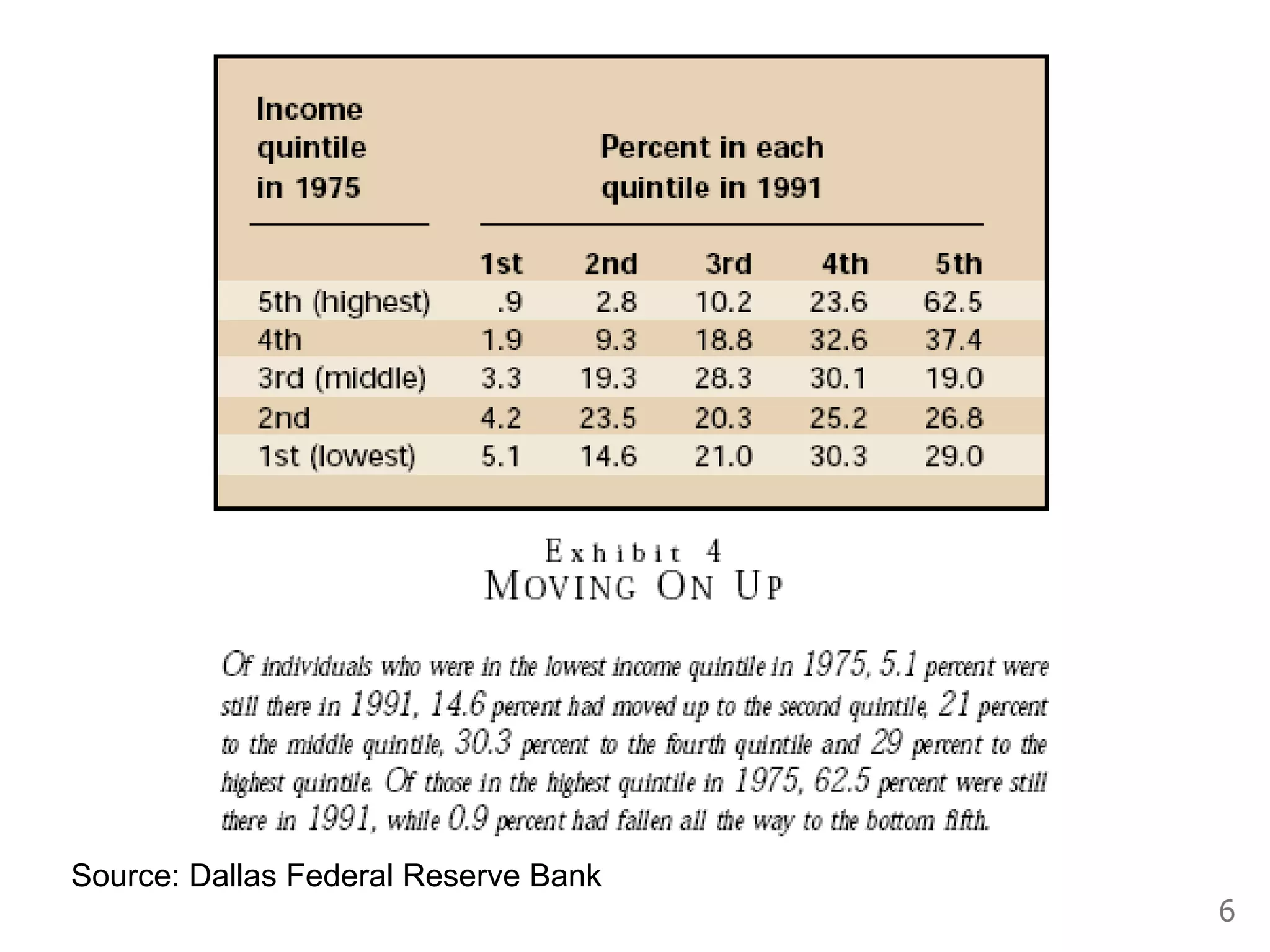
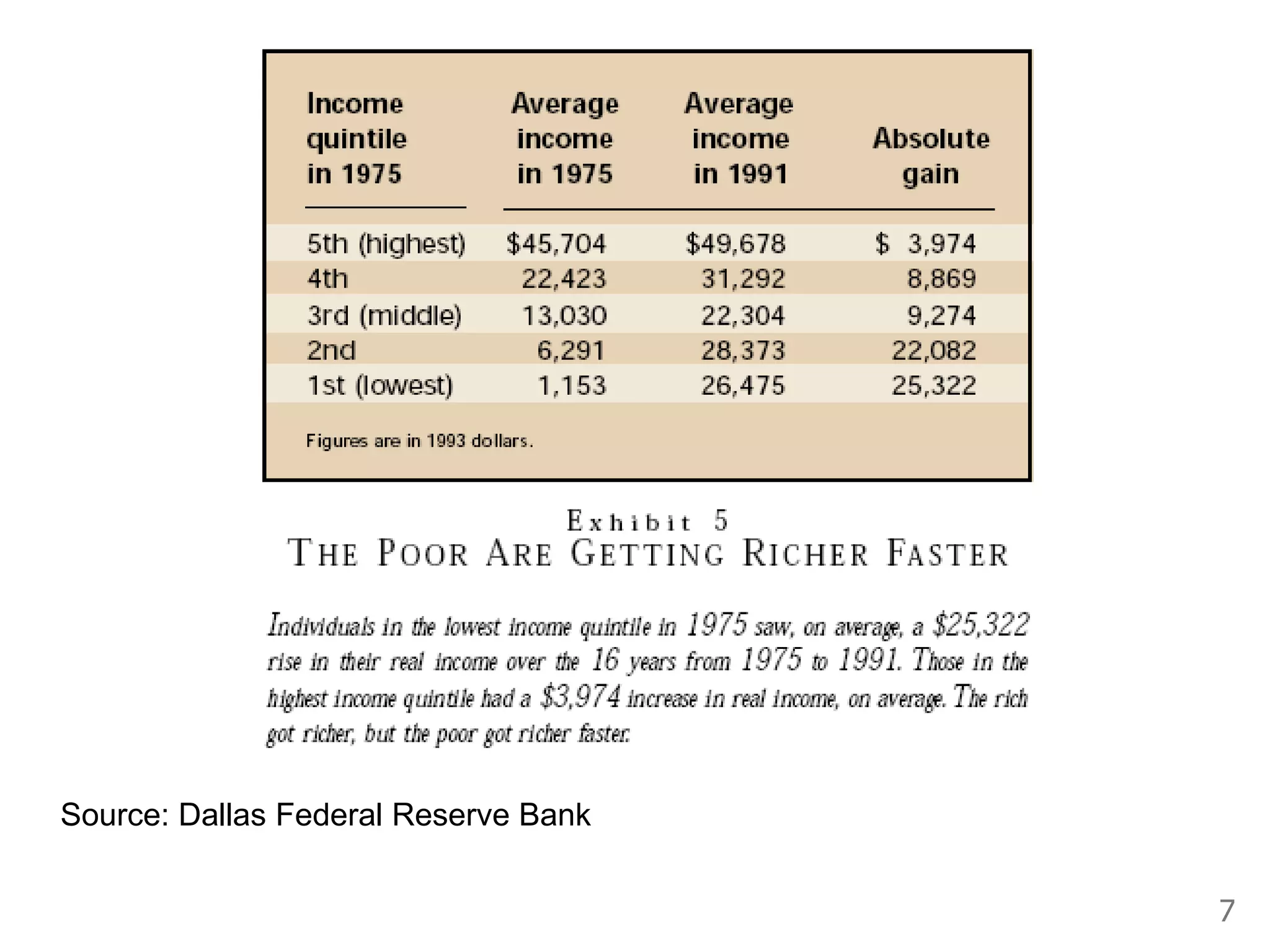
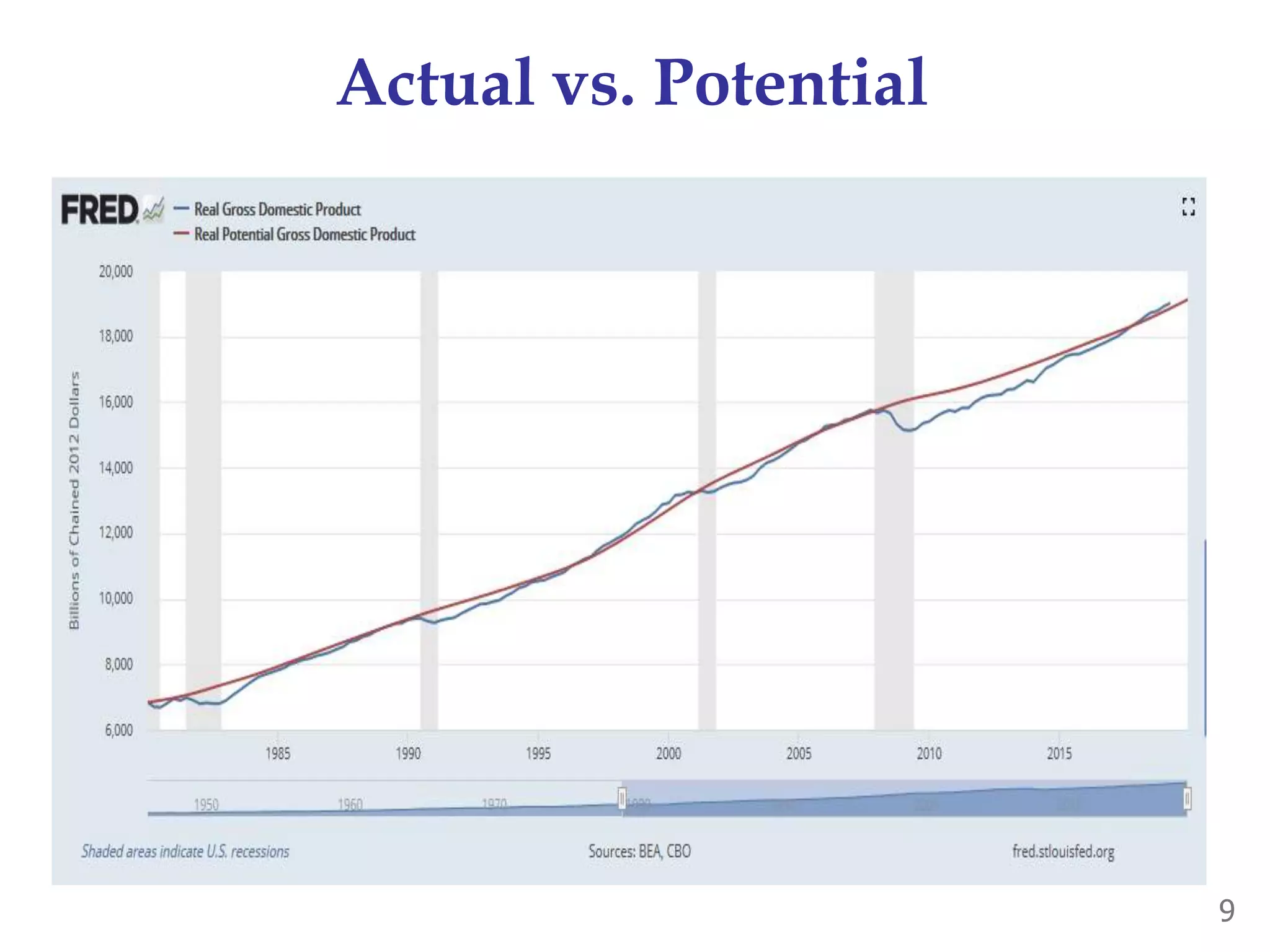
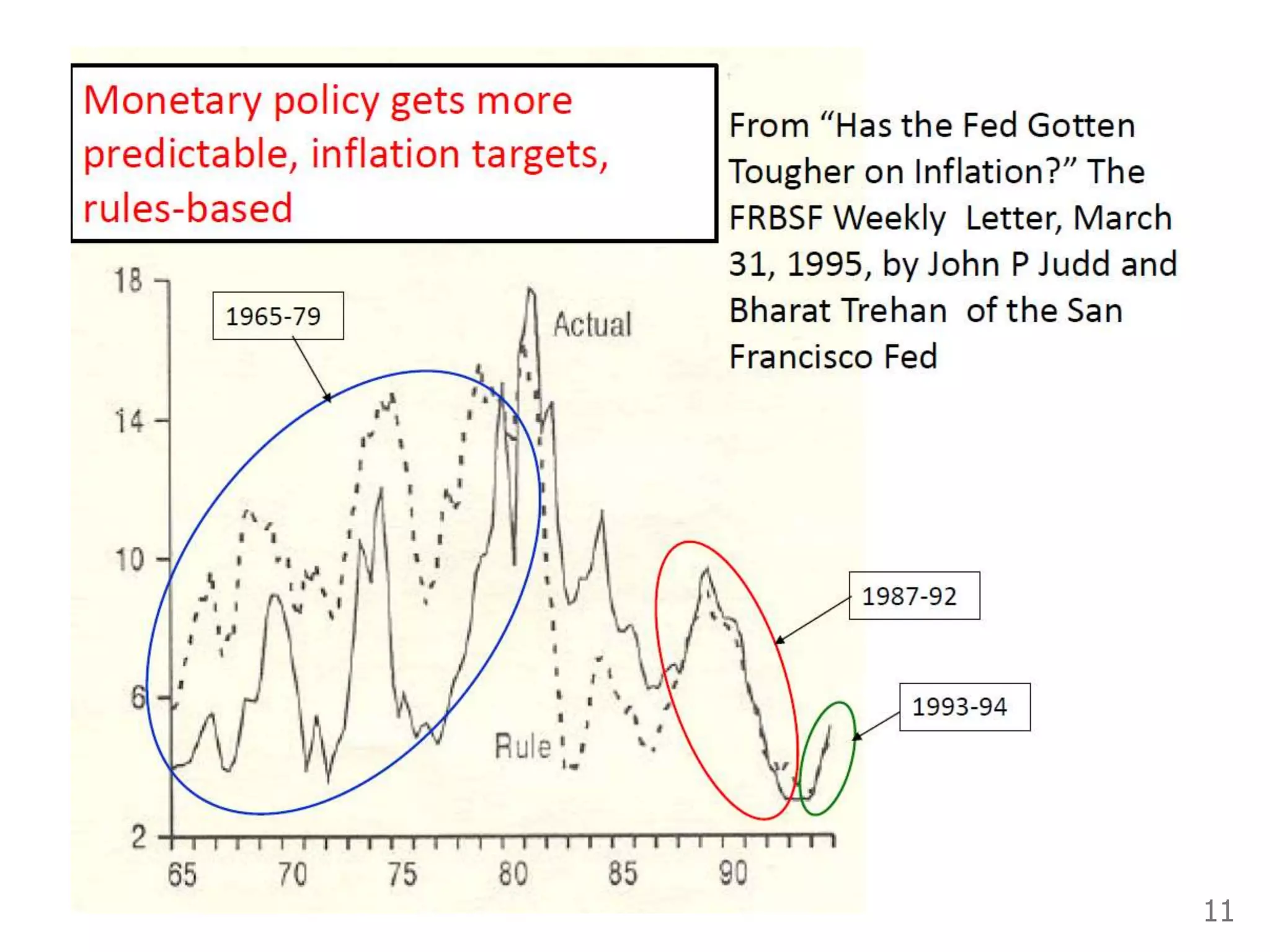
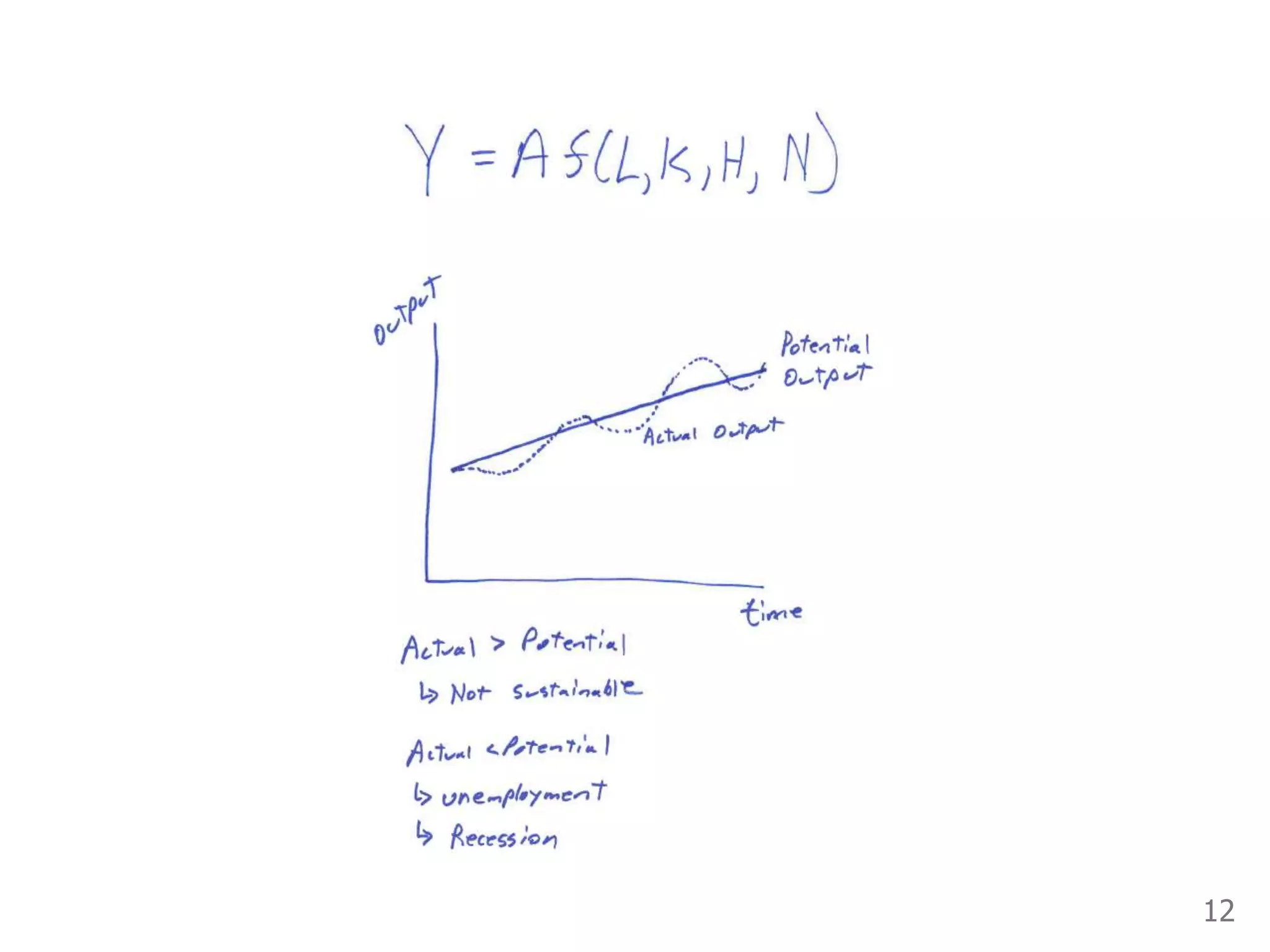
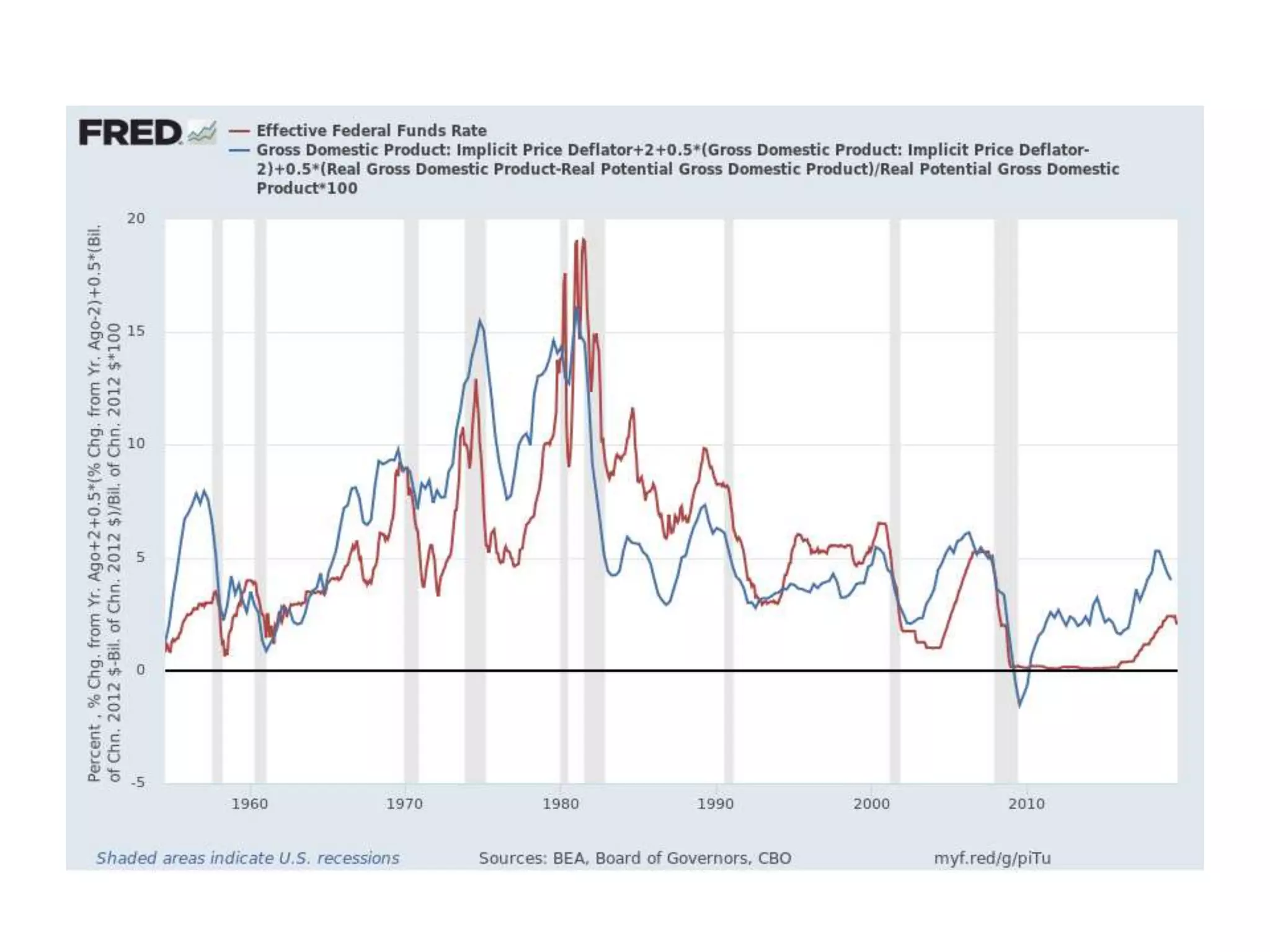
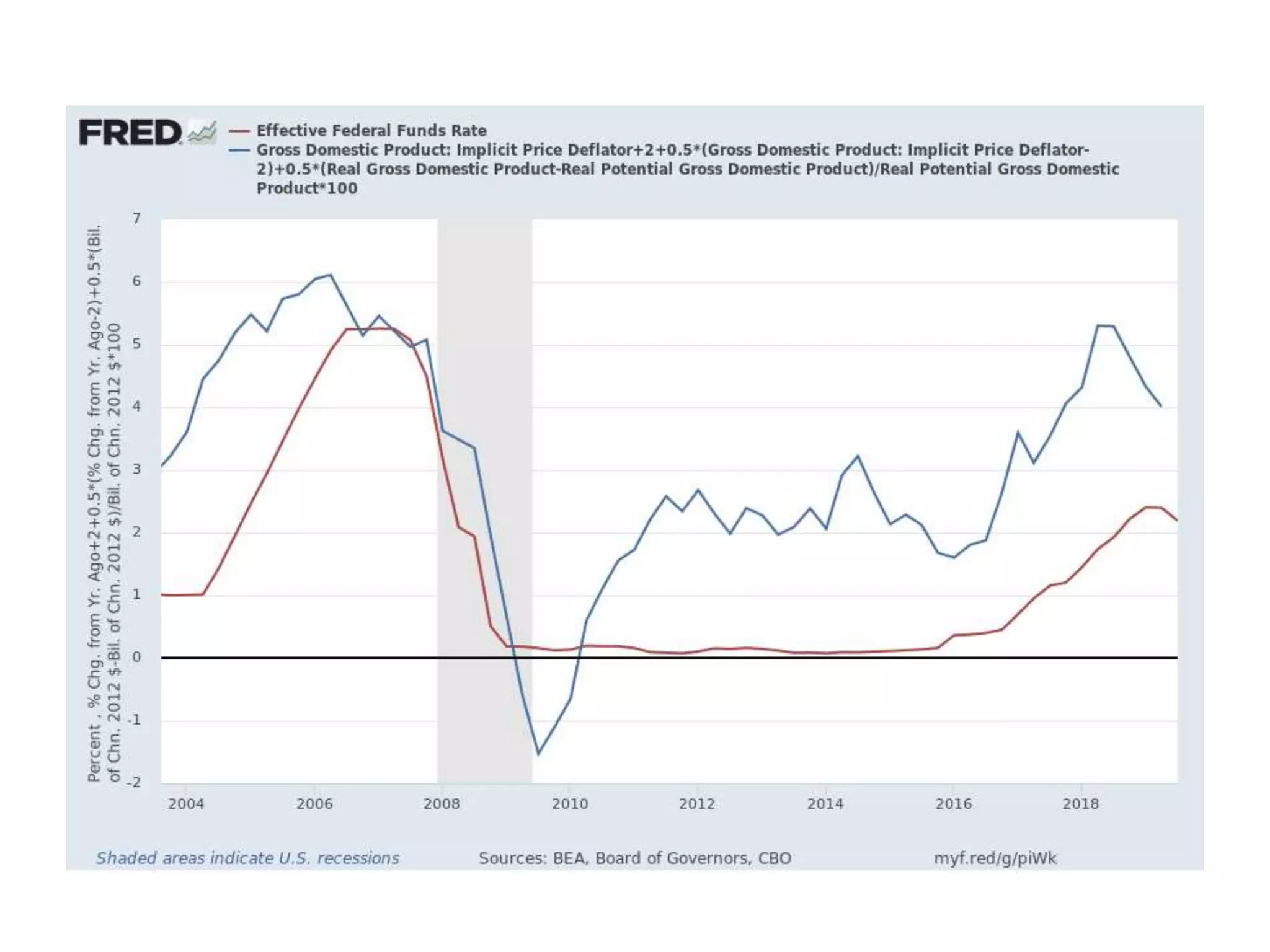
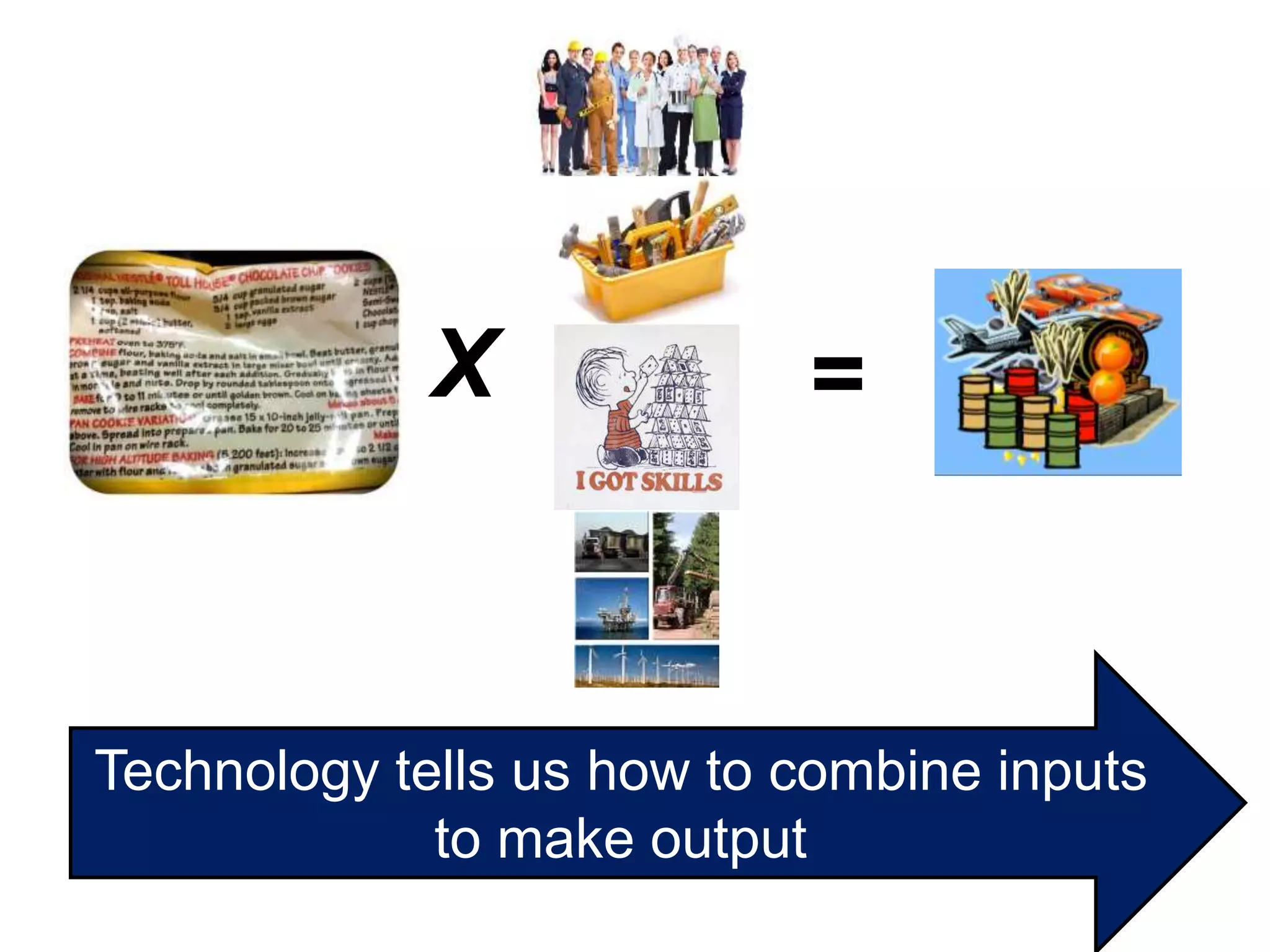
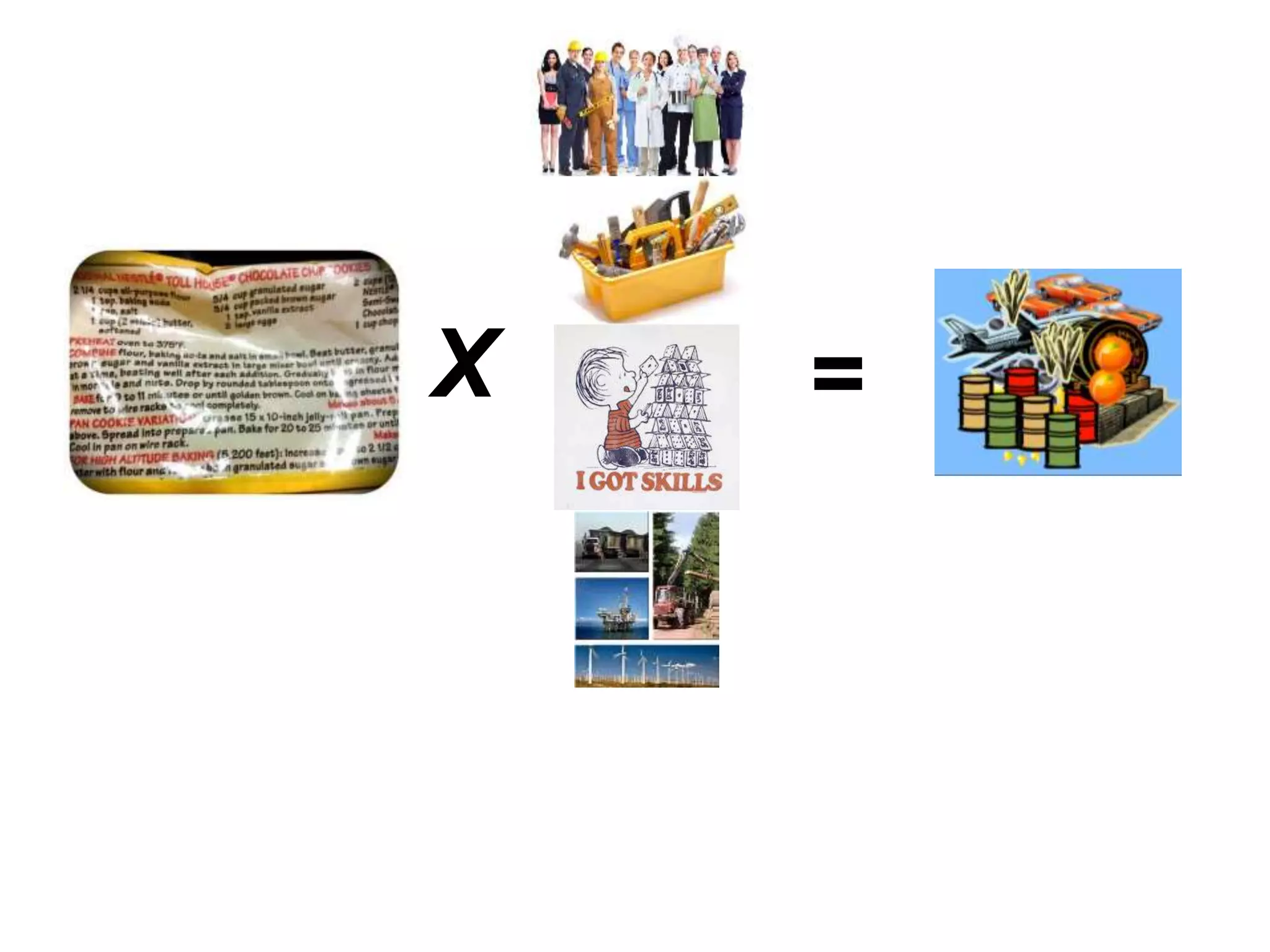
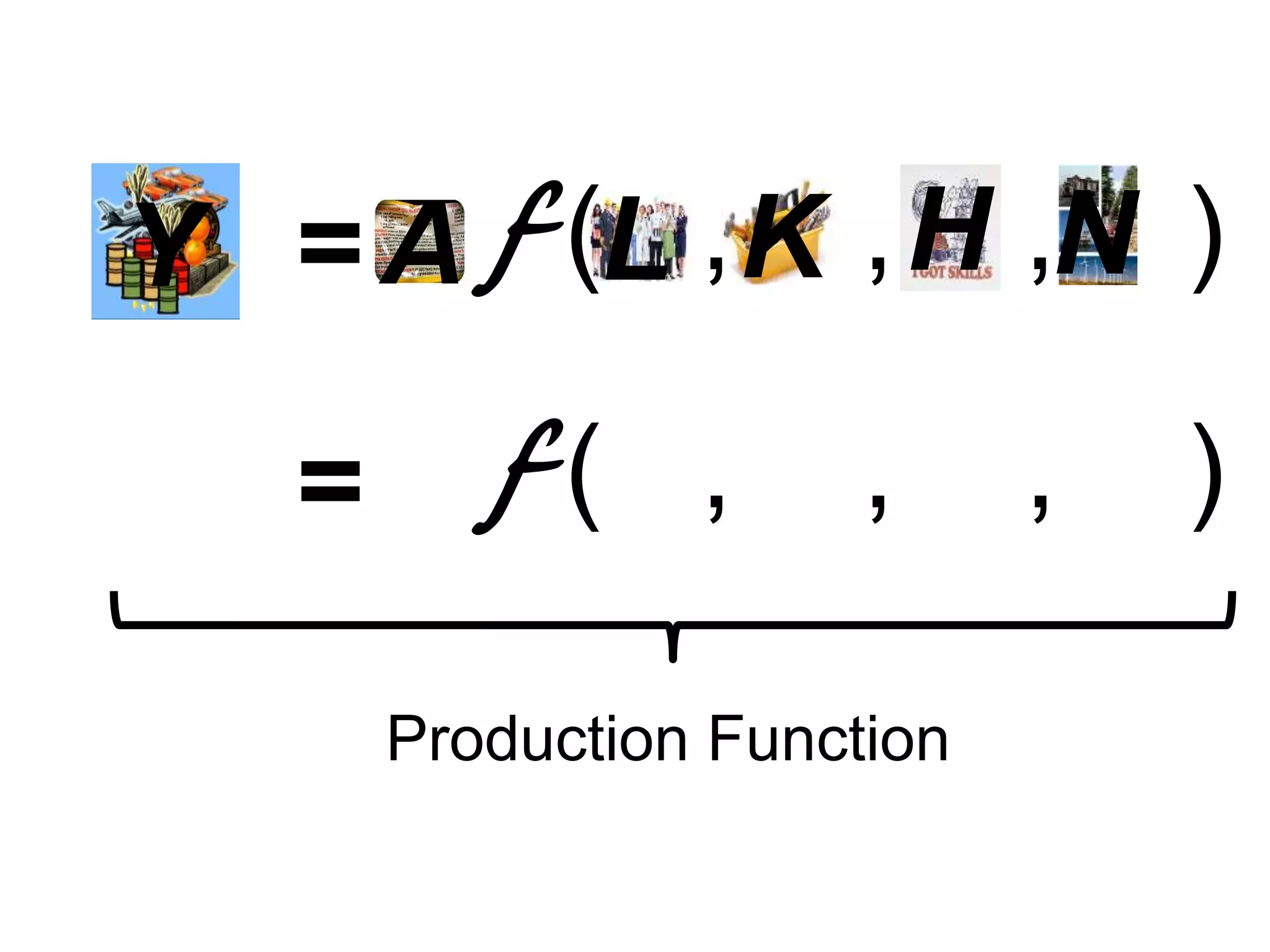
While production growth and industrialization have lifted living standards globally, unrestrained growth poses environmental risks. Some key points:
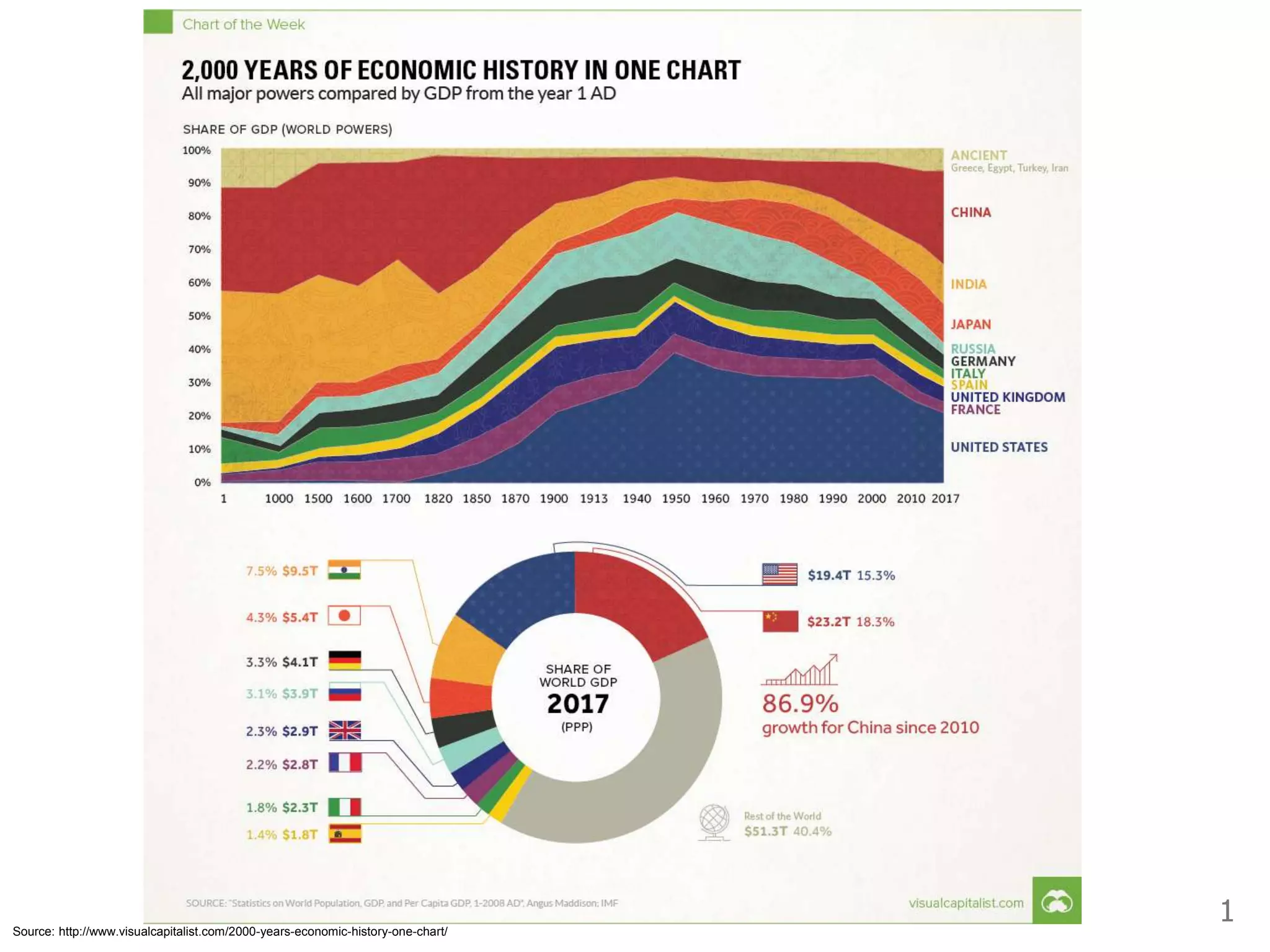
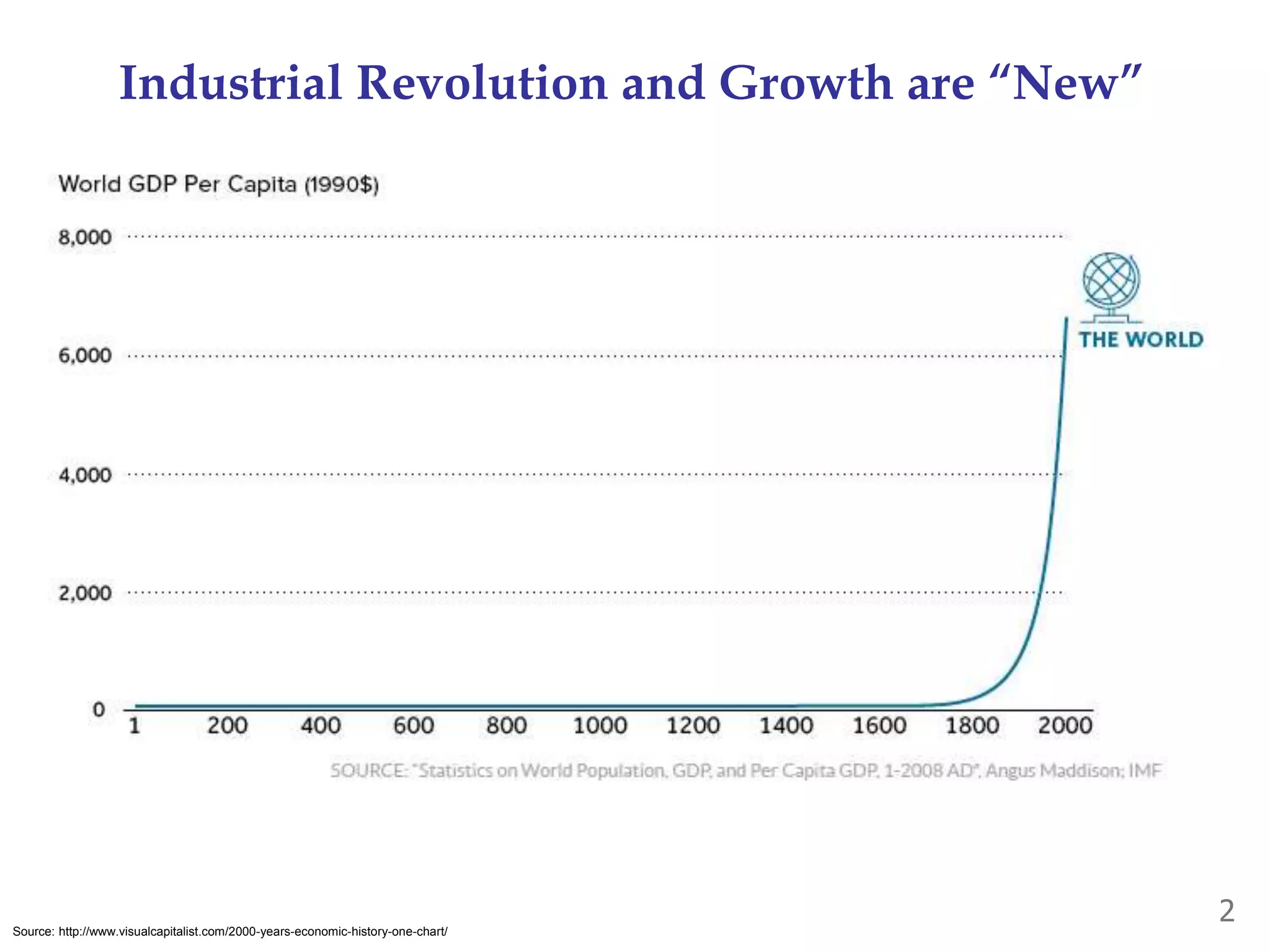
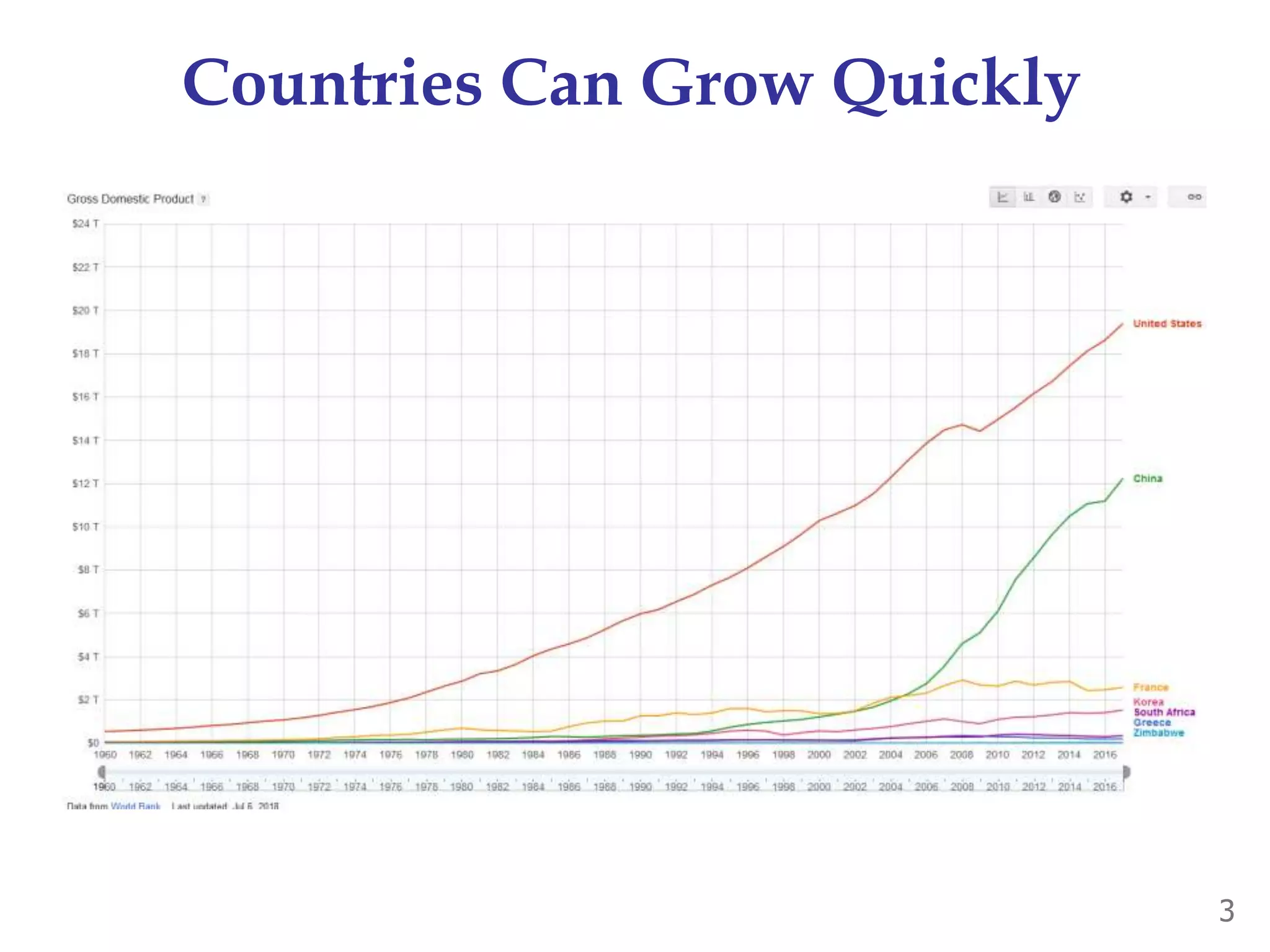
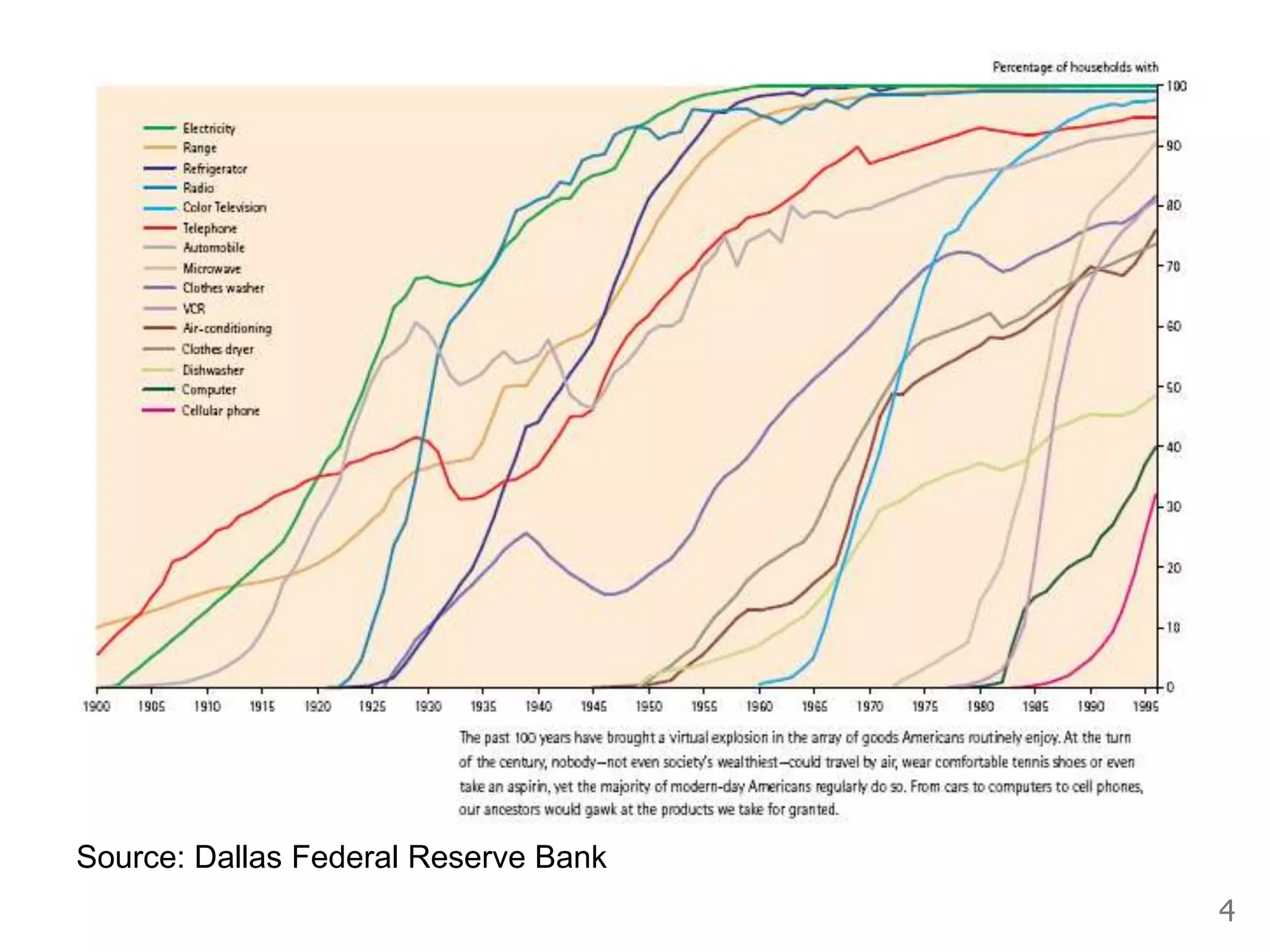
- Industrialization and economic growth are relatively new phenomena historically. Most countries grew quickly after industrializing.
- Higher production and GDP per capita are generally associated with lower poverty, but environmental impacts must be addressed.
- Productivity gains, through more/better capital, skills, technology and resource use, are important for growth and living standards. But policies are needed to encourage sustainable practices.
- There are no simple answers, as both economic development and environmental protection are important objectives. Balanced and innovative solutions are needed.