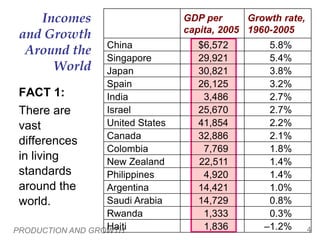
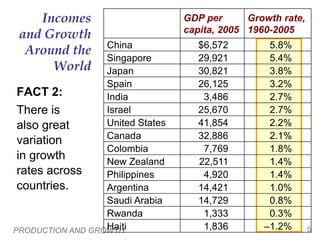
This document discusses differences in living standards and economic growth rates around the world. It begins by showing data on GDP per capita and other indicators for families in the UK, Mexico, and Mali to illustrate vast differences in living standards globally. Tables then show data on GDP per capita and growth rates for various countries from 1960-2005, demonstrating both differences in incomes and variation in growth rates. The document poses questions about why some countries are richer and grow faster than others and what policies may help raise growth rates and living standards. It then discusses various determinants of productivity that influence economic growth and living standards.








![PRODUCTION AND GROWTH 10
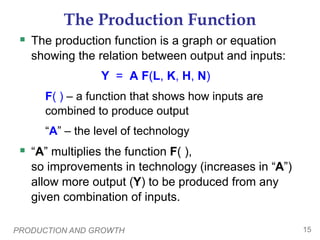
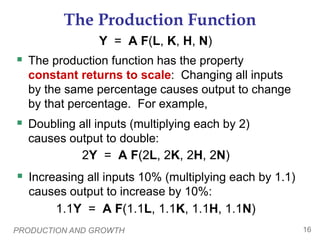
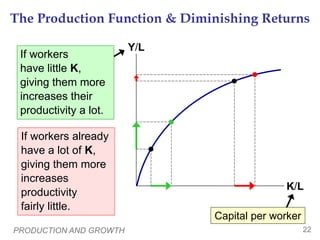
Physical Capital Per Worker
Recall: The stock of equipment and structures
used to produce g&s is called [physical] capital,
denoted K.
K/L = capital per worker.
Productivity is higher when the average worker
has more capital (machines, equipment, etc.).
i.e.,
an increase in K/L causes an increase in Y/L.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apmacroeconchapter25powerpointforstudents-231111022725-b7677d4b/85/AP_MacroEcon_Chapter_25_Powerpoint_For_Students-ppt-11-320.jpg)