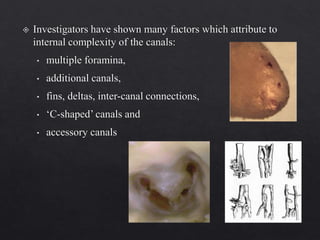
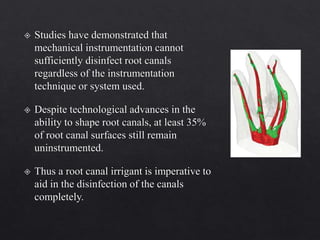
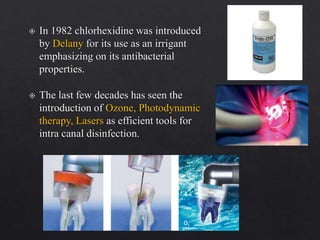
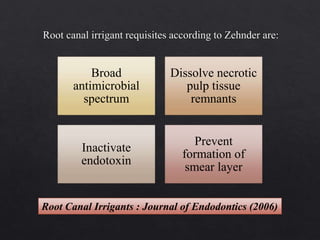
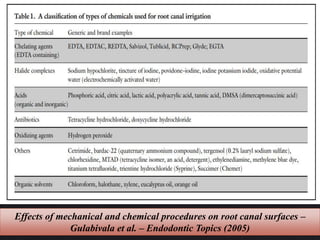
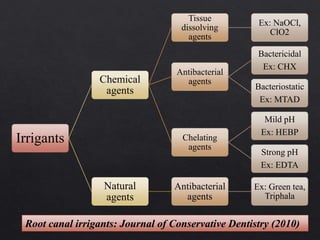
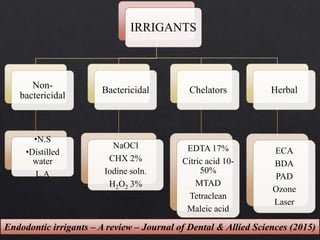
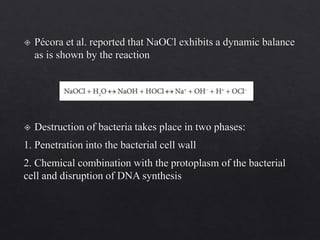
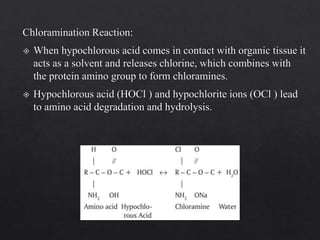
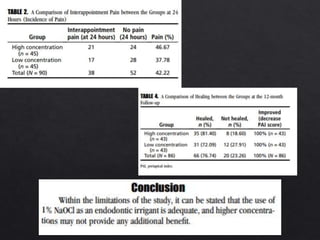
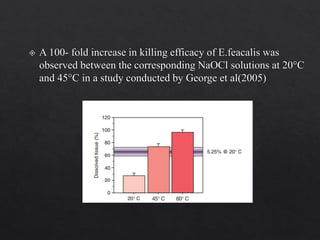
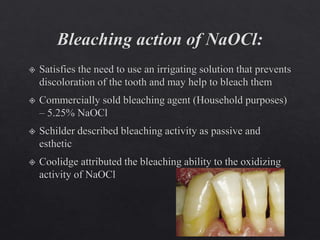
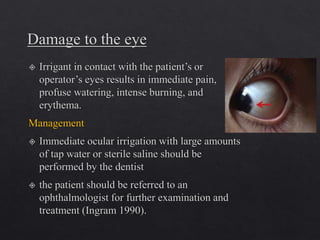
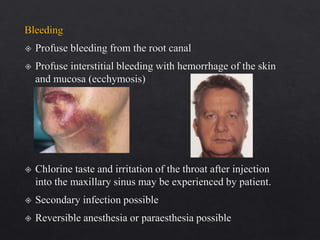
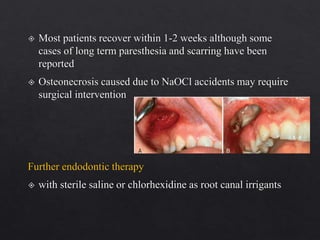
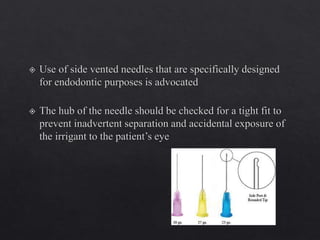
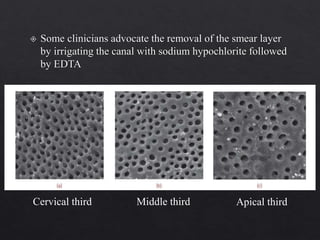
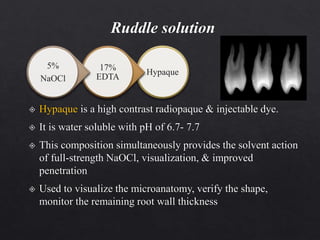
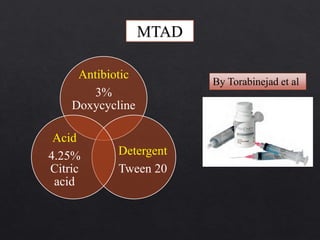
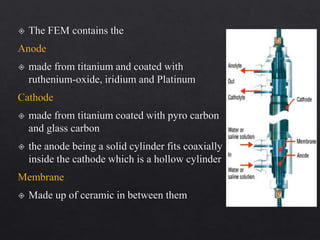
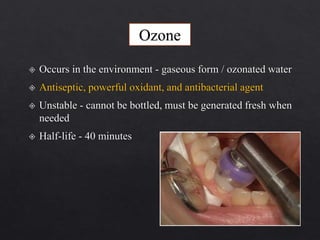
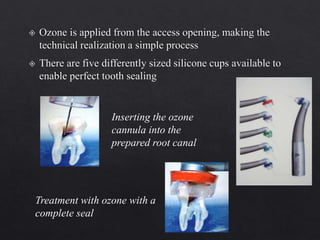
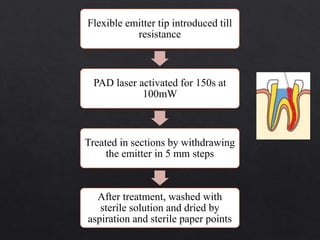
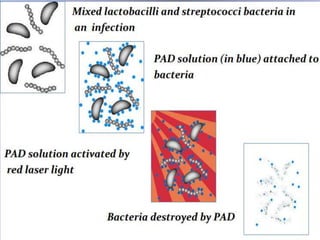
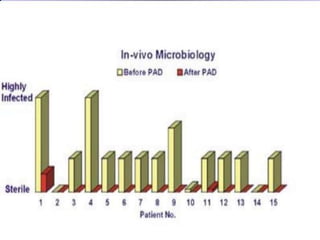
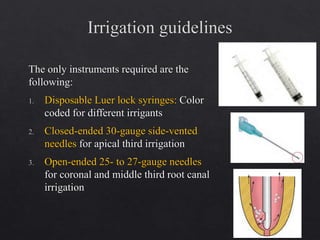
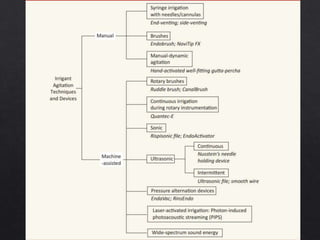
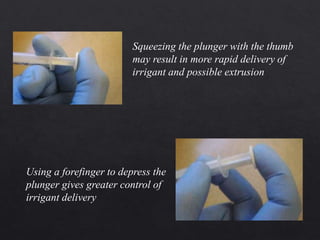
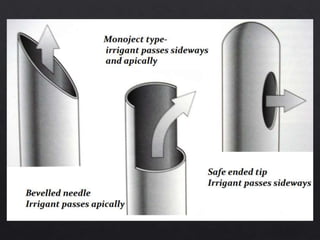
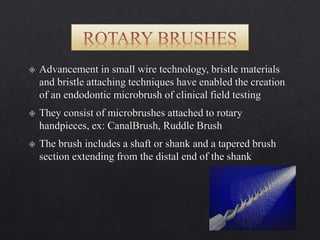
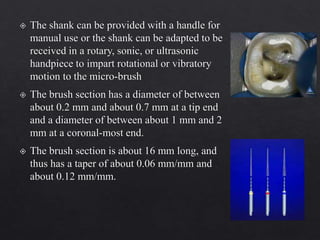
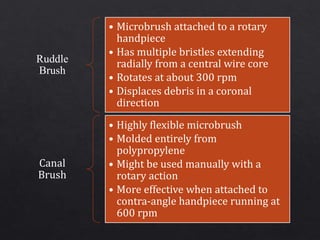
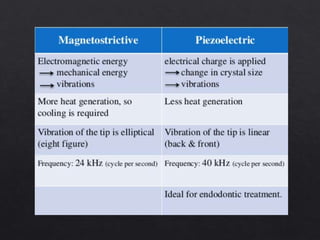
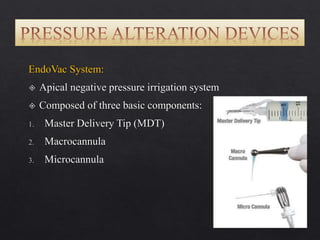
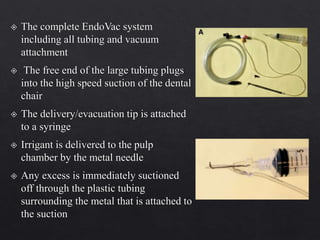
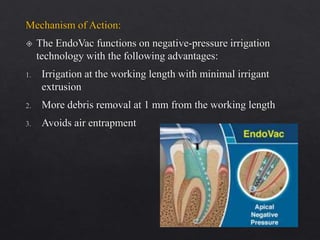
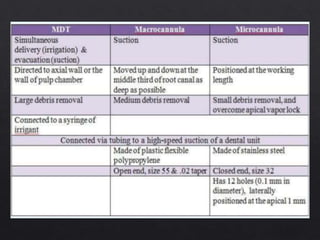
The document outlines various root canal irrigants used in endodontics, specifically their functions, mechanisms, and limitations. Key irrigants like sodium hypochlorite, EDTA, and chlorhexidine are highlighted, along with newer options such as HEBP and ozone therapy. It also discusses the advantages and disadvantages of different irrigation techniques and the importance of effective infection control in root canal procedures.