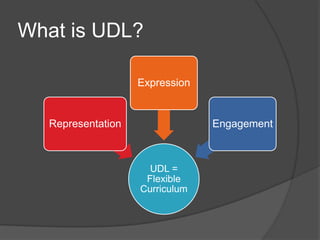
This document introduces Universal Design for Learning (UDL), which provides flexible options for representation, expression, and engagement to accommodate learner variability. UDL aims to support students with learning disabilities through multiple means of visualization and organization, reading and writing, and collaboration and communication. Examples of UDL strategies are provided for each area, such as concept mapping, annotating, and learning management systems. The document references guidelines from CAST and notes image sources.