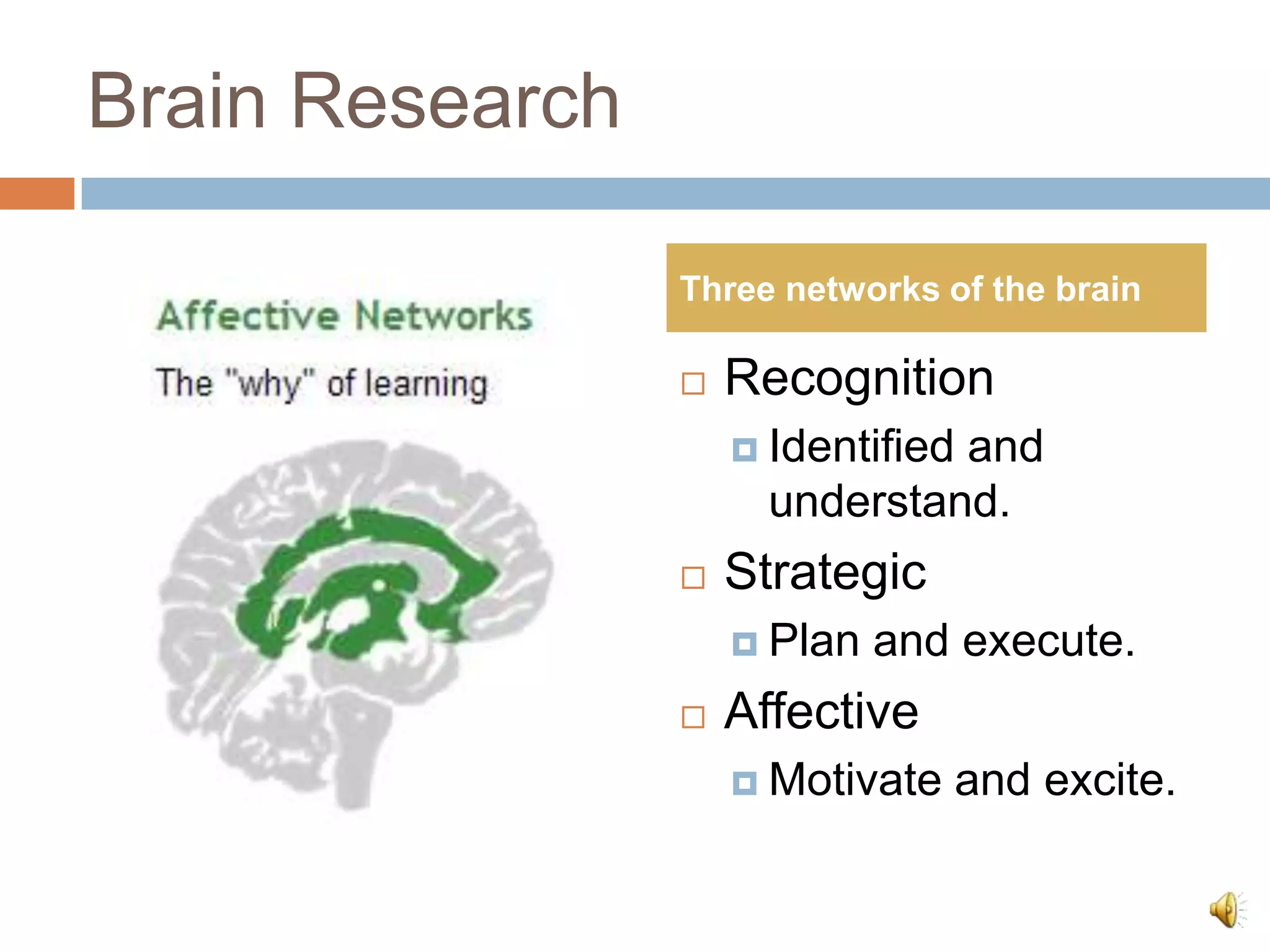
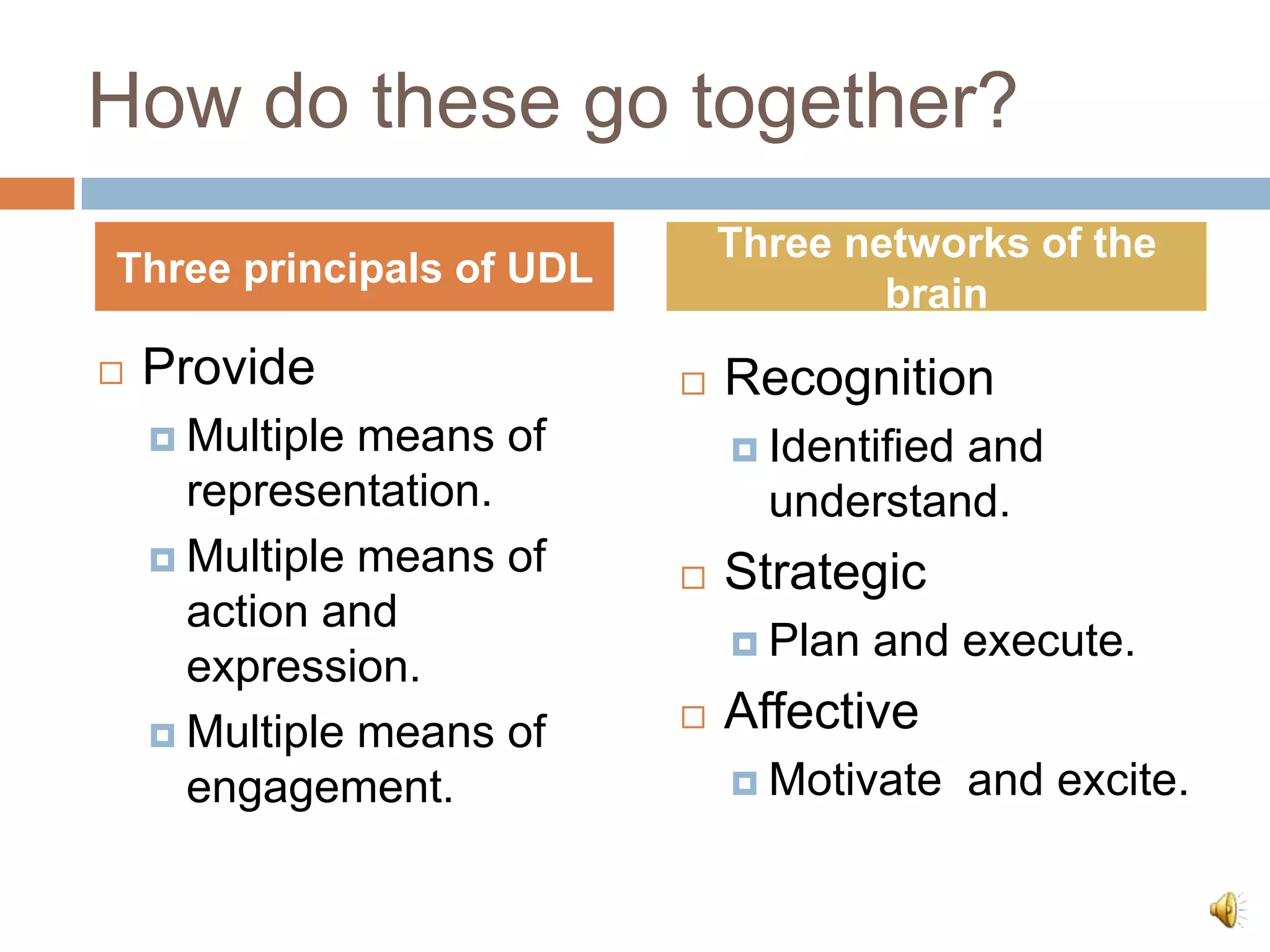
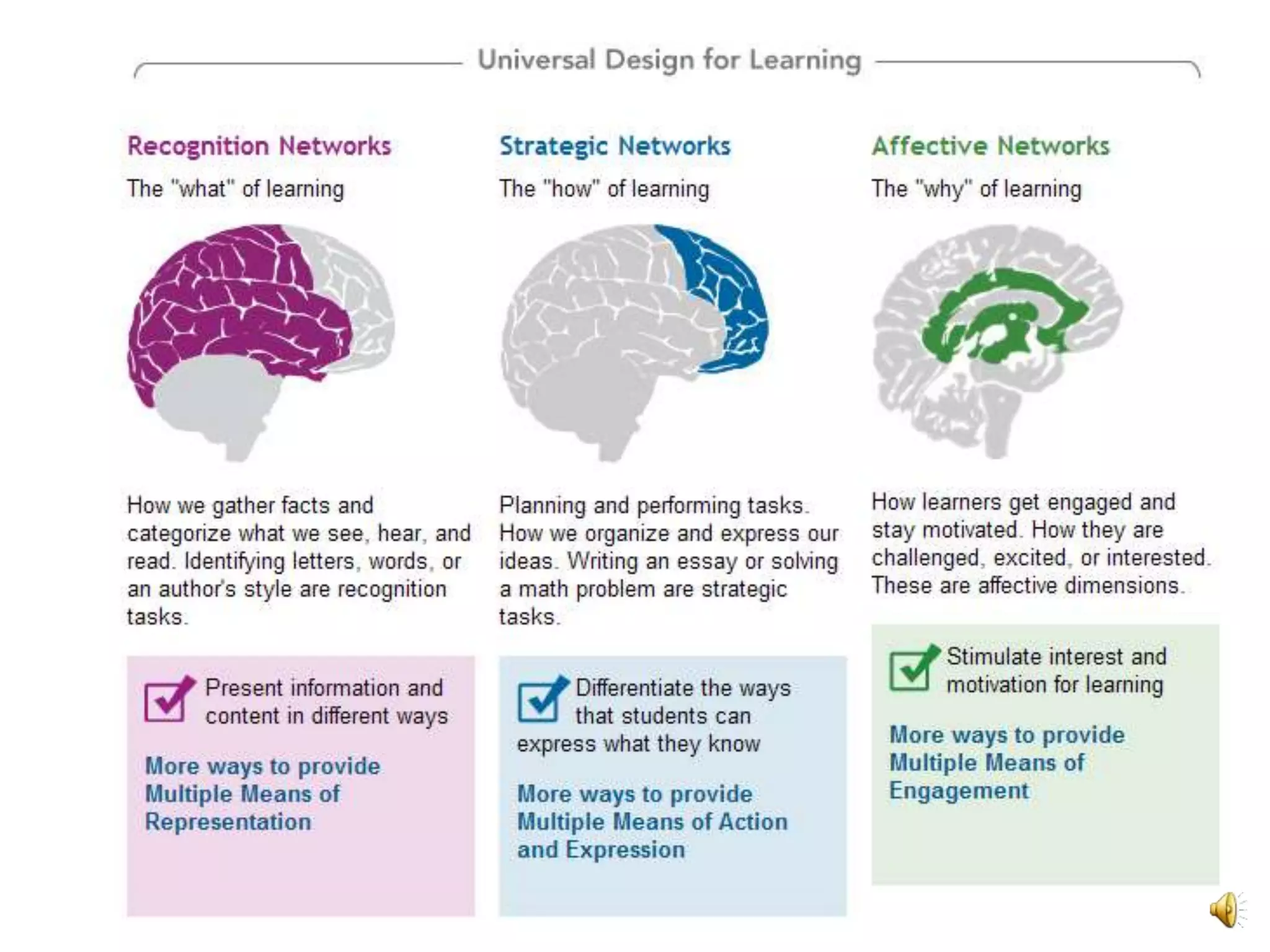
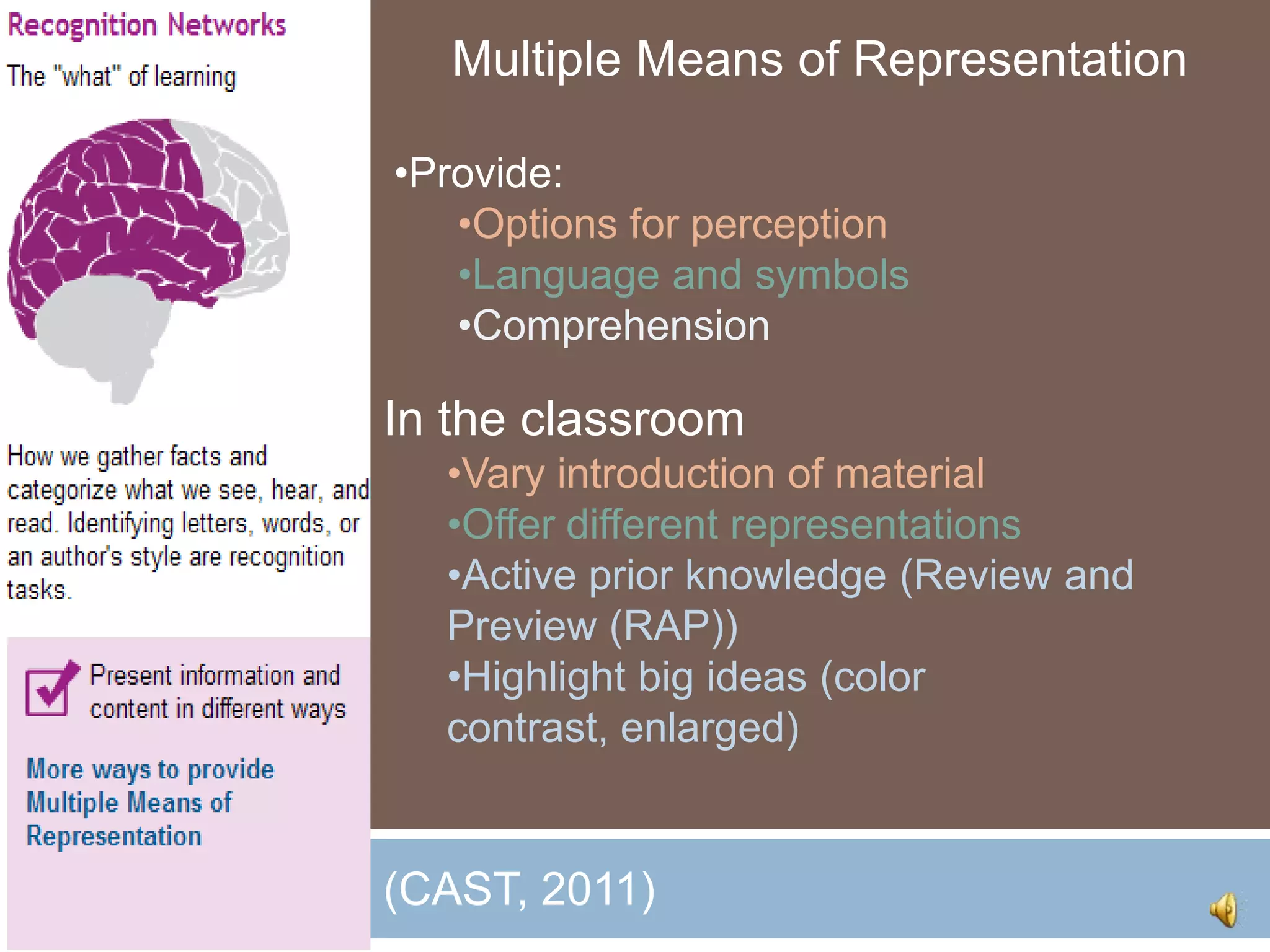
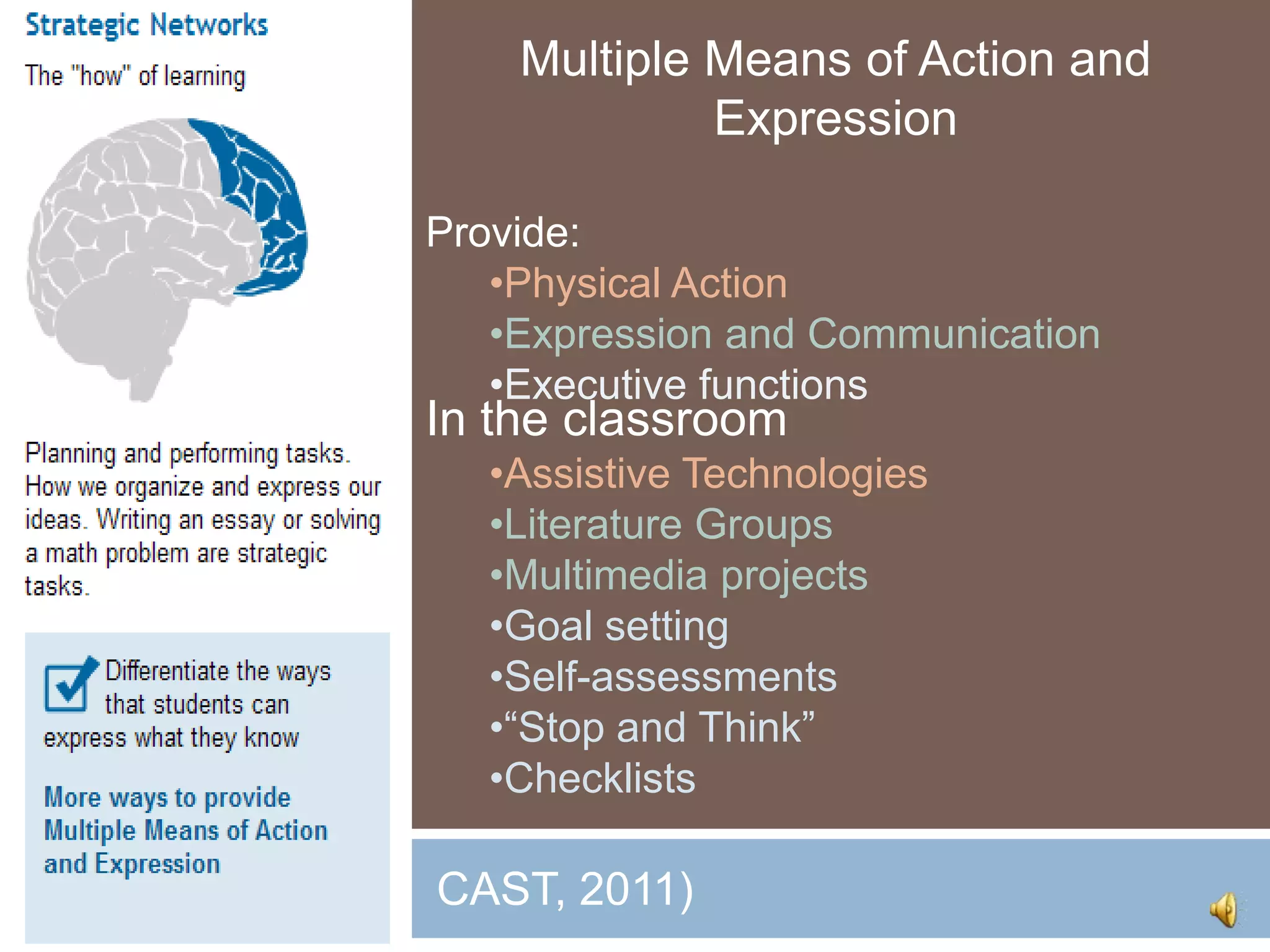
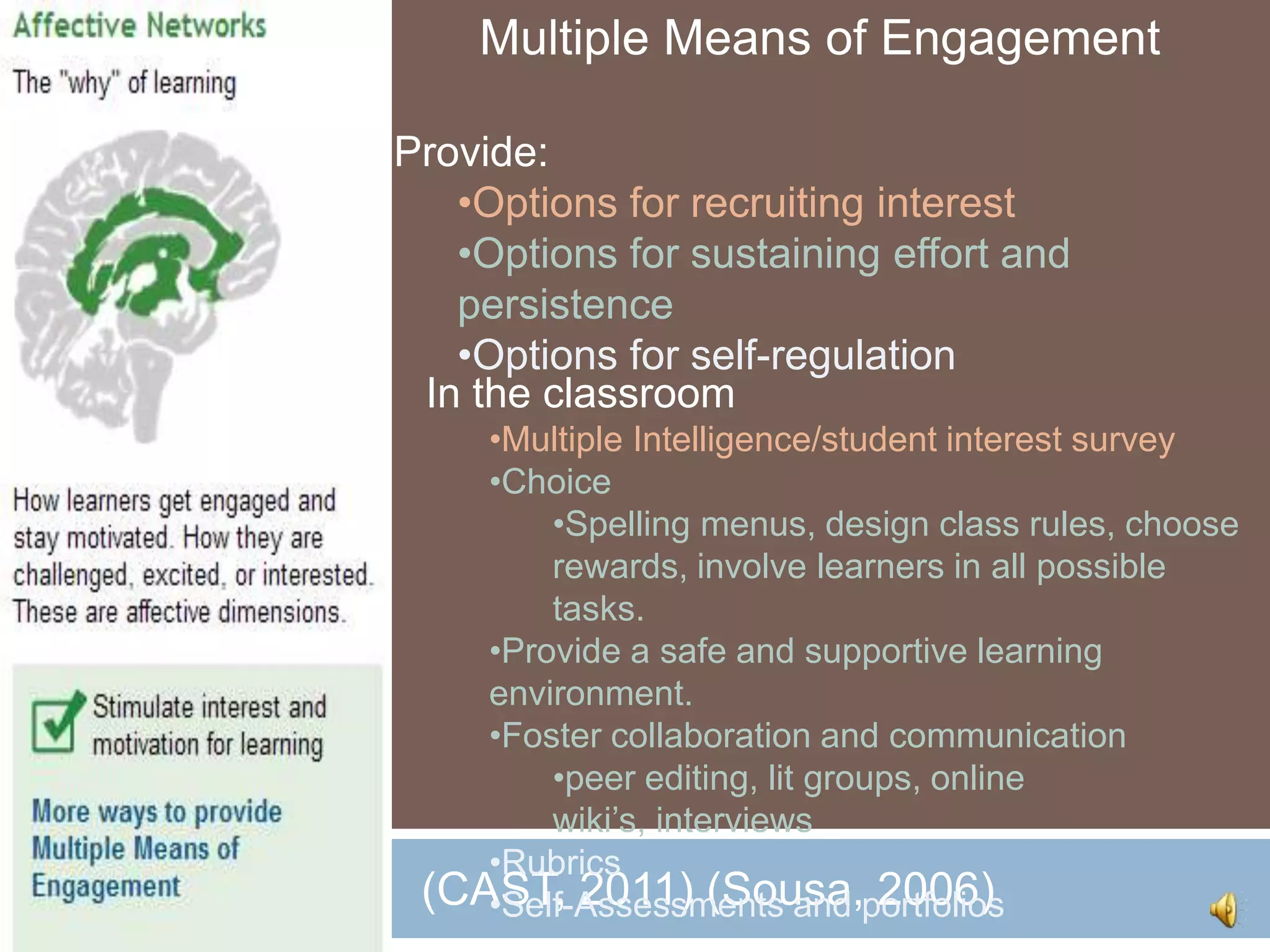
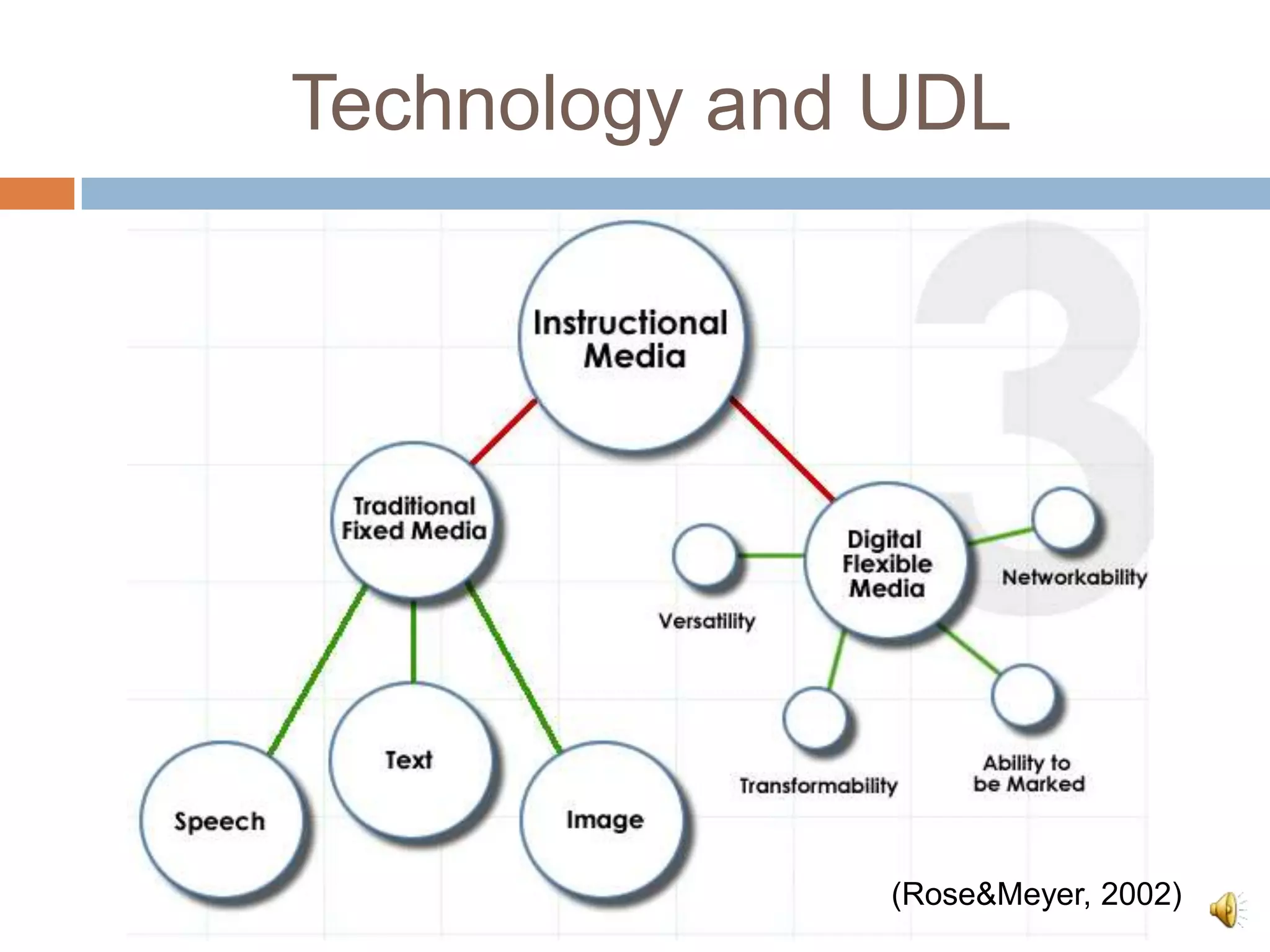
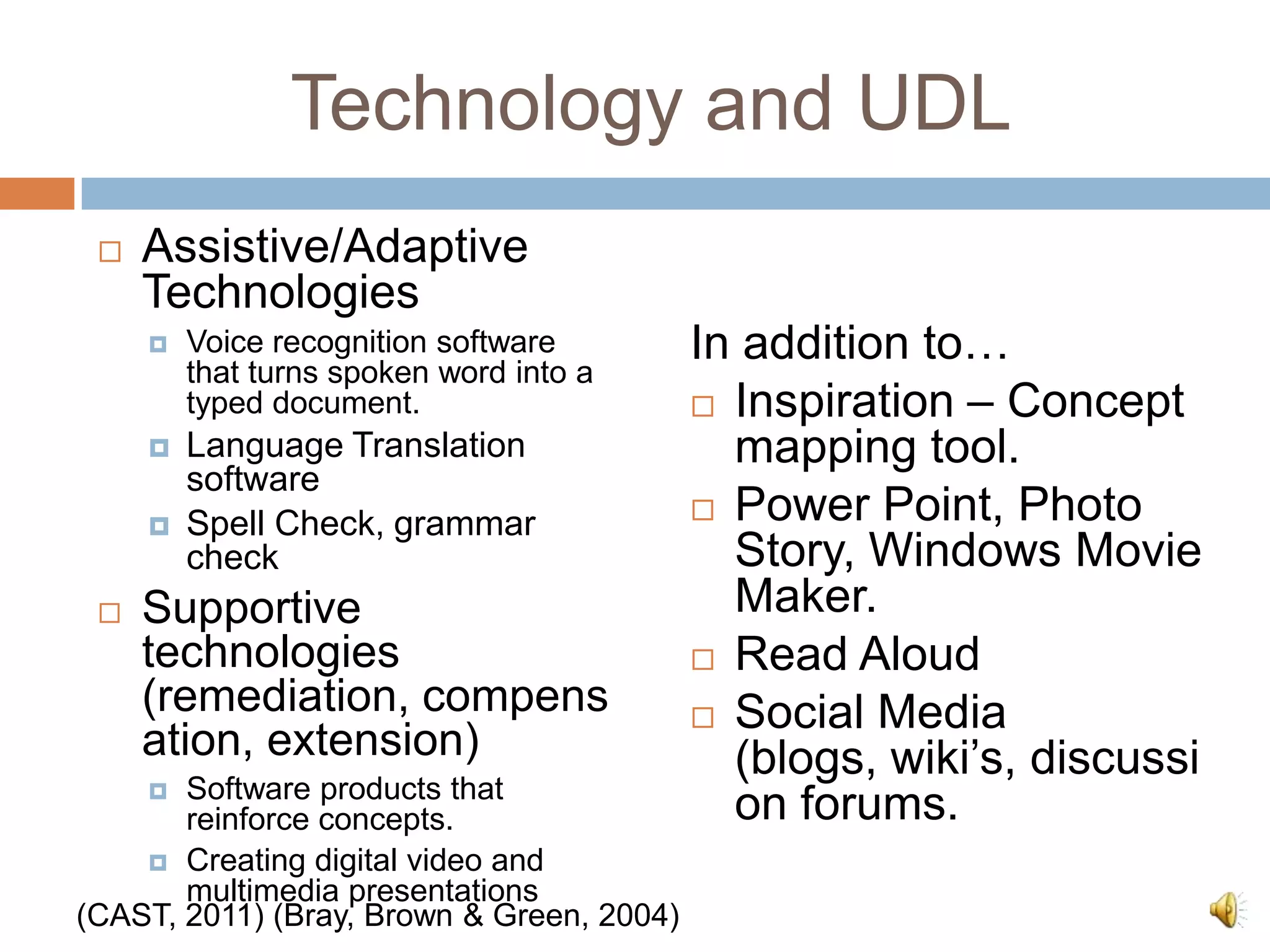
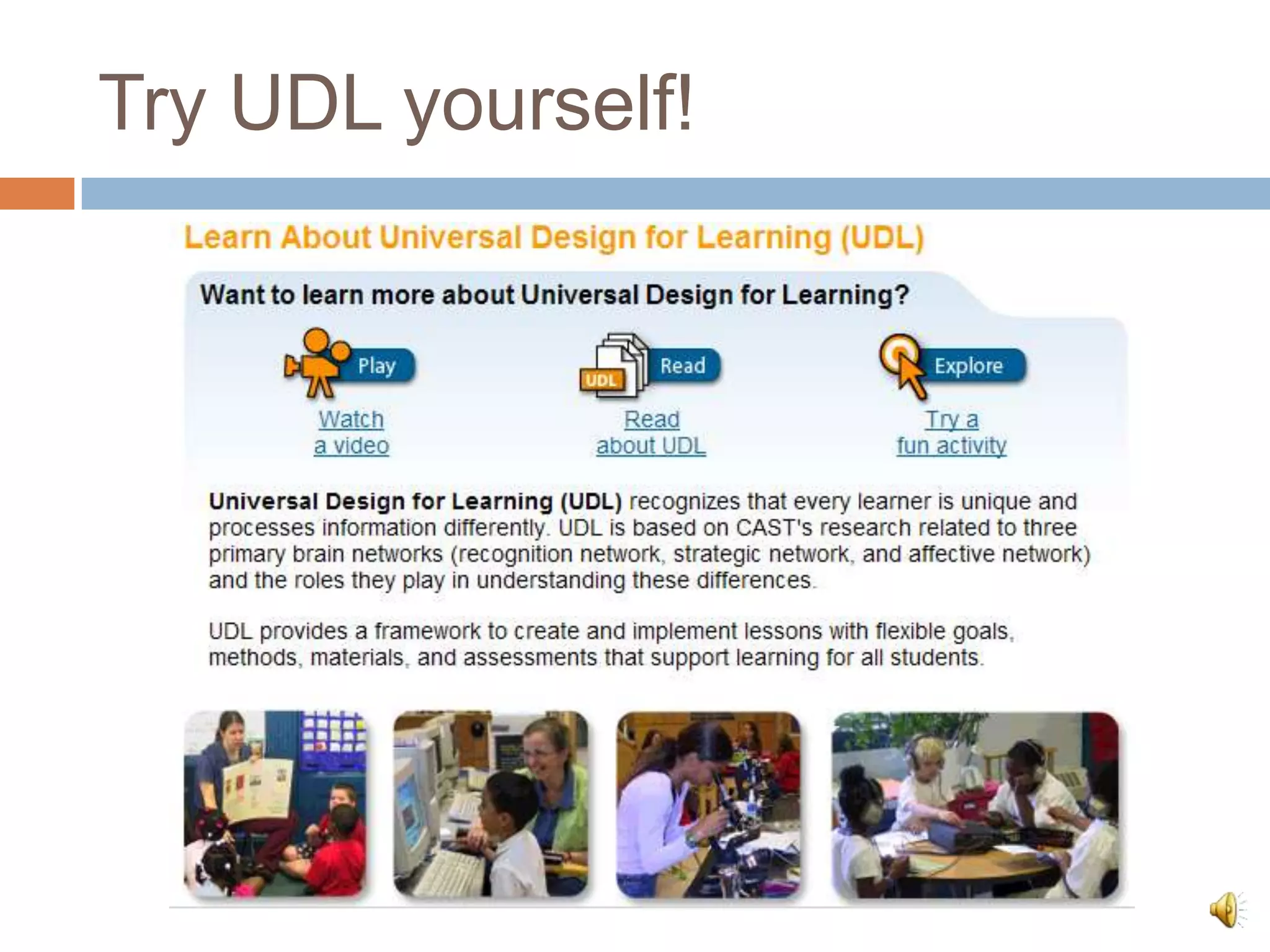
The document discusses Universal Design for Learning (UDL) and its principles that aim to cater to diverse learning needs by offering multiple means of representation, action and expression, and engagement. It emphasizes the importance of understanding how students learn and providing them with various strategies and technologies to reach their potential. Additionally, it offers resources and references for implementing UDL in educational settings.