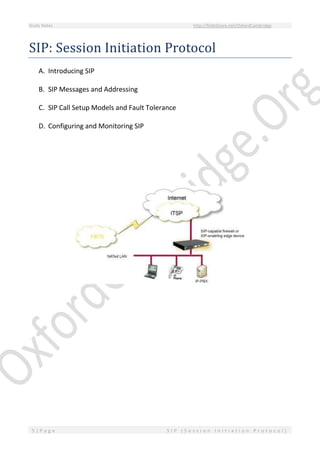
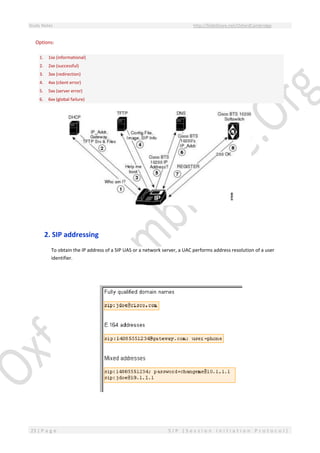
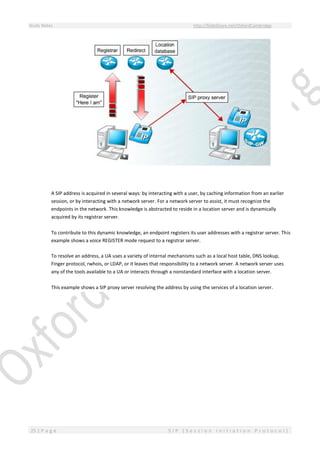
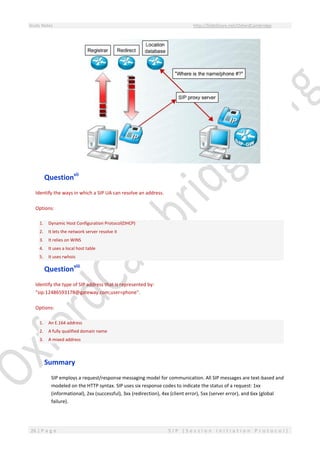
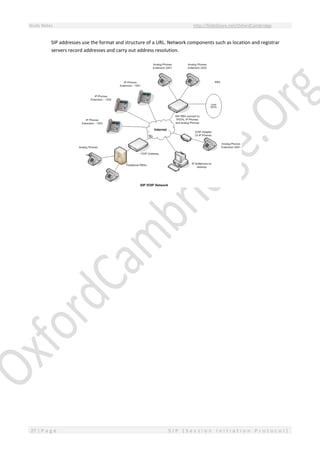
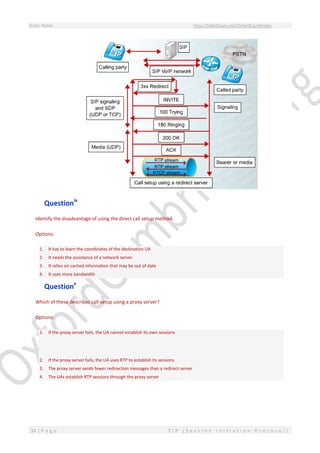
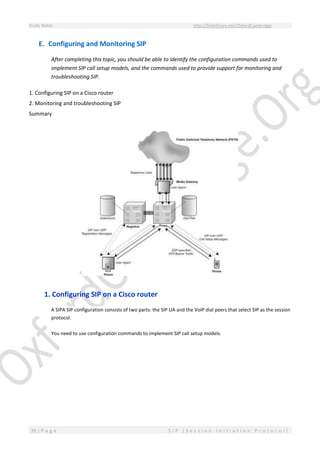
This document provides an overview of Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) including its components and standards. SIP is an application layer control protocol that establishes, modifies and terminates multimedia sessions and calls. It can be used for voice and video calls over Internet Protocol (IP). The key components of SIP include user agents (UAs), proxy servers, redirect servers, registrar servers and location servers. UAs contain user agent clients (UACs) that initiate requests and user agent servers (UASs) that respond to requests. Common UAs are IP phones and gateways.







![Study Notes http://SlideShare.net/OxfordCambridge
11 | P a g e S I P ( S e s s i o n I n i t i a t i o n P r o t o c o l )
The Cisco ATA 186 supports SIP UA functionality. With two Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) ports and a single
Ethernet port, the ATA 186 provides a low-cost means to connect analog phones to a SIP network.
The ATA 186 also delivers traditional desktop functionality such as call hold, transfer, conferencing, caller ID,
and lighted call-waiting and message waiting indicators.
Cisco packet voice gateways
The Cisco Series 1700 Modular Access Routers that are voice-capable, Cisco 2600 Series multiservice
platforms, Cisco 3800 Series Integrated Services Routers, 3700 Series Integrated Services Routers, Cisco
AS5000 Series Universal Gateways, and Cisco 7200 Series voice gateways all support SIP UA functionality.
These products provide a means of connecting SIP networks to traditional time-division multiplexing (TDM)
networks via T1, E1, digital service level 3 (DS3), channel associated signaling (CAS), PRI or BRI, R2 signaling,
FXS, Foreign Exchange Office (FXO), or ear and mouth (E&M) interfaces.
Cisco packet voice gateways are used to build the largest packet telephony networks in the world.
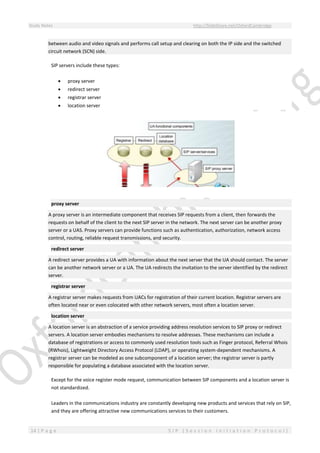
Cisco SIP Proxy Server
The Cisco SIP Proxy Server provides the functionality of a SIP proxy, SIP redirect, SIP registrar, and SIP location
services server.
The Cisco SIP Proxy Server provides the foundation for call routing within SIP networks; it can interwork with
traditional SIP location services, such as DNS or telephone number mapping (E.164 number [ENUM]), with
feature servers via a SIP redirect message, and with H.323 location services using standard location request
(LRQ) messages.
The Cisco SIP Proxy Server runs on either Solaris or Linux operating systems.
The last three Cisco SIP products deployed in live networks spanning a variety of applications and continents
are
Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch
Cisco PGW 2200 PSTN Gateway
Cisco PIX Security Appliance and Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA)
Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch
The Cisco BTS 10200 Softswitch provides softswitch functionality to Class 4 and Class 5 networks, and provides
SIP-to-Signaling System 7 (SS7) gateway functionality for American National Standards Institute (ANSI)
standardized networks.
The BTS 10200 Softswitch supports SIP UA functionality in conjunction with a Cisco packet voice media
gateway, such as a Cisco AS5000 Series Universal Gateway or a Cisco MGX 8000 Series Voice Gateway.
Cisco PGW 2200 PSTN Gateway
The Cisco PGW 2200 PSTN Gateway provides softswitch functionality for Class 4 networks, as well as Internet
offload and SIP-to-SS7 gateway functionality for international networks.
The PGW 2200 PSTN Gateway supports ISDN User Part (ISUP) certification in over 130 countries.
The PGW 2200 PSTN Gateway supports SIP UA functionality in conjunction with a Cisco packet voice media
gateway such as an AS5000 Series Universal Gateway or MGX 8000 Series Voice Gateway.
Cisco PIX Security Appliance and Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipmobilityconcepts-studynotes-140317171527-phpapp01/85/SIP-Session-Initiation-Protocol-Study-Notes-11-320.jpg)











![Study Notes http://SlideShare.net/OxfordCambridge
42 | P a g e S I P ( S e s s i o n I n i t i a t i o n P r o t o c o l )
1. show call active voice
2. show sip-ua retry
3. show sip-ua statistics
4. show sip-ua status
2. Monitoring and troubleshooting SIP
You can use the show and debug commands to provide support for monitoring and troubleshooting SIP.
There are six show commands that are valuable when examining the status of SIP components and
troubleshooting:
show call active voice [brief]
show call history voice [last n | record | brief]
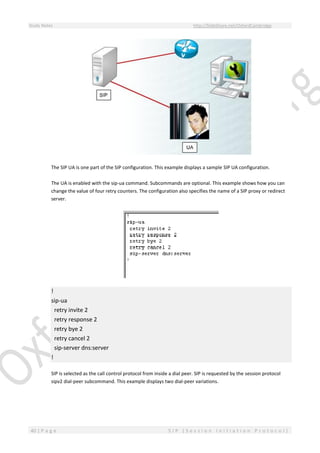
show sip-ua retry
show sip-ua statistics
show sip-ua status
show sip-ua timers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipmobilityconcepts-studynotes-140317171527-phpapp01/85/SIP-Session-Initiation-Protocol-Study-Notes-42-320.jpg)
![Study Notes http://SlideShare.net/OxfordCambridge
43 | P a g e S I P ( S e s s i o n I n i t i a t i o n P r o t o c o l )
show call active voice [brief]
The show call active voice [brief] command displays the status, statistics, and parameters for all active voice
calls.
show call history voice [last n | record | brief]
The show call history voice [last n | record | brief] command displays call records from the history buffer.
show sip-ua retry
The show sip-ua retry command displays the SIP protocol retry counts. High counts should be investigated.
show sip-ua statistics
The show sip-ua statistics command displays the SIP UA response, traffic, and retry statistics.
show sip-ua status
The show sip-ua status command displays the SIP UA listener status, which should be enabled.
show sip-ua timers
The show sip-ua timers command displays the current value of the SIP UA timers (shown in the figure).
There are seven debug commands that are valuable when examining the status of SIP components and
troubleshooting. Here are the first four commands:
debug voip ccapi inout
debug ccsip all
debug ccsip calls
debug ccsip errors
debug voip ccapi inout
The debug voip ccapi inout command shows every interaction with the call control application programming
interface (API) on both the telephone interface and on the VoIP side. By monitoring the output, you can follow
the progress of a call from the inbound interface or VoIP peer to the outbound side of the call. This debug
command is very active, so you must use it sparingly in a live network.
debug ccsip all](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipmobilityconcepts-studynotes-140317171527-phpapp01/85/SIP-Session-Initiation-Protocol-Study-Notes-43-320.jpg)












































