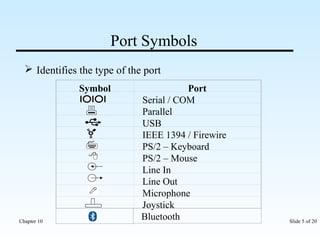
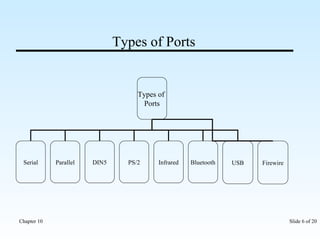
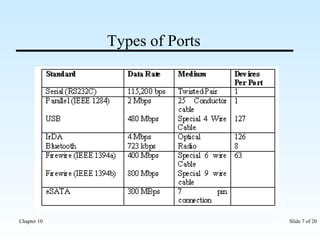
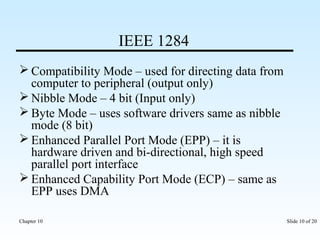
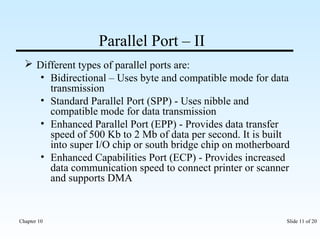
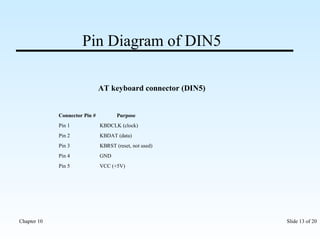
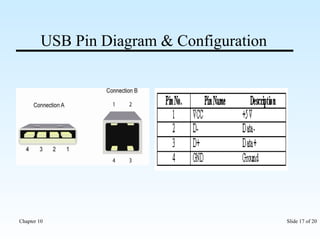
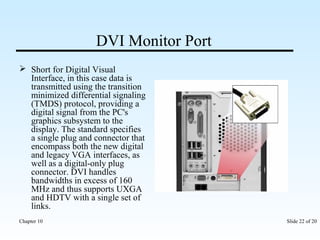
The document discusses various input/output ports and devices used to connect peripheral devices to computers. It begins by listing the chapter objectives which are to introduce ports, identify different port types, configure IRQ settings, and troubleshoot port issues. It then explains what ports are and shows symbols for common port types like serial, parallel, USB, PS/2, and infrared. The document provides details on specific ports like serial, parallel, PS/2, USB, IEEE 1394, and infrared; describes interrupt request lines; and offers tips for troubleshooting port and IRQ issues.