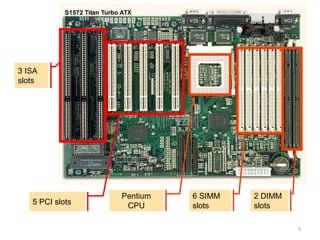
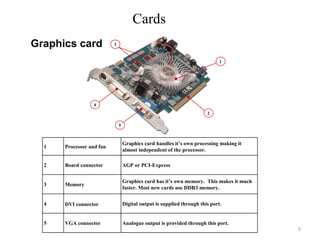
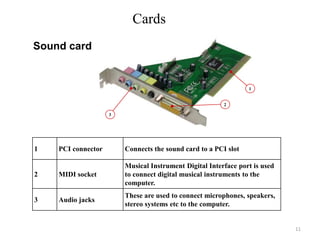
The document discusses different types of buses, interfaces, and cards used in computer systems. It provides examples of expansion buses like ISA and PCI that provide slots on the motherboard. Disk interfaces like ATA, IDE, and SCSI are covered that connect hard disks. External buses like parallel, serial, USB are described along with communication buses for connecting systems. Common cards like graphics cards with DVI/VGA ports and sound cards with audio jacks are detailed.