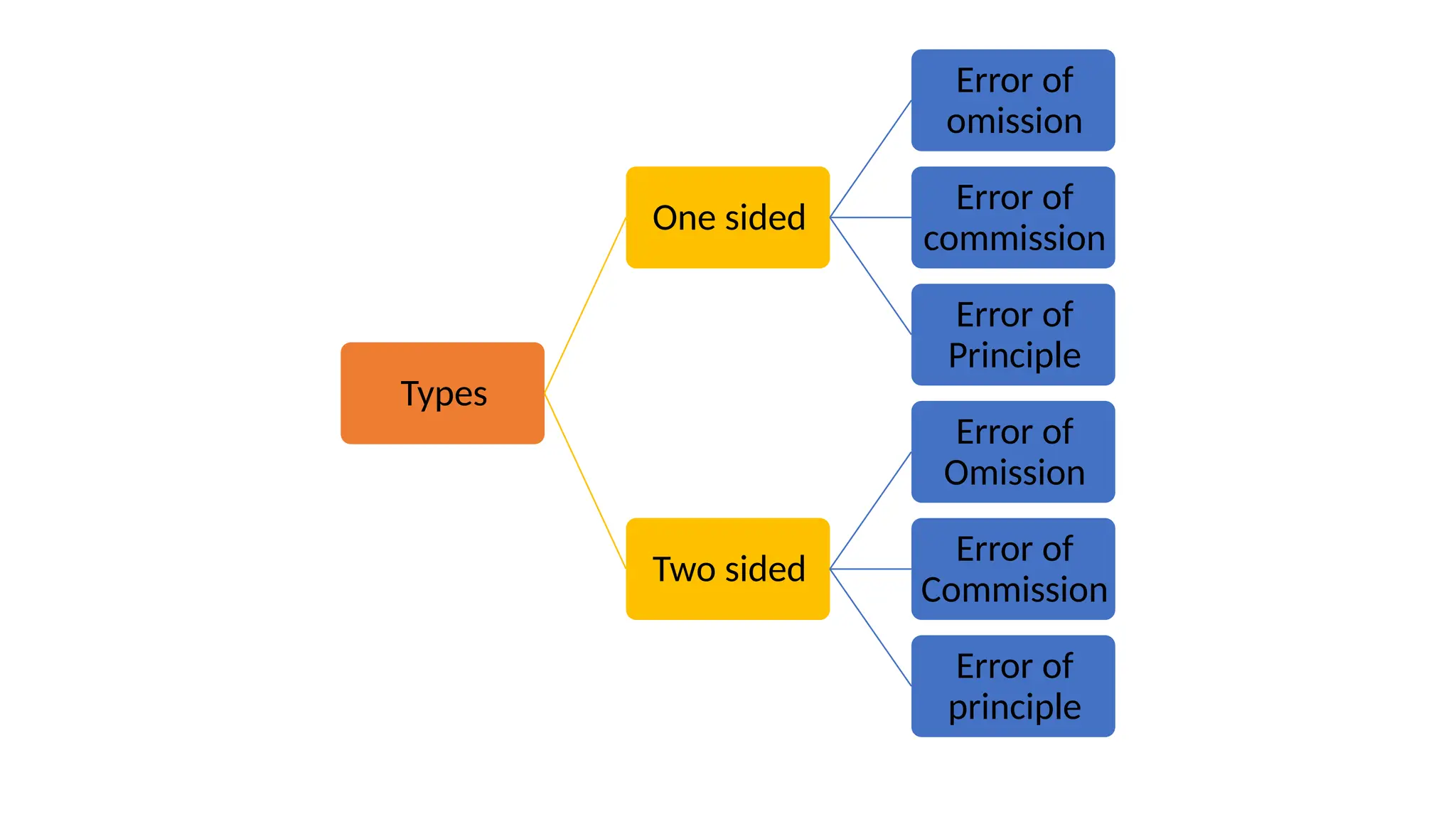
The document discusses accounting errors, which are inaccuracies in financial records that can misrepresent a company's financial position. It categorizes errors into one-sided and two-sided, as well as specific types such as omission, commission, and principle errors, detailing their implications on financial statements. Examples of various errors are provided to illustrate how these inaccuracies can arise and the importance of correction for maintaining reliable financial information.