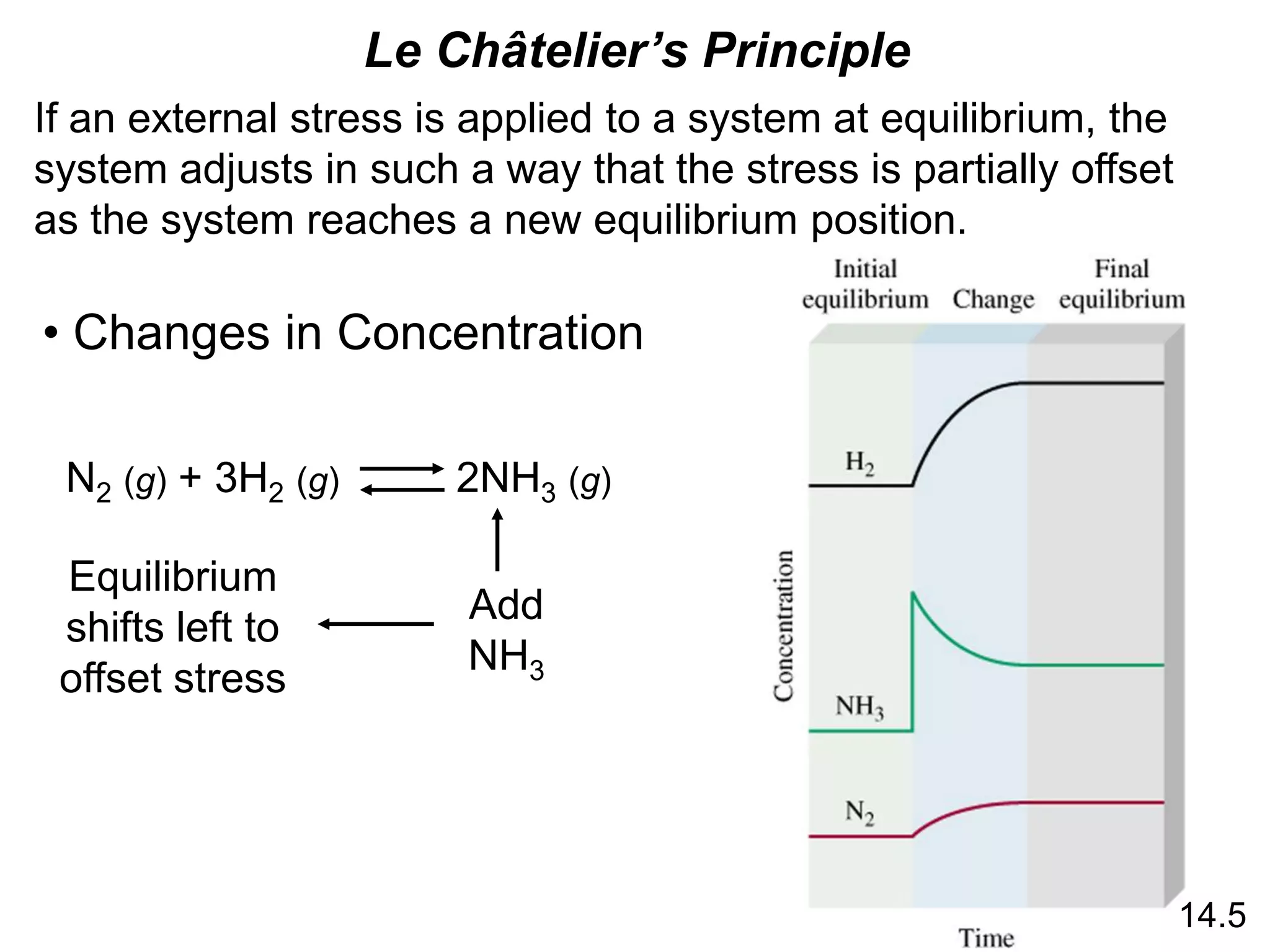
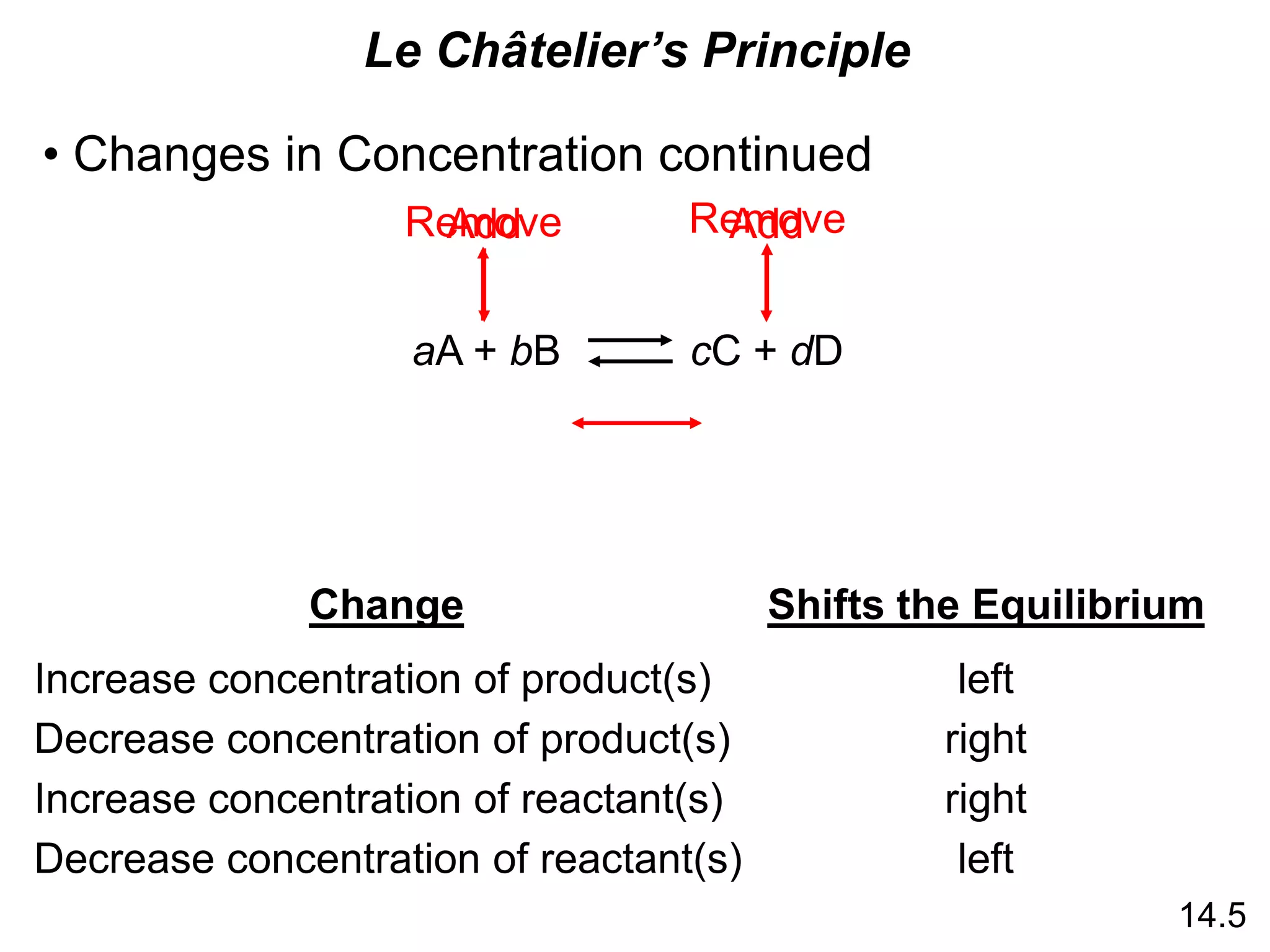
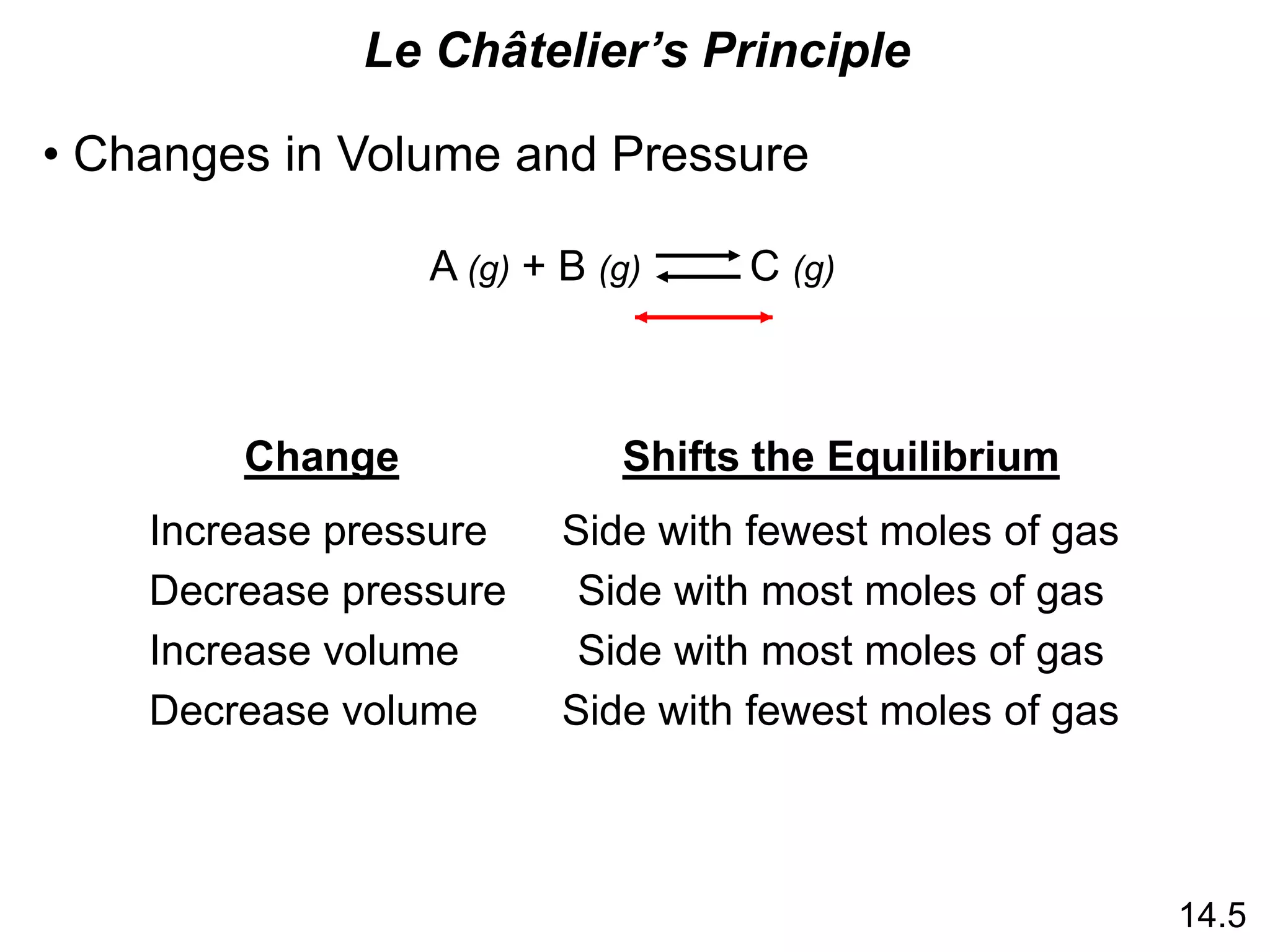
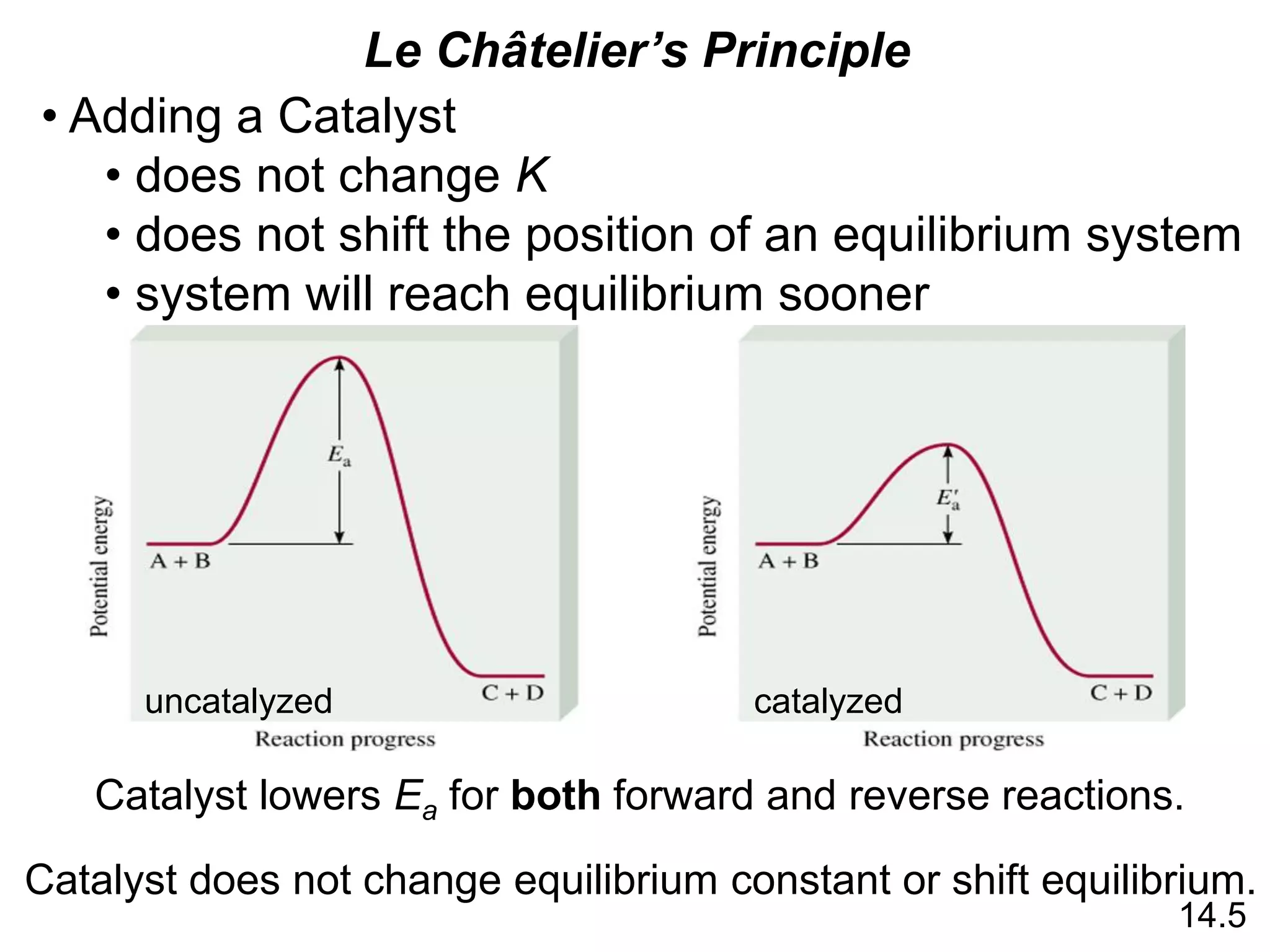
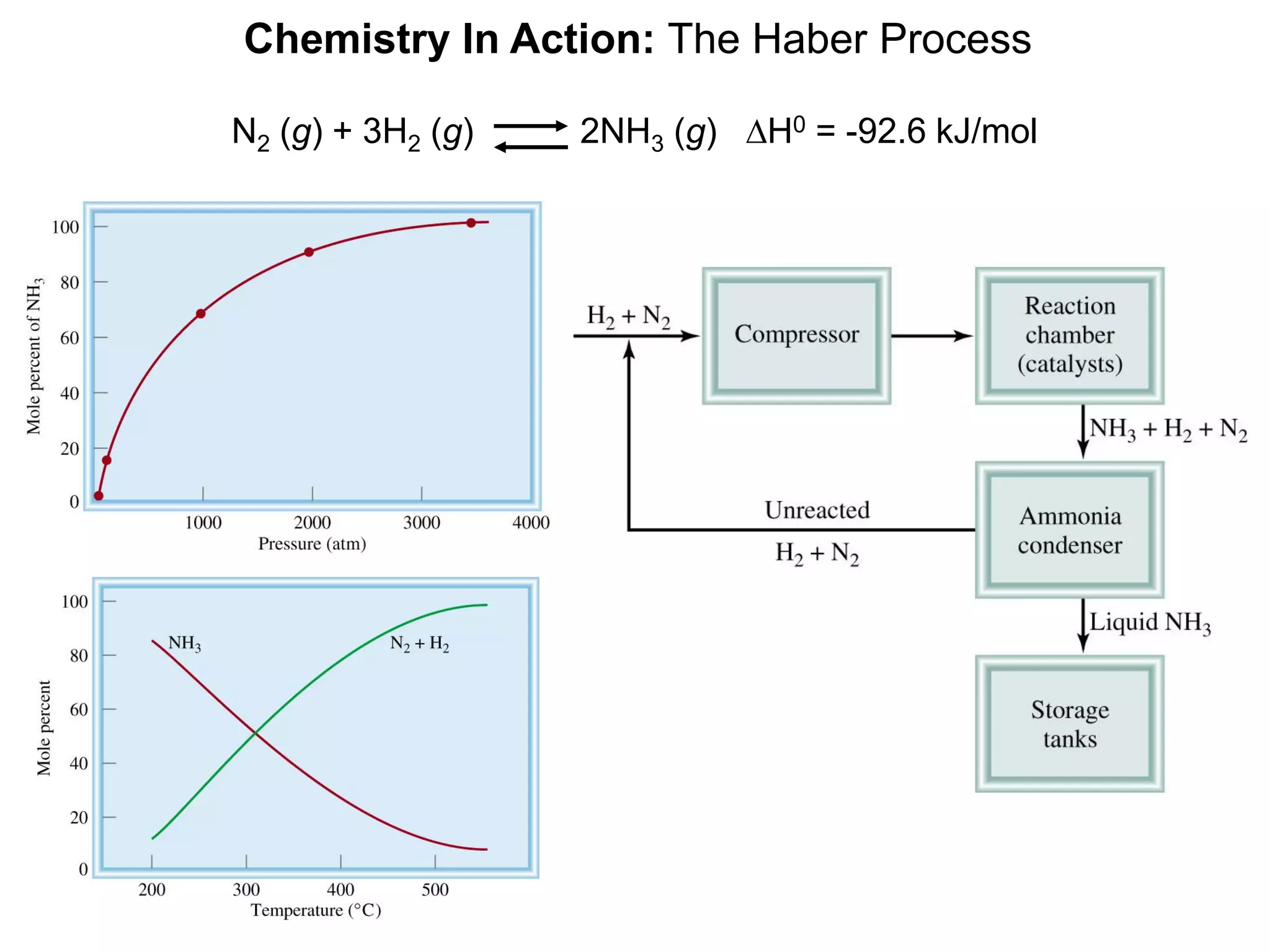
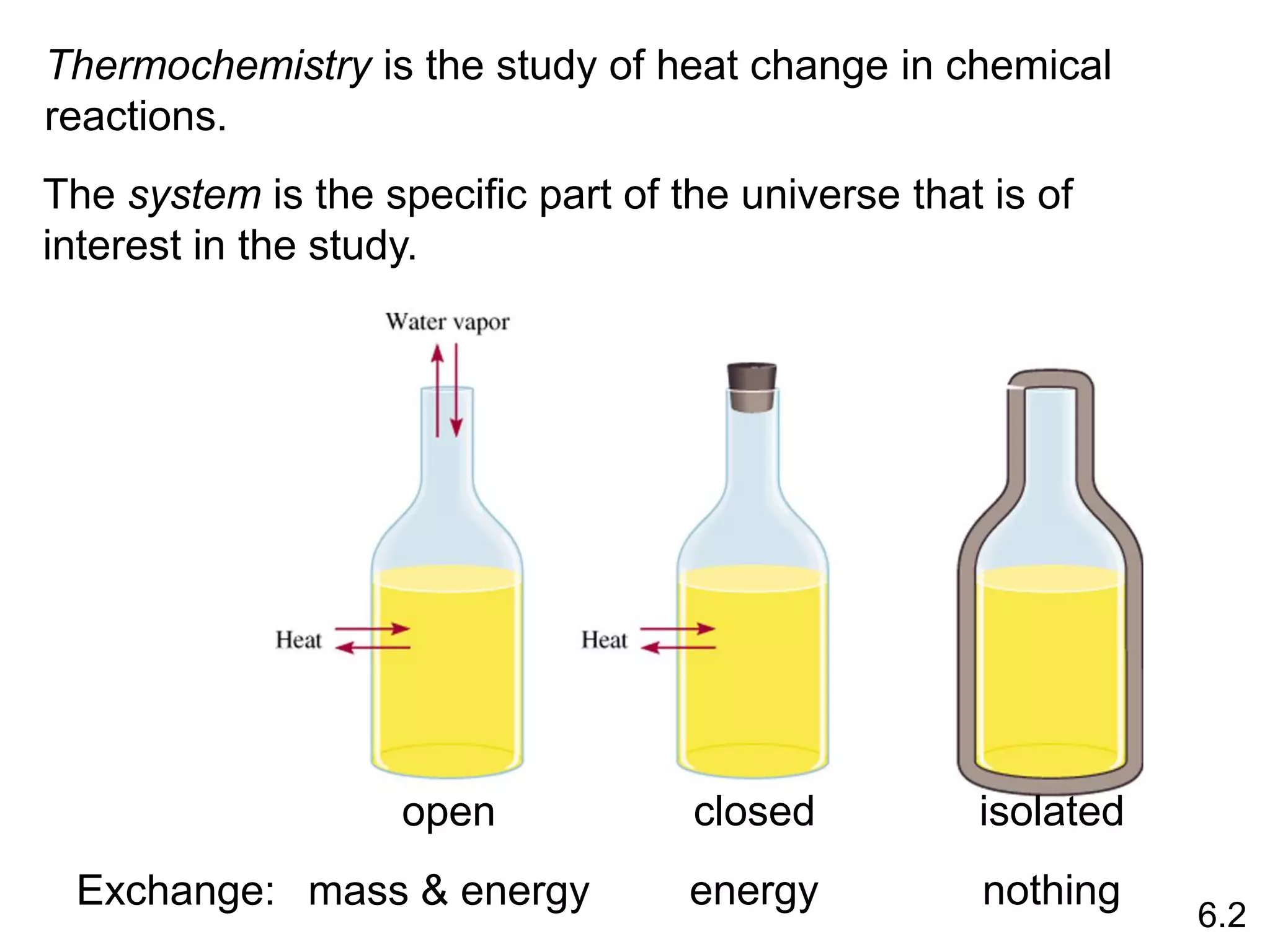
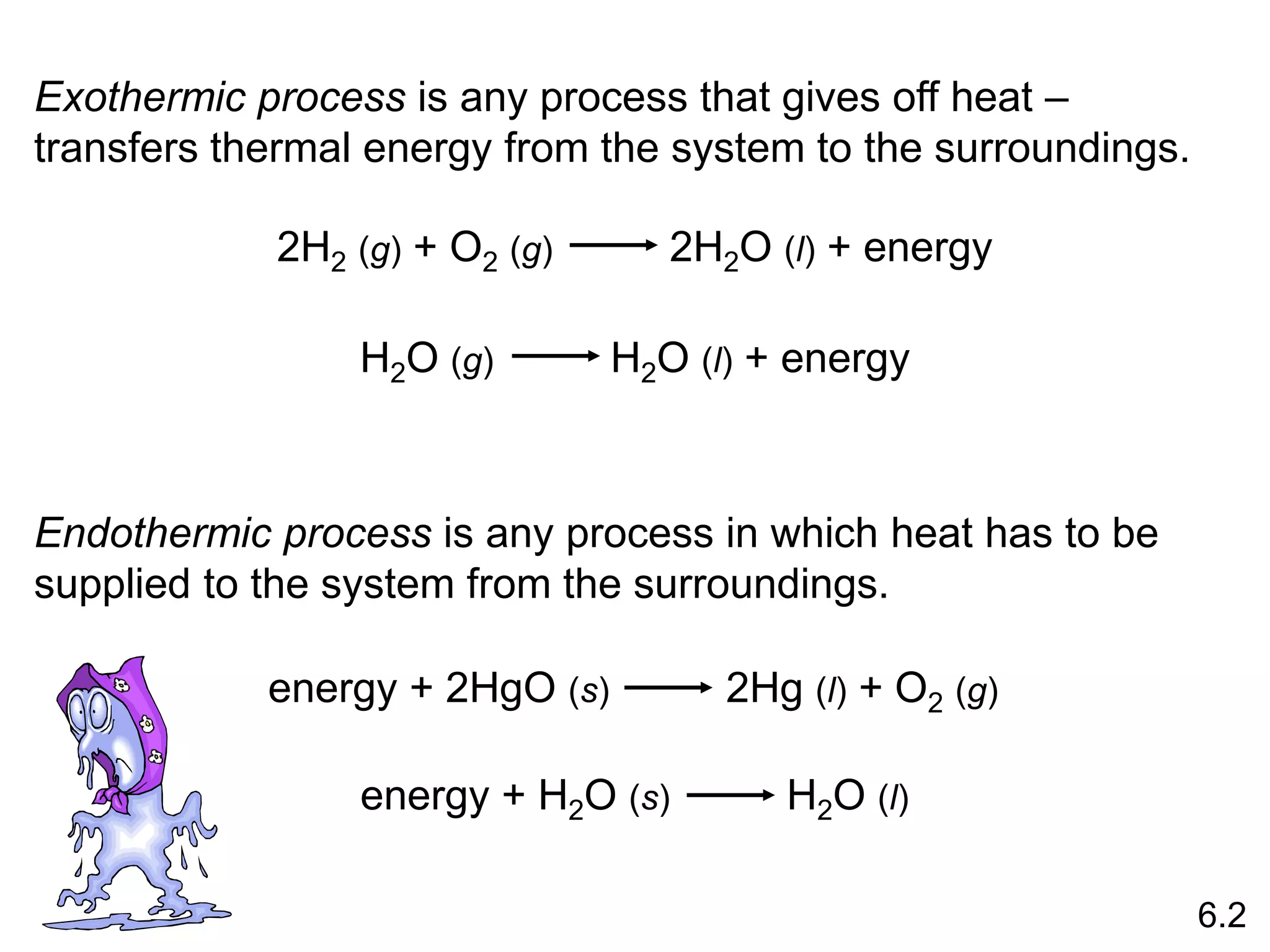
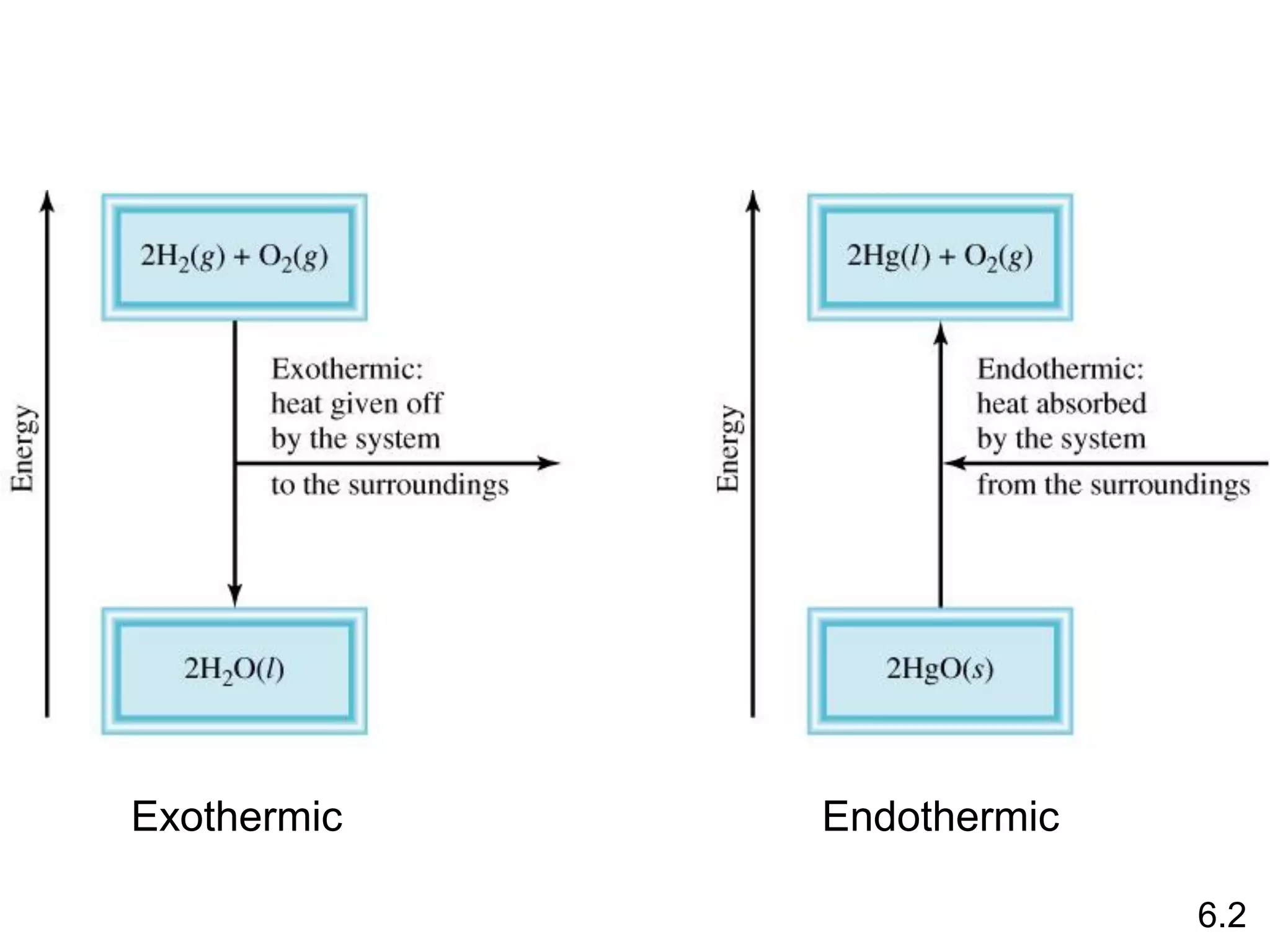
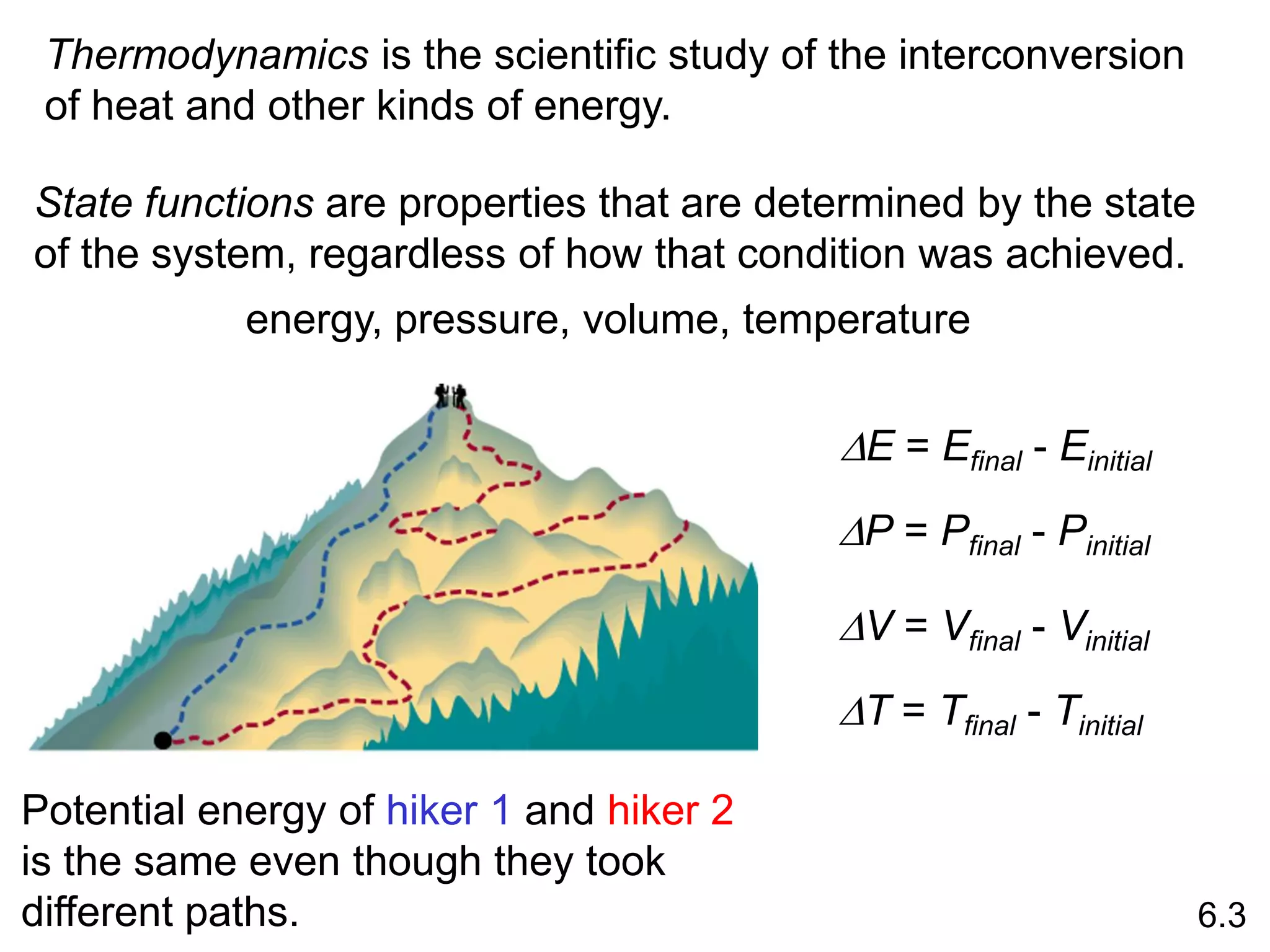
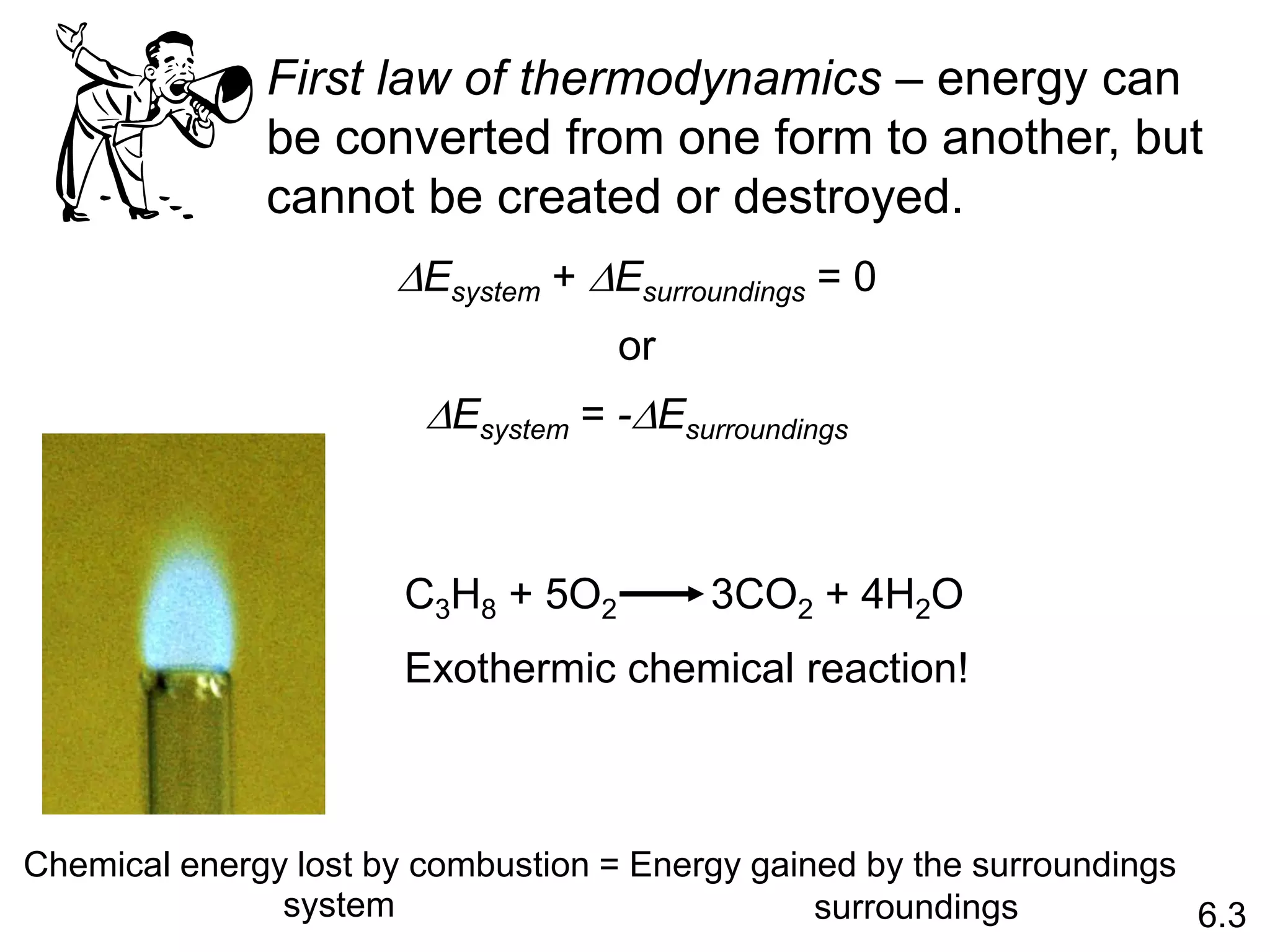
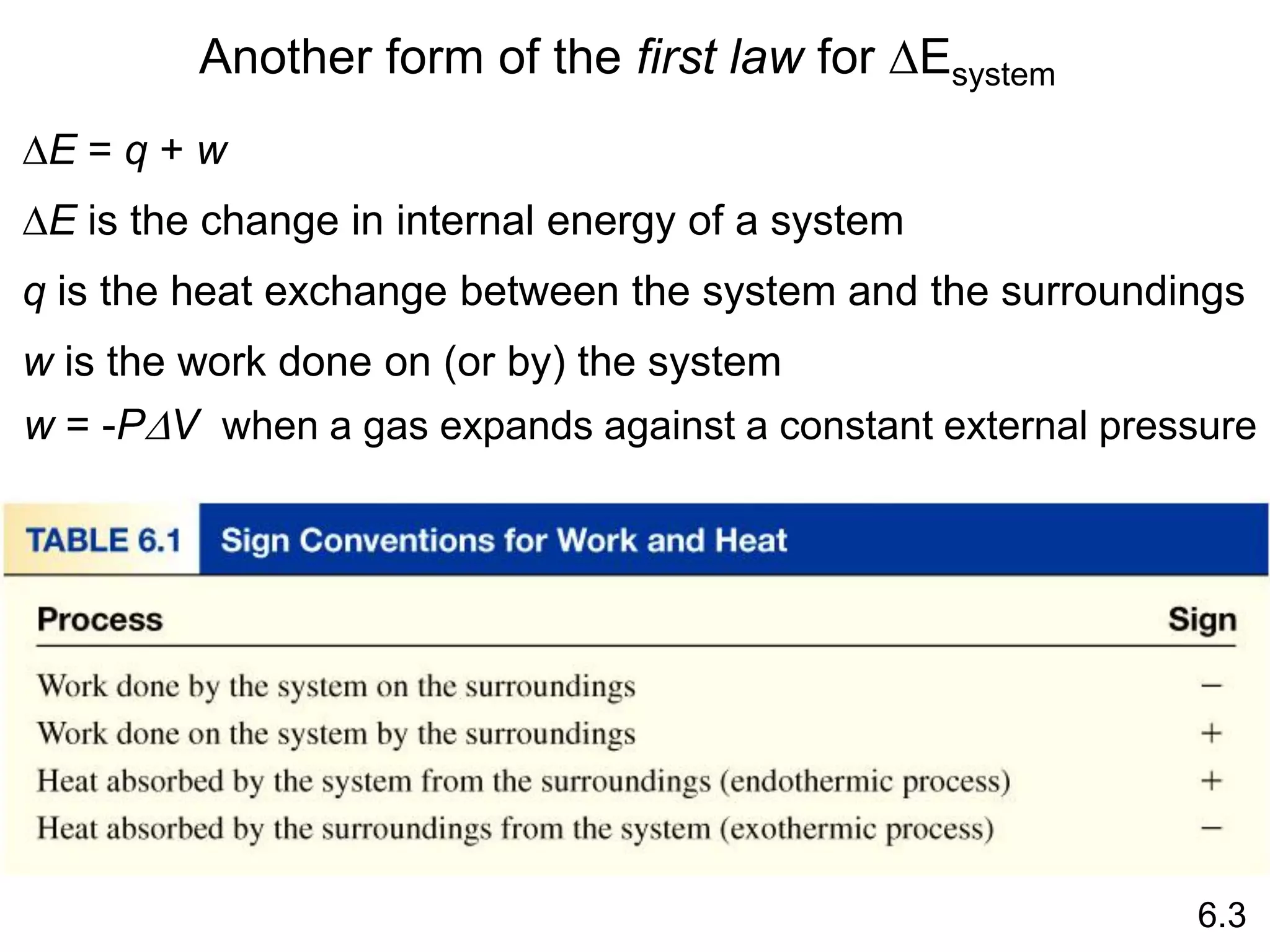
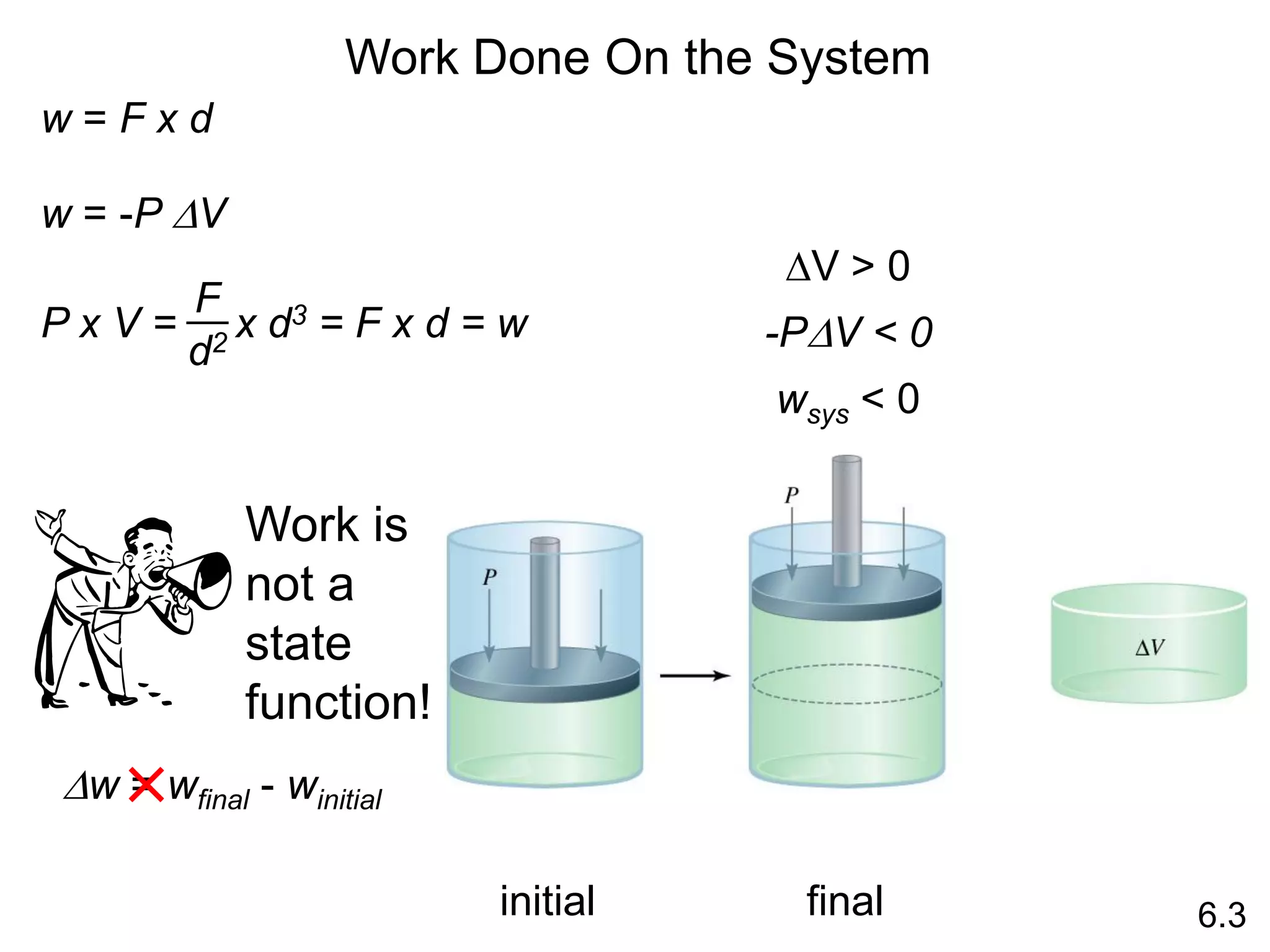
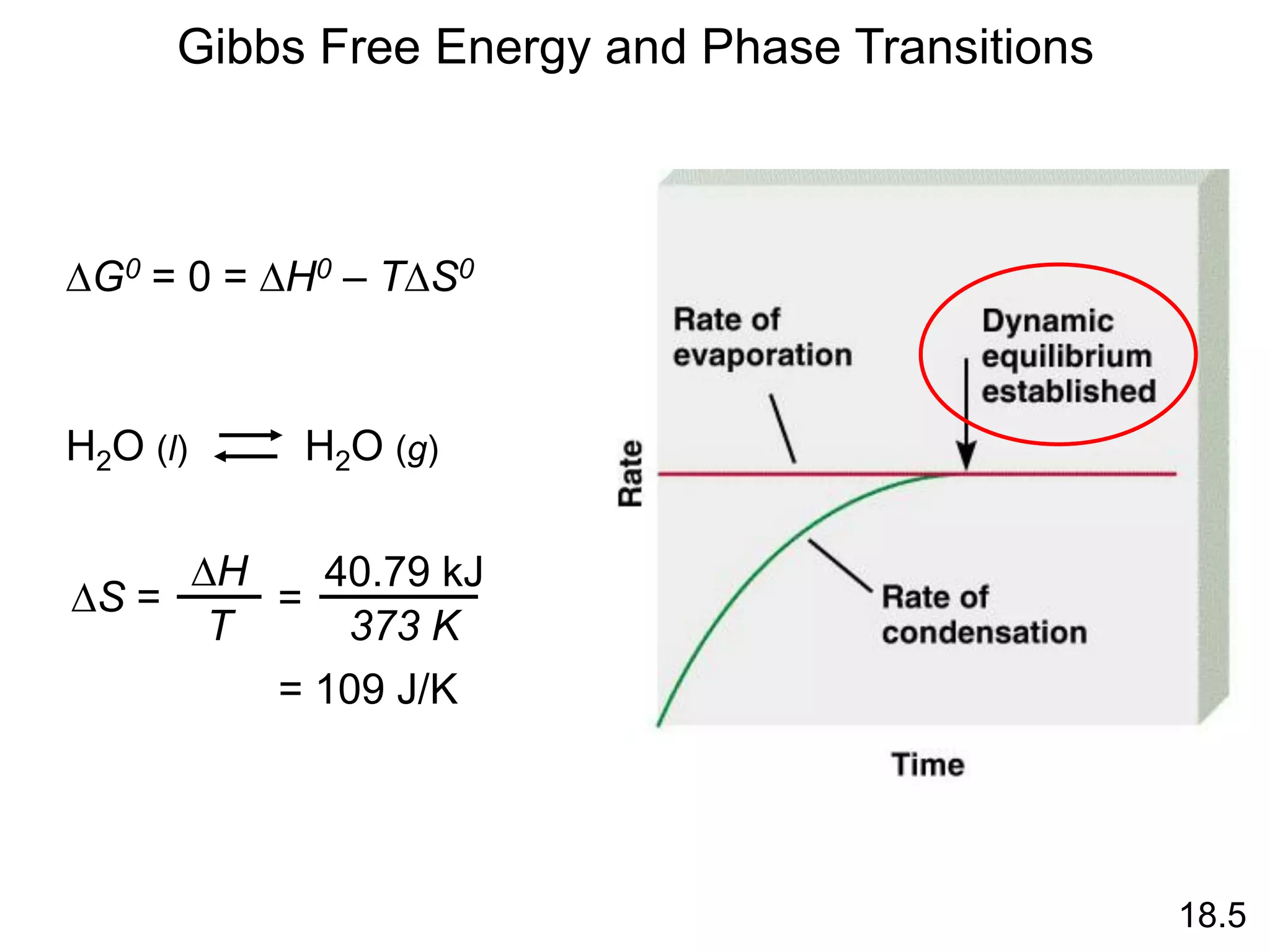
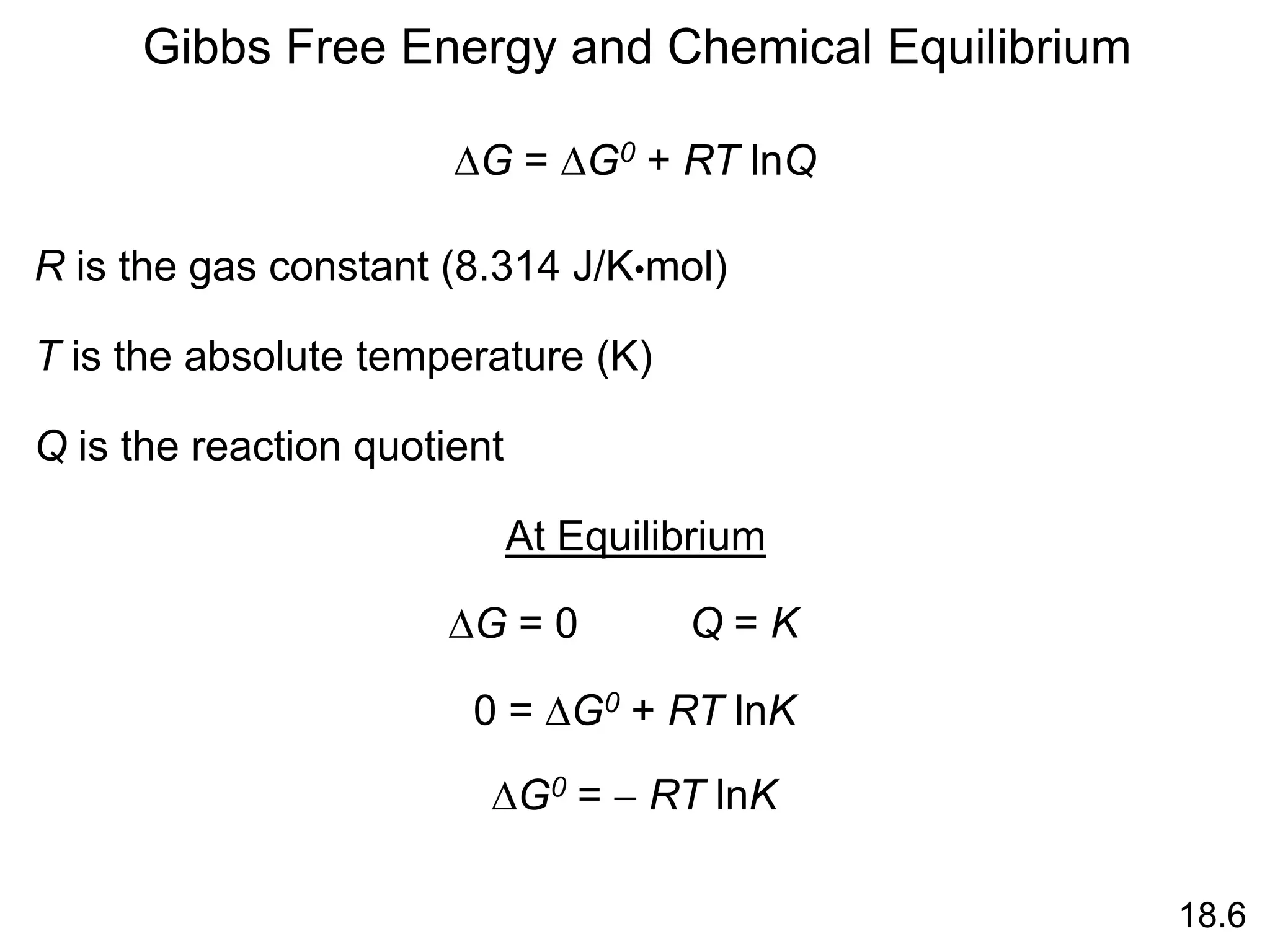
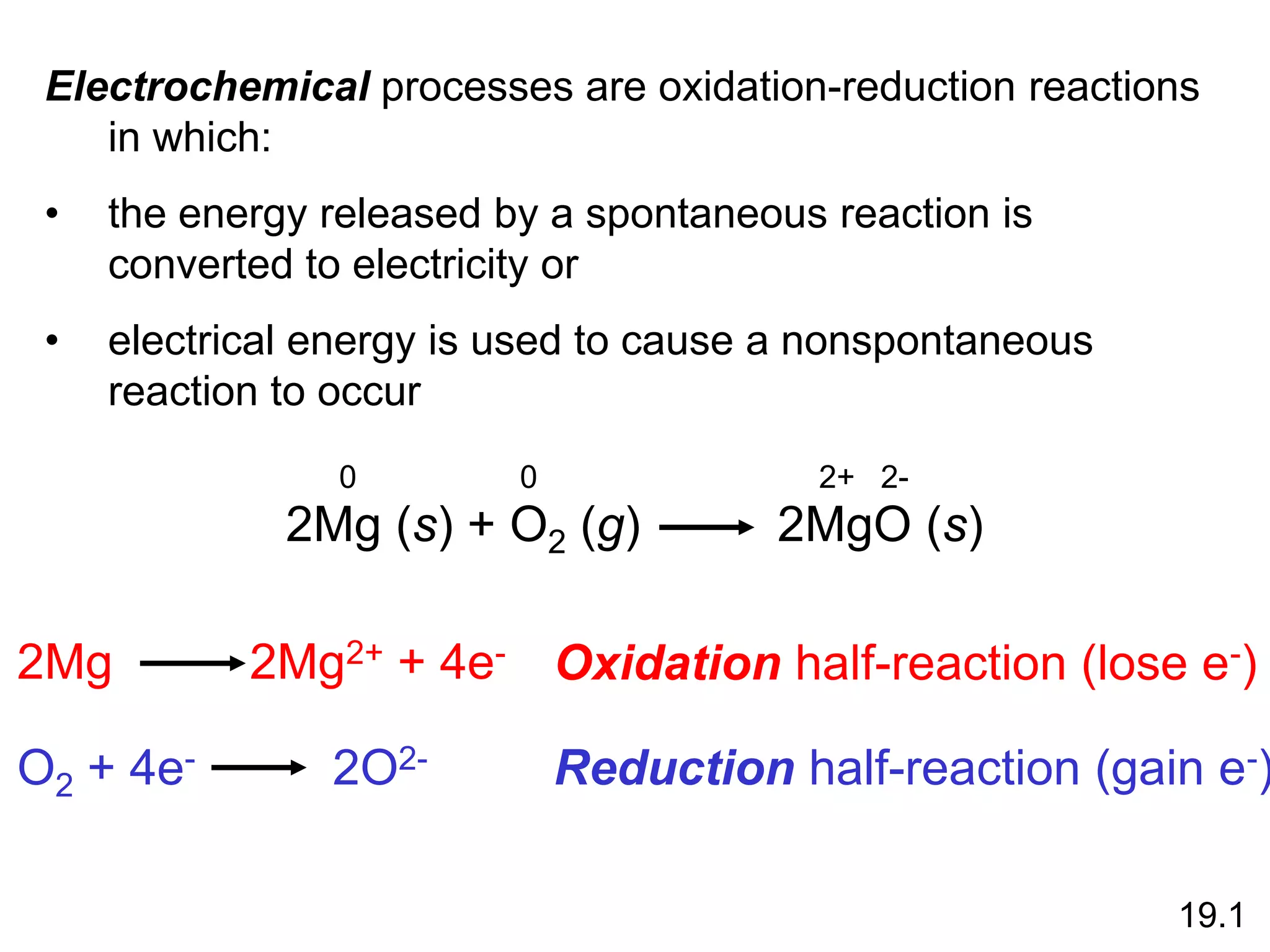
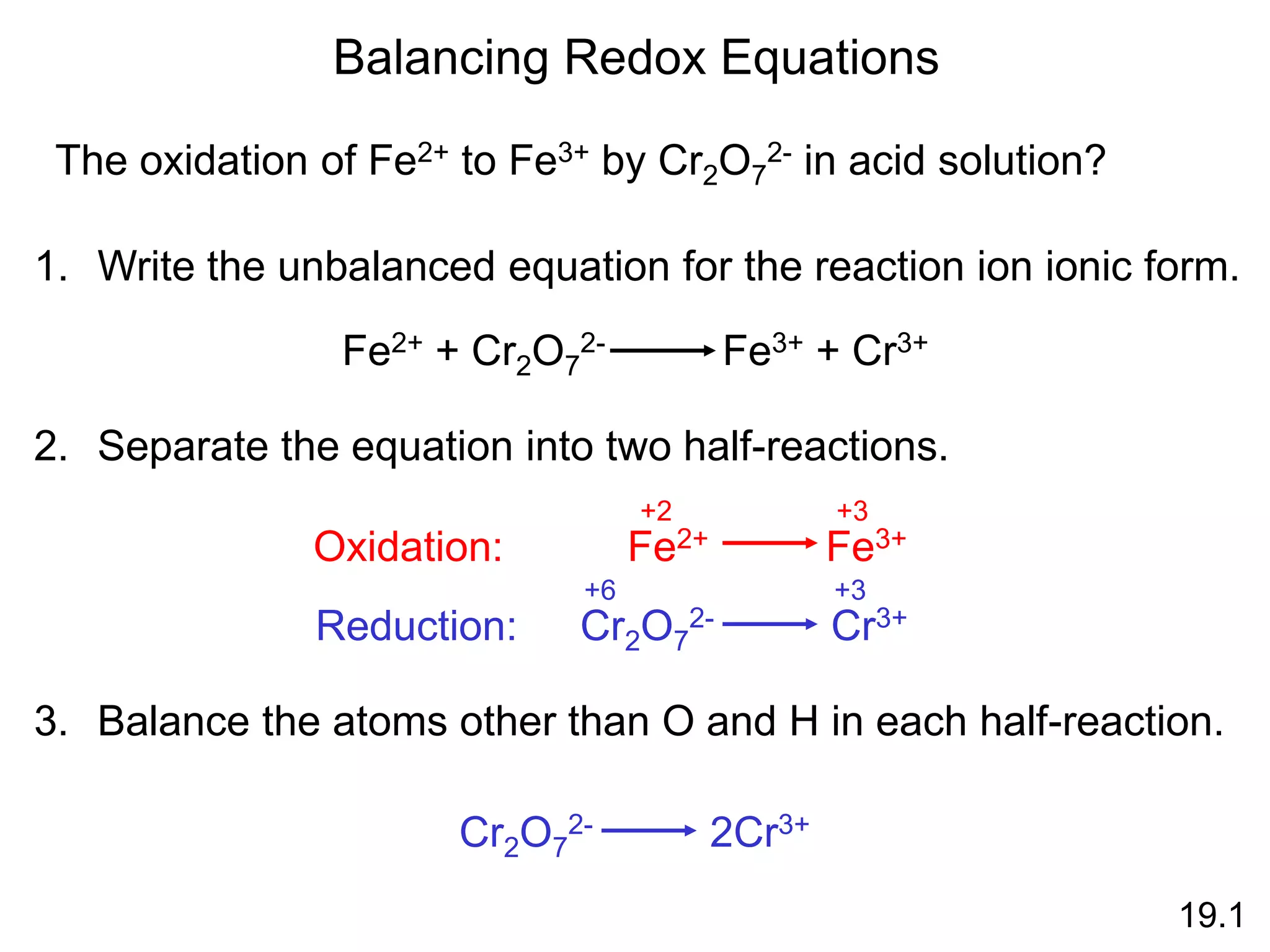
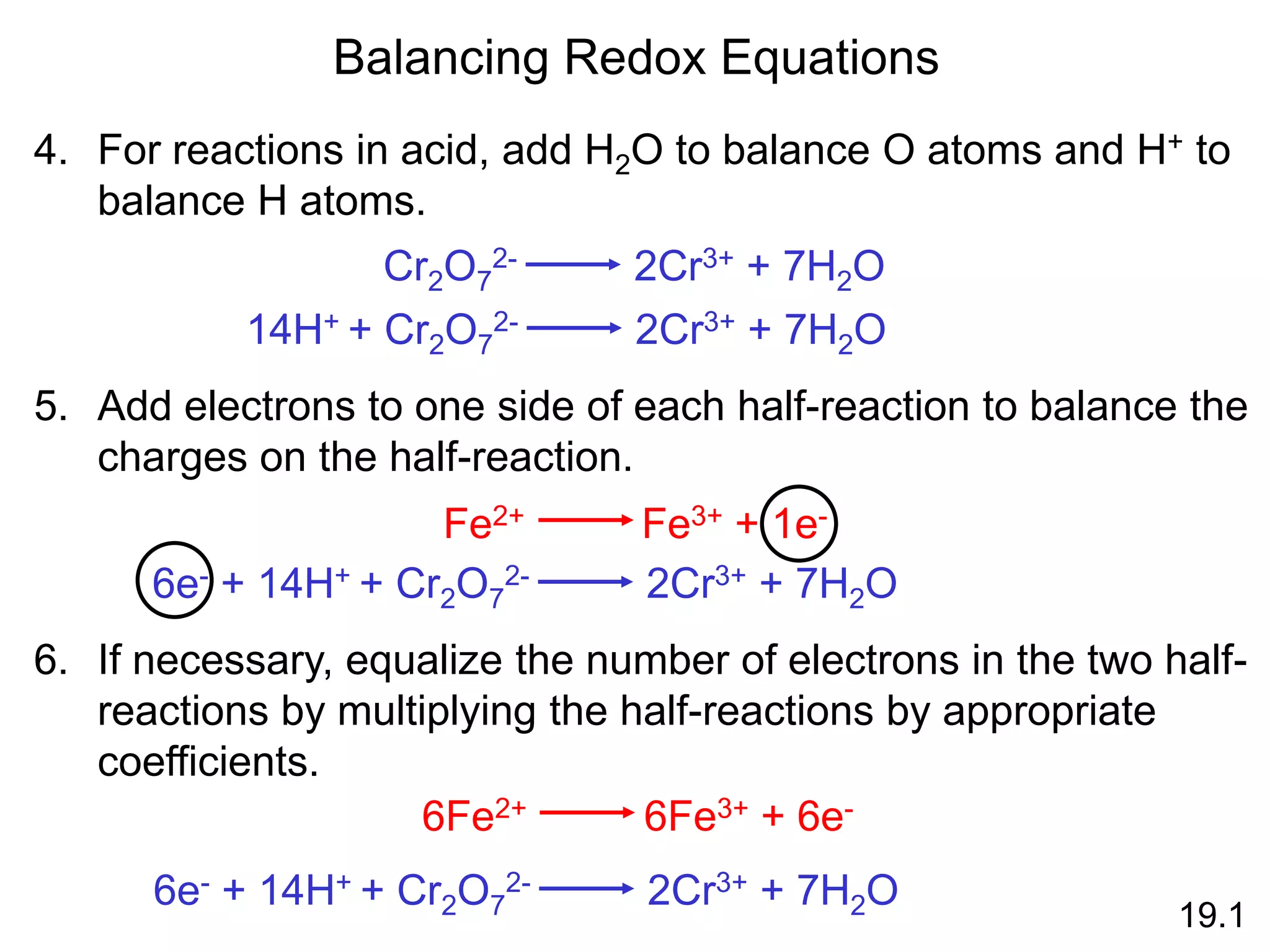
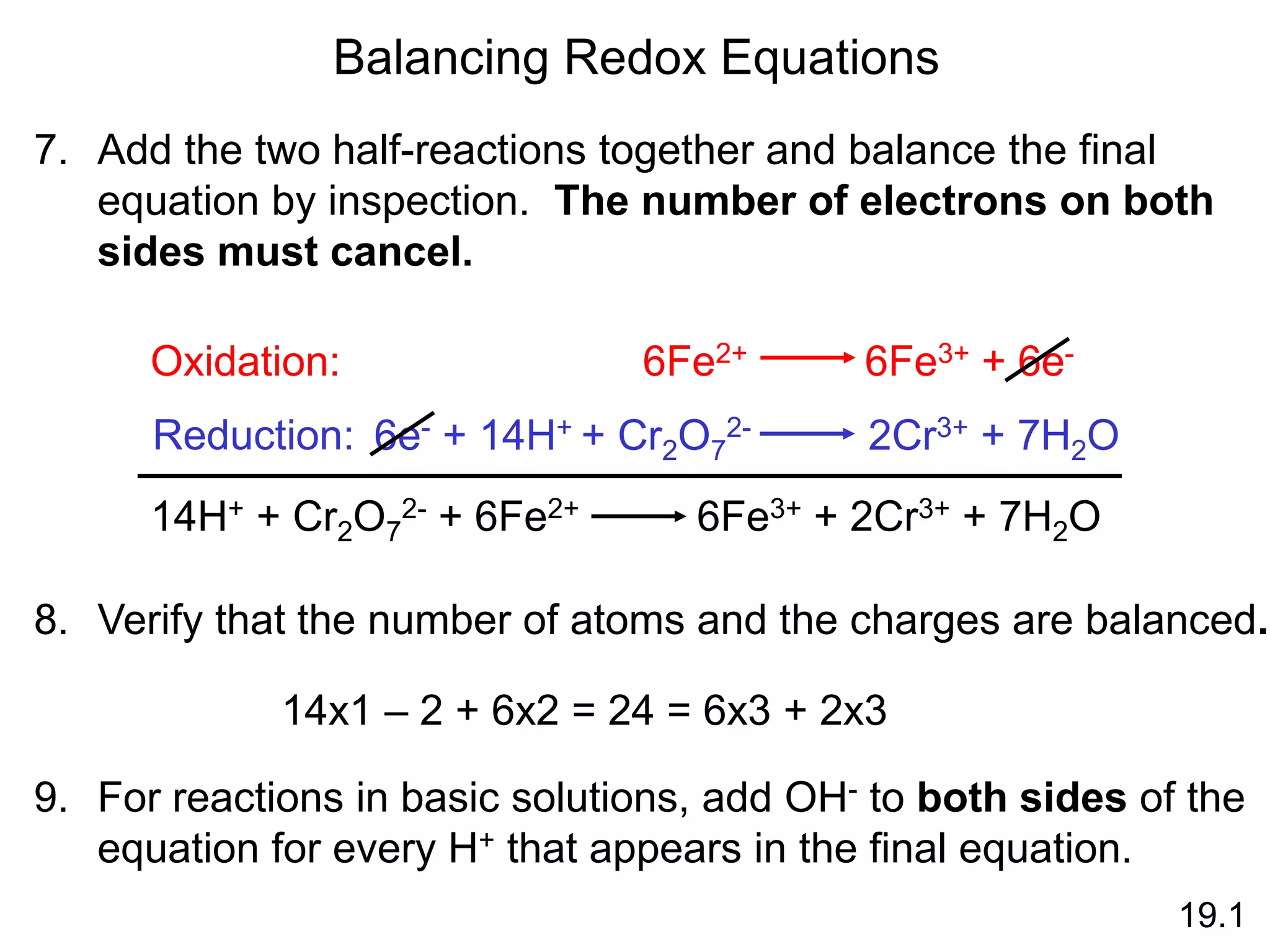
Chemical equilibrium is a state where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal and the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant. Equilibrium is achieved when these conditions are met. The equilibrium constant, K, provides a quantitative measure of the position of equilibrium and can be expressed in terms of concentrations or pressures depending on whether the reaction involves gases or solutions. Factors such as concentration, pressure, temperature, and catalysis can influence the position of equilibrium based on Le Chatelier's principle.


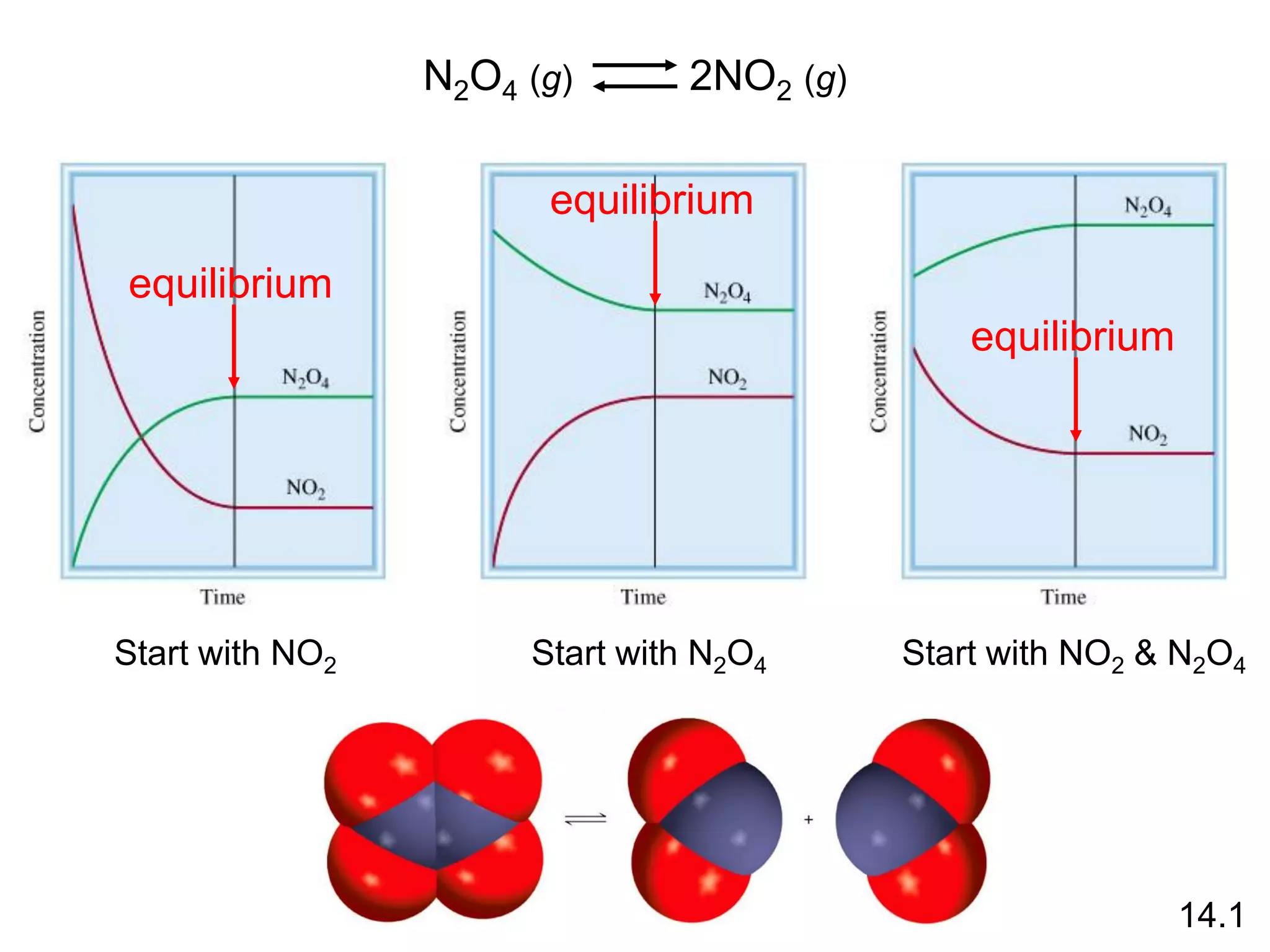
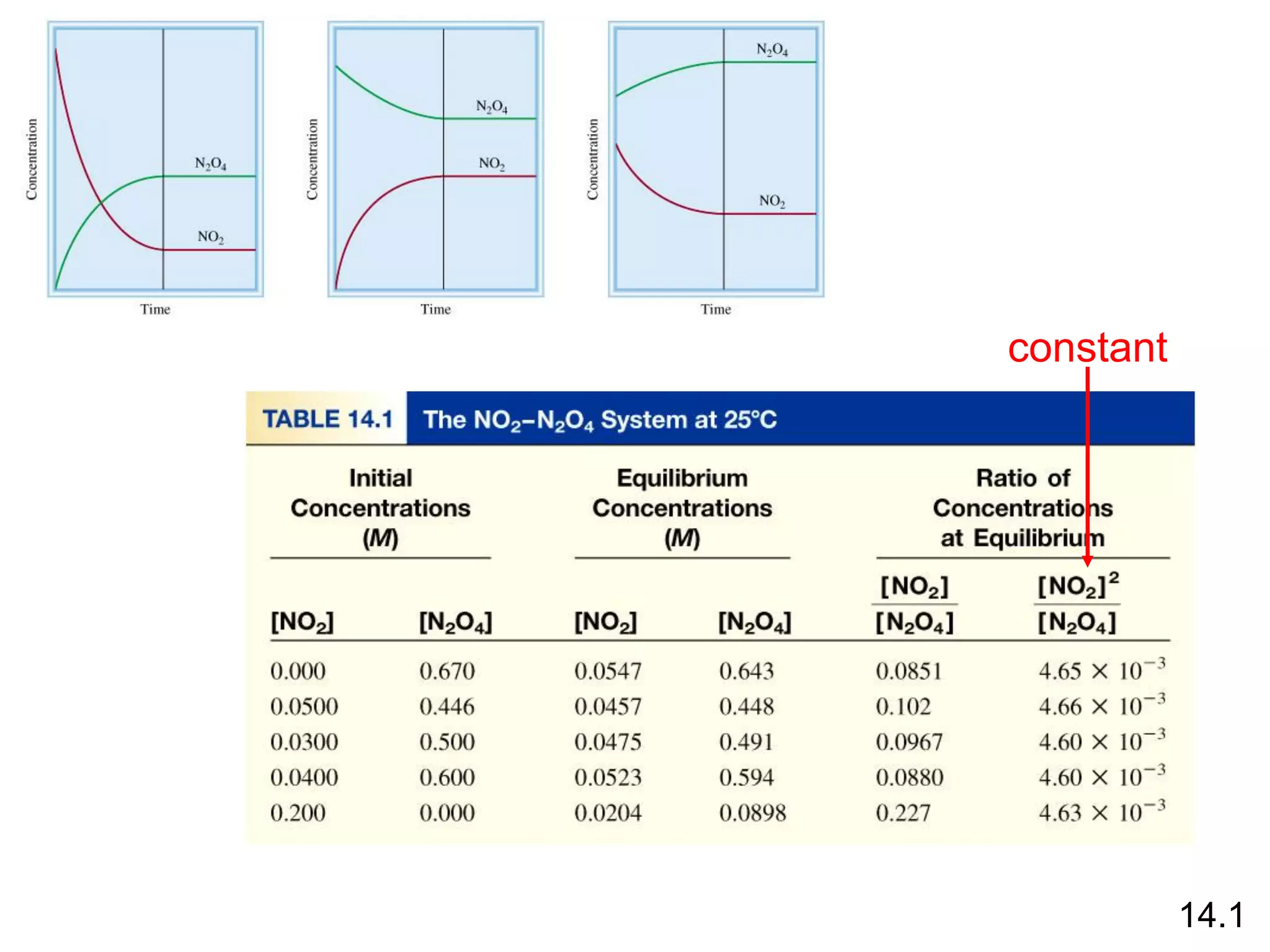
![N2O4 (g) 2NO2 (g)
= 4.63 x 10-3
K =
[NO2]2
[N2O4]
aA + bB cC + dD
K =
[C]c[D]d
[A]a[B]b
Law of Mass Action
14.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-5-2048.jpg)
![K >> 1
K << 1
Lie to the right Favor products
Lie to the left Favor reactants
Equilibrium Will
K =
[C]c[D]d
[A]a[B]b
aA + bB cC + dD
14.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-6-2048.jpg)
![Homogenous equilibrium applies to reactions in which all
reacting species are in the same phase.
N2O4 (g) 2NO2 (g)
Kc =
[NO2]2
[N2O4]
Kp =
NO2
P2
N2O4
P
aA (g) + bB (g) cC (g) + dD (g)
14.2
Kp = Kc(RT)Dn
Dn = moles of gaseous products – moles of gaseous reactants
= (c + d) – (a + b)
In most cases
Kc Kp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-7-2048.jpg)
![Homogeneous Equilibrium
CH3COOH (aq) + H2O (l) CH3COO- (aq) + H3O+ (aq)
Kc =
‘
[CH3COO-][H3O+]
[CH3COOH][H2O]
[H2O] = constant
Kc =
[CH3COO-][H3O+]
[CH3COOH]
= Kc [H2O]
‘
General practice not to include units for the
equilibrium constant.
14.2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-8-2048.jpg)
![The equilibrium concentrations for the reaction between
carbon monoxide and molecular chlorine to form COCl2 (g)
at 740C are [CO] = 0.012 M, [Cl2] = 0.054 M, and [COCl2] =
0.14 M. Calculate the equilibrium constants Kc and Kp.
CO (g) + Cl2 (g) COCl2 (g)
Kc =
[COCl2]
[CO][Cl2]
=
0.14
0.012 x 0.054
= 220
Kp = Kc(RT)Dn
Dn = 1 – 2 = -1 R = 0.0821 T = 273 + 74 = 347 K
Kp = 220 x (0.0821 x 347)-1 = 7.7
14.2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-9-2048.jpg)
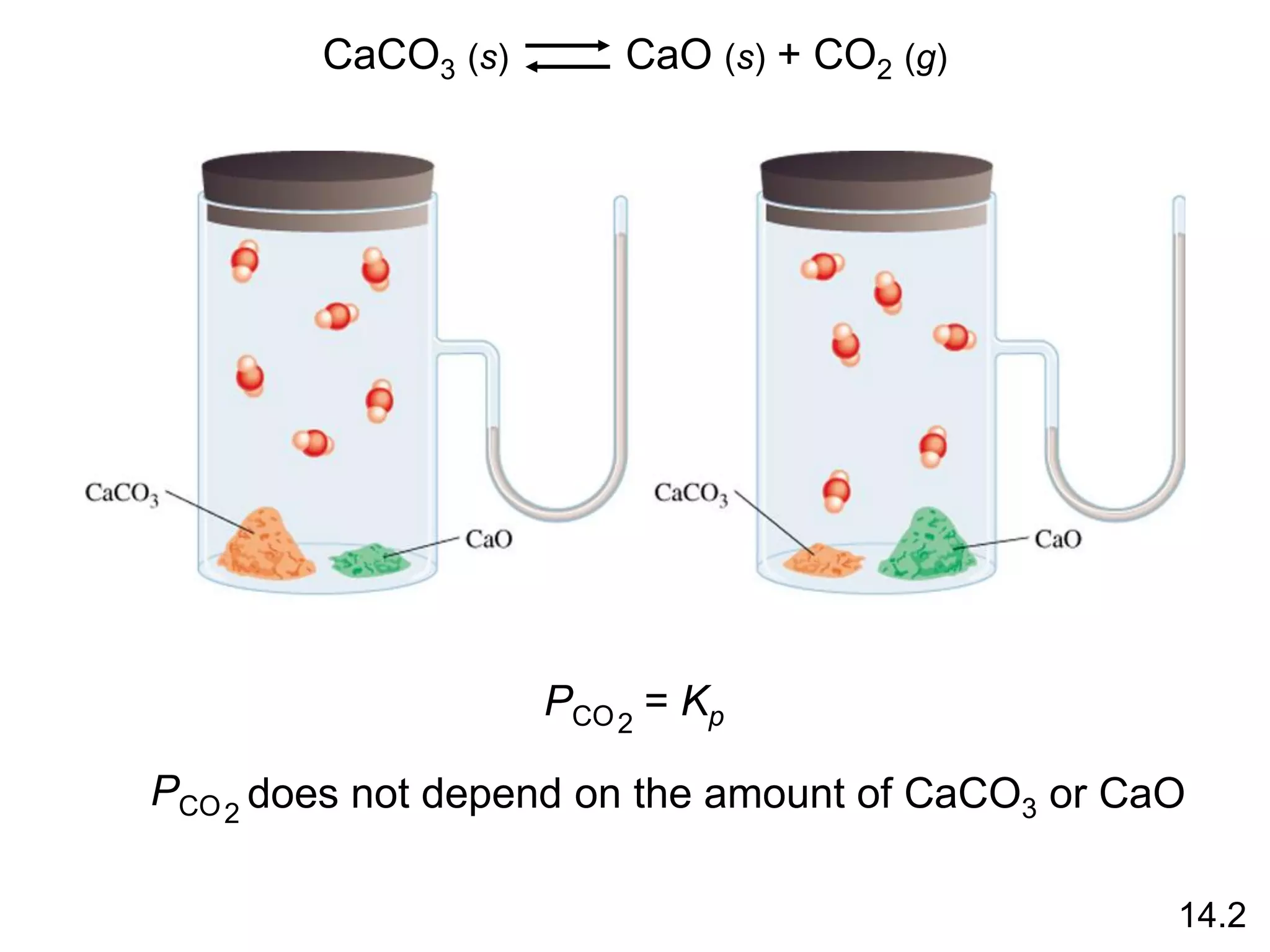
![Heterogenous equilibrium applies to reactions in which
reactants and products are in different phases.
CaCO3 (s) CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
Kc =
‘
[CaO][CO2]
[CaCO3]
[CaCO3] = constant
[CaO] = constant
Kc = [CO2] = Kc x
‘
[CaCO3]
[CaO]
Kp = PCO2
The concentration of solids and pure liquids are not
included in the expression for the equilibrium constant.
14.2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-11-2048.jpg)

![A + B C + D
C + D E + F
A + B E + F
Kc =
‘
[C][D]
[A][B]
Kc =
‘‘
[E][F]
[C][D]
[E][F]
[A][B]
Kc =
Kc
‘
Kc‘
‘
Kc
Kc = Kc‘
‘
Kc
‘ x
If a reaction can be expressed as the sum of
two or more reactions, the equilibrium
constant for the overall reaction is given by
the product of the equilibrium constants of
the individual reactions.
14.2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-14-2048.jpg)
![N2O4 (g) 2NO2 (g)
= 4.63 x 10-3
K =
[NO2]2
[N2O4]
2NO2 (g) N2O4 (g)
K =
[N2O4]
[NO2]2
‘ =
1
K
= 216
When the equation for a reversible reaction
is written in the opposite direction, the
equilibrium constant becomes the reciprocal
of the original equilibrium constant.
14.2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-15-2048.jpg)

![14.3
Chemical Kinetics and Chemical Equilibrium
A + 2B AB2
kf
kr
ratef = kf [A][B]2
rater = kr [AB2]
Equilibrium
ratef = rater
kf [A][B]2 = kr [AB2]
kf
kr
[AB2]
[A][B]2
= Kc =](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-17-2048.jpg)
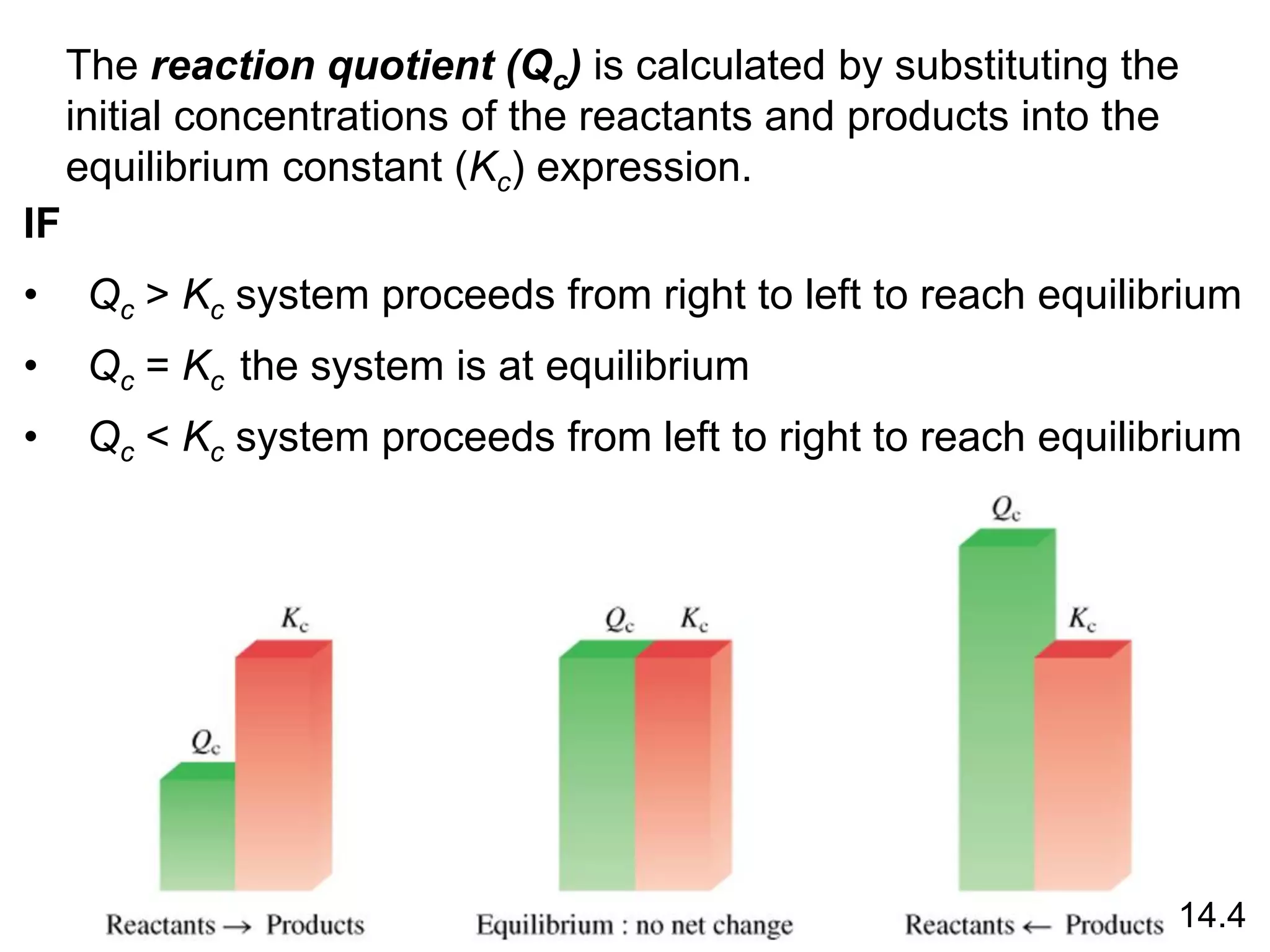

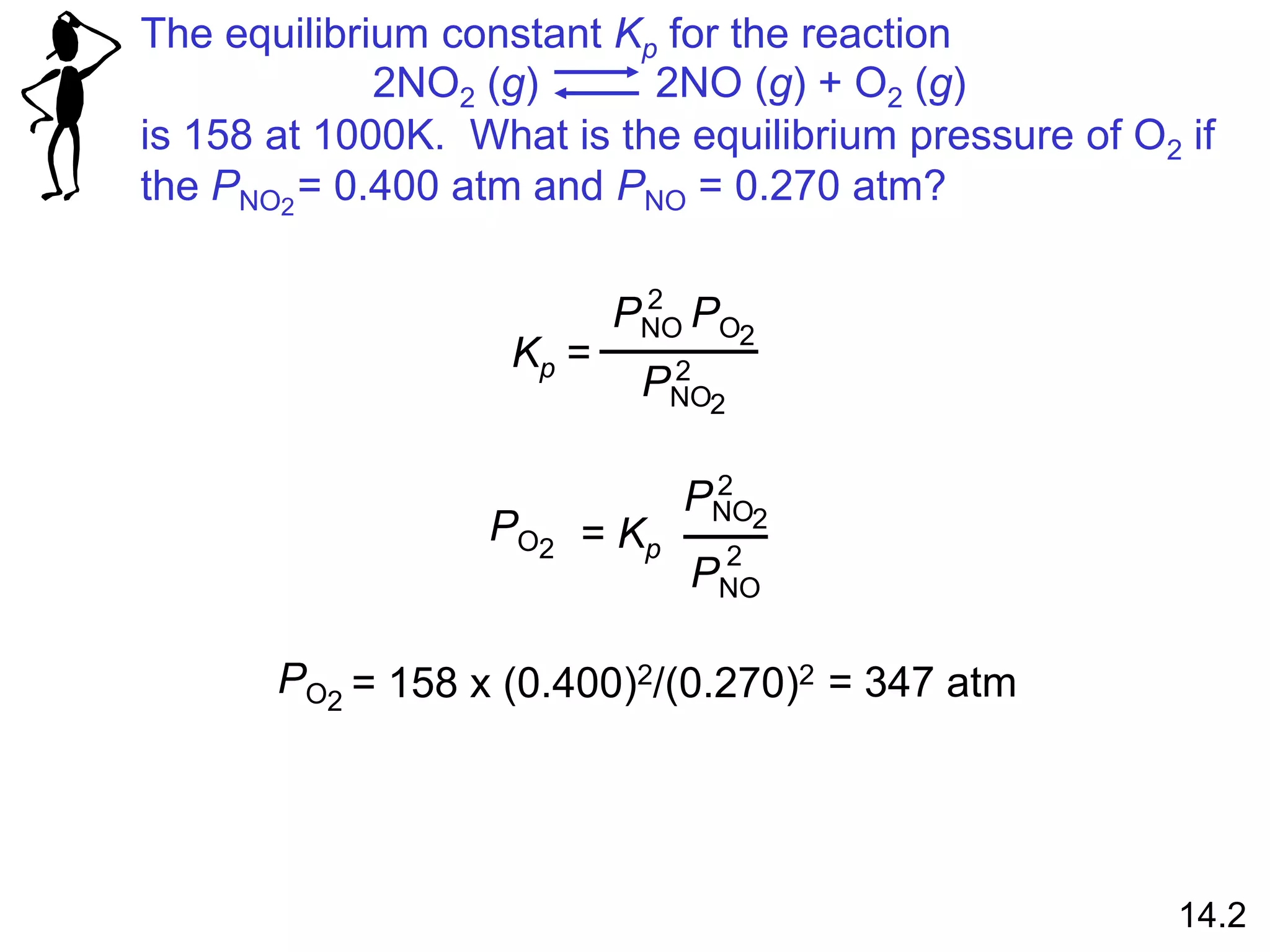
![At 12800C the equilibrium constant (Kc) for the reaction
Is 1.1 x 10-3. If the initial concentrations are [Br2] = 0.063
M and [Br] = 0.012 M, calculate the concentrations of these
species at equilibrium.
Br2 (g) 2Br (g)
Br2 (g) 2Br (g)
Let x be the change in concentration of Br2
Initial (M)
Change (M)
Equilibrium (M)
0.063 0.012
-x +2x
0.063 - x 0.012 + 2x
[Br]2
[Br2]
Kc = Kc =
(0.012 + 2x)2
0.063 - x
= 1.1 x 10-3 Solve for x
14.4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-20-2048.jpg)
![Kc =
(0.012 + 2x)2
0.063 - x
= 1.1 x 10-3
4x2 + 0.048x + 0.000144 = 0.0000693 – 0.0011x
4x2 + 0.0491x + 0.0000747 = 0
ax2 + bx + c =0
-b ± b2 – 4ac
2a
x =
Br2 (g) 2Br (g)
Initial (M)
Change (M)
Equilibrium (M)
0.063 0.012
-x +2x
0.063 - x 0.012 + 2x
x = -0.00178
x = -0.0105
At equilibrium, [Br] = 0.012 + 2x = -0.009 M or 0.00844 M
At equilibrium, [Br2] = 0.062 – x = 0.0648 M
14.4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-21-2048.jpg)

![Chemistry In Action
Life at High Altitudes and Hemoglobin Production
Kc =
[HbO2]
[Hb][O2]
Hb (aq) + O2 (aq) HbO2 (aq)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-27-2048.jpg)




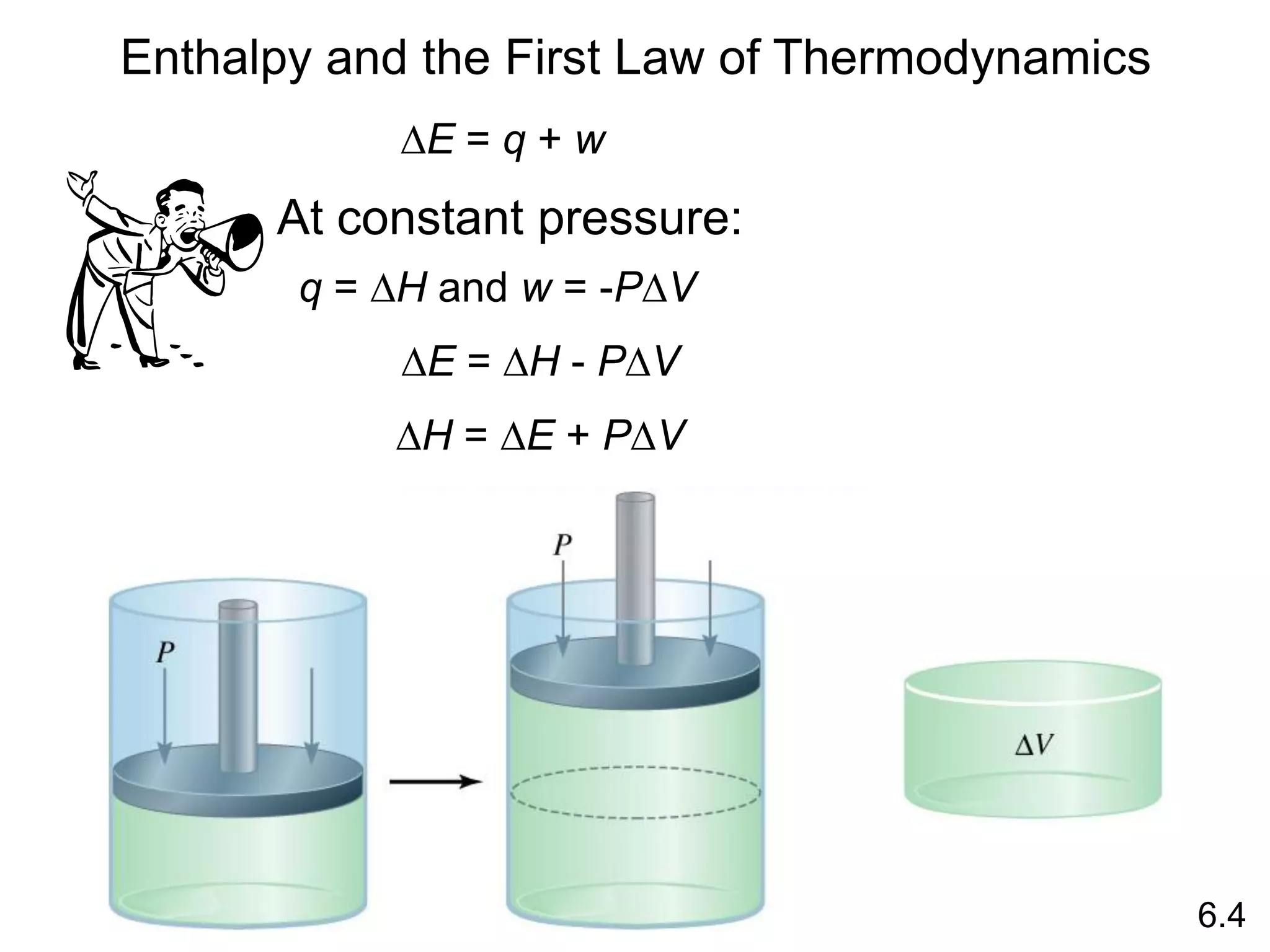
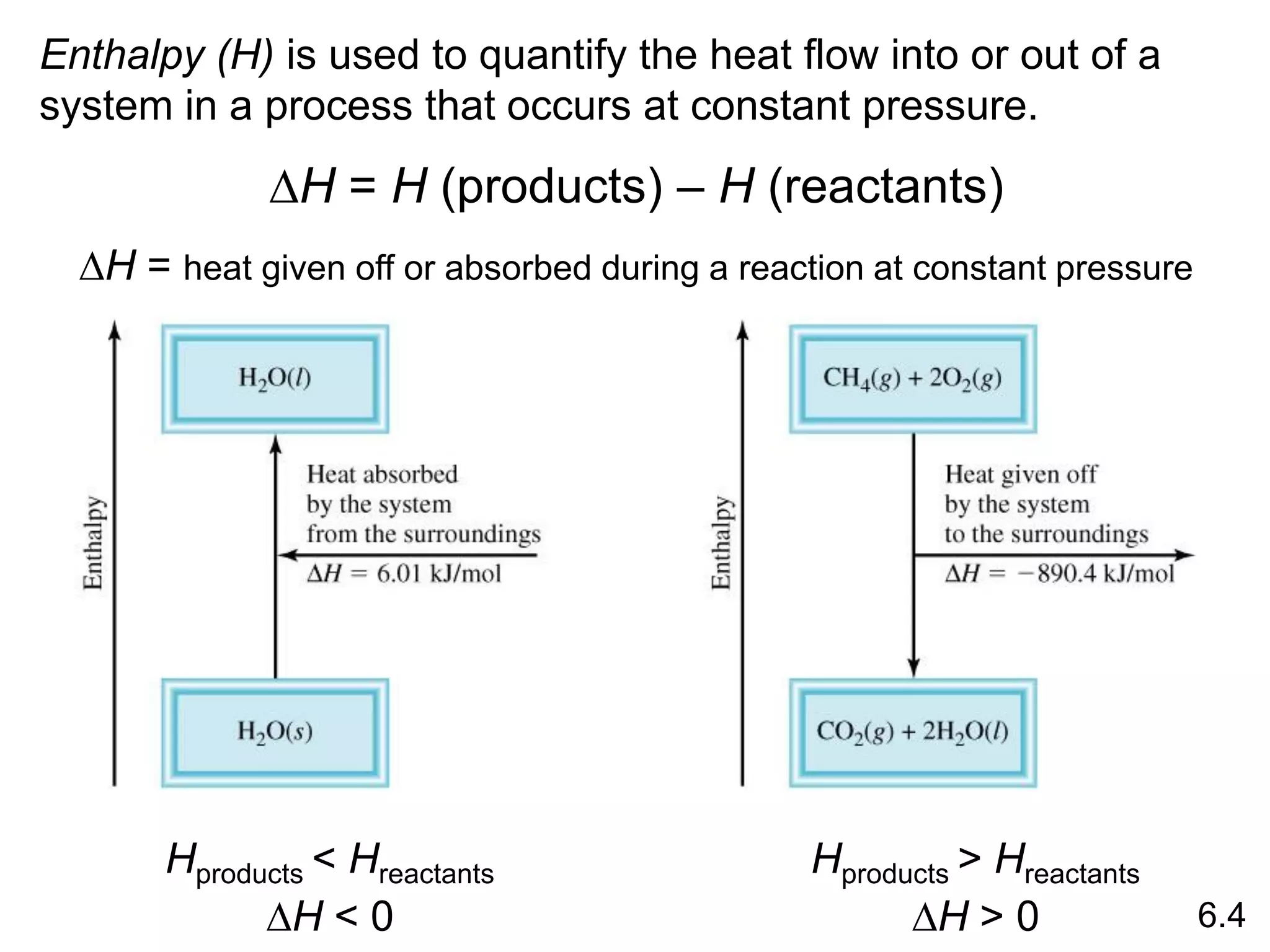

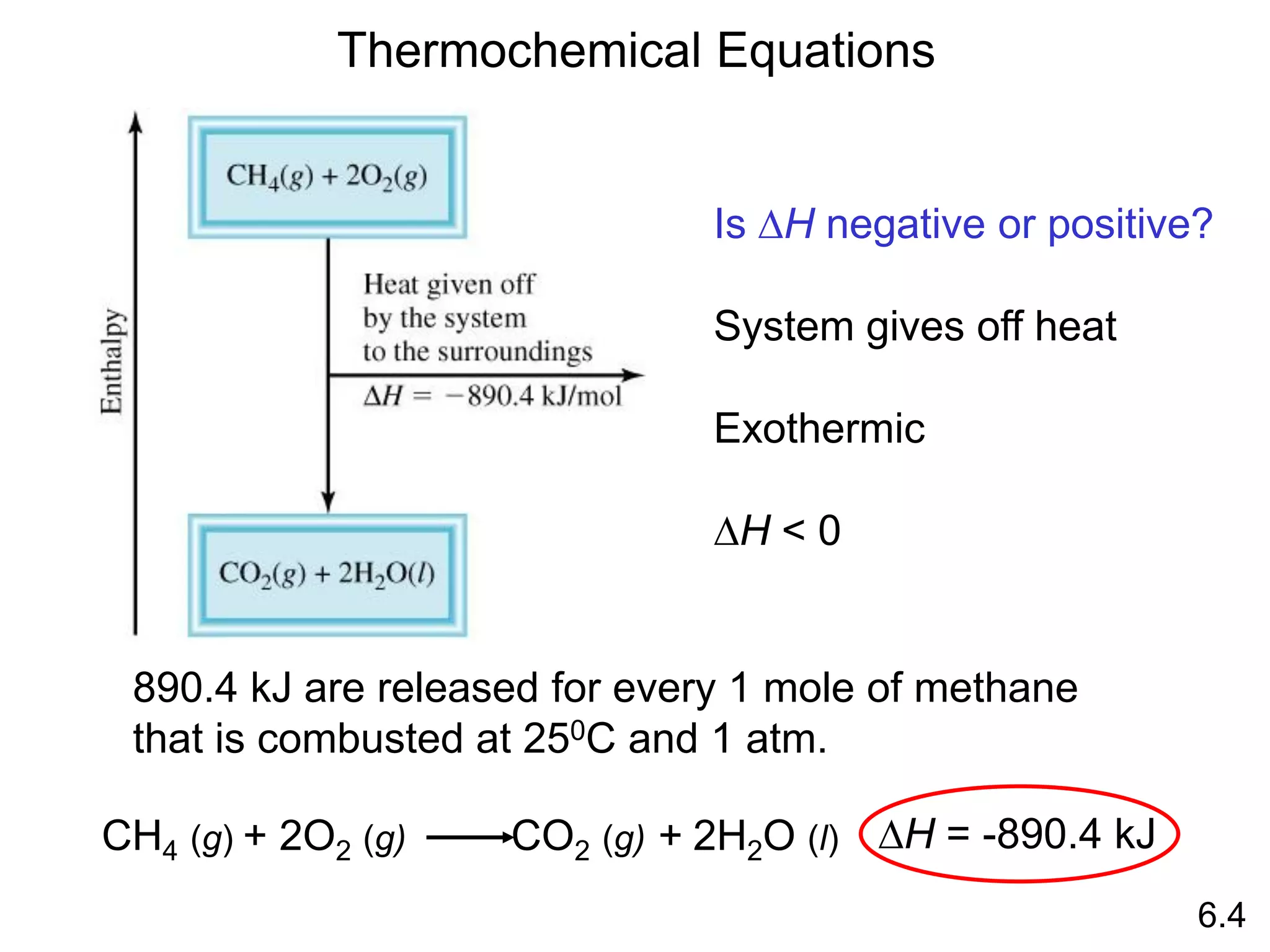

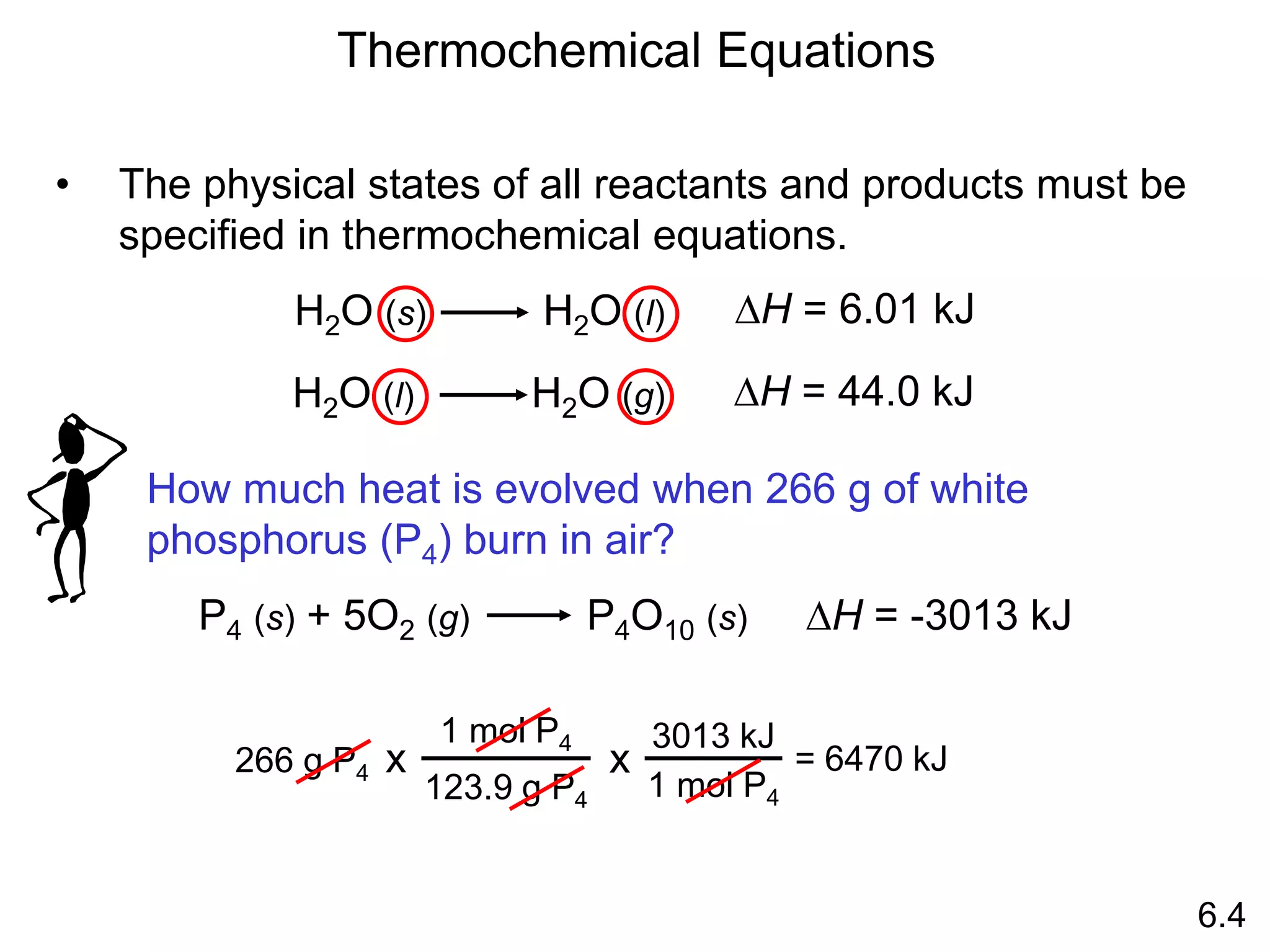


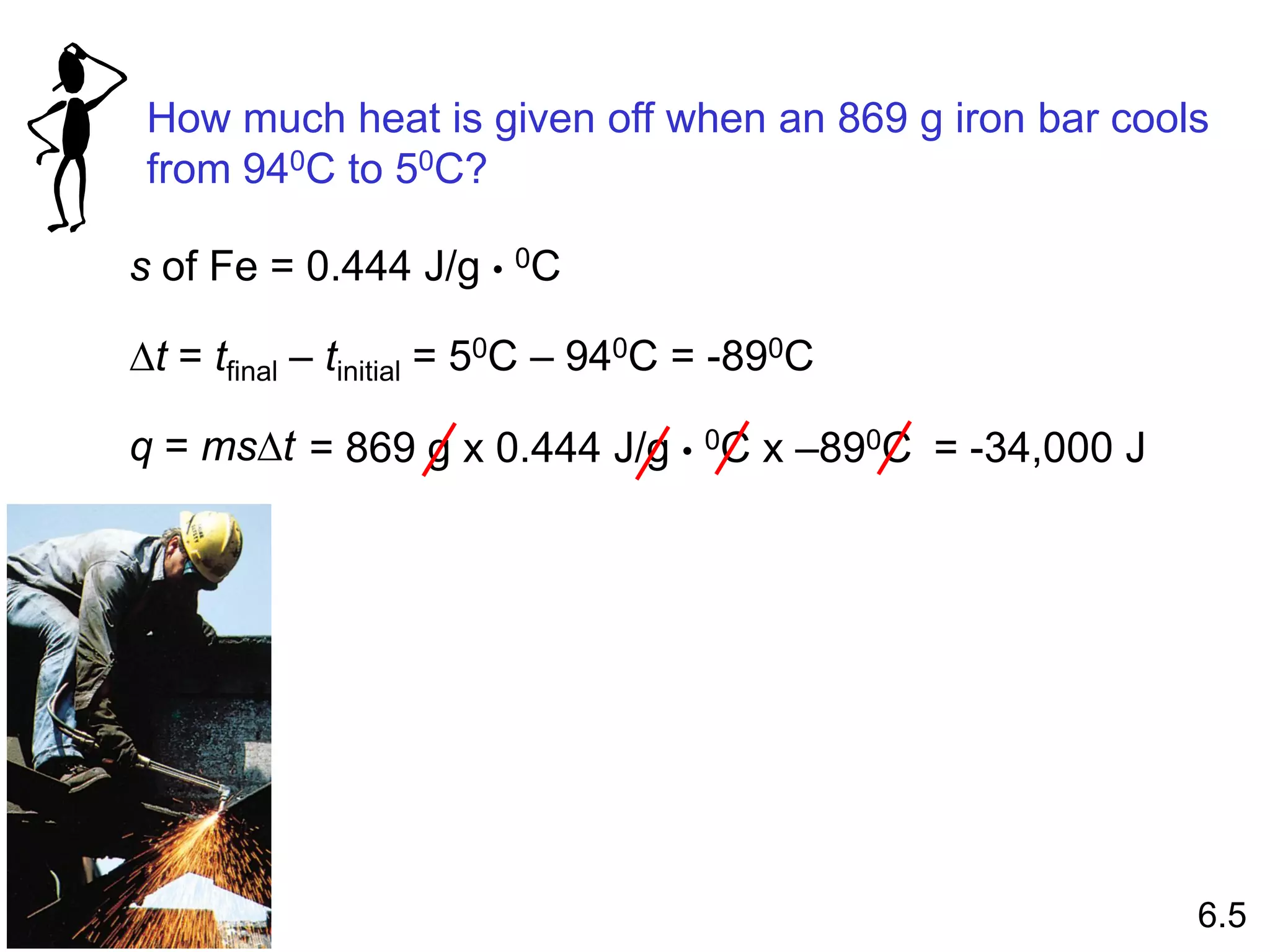
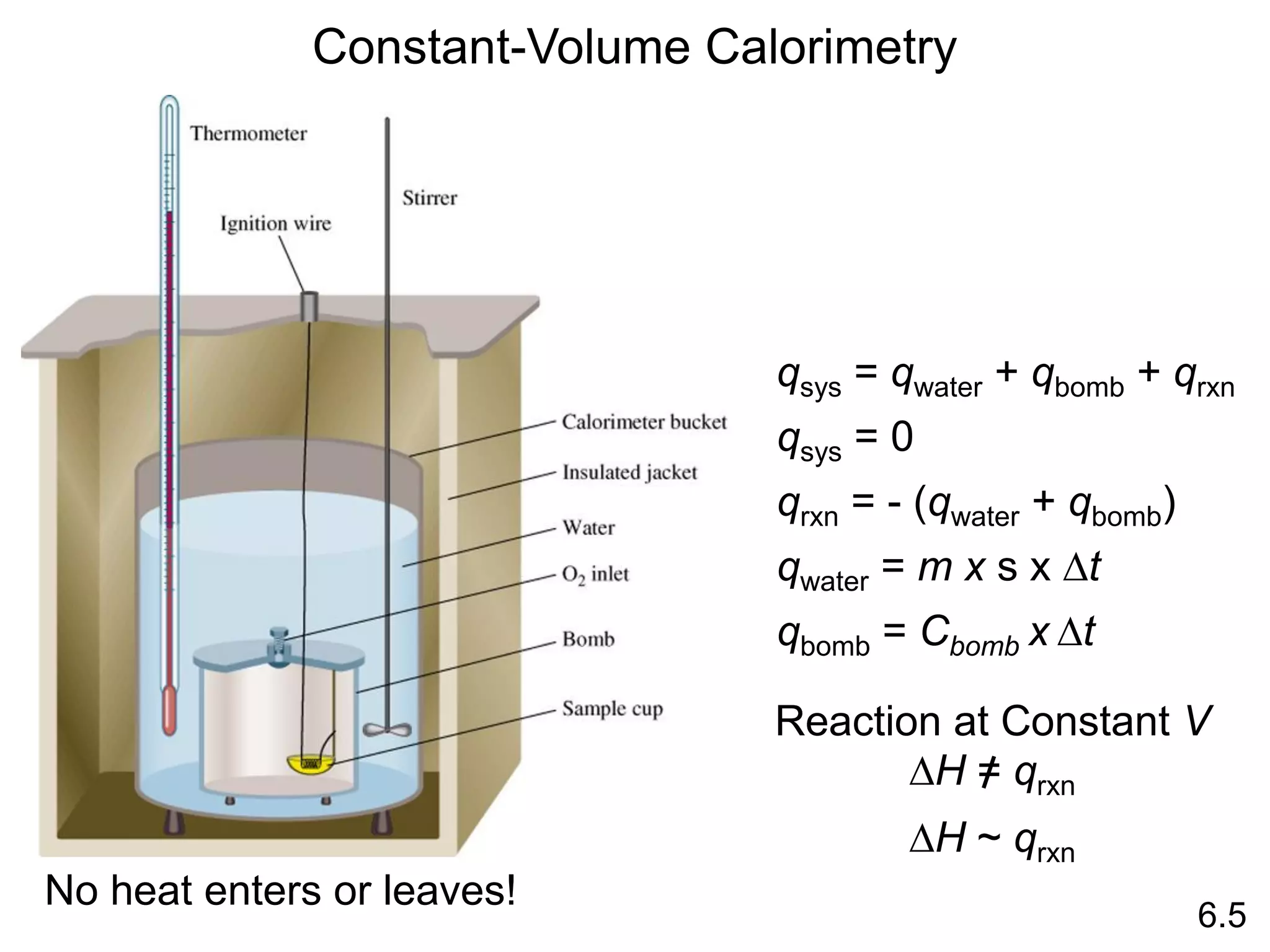
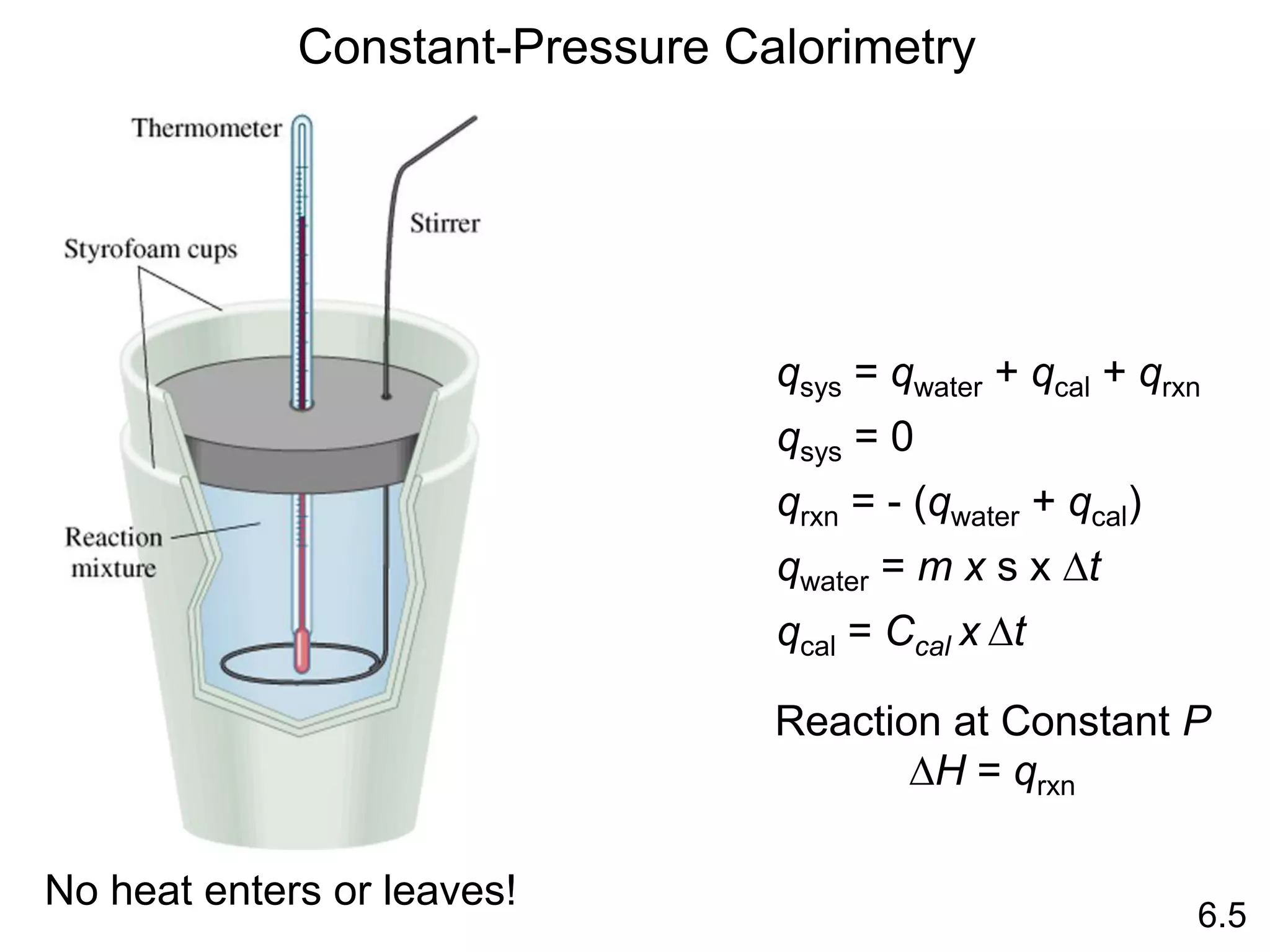
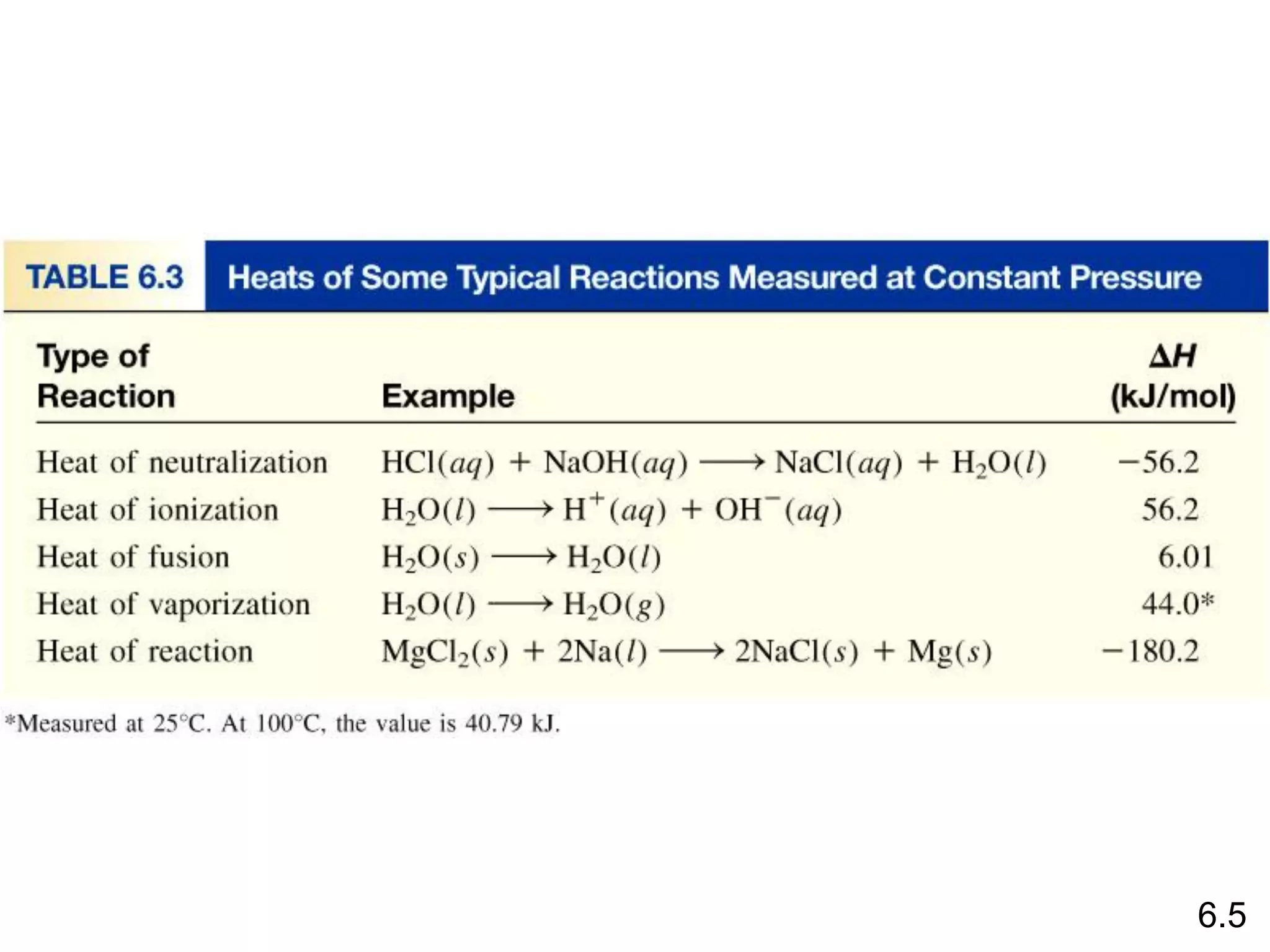
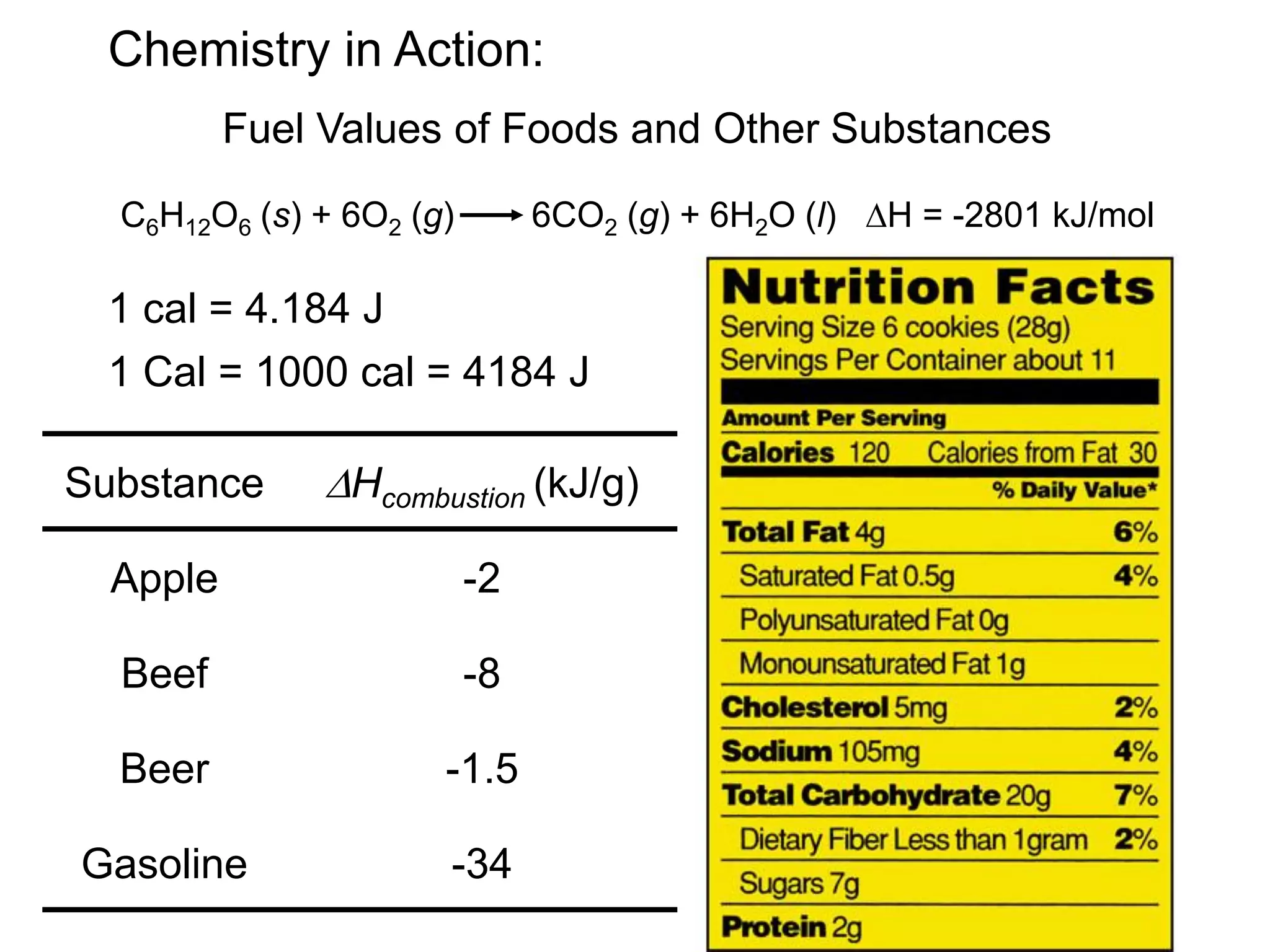

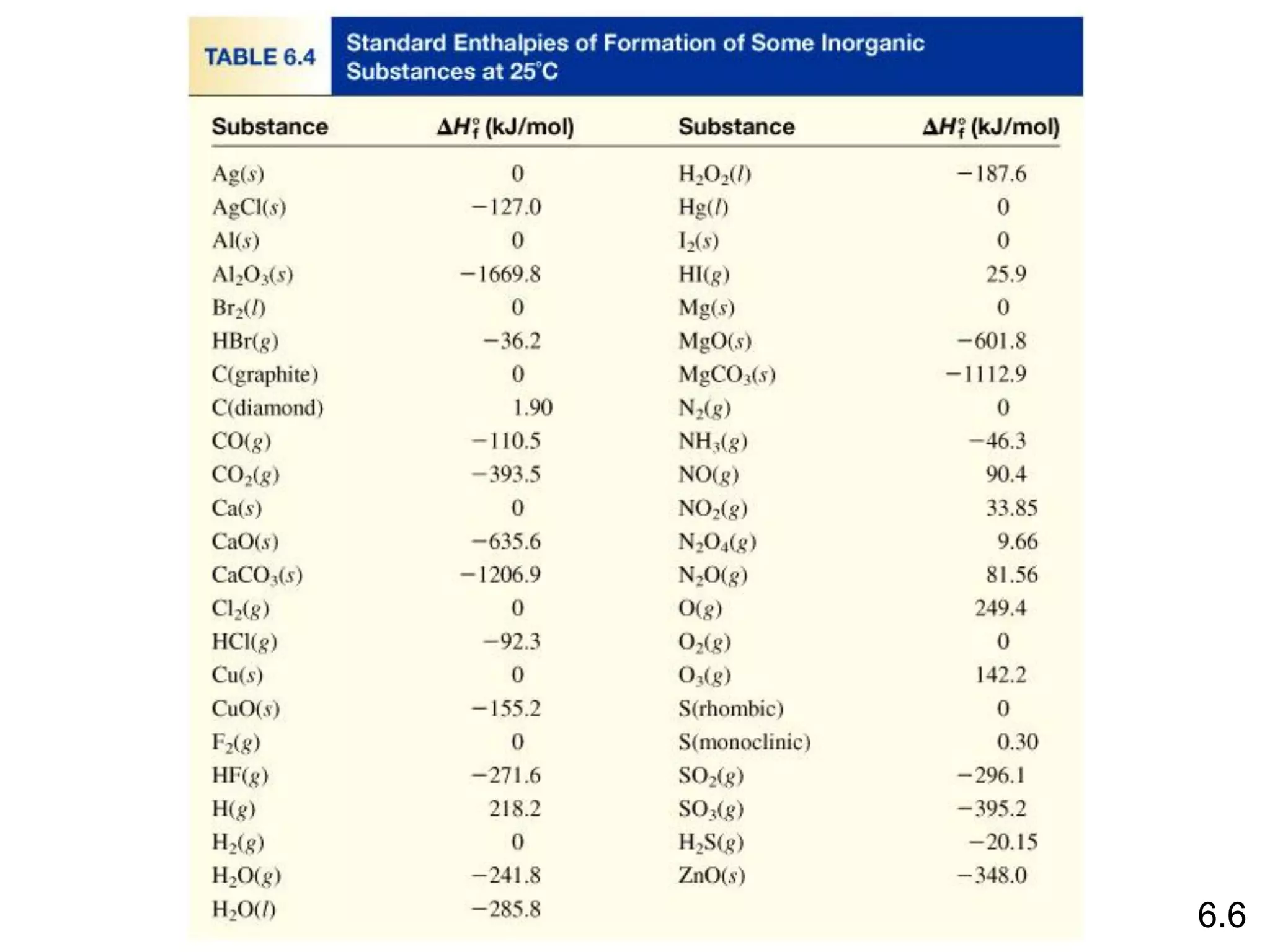
![The standard enthalpy of reaction (DH0 ) is the enthalpy of a
reaction carried out at 1 atm.
rxn
aA + bB cC + dD
DH0
rxn dDH0 (D)
f
cDH0 (C)
f
= [ + ] - bDH0 (B)
f
aDH0 (A)
f
[ + ]
DH0
rxn nDH0 (products)
f
= S mDH0 (reactants)
f
S
-
6.6
Hess’s Law: When reactants are converted to products, the
change in enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes
place in one step or in a series of steps.
(Enthalpy is a state function. It doesn’t matter how you get
there, only where you start and end.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-57-2048.jpg)


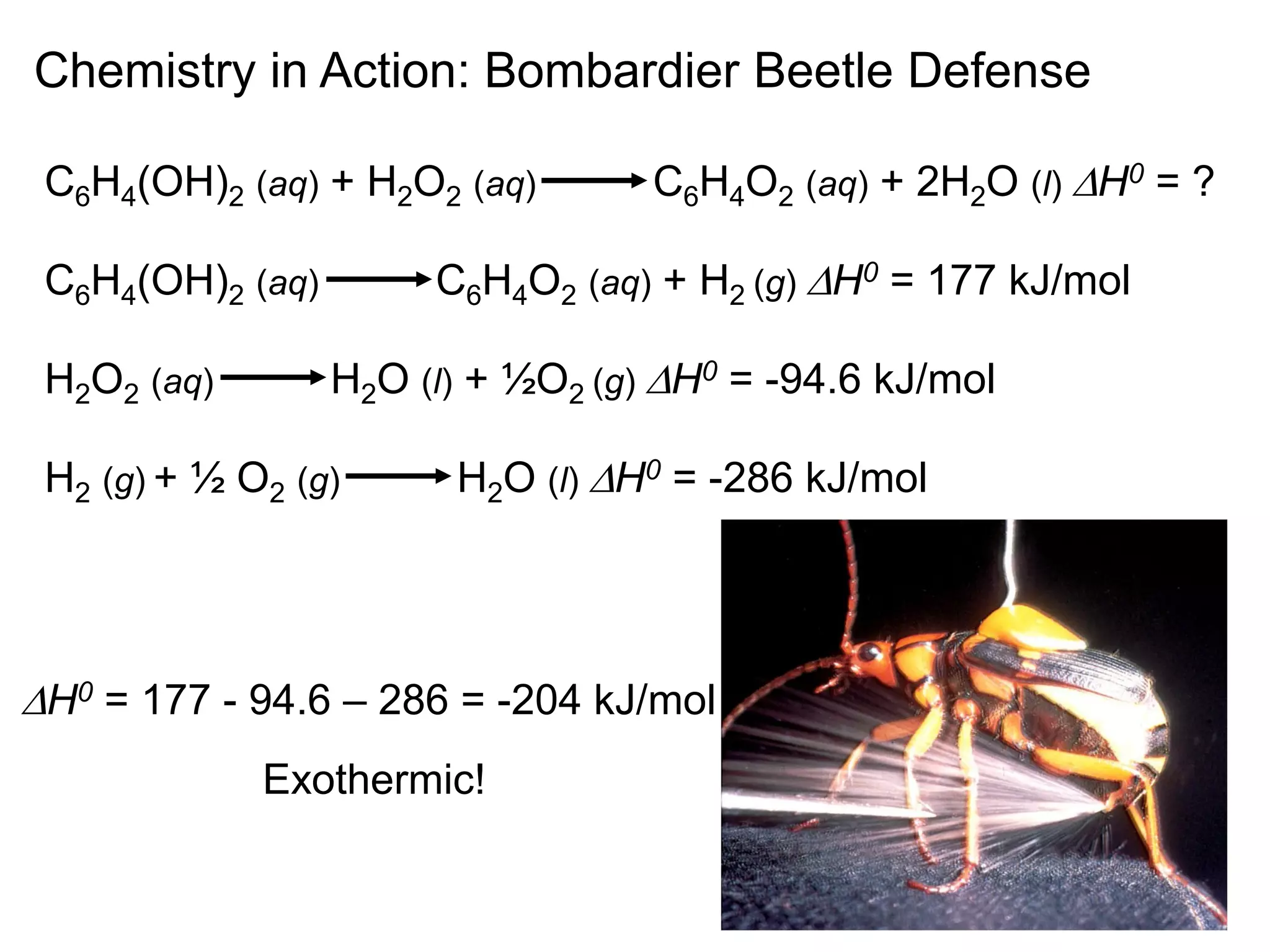
![Benzene (C6H6) burns in air to produce carbon dioxide and
liquid water. How much heat is released per mole of
benzene combusted? The standard enthalpy of formation
of benzene is 49.04 kJ/mol.
2C6H6 (l) + 15O2 (g) 12CO2 (g) + 6H2O (l)
DH0
rxn nDH0 (products)
f
= S mDH0 (reactants)
f
S
-
DH0
rxn 6DH0 (H2O)
f
12DH0 (CO2)
f
= [ + ] - 2DH0 (C6H6)
f
[ ]
DH0
rxn = [ 12x–393.5 + 6x–187.6 ] – [ 2x49.04 ] = -5946 kJ
-5946 kJ
2 mol
= - 2973 kJ/mol C6H6
6.6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-60-2048.jpg)




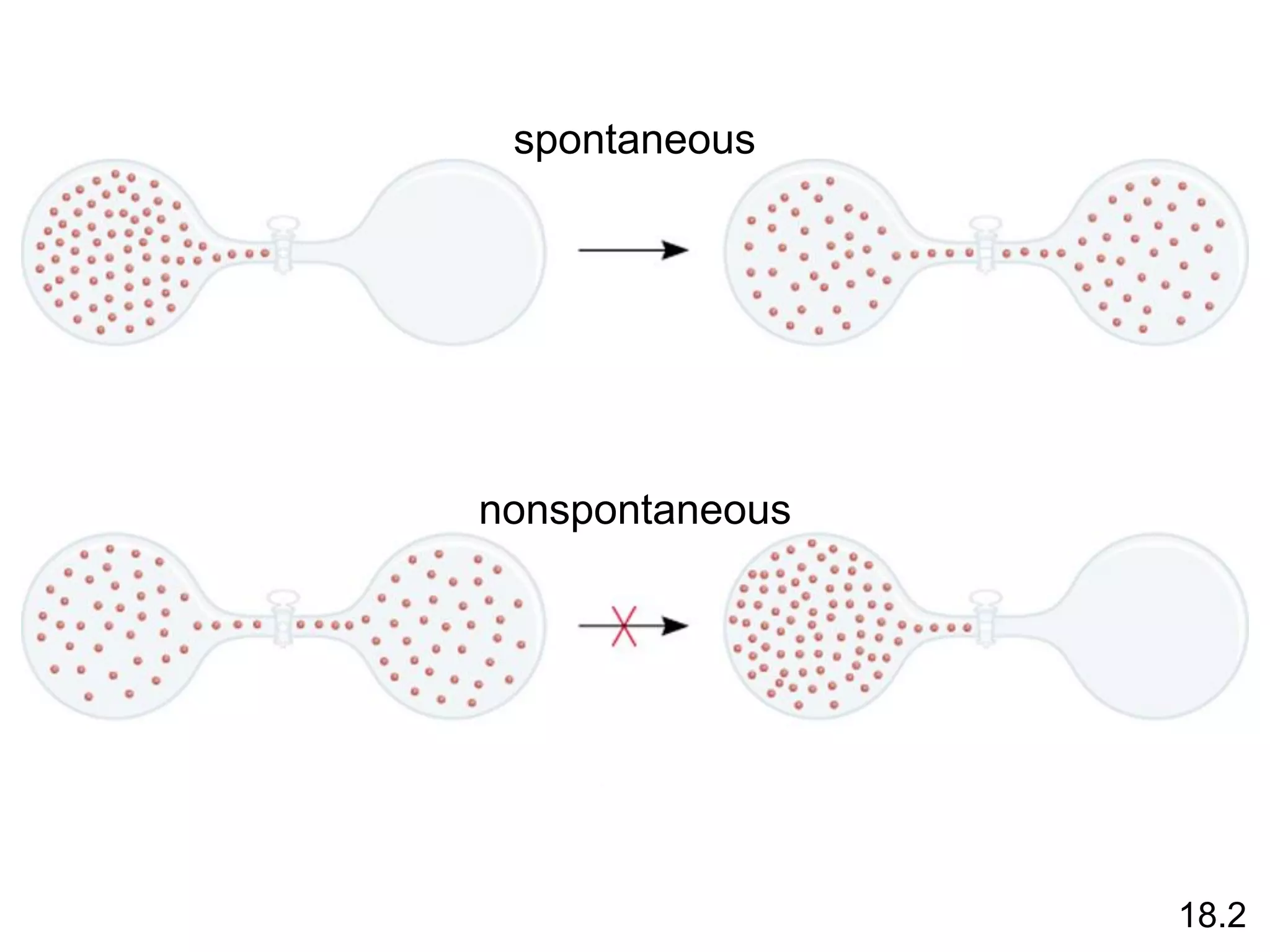
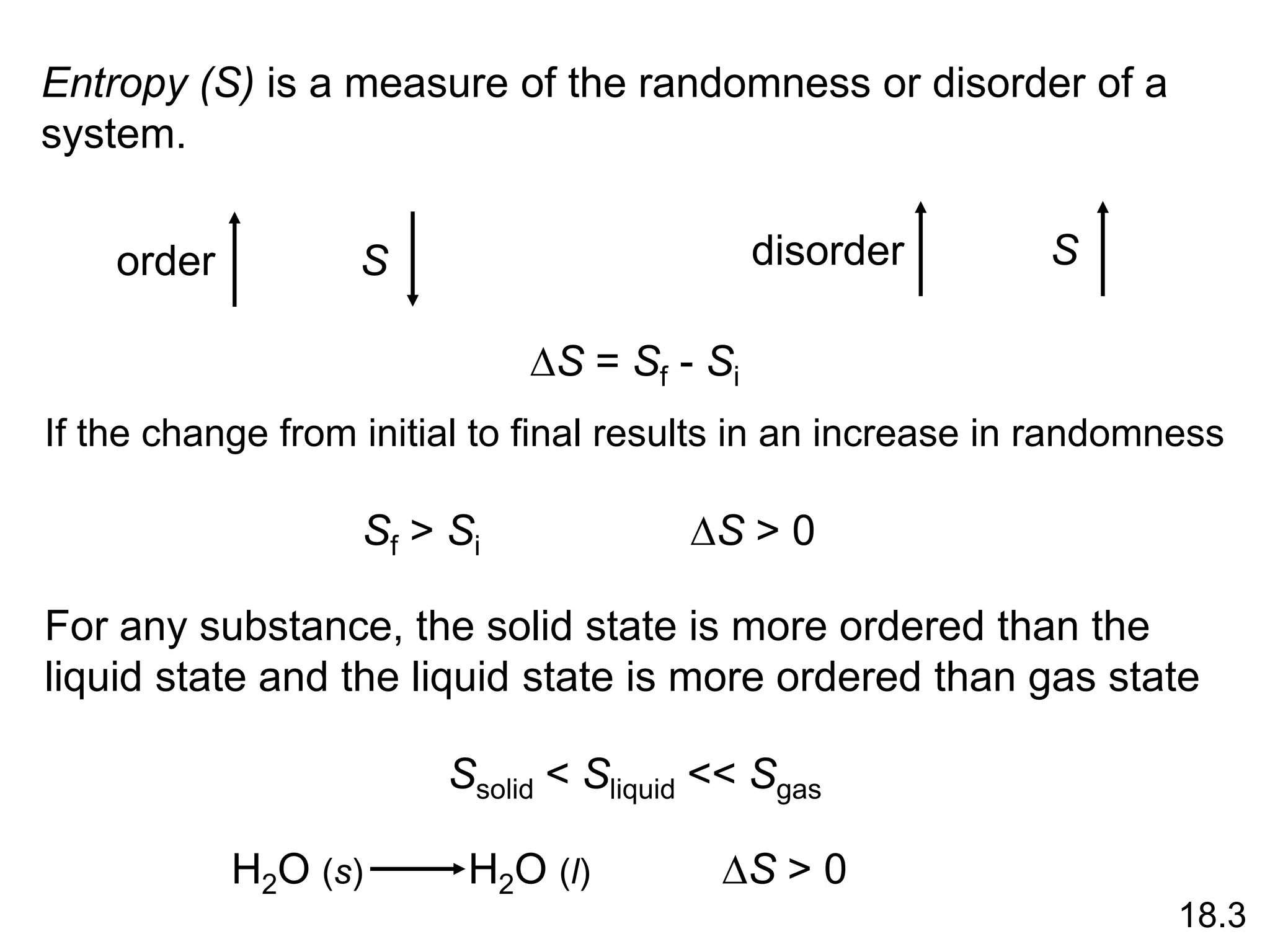
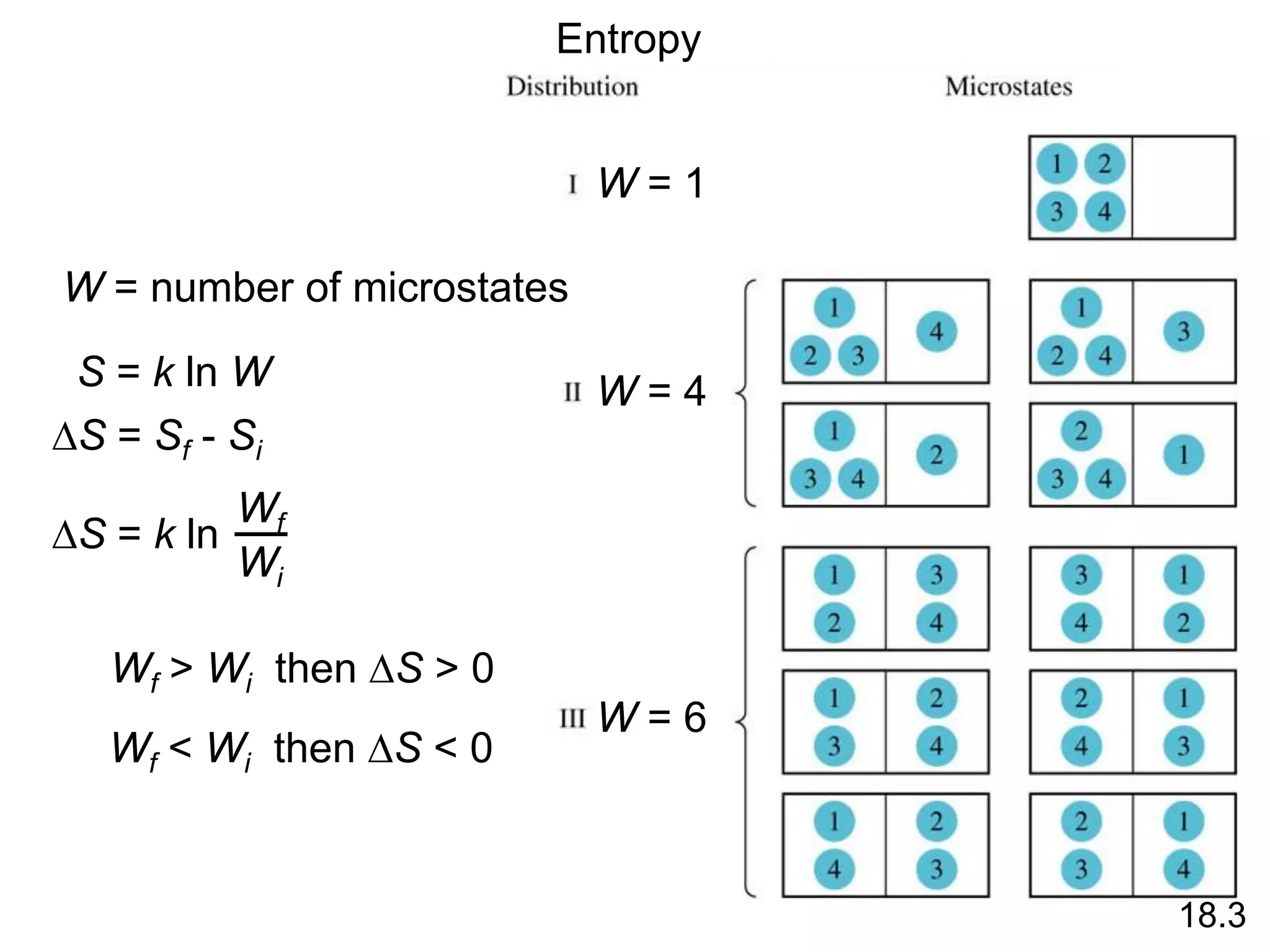
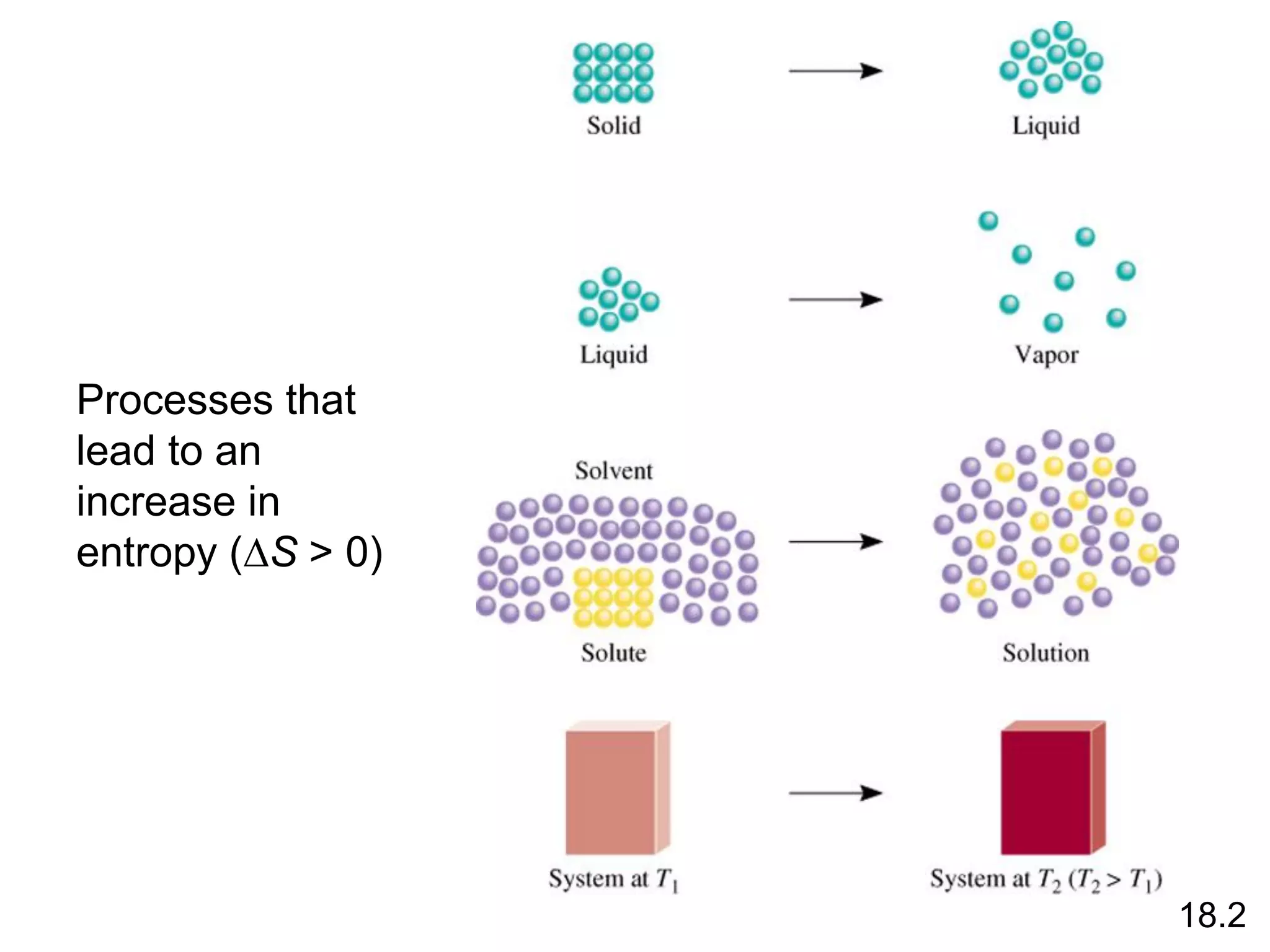

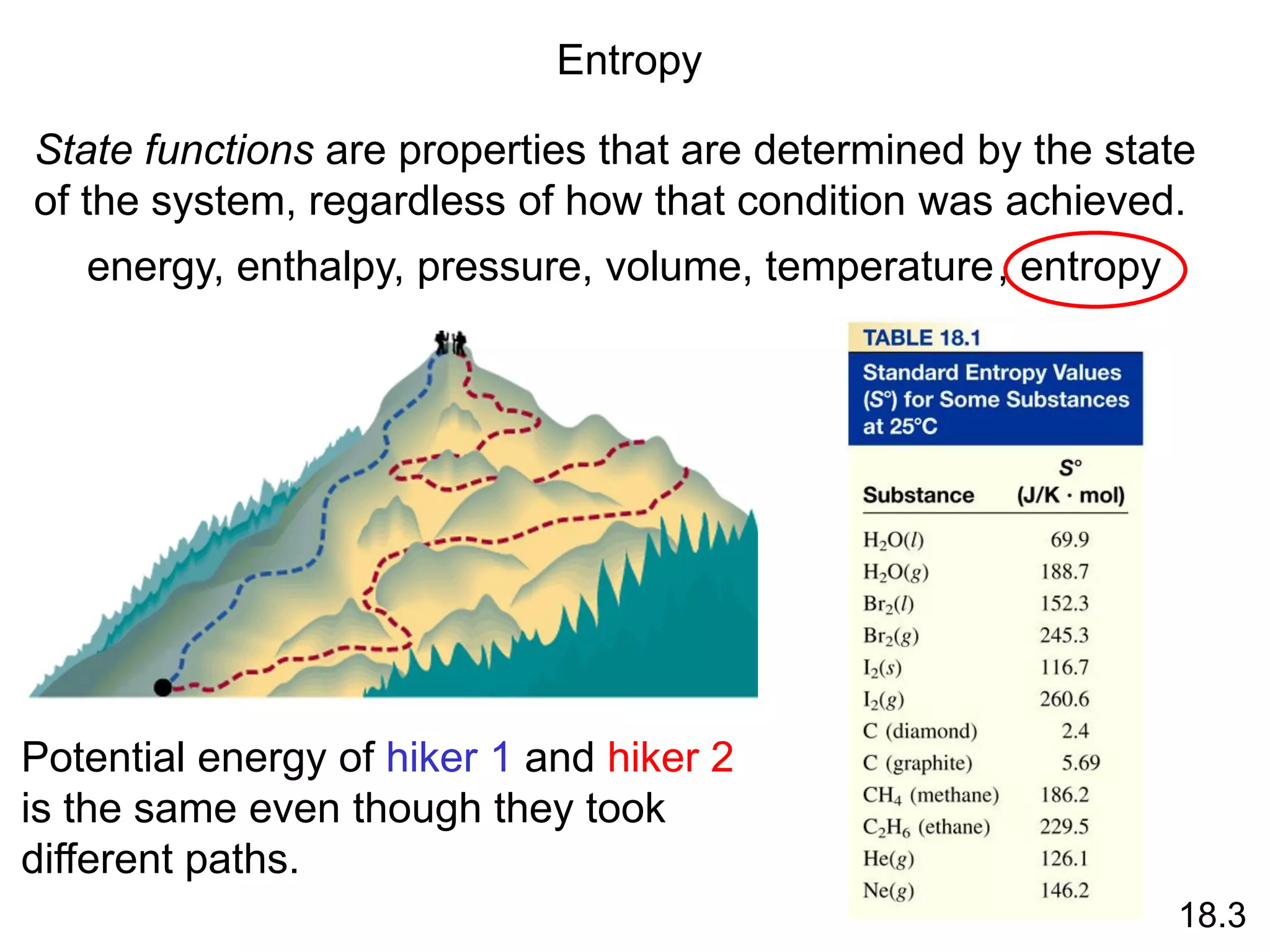
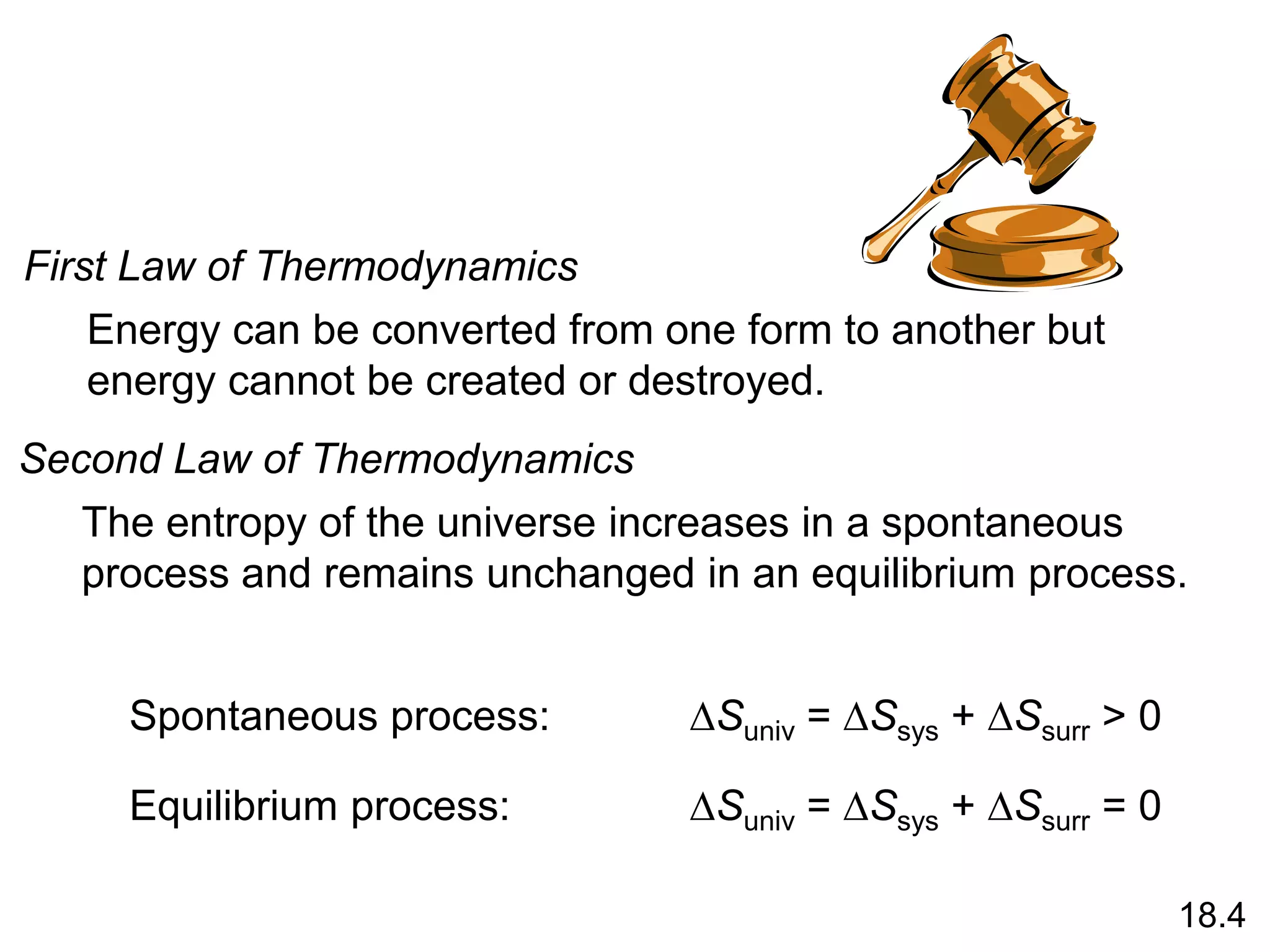
![Entropy Changes in the System (DSsys)
aA + bB cC + dD
DS0
rxn dS0(D)
cS0(C)
= [ + ] - bS0(B)
aS0(A)
[ + ]
DS0
rxn nS0(products)
= S mS0(reactants)
S
-
The standard entropy of reaction (DS0 ) is the entropy change
for a reaction carried out at 1 atm and 250C.
rxn
18.4
What is the standard entropy change for the following
reaction at 250C? 2CO (g) + O2 (g) 2CO2 (g)
S0(CO) = 197.9 J/K•mol
S0(O2) = 205.0 J/K•mol
S0(CO2) = 213.6 J/K•mol
DS0
rxn = 2 x S0(CO2) – [2 x S0(CO) + S0 (O2)]
DS0
rxn = 427.2 – [395.8 + 205.0] = -173.6 J/K•mol](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-74-2048.jpg)

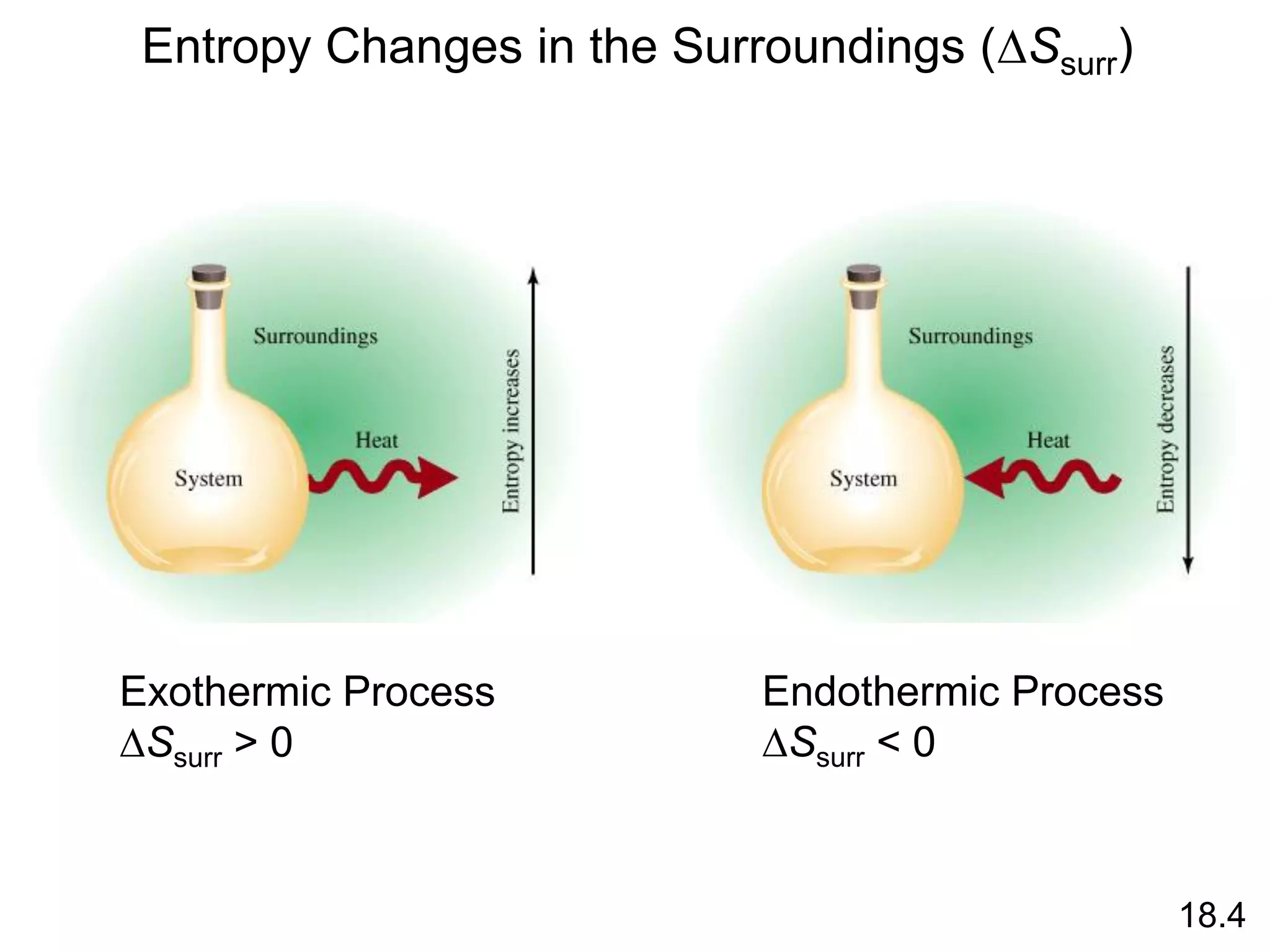

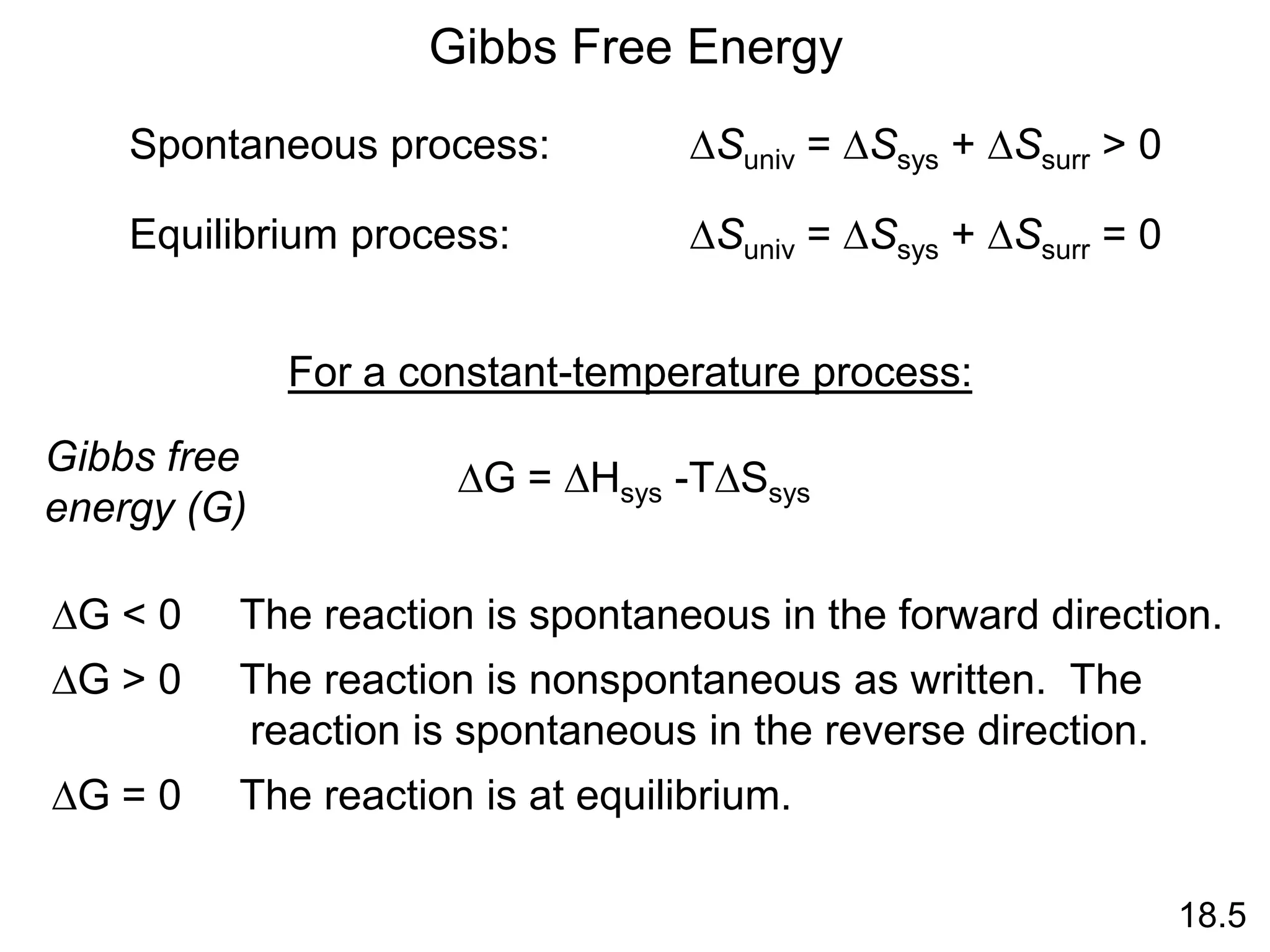
![18.5
aA + bB cC + dD
DG0
rxn dDG0 (D)
f
cDG0 (C)
f
= [ + ] - bDG0 (B)
f
aDG0 (A)
f
[ + ]
DG0
rxn nDG0 (products)
f
= S mDG0 (reactants)
f
S
-
The standard free-energy of reaction (DG0 ) is the free-
energy change for a reaction when it occurs under standard-
state conditions.
rxn
Standard free energy of formation
(DG0) is the free-energy change
that occurs when 1 mole of the
compound is formed from its
elements in their standard states.
f
DG0 of any element in its stable
form is zero.
f](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-79-2048.jpg)
![2C6H6 (l) + 15O2 (g) 12CO2 (g) + 6H2O (l)
DG0
rxn nDG0 (products)
f
= S mDG0 (reactants)
f
S
-
What is the standard free-energy change for the following
reaction at 25 0C?
DG0
rxn 6DG0 (H2O)
f
12DG0 (CO2)
f
= [ + ] - 2DG0 (C6H6)
f
[ ]
DG0
rxn = [ 12x–394.4 + 6x–237.2 ] – [ 2x124.5 ] = -6405 kJ
Is the reaction spontaneous at 25 0C?
DG0 = -6405 kJ < 0
spontaneous
18.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-80-2048.jpg)









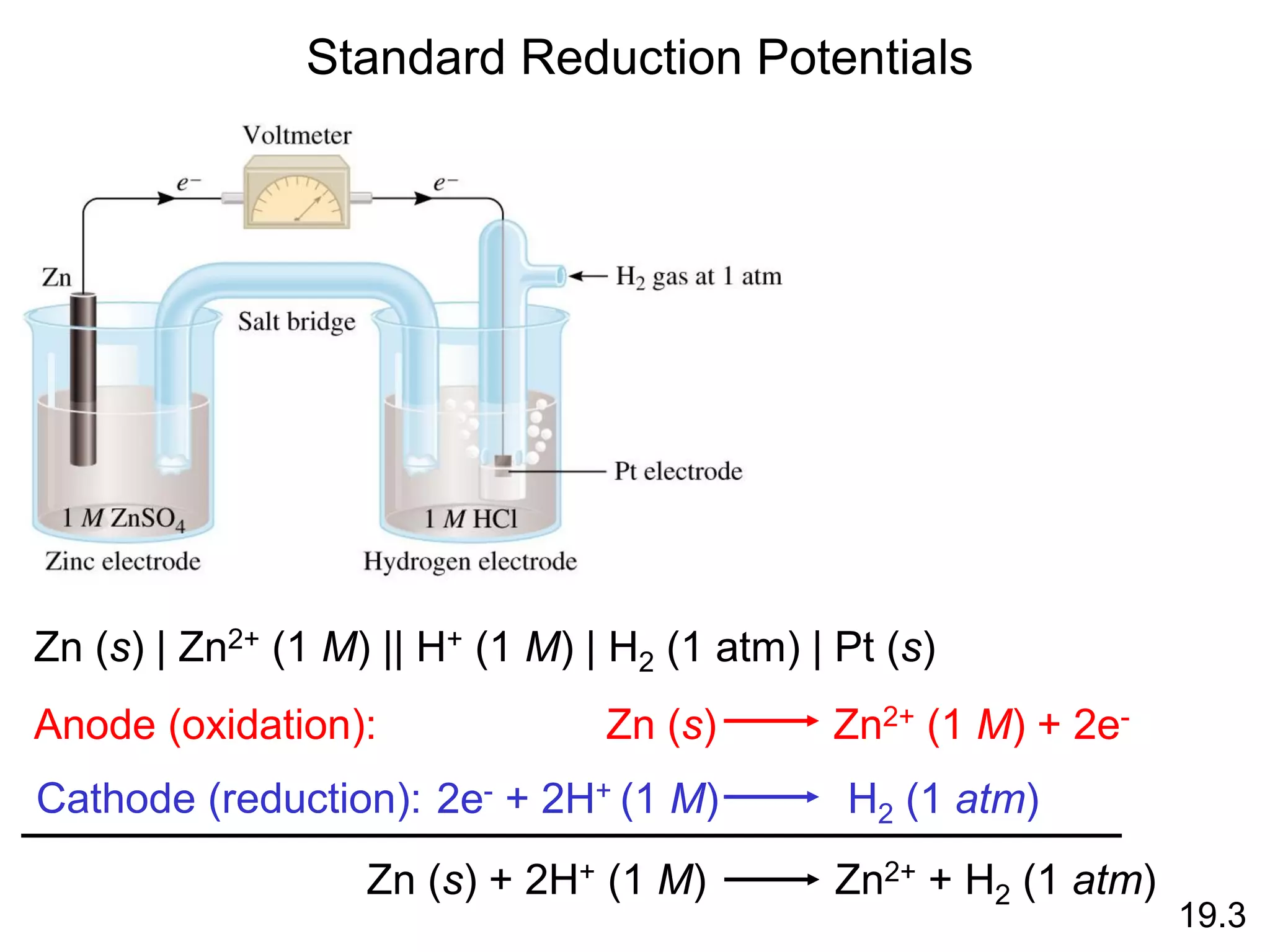
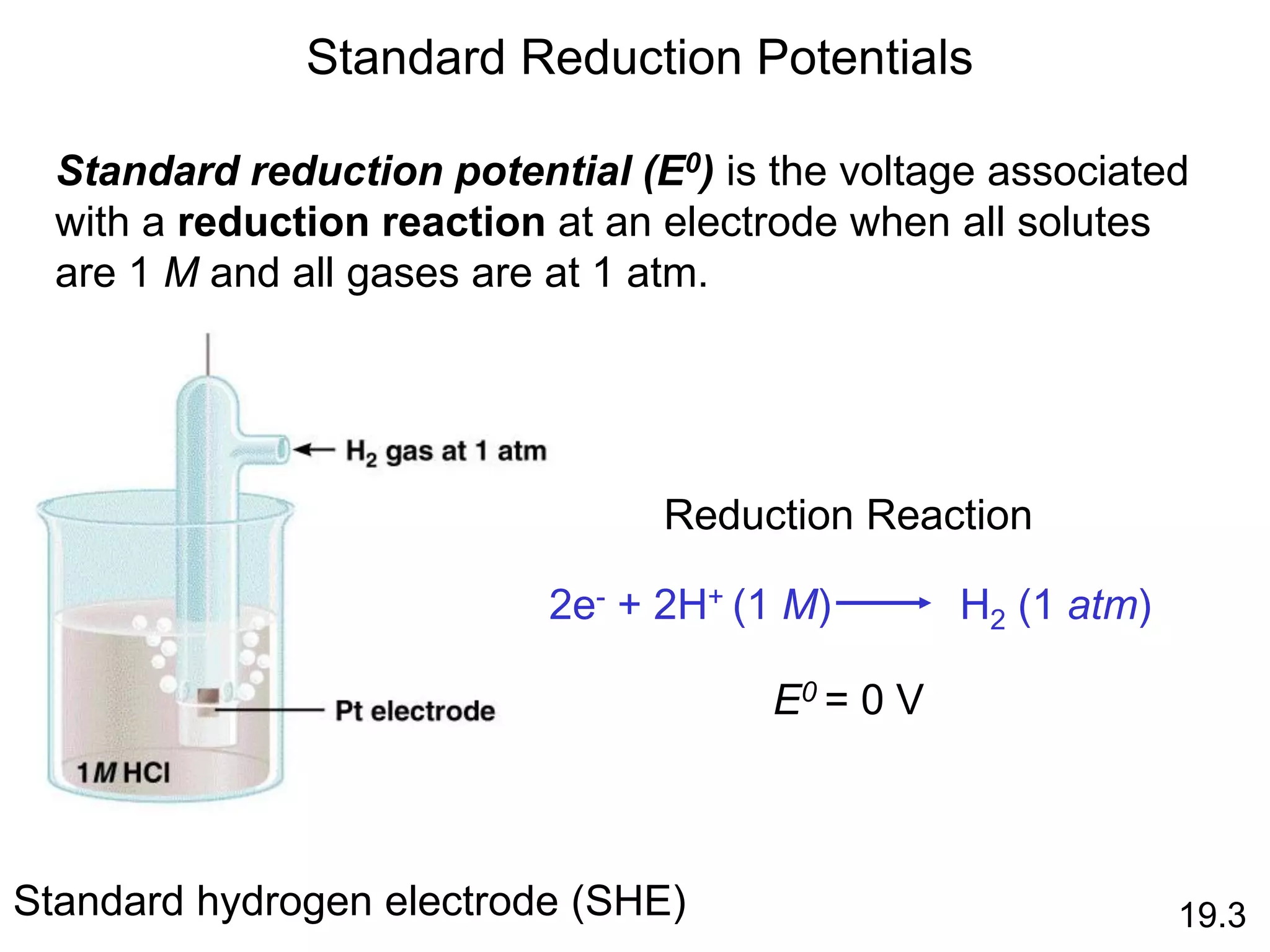
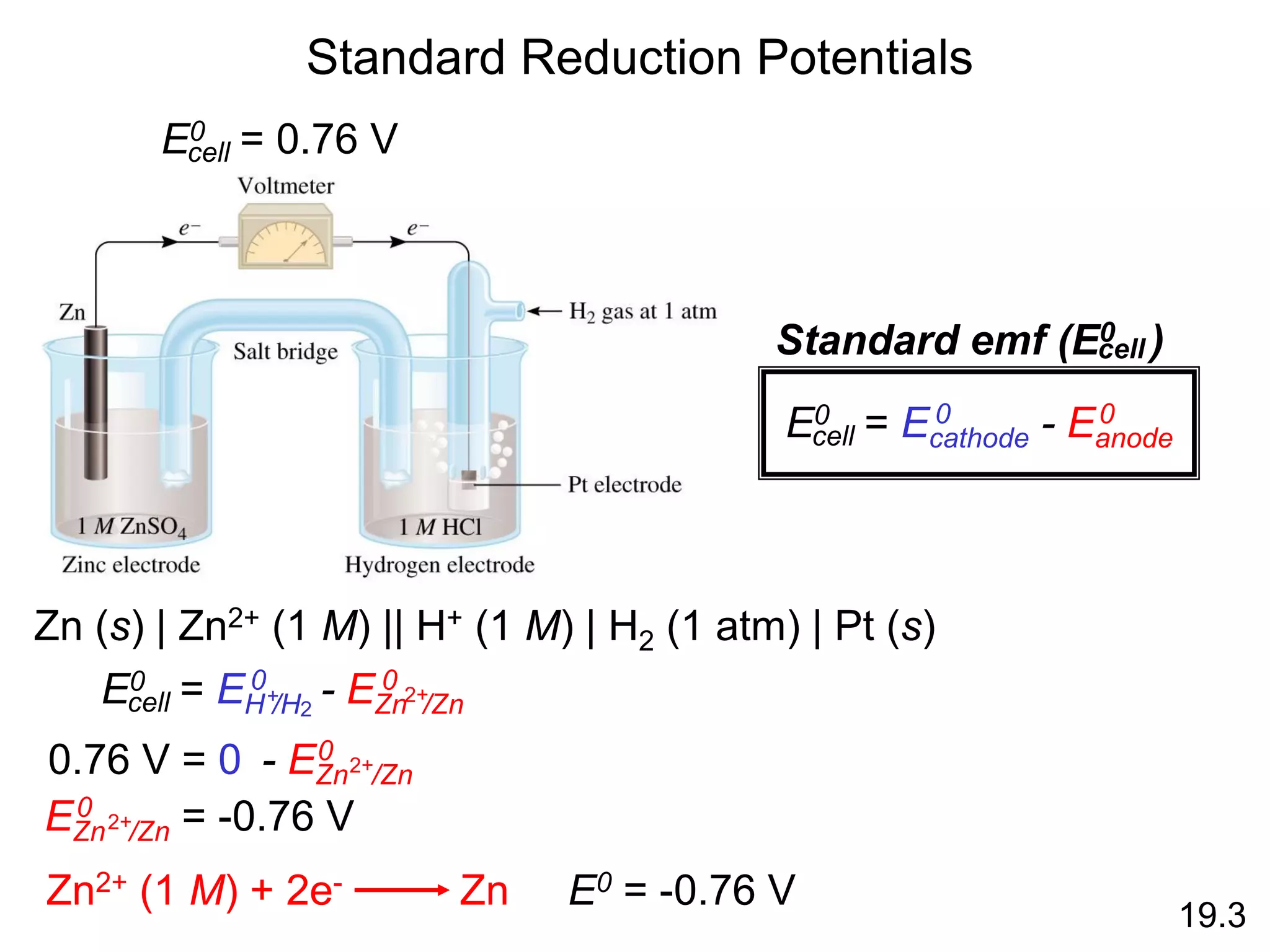
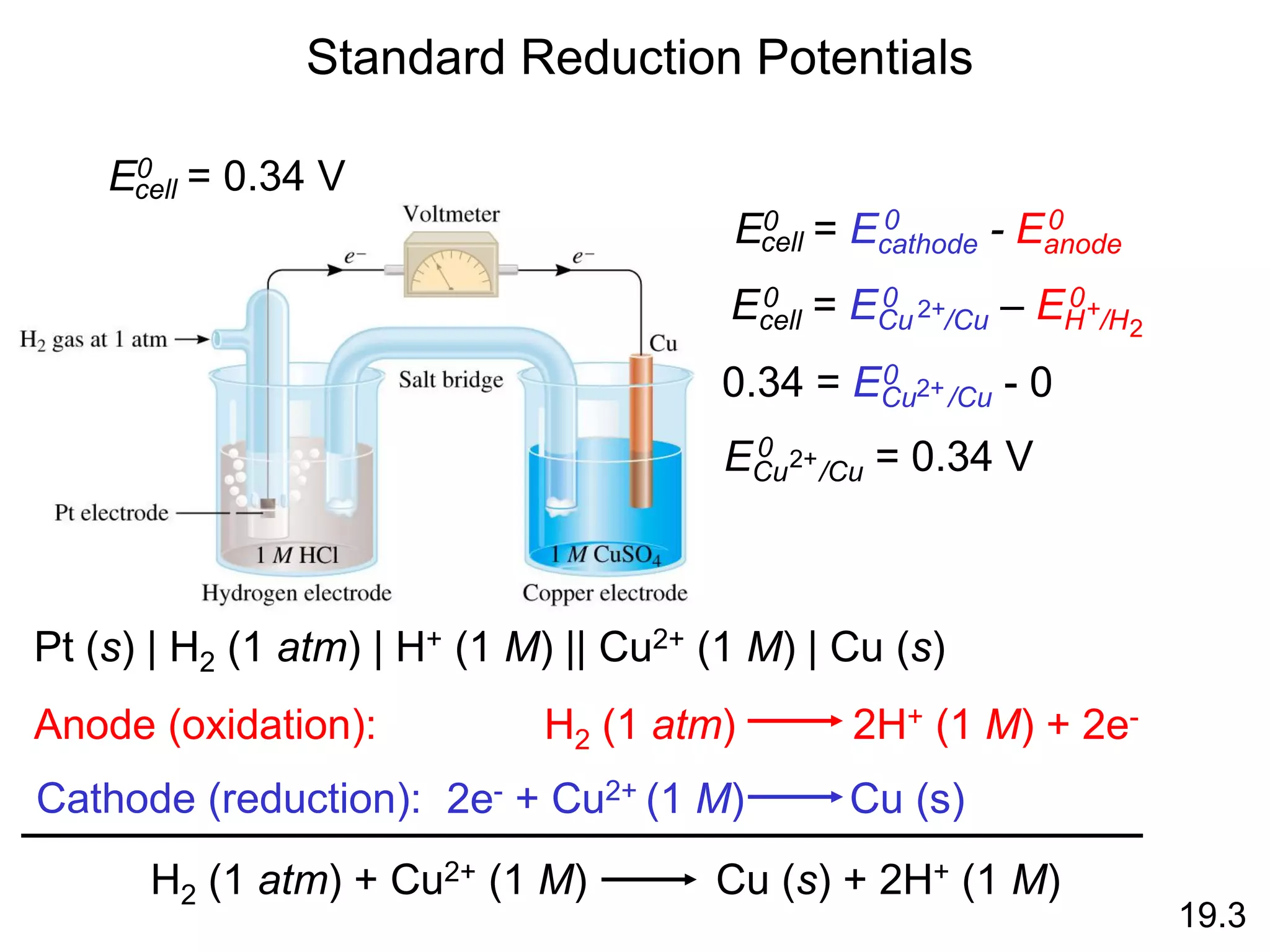
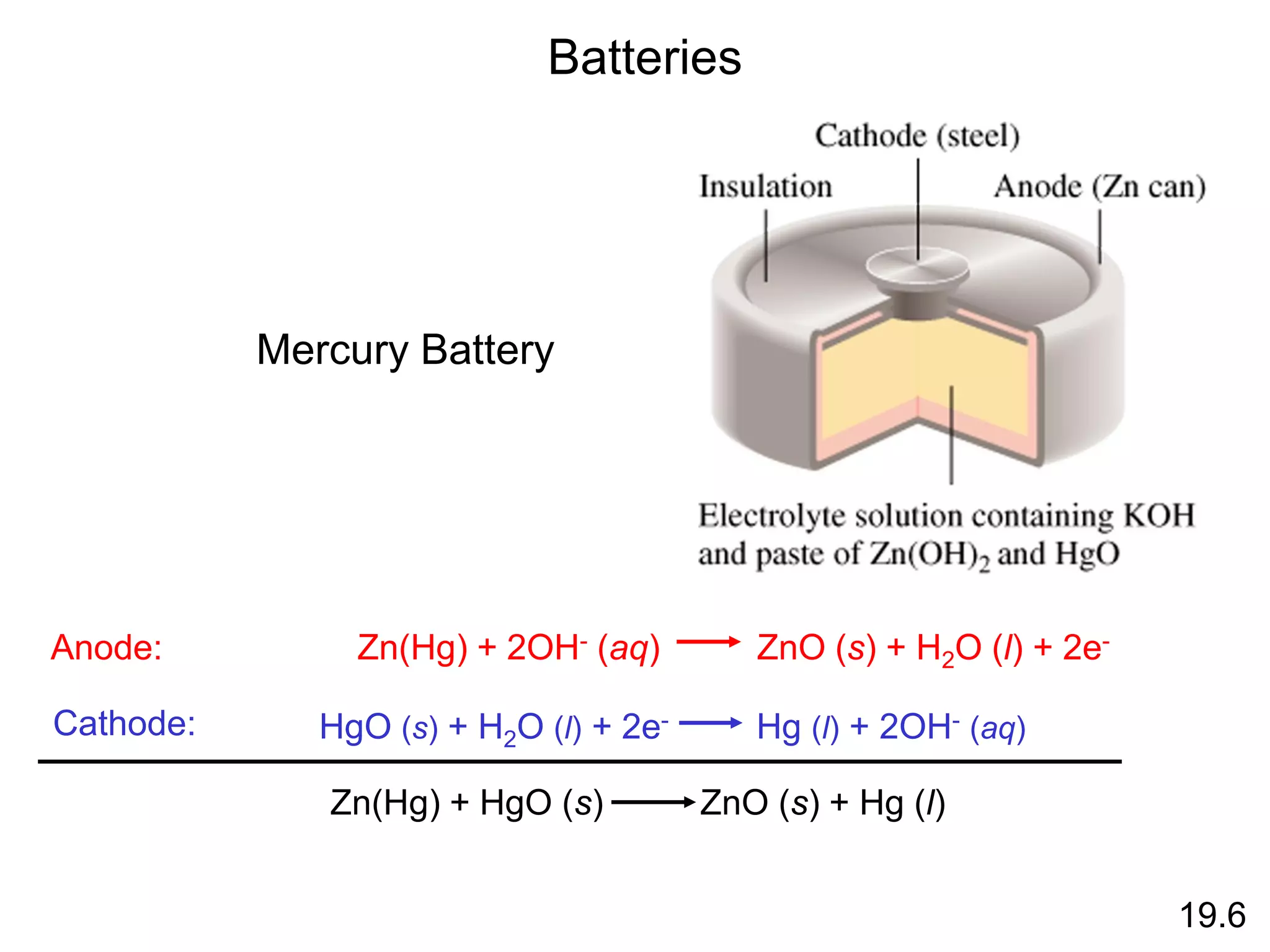
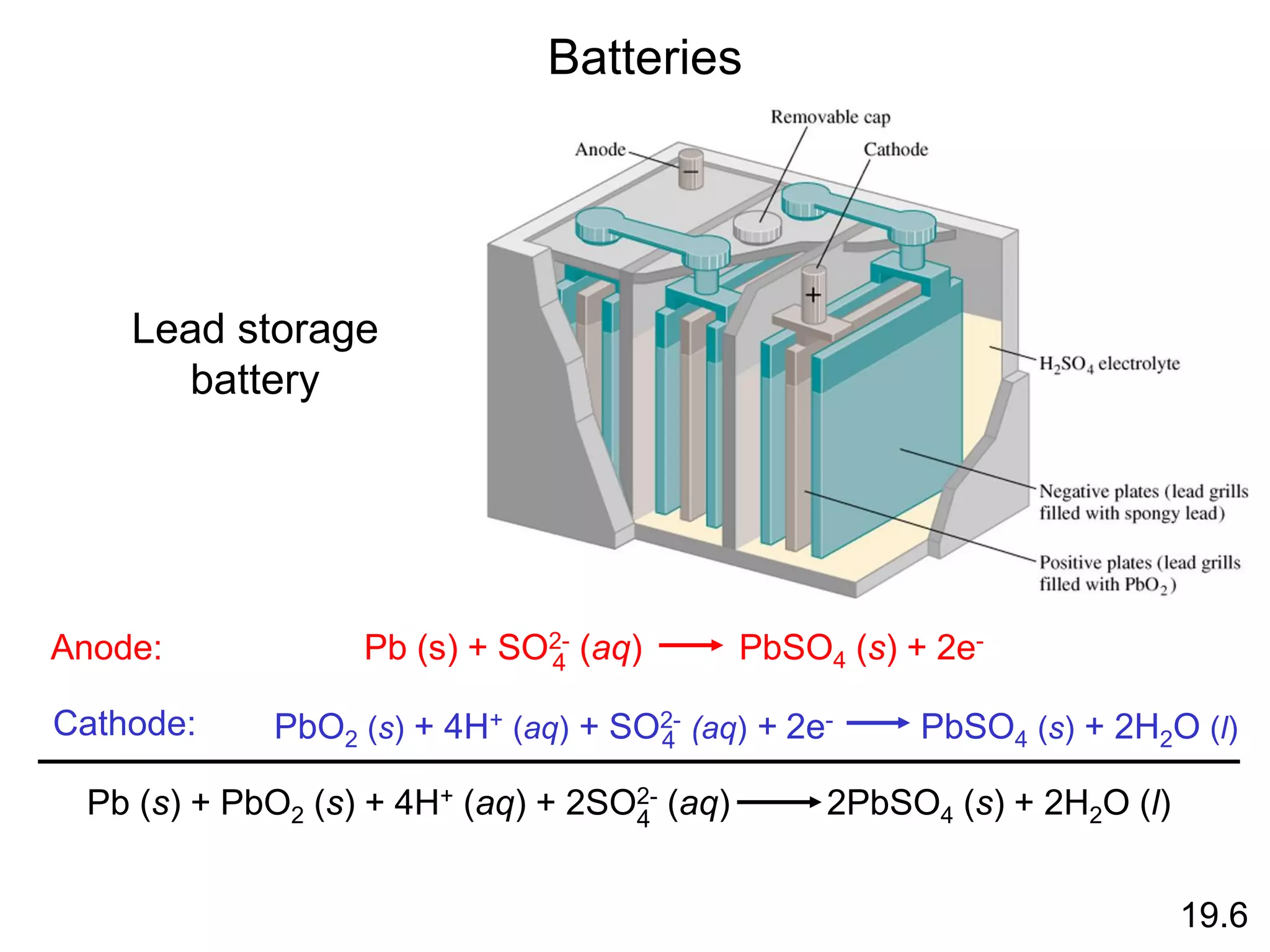
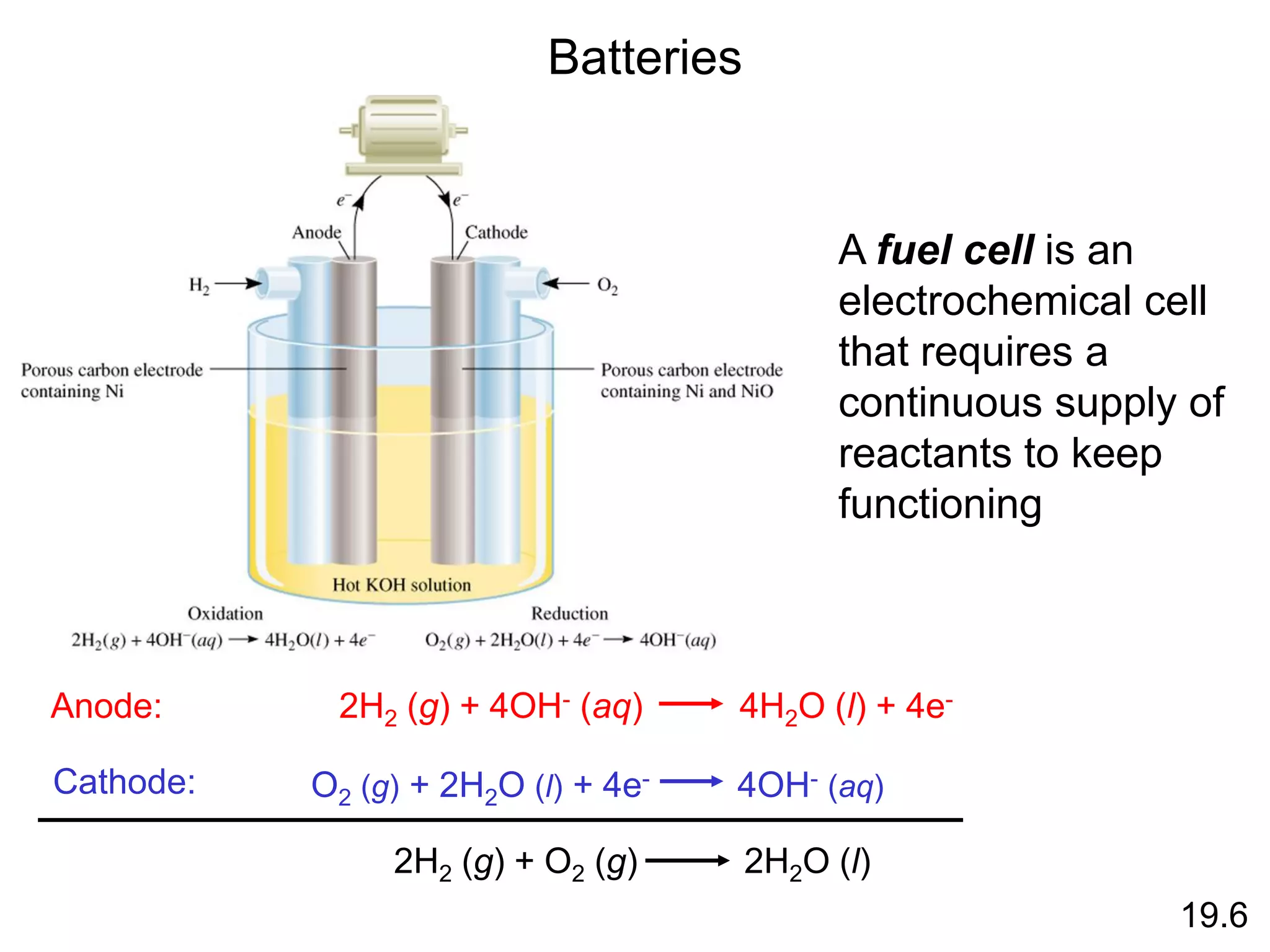
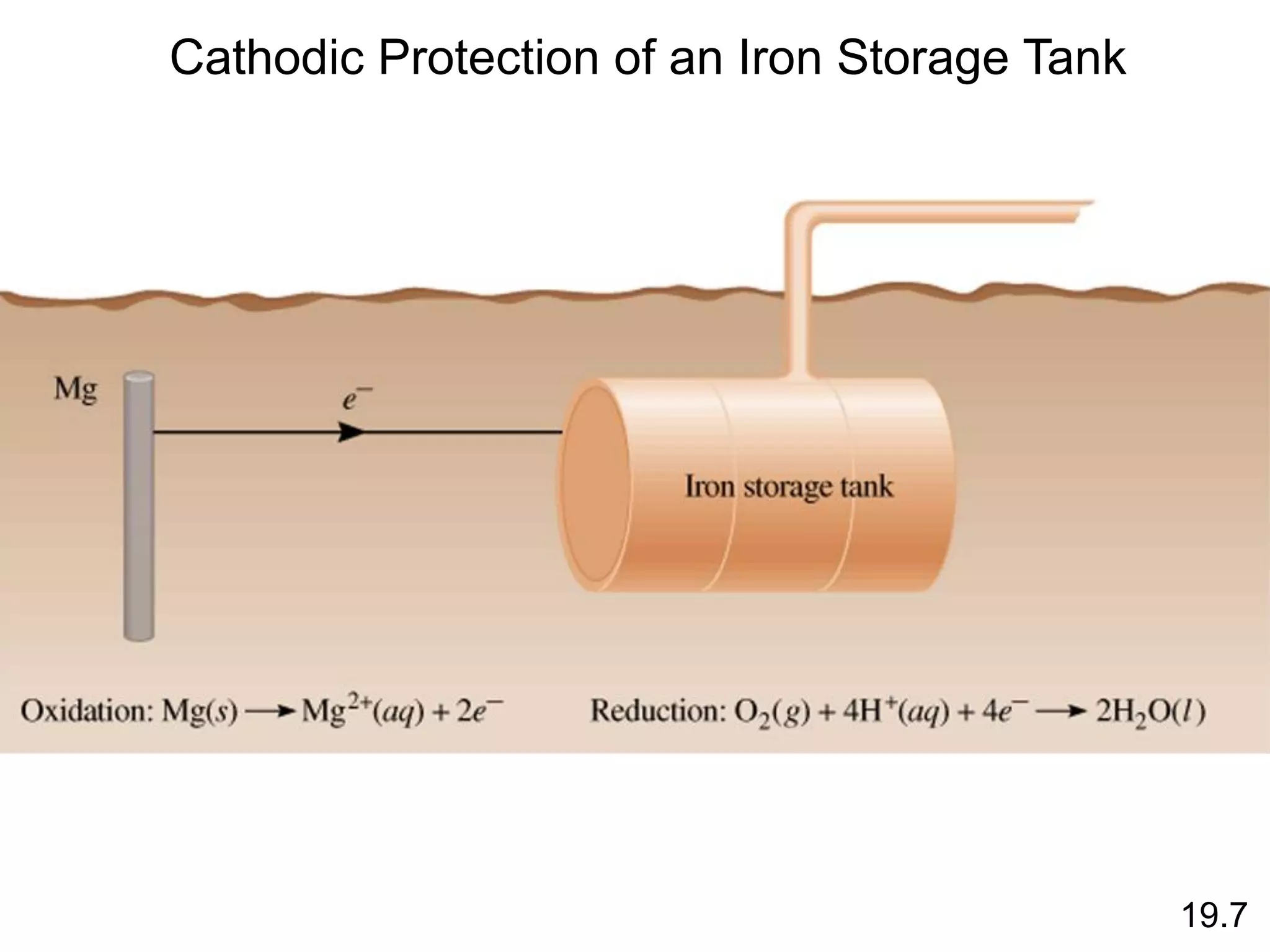
![Galvanic Cells
19.2
The difference in electrical
potential between the anode
and cathode is called:
• cell voltage
• electromotive force (emf)
• cell potential
Cell Diagram
Zn (s) + Cu2+ (aq) Cu (s) + Zn2+ (aq)
[Cu2+] = 1 M & [Zn2+] = 1 M
Zn (s) | Zn2+ (1 M) || Cu2+ (1 M) | Cu (s)
anode cathode](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-99-2048.jpg)


![Will the following reaction occur spontaneously at 250C if
[Fe2+] = 0.60 M and [Cd2+] = 0.010 M?
Fe2+ (aq) + Cd (s) Fe (s) + Cd2+ (aq)
2e- + Fe2+ 2Fe
Cd Cd2+ + 2e-
Oxidation:
Reduction:
n = 2
E0 = -0.44 – (-0.40)
E0 = -0.04 V
E0 = EFe /Fe – ECd /Cd
0 0
2+ 2+
-
0.0257 V
n
ln Q
E0
E =
-
0.0257 V
2
ln
-0.04 V
E =
0.010
0.60
E = 0.013
E > 0 Spontaneous
19.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-110-2048.jpg)







![Chemical Kinetics
Thermodynamics – does a reaction take place?
Kinetics – how fast does a reaction proceed?
Reaction rate is the change in the concentration of a
reactant or a product with time (M/s).
A B
rate = -
D[A]
Dt
rate =
D[B]
Dt
D[A] = change in concentration of A over
time period Dt
D[B] = change in concentration of B over
time period Dt
Because [A] decreases with time, D[A] is negative.
13.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-125-2048.jpg)
![A B
13.1
rate = -
D[A]
Dt
rate =
D[B]
Dt
time](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-126-2048.jpg)
![Br2 (aq) + HCOOH (aq) 2Br- (aq) + 2H+ (aq) + CO2 (g)
time
393 nm
light
Detector
D[Br2] a DAbsorption
13.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-128-2048.jpg)
![Br2 (aq) + HCOOH (aq) 2Br– (aq) + 2H+ (aq) + CO2 (g)
average rate = –
D[Br2]
Dt
= –
[Br2]final – [Br2]initial
tfinal - tinitial
slope of
tangent
slope of
tangent slope of
tangent
instantaneous rate = rate for specific instance in time
13.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-129-2048.jpg)
![rate a [Br2]
rate = k [Br2]
k =
rate
[Br2]
13.1
= rate constant
= 3.50 x 10–3 s–1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-130-2048.jpg)
![Reaction Rates and Stoichiometry
13.1
2A B
Two moles of A disappear for each mole of B that is formed.
rate =
D[B]
Dt
rate = –
D[A]
Dt
1
2
aA + bB cC + dD
rate = –
D[A]
Dt
1
a
= –
D[B]
Dt
1
b
=
D[C]
Dt
1
c
=
D[D]
Dt
1
d](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-131-2048.jpg)
![Write the rate expression for the following reaction:
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) CO2 (g) + 2H2O (g)
rate = –
D[CH4]
Dt
= –
D[O2]
Dt
1
2
=
D[H2O]
Dt
1
2
=
D[CO2]
Dt
13.1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-132-2048.jpg)
![The Rate Law
13.2
The rate law expresses the relationship of the rate of a reaction
to the rate constant and the concentrations of the reactants
raised to some powers.
aA + bB cC + dD
Rate = k [A]x[B]y
reaction is xth order in A
reaction is yth order in B
reaction is (x + y)th order overall](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-133-2048.jpg)
![F2 (g) + 2ClO2 (g) 2FClO2 (g)
Determine x and y in the rate law Rate = k [F2]x[ClO2]y
Double [F2] with [ClO2] held constant:
The rate doubles
Therefore, x = 1
Quadruple [ClO2] with [F2] held constant:
The rate quadruples
Therefore, y = 1 The rate law is
Rate = k [F2]1[ClO2]1
13.2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-134-2048.jpg)
![F2 (g) + 2ClO2 (g) 2FClO2 (g)
rate = k [F2][ClO2]
Rate Laws
• Rate laws are always determined experimentally.
• Reaction order is always defined in terms of reactant
(not product) concentrations.
• The order of a reactant is not related to the
stoichiometric coefficient of the reactant in the balanced
chemical equation.
1
13.2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-135-2048.jpg)
![Determine the rate law and calculate the rate constant for
the following reaction from the following data:
S2O8
2– (aq) + 3I– (aq) 2SO4
2– (aq) + I3
– (aq)
Experiment [S2O8
2 – ] [I – ]
Initial Rate
(M/s)
1 0.08 0.034 2.2 x 10–4
2 0.08 0.017 1.1 x 10–4
3 0.16 0.017 2.2 x 10–4
rate = k [S2O8
2–]x[I–]y
Double [I–], rate doubles (experiment 1 & 2)
y = 1
Double [S2O8
2–], rate doubles (experiment 2 & 3)
x = 1
k =
rate
[S2O8
2–][I–]
=
2.2 x 10–4 M/s
(0.08 M)(0.034 M)
= 0.08/M•s
13.2
rate = k [S2O8
2–][I–]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-136-2048.jpg)
![First-Order Reactions
13.3
A product rate = -
D[A]
Dt
rate = k [A]
k =
rate
[A]
= 1/s or s-1
M/s
M
=
D[A]
Dt
= k [A]
–
[A] is the concentration of A at any time t
[A]0 is the concentration of A at time t=0
[A] = [A]0exp(–kt) ln[A] = ln[A]0 – kt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-137-2048.jpg)
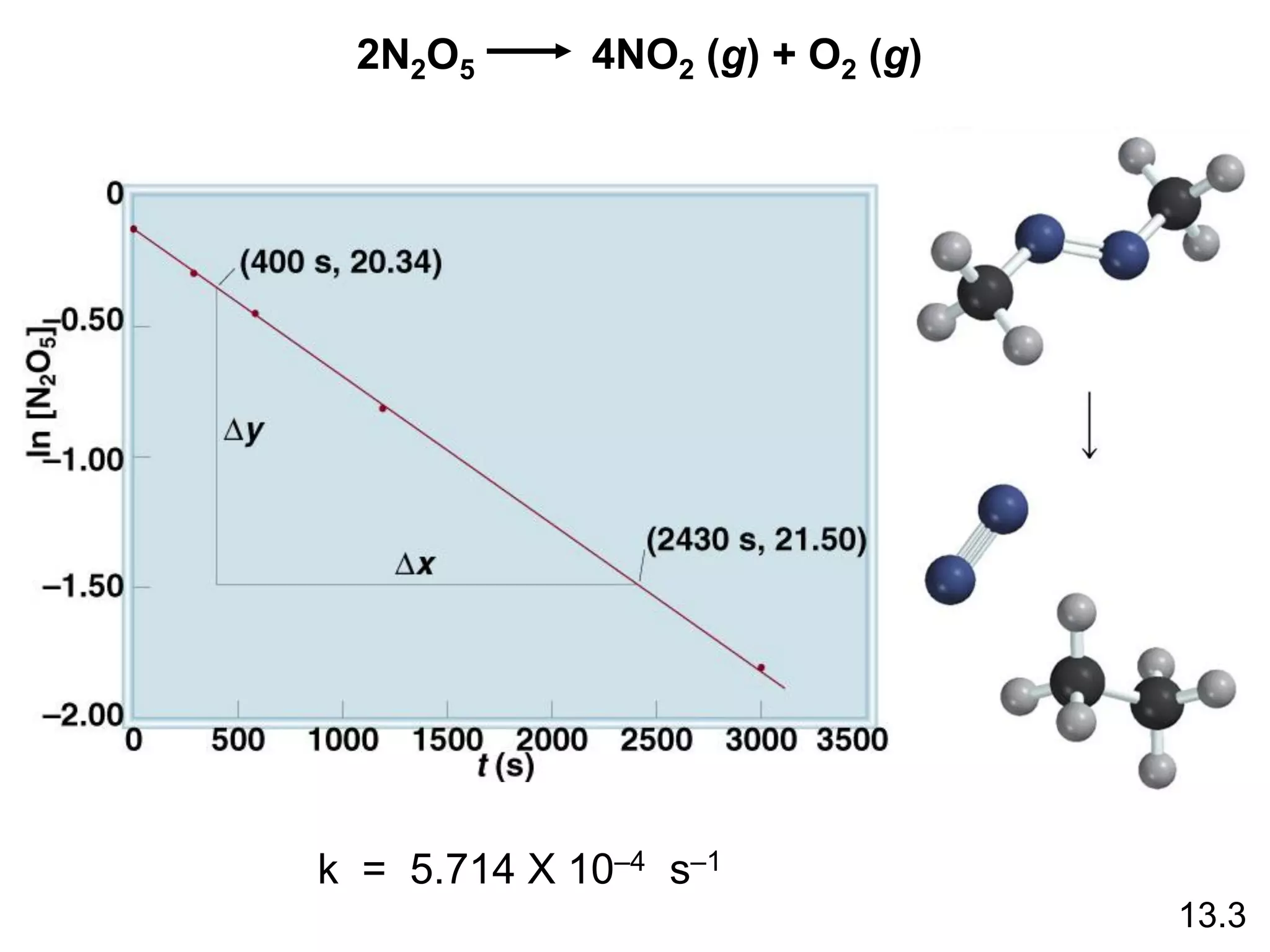
![The reaction 2A B is first order in A with a rate
constant of 2.8 x 10–2 s–1 at 800C. How long will it take for
A to decrease from 0.88 M to 0.14 M ?
ln[A]t = ln[A]0 – kt
kt = ln[A]0 – ln[A]
t =
ln[A]0 – ln[A]
k
= 66 s
[A]0 = 0.88 M
[A]t = 0.14 M
ln
[A]0
[A]
k
=
ln
0.88 M
0.14 M
2.8 x 10–2 s–1
=
13.3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-139-2048.jpg)
![Half-Life of First-Order Reactions
13.3
The half-life, t½, is the time required for the concentration of a
reactant to decrease to half of its initial concentration.
t½ = t when [A] = [A]0/2
ln
[A]0
[A]0/2
k
=
t½
ln2
k
=
0.693
k
=
What is the half-life of N2O5 if it decomposes with a rate
constant of 5.7 x 10–4 s–1?
t½
ln2
k
=
0.693
5.7 x 10–4 s–1
= = 1200 s = 20 minutes
How do you know decomposition is first order?
units of k (s-1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-140-2048.jpg)
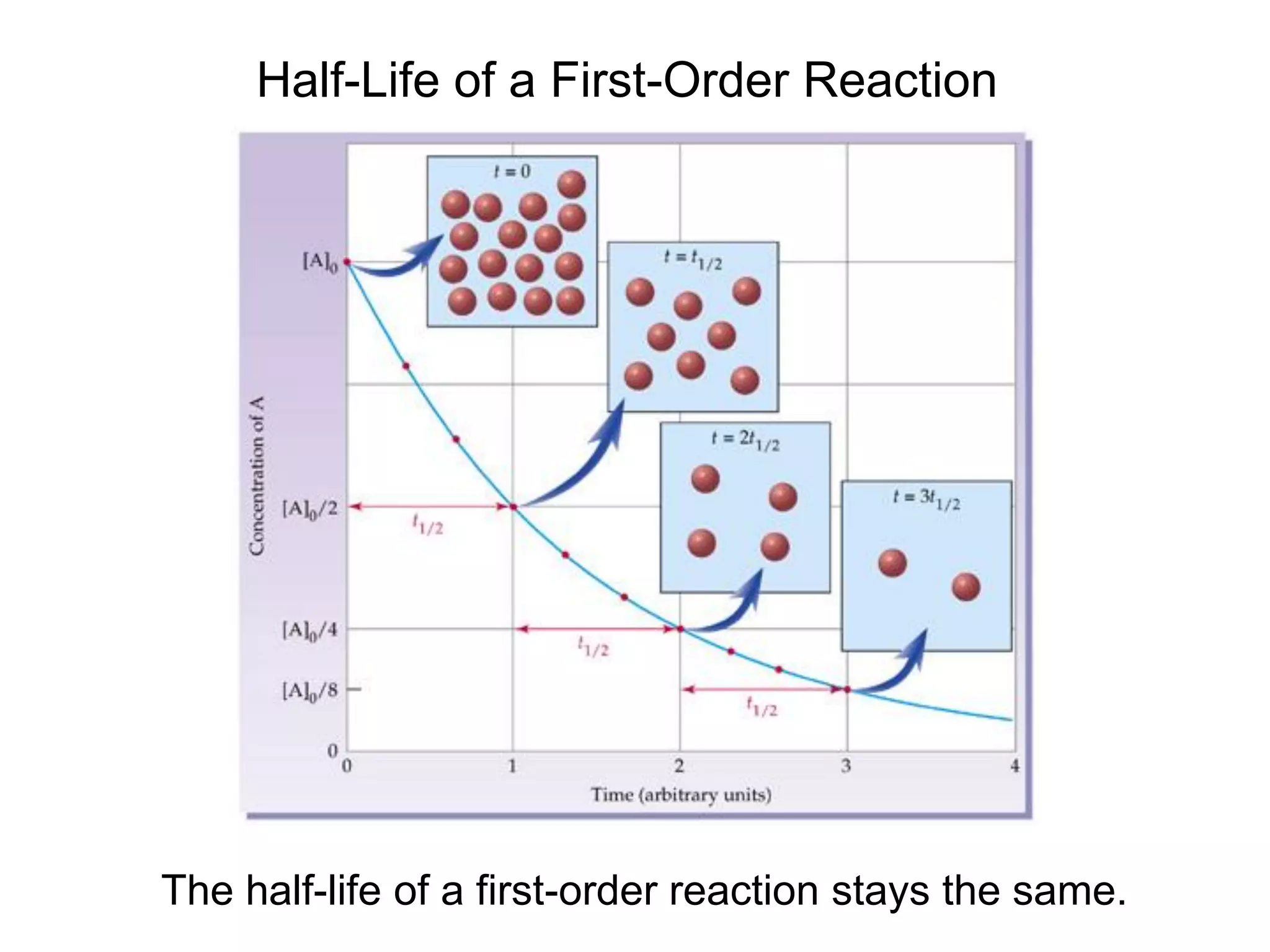
![Comparison of Graphs for a First-Order Reaction
A straight line is obtained from a graph of ln[A] vs. time,
characteristic of a first-order reaction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-142-2048.jpg)
![Second-Order Reactions
13.3
A product rate = -
D[A]
Dt
rate = k [A]2
k =
rate
[A]2
= 1/M•s
M/s
M2
=
D[A]
Dt
= k [A]2
–
[A] is the concentration of A at any time t
[A]0 is the concentration of A at time t=0
1
[A]
=
1
[A]0
+ kt
t½ = t when [A] = [A]0/2
t½ =
1
k[A]0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-143-2048.jpg)
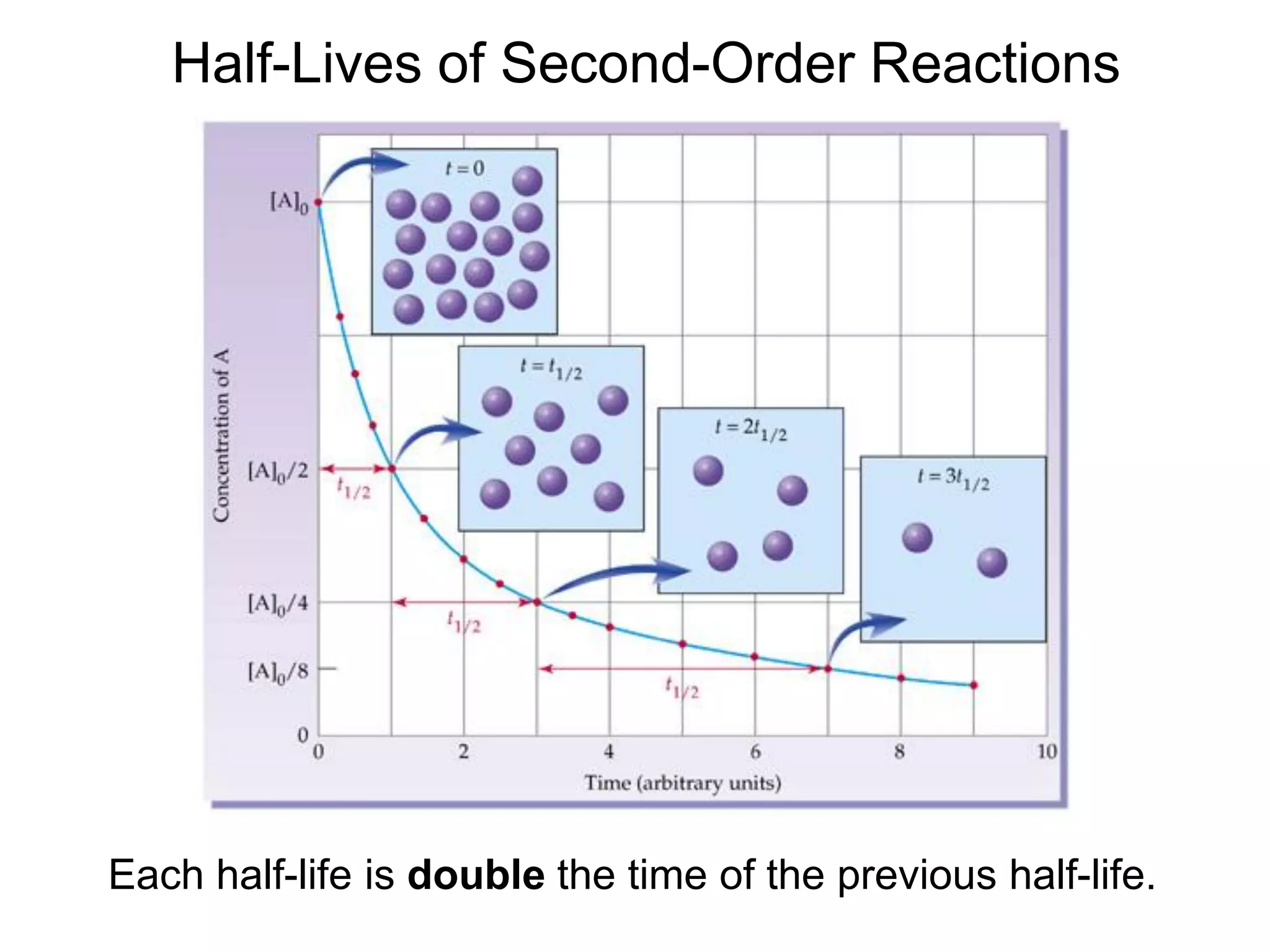
![Second-Order Reaction
Comparison of Graphs
The data give a straight line when plotting 1/[A] vs. time,
characteristic of a second-order reaction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-145-2048.jpg)
![Zero-Order Reactions
13.3
A product rate = -
D[A]
Dt
rate = k [A]0 = k
k =
rate
[A]0
= M/s
D[A]
Dt
= k
–
[A] is the concentration of A at any time t
[A]0 is the concentration of A at time t = 0
t½ = t when [A] = [A]0/2
t½ =
[A]0
2k
[A] = [A]0 – kt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-146-2048.jpg)

![Summary of the Kinetics of Zero-Order, First-Order
and Second-Order Reactions
Order Rate Law
Concentration-Time
Equation Half-Life
0
1
2
rate = k
rate = k [A]
rate = k [A]2
ln[A] = ln[A]0 - kt
1
[A]
=
1
[A]0
+ kt
[A] = [A]0 - kt
t½
ln2
k
=
t½ =
[A]0
2k
t½ =
1
k[A]0
13.3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-148-2048.jpg)
![Comparison of Graphs for H2O2 Decomposition
The reaction is
second order
with rate law
Rate = k[H2O2]2
From www.sparknotes.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-149-2048.jpg)


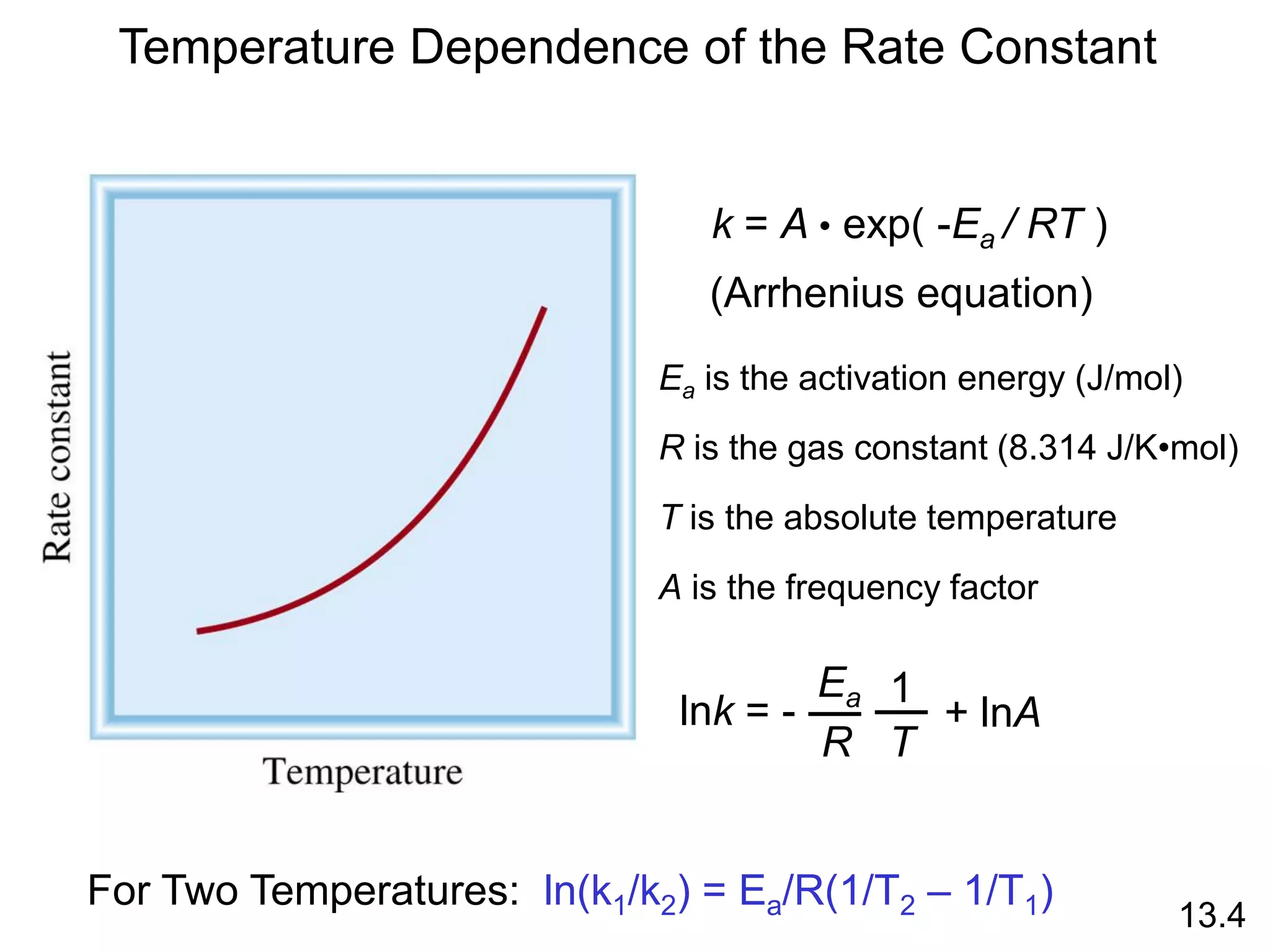
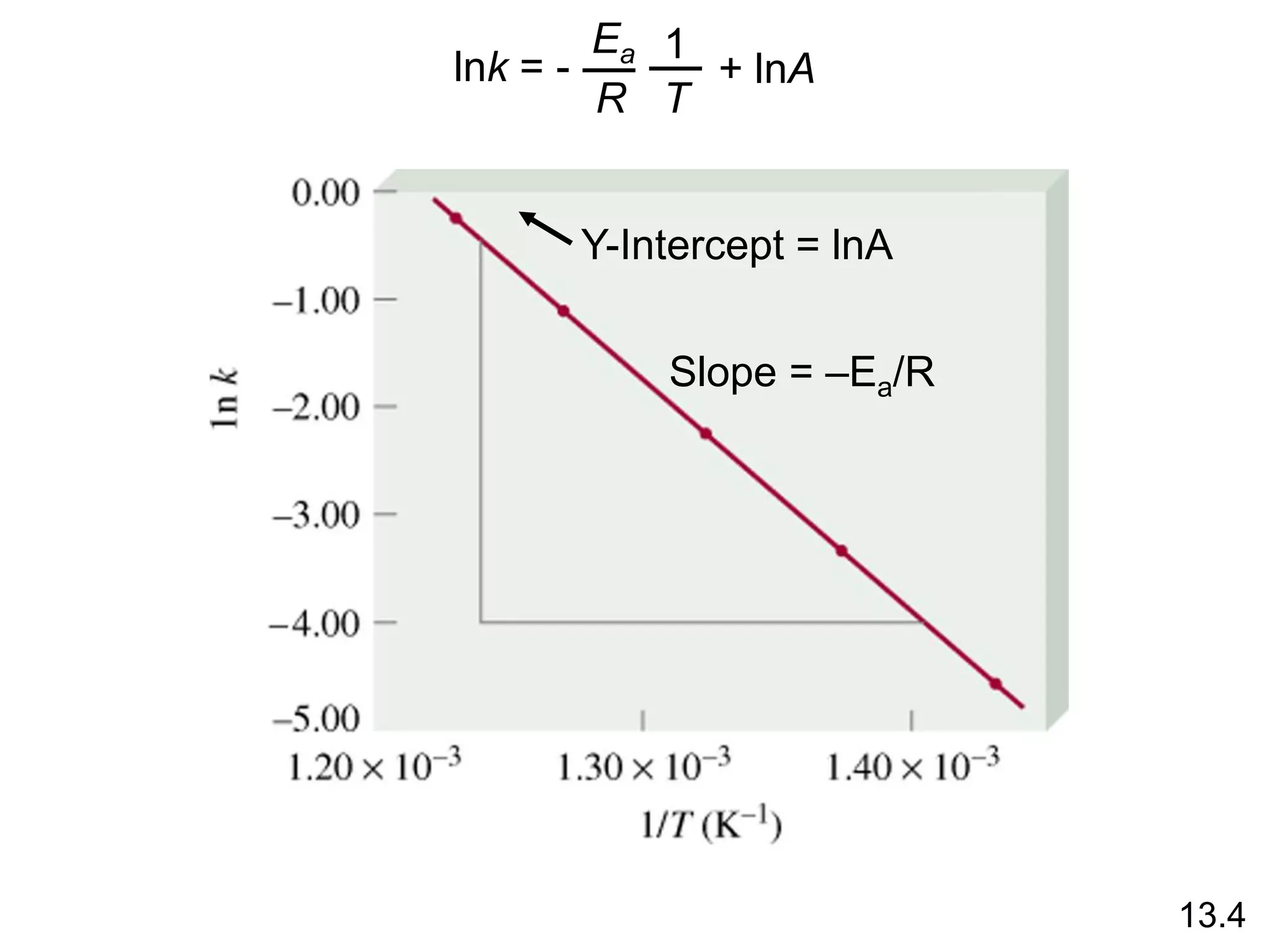
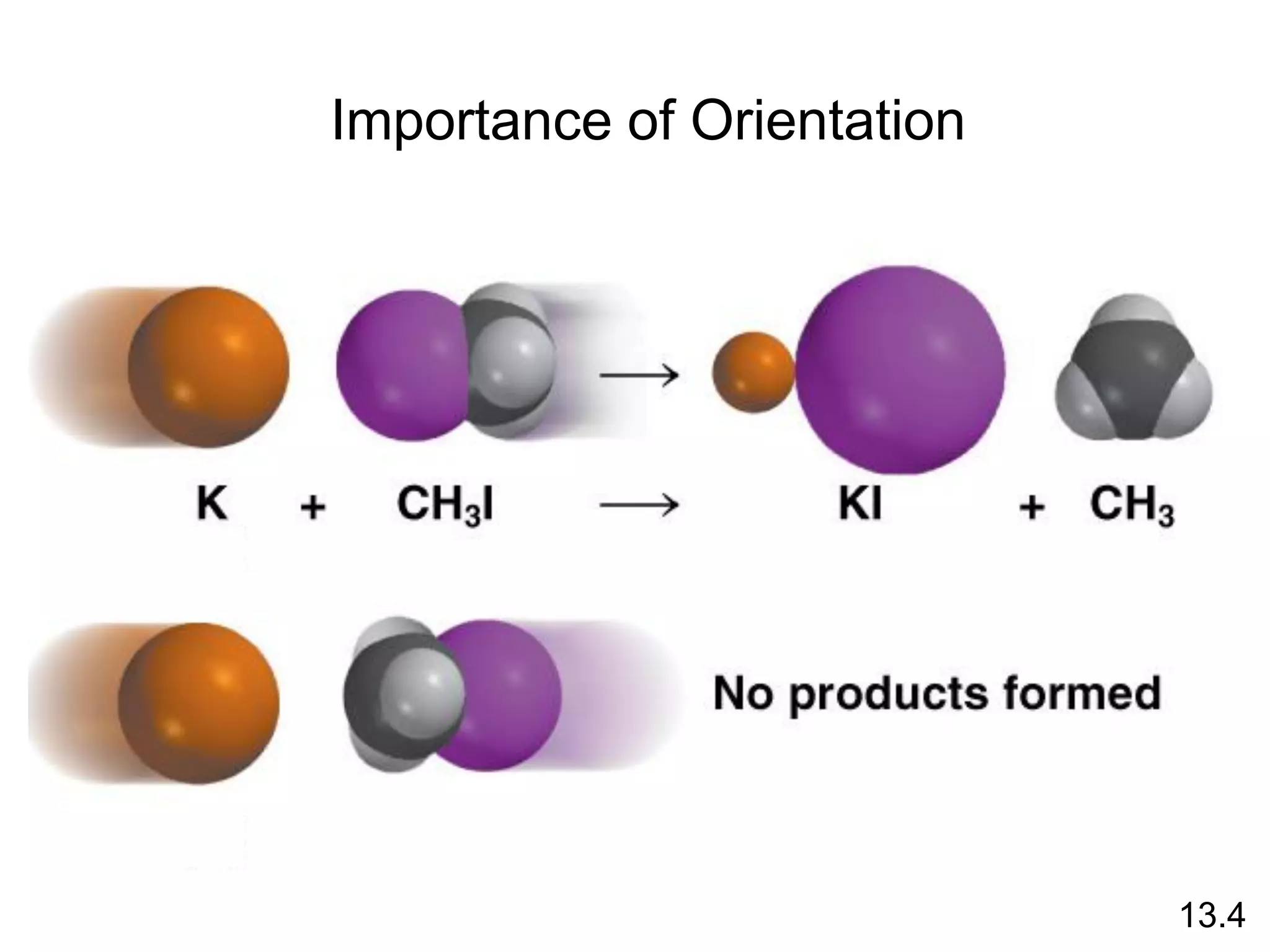
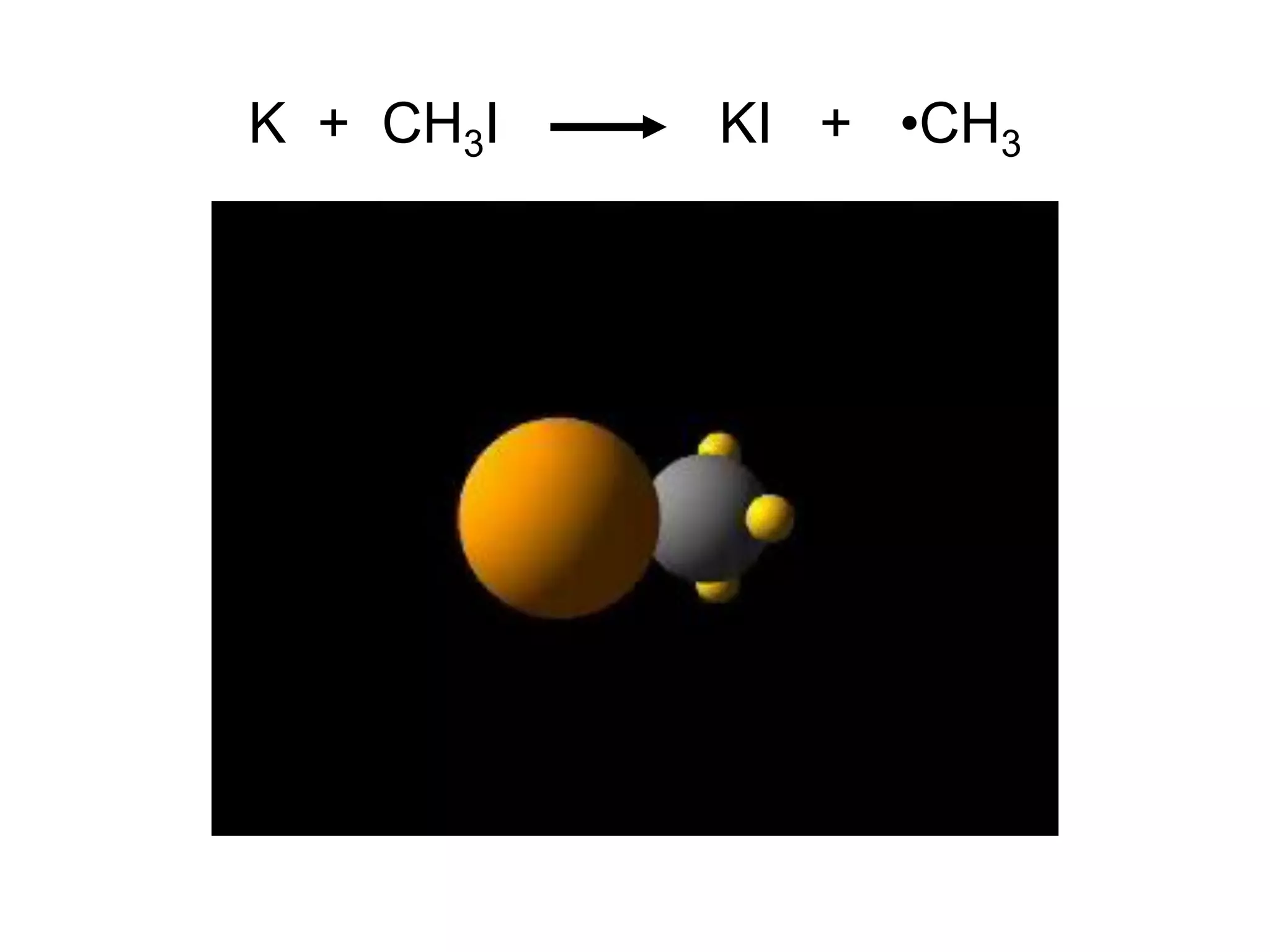
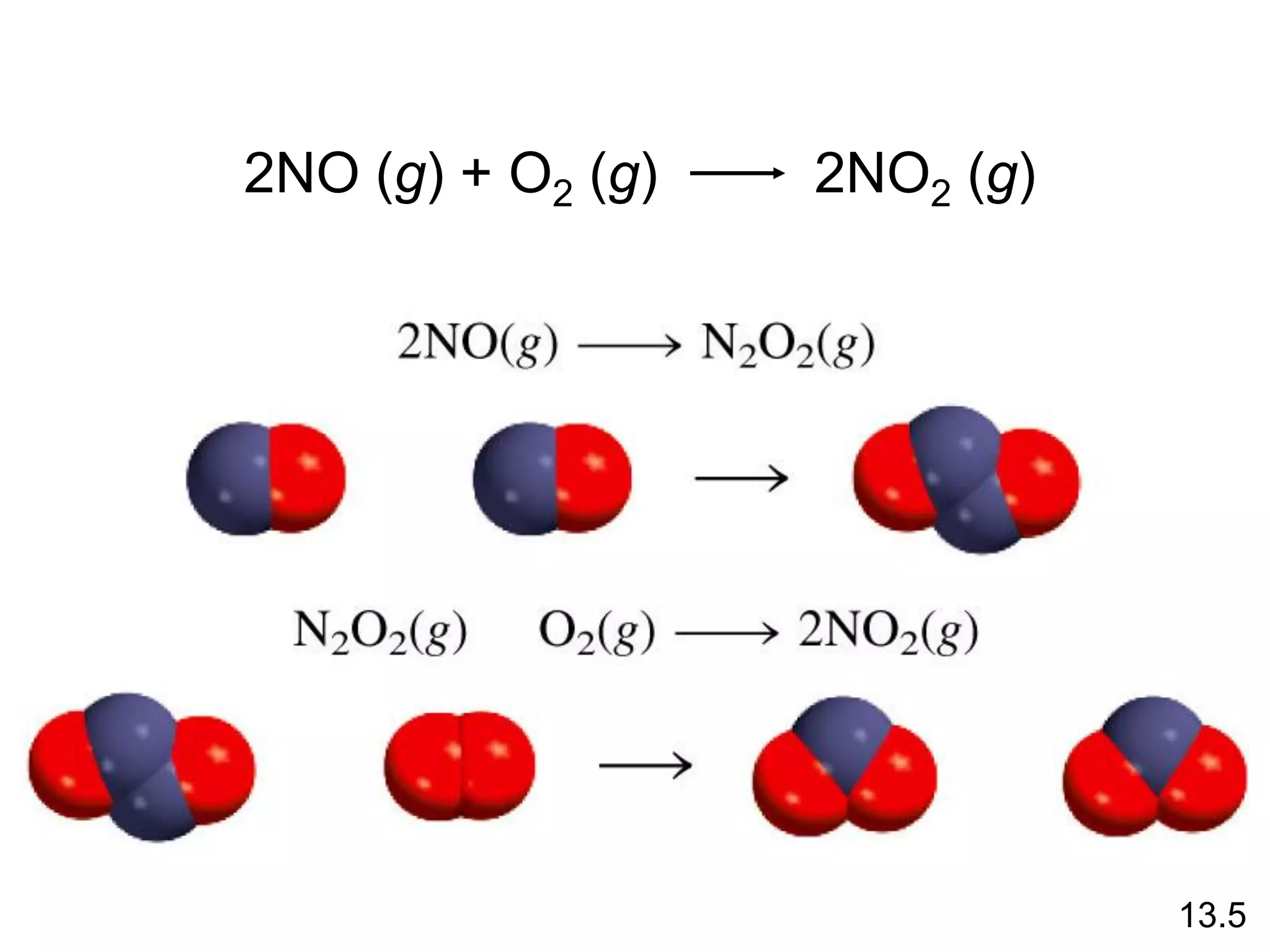
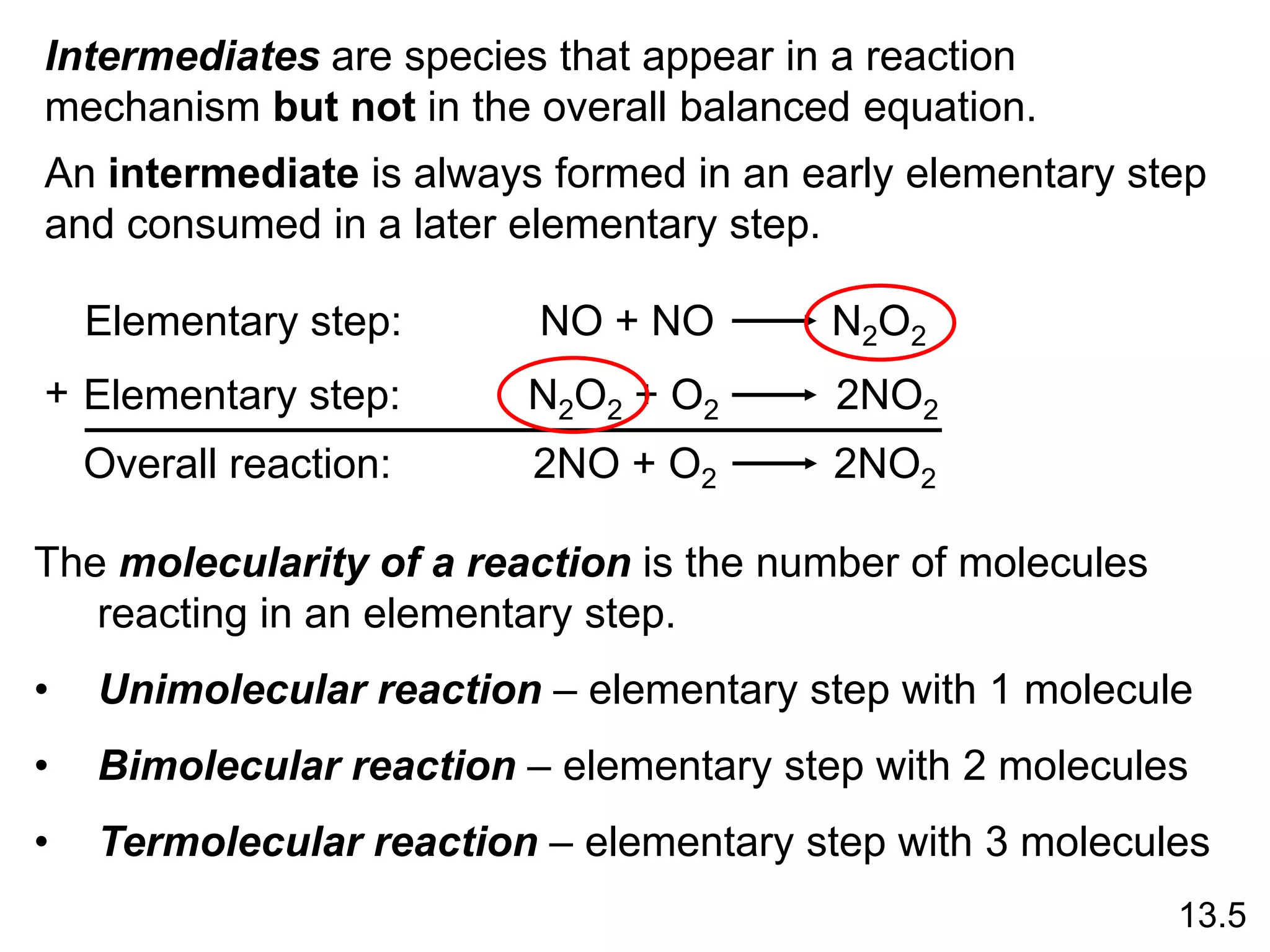
![Unimolecular reaction A products rate = k [A]
Bimolecular reaction A + B products rate = k [A][B]
Bimolecular reaction A + A products rate = k [A]2
Rate Laws and Elementary Steps
13.5
Writing plausible reaction mechanisms:
• The sum of the elementary steps must give the overall
balanced equation for the reaction.
• The rate-determining step should predict the same rate
law that is determined experimentally.
The rate-determining step is the slowest step in the
sequence of steps leading to product formation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-159-2048.jpg)

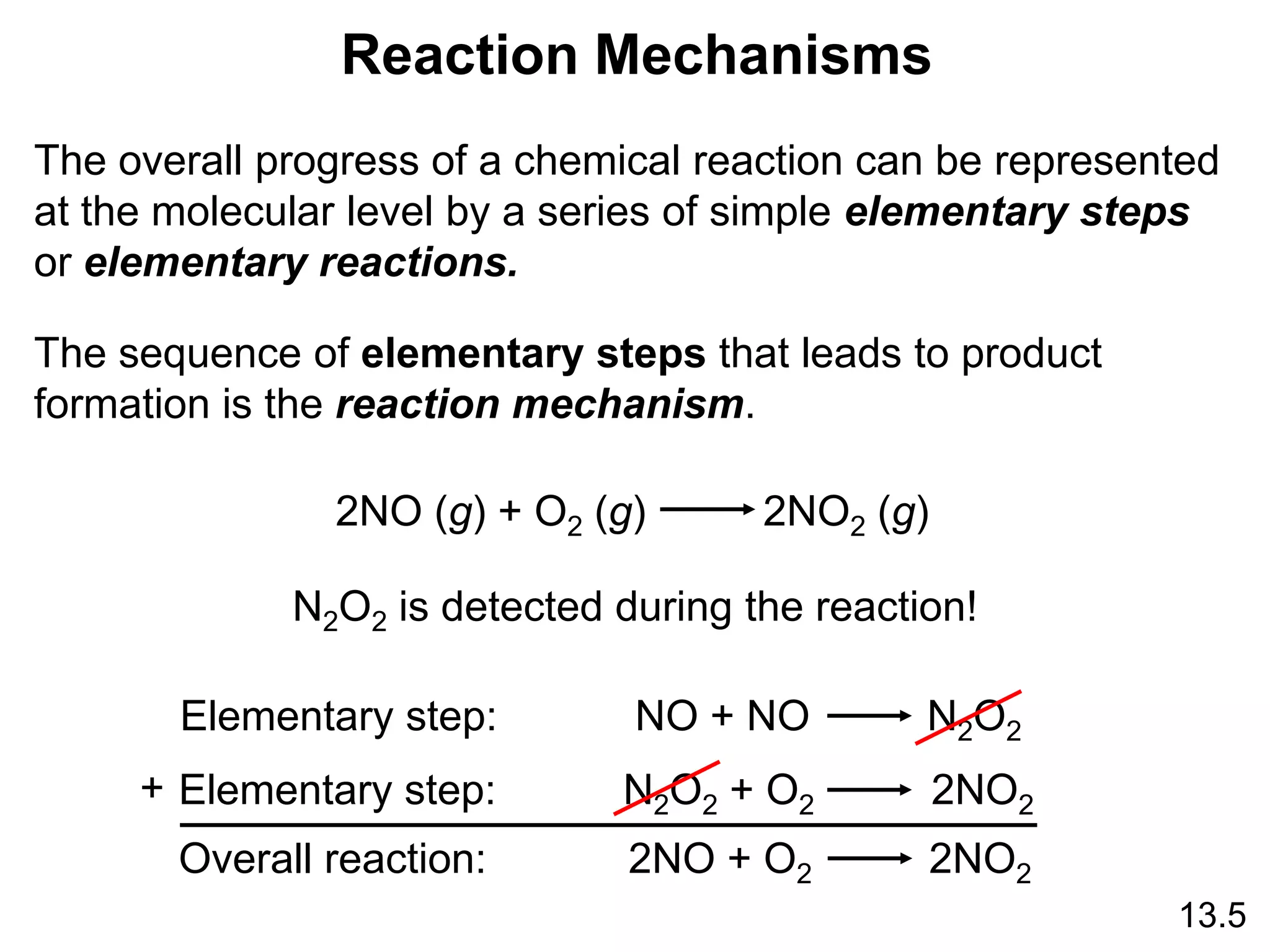
![The experimental rate law for the reaction between NO2
and CO to produce NO and CO2 is rate = k[NO2]2. The
reaction is believed to occur via two steps:
Step 1: NO2 + NO2 NO + NO3
Step 2: NO3 + CO NO2 + CO2
What is the equation for the overall reaction?
NO2+ CO NO + CO2
What is the intermediate?
NO3
What can you say about the relative rates of steps 1 and 2?
rate = k[NO2]2 is the rate law for step 1 so
step 1 must be slower than step 2
13.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-161-2048.jpg)
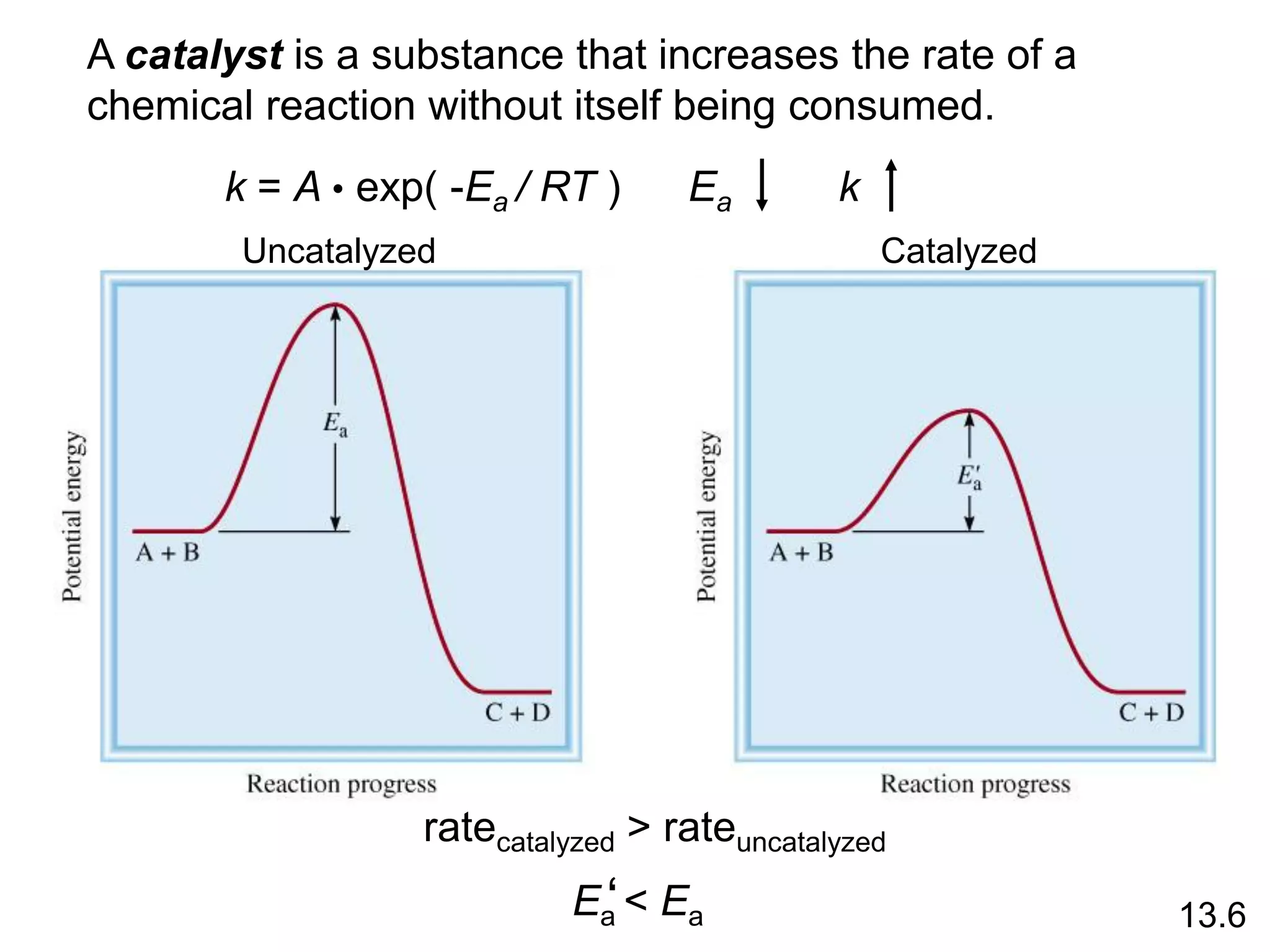

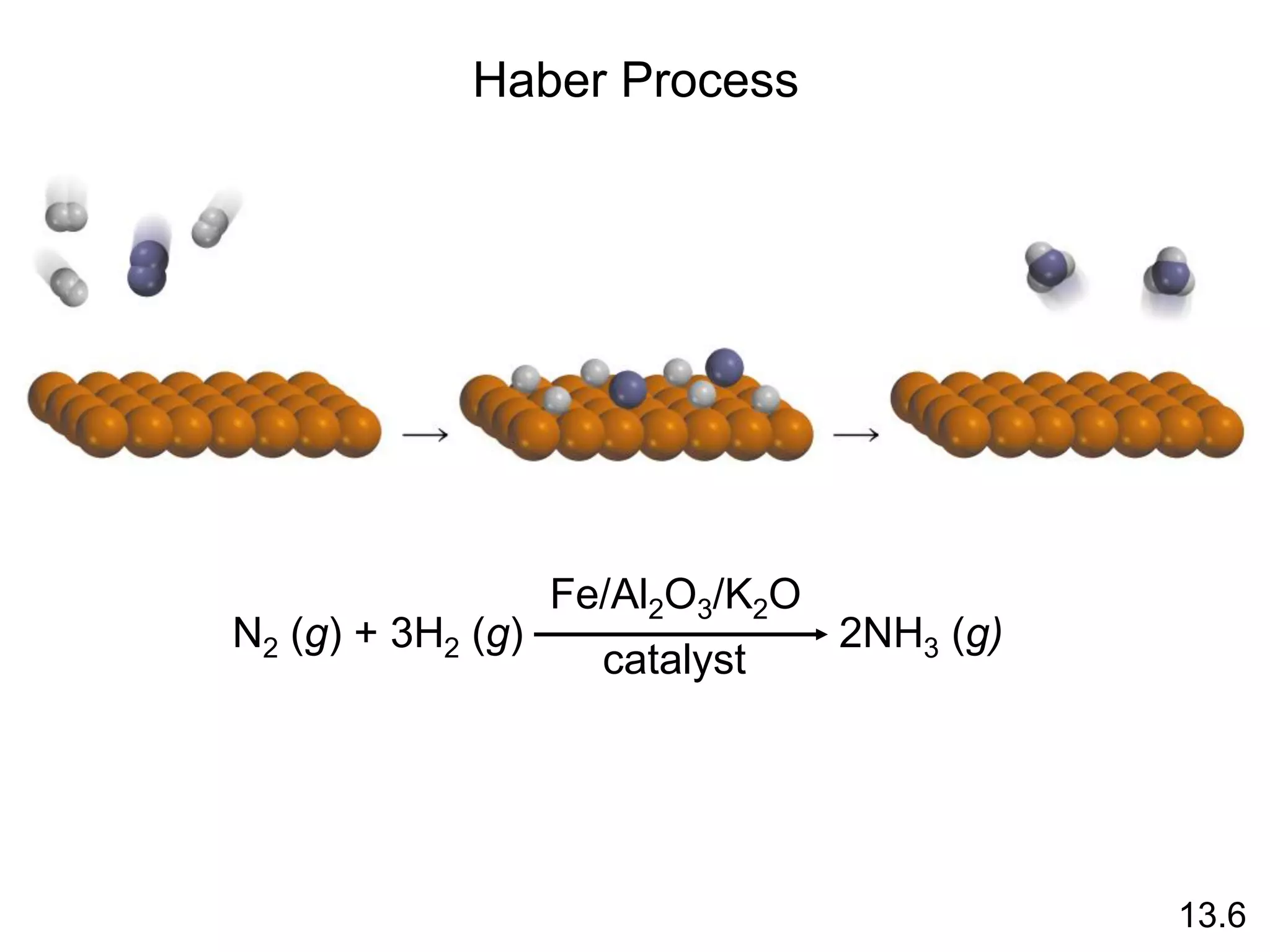
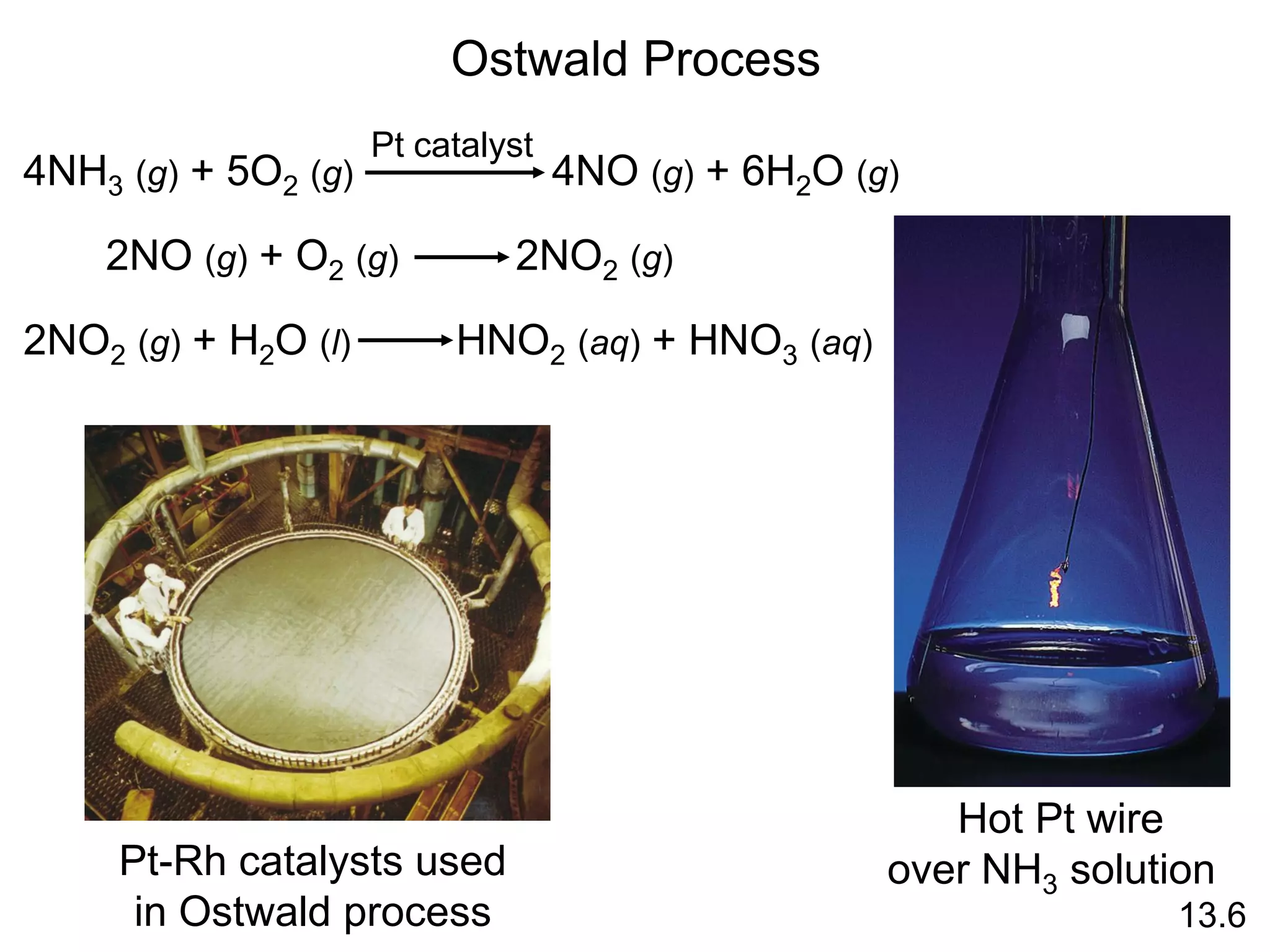
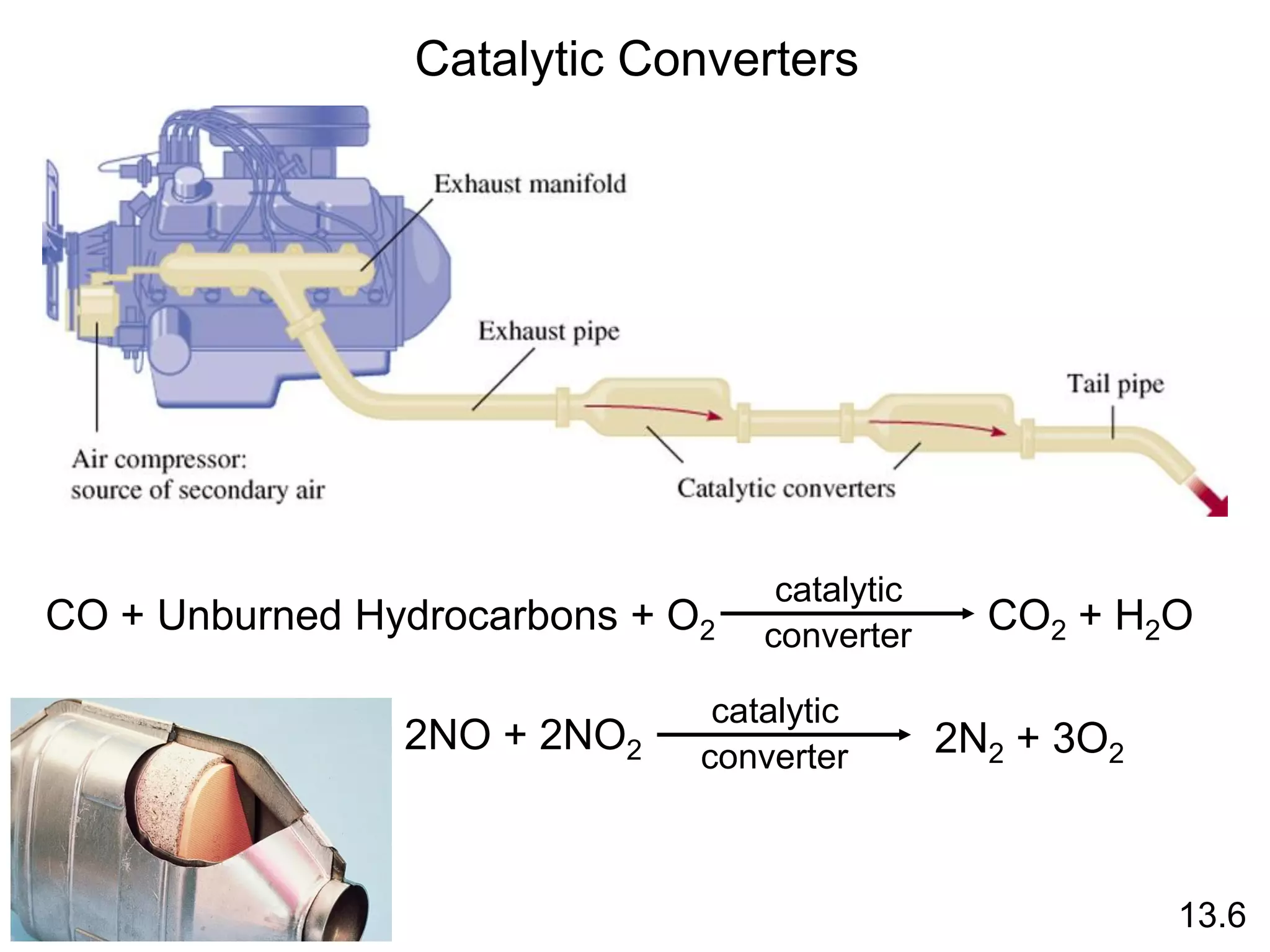

![uncatalyzed
enzyme
catalyzed
13.6
rate =
D[P]
Dt
rate = k [ES]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductoryphysicalchemistrylecturenote-210809120757/75/Introductory-physical-chemistry-lecture-note-168-2048.jpg)
