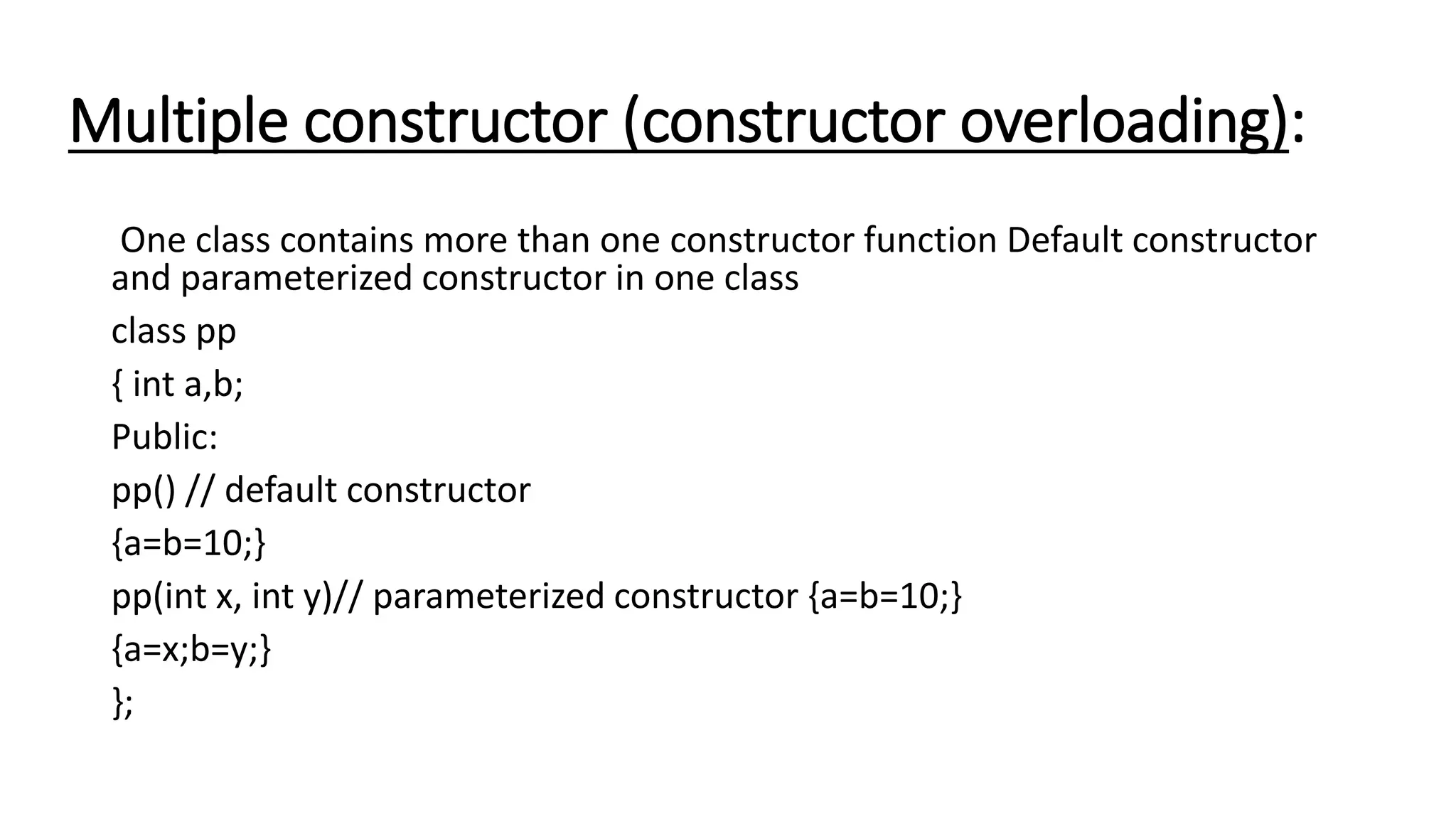
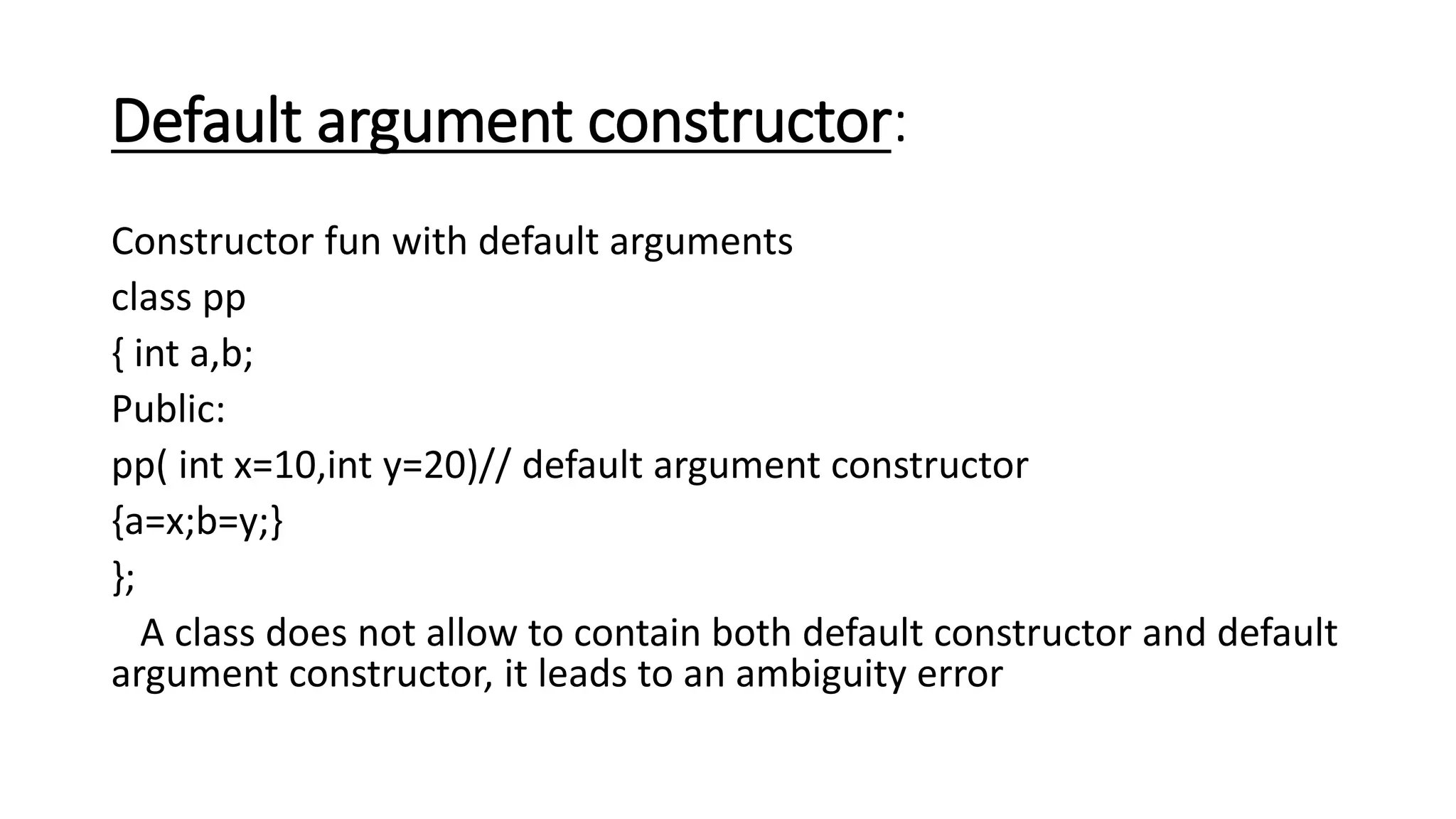
Constructors are special member functions that are automatically called when an object is created. They initialize the data members of a class. There are different types of constructors like default, parameterized, multiple, default argument, dynamic initialization, dynamic, and copy constructors. The default constructor does not take any parameters while the parameterized constructor takes parameters to initialize the data members. Multiple constructors allow constructor overloading. The copy constructor allows creating a new object from an existing one. Constructors ensure data members are initialized when an object is declared.