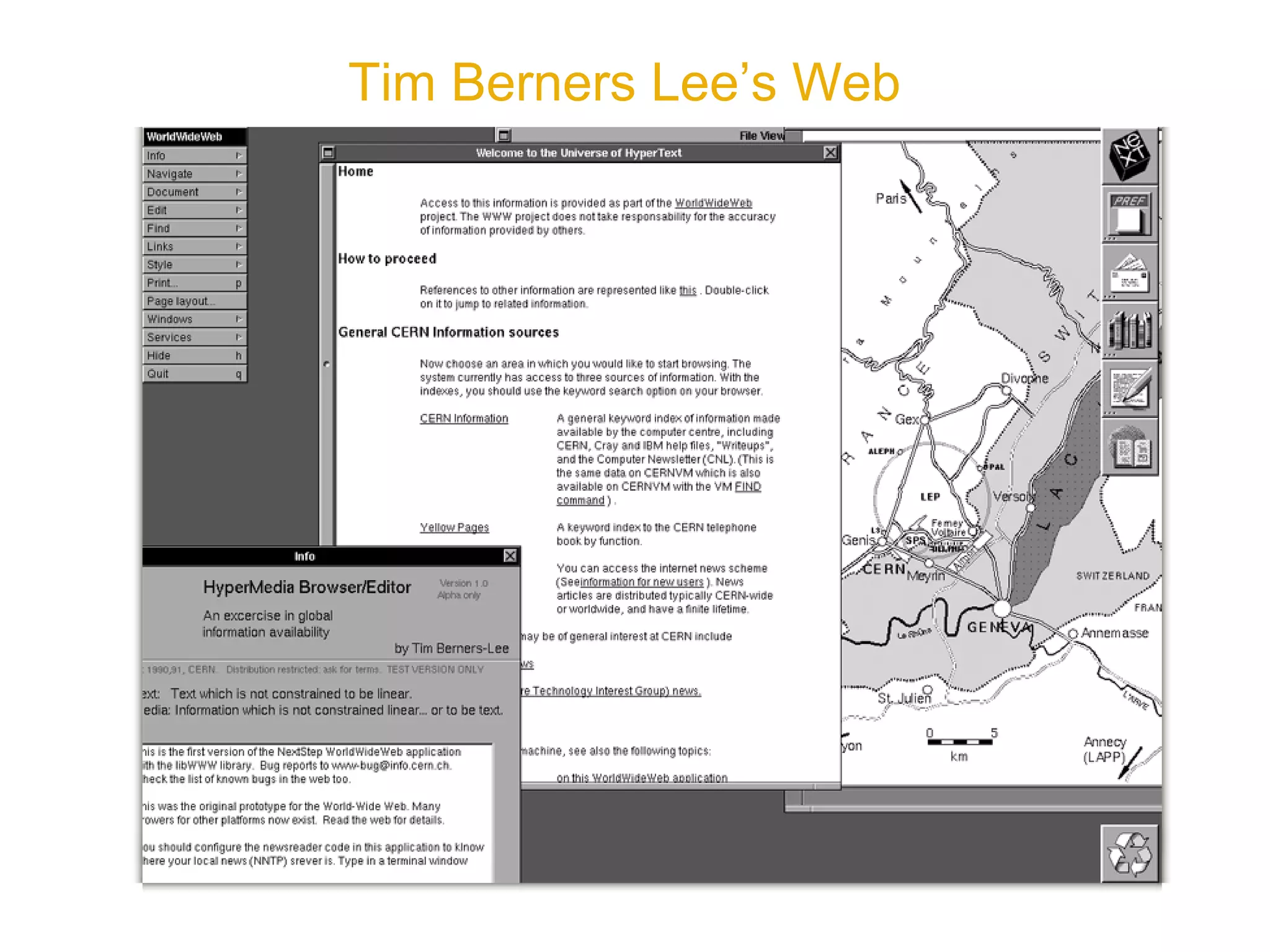
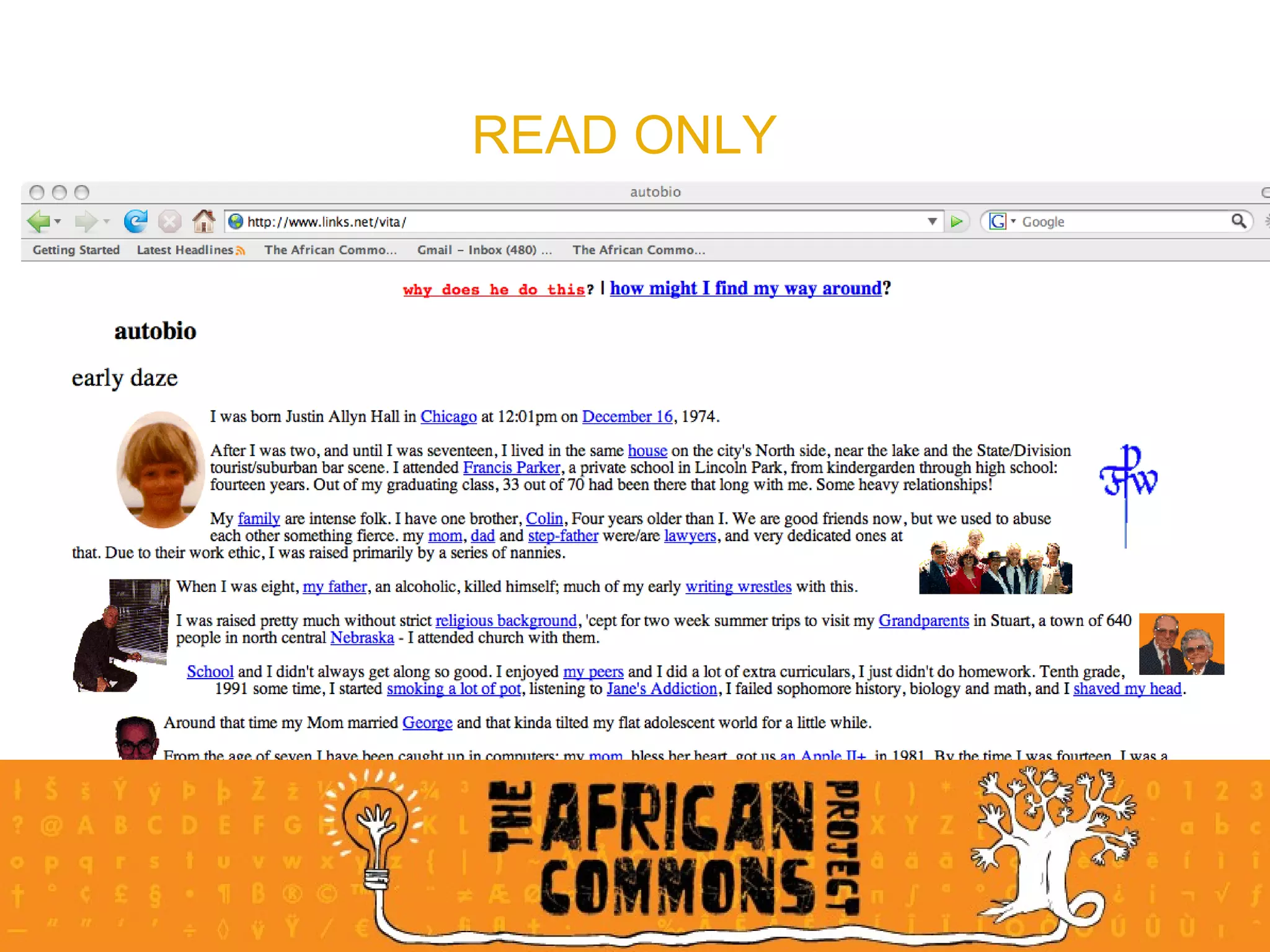
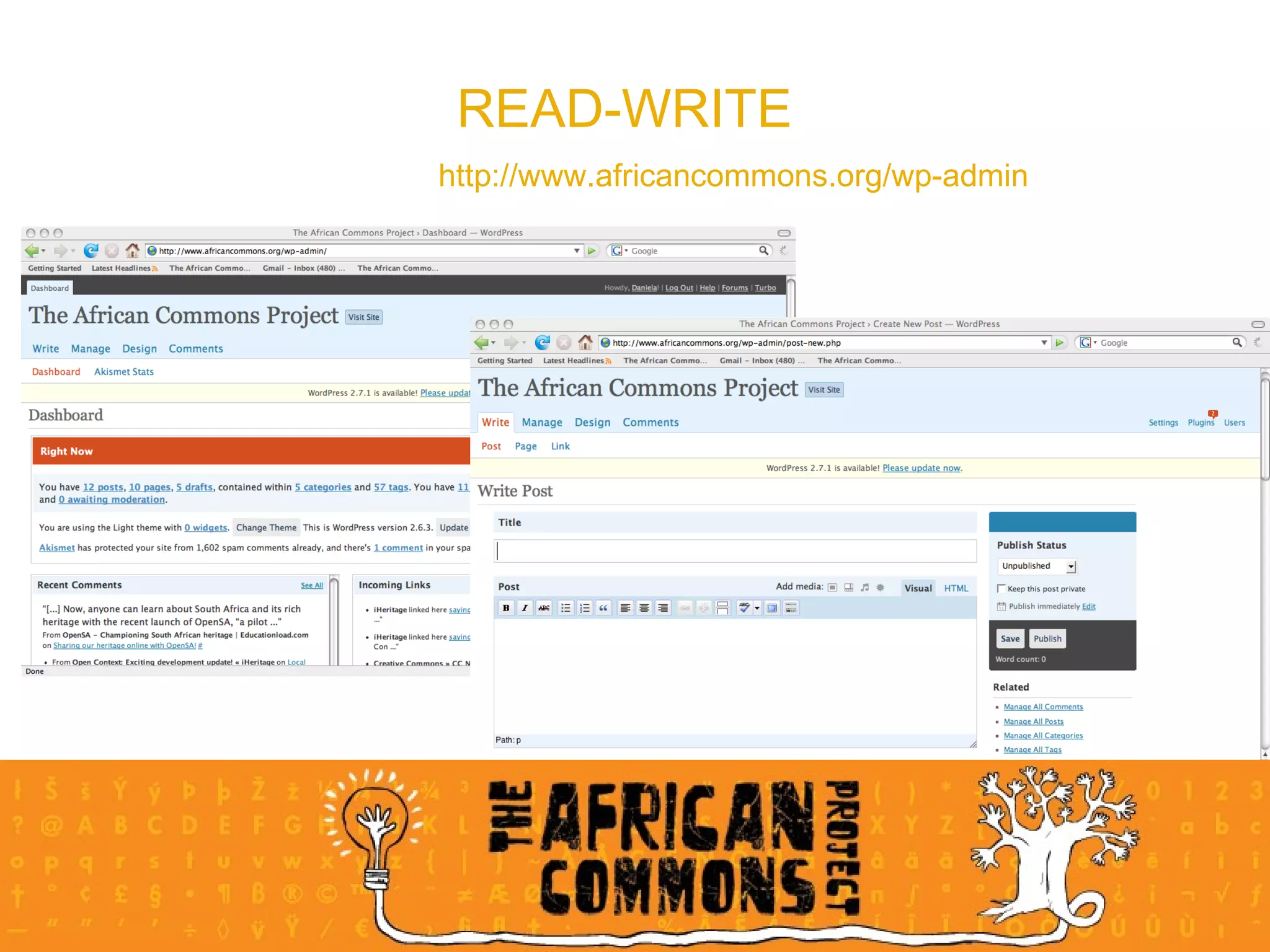
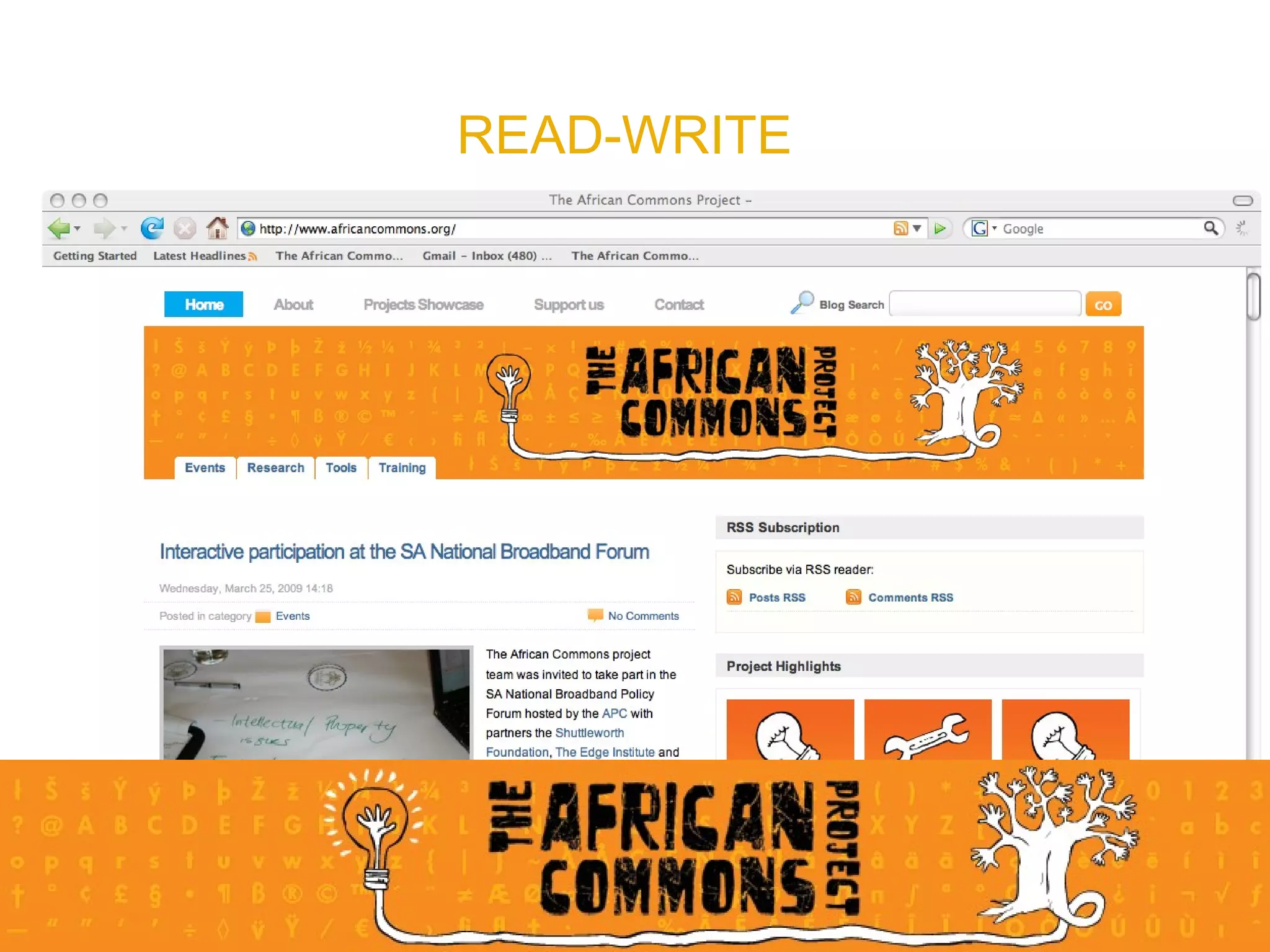
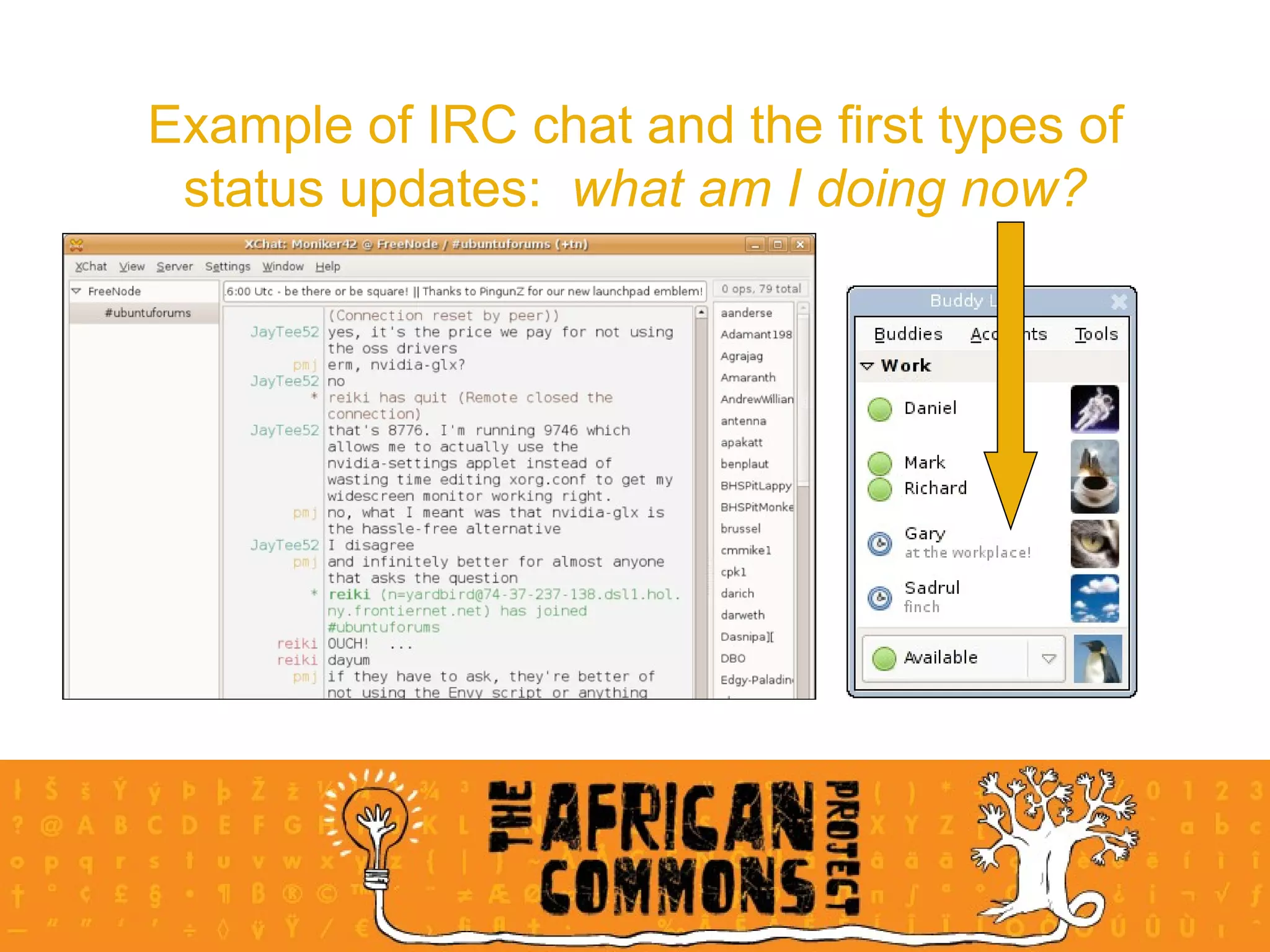
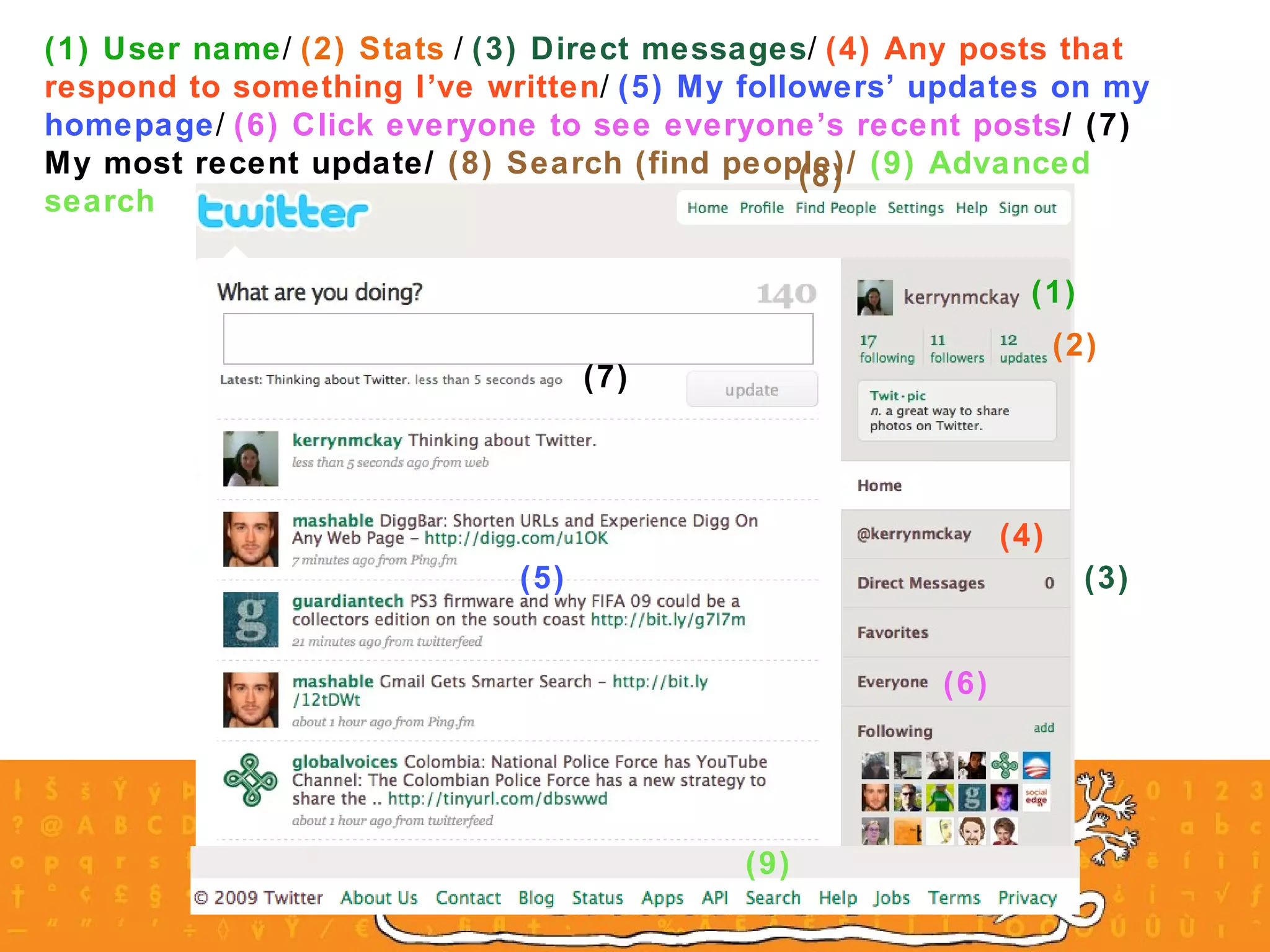
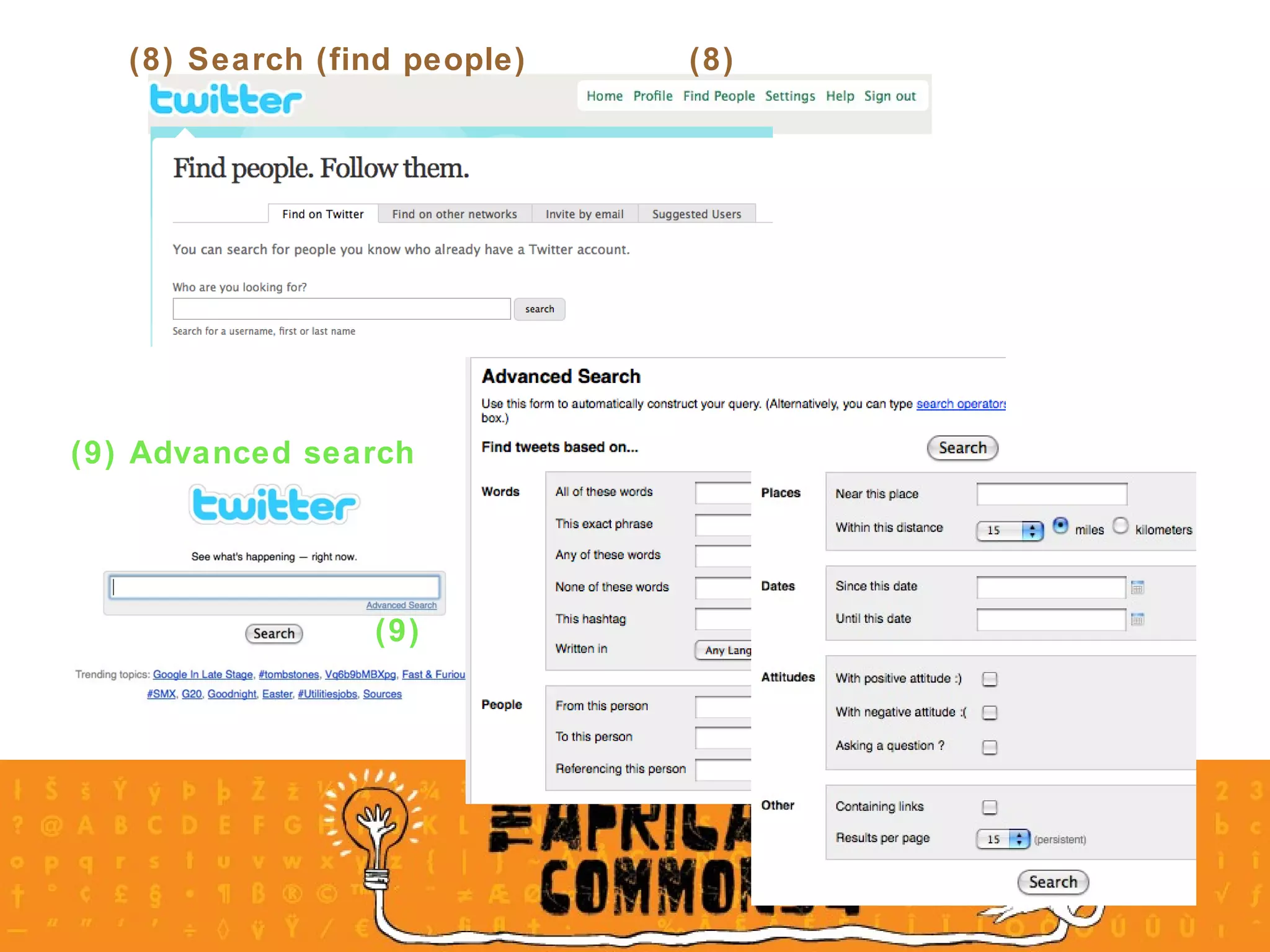
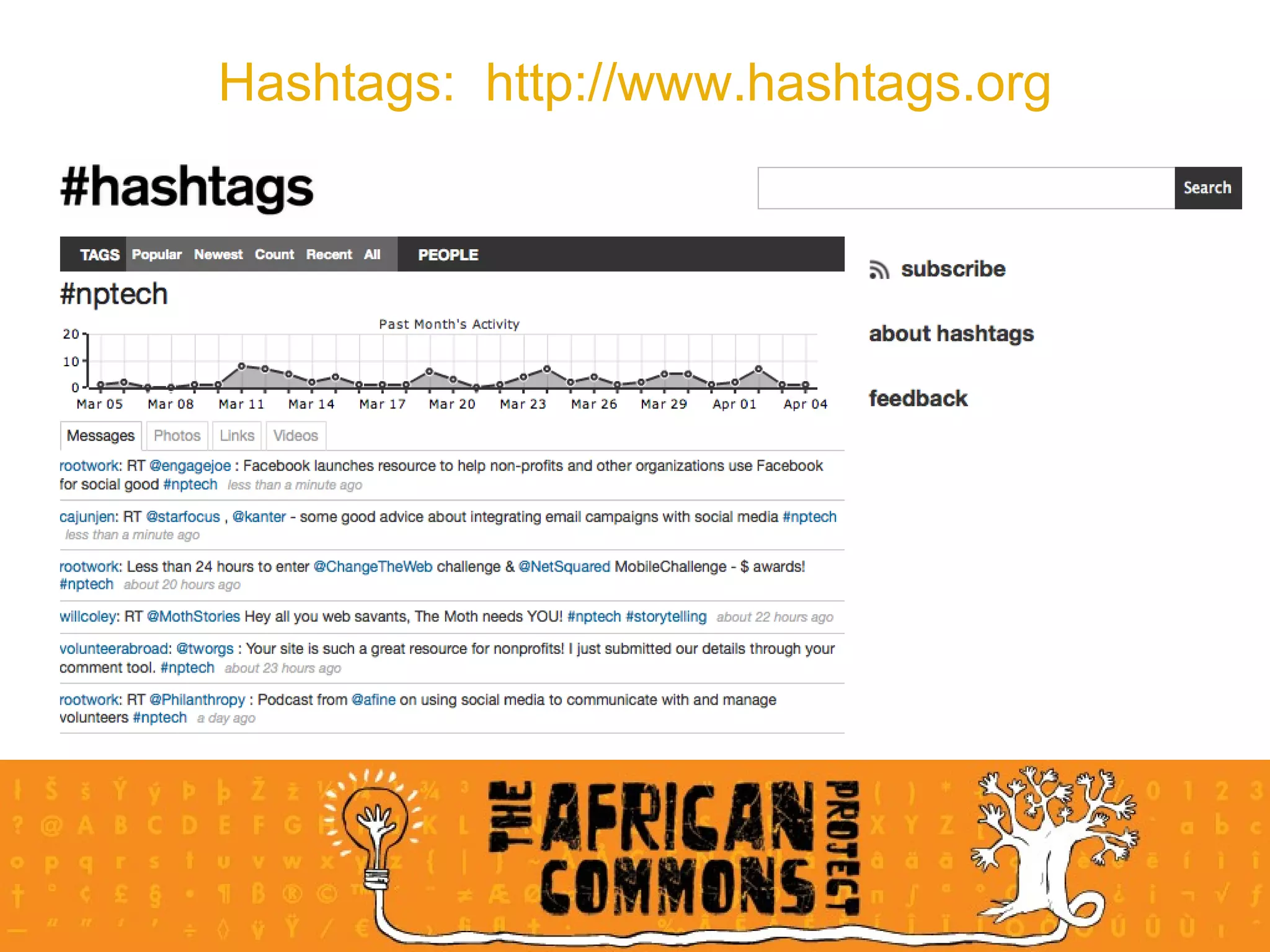
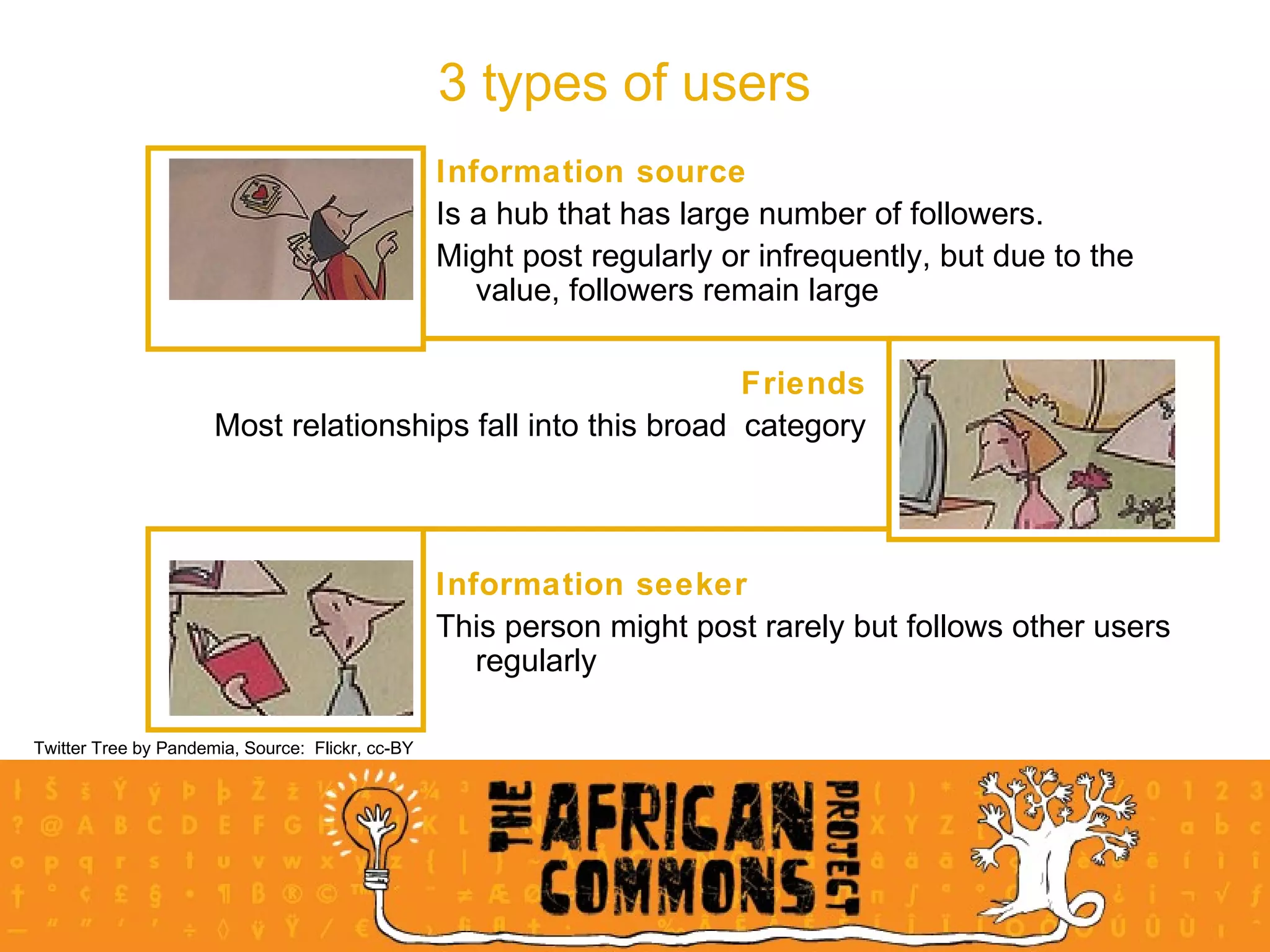
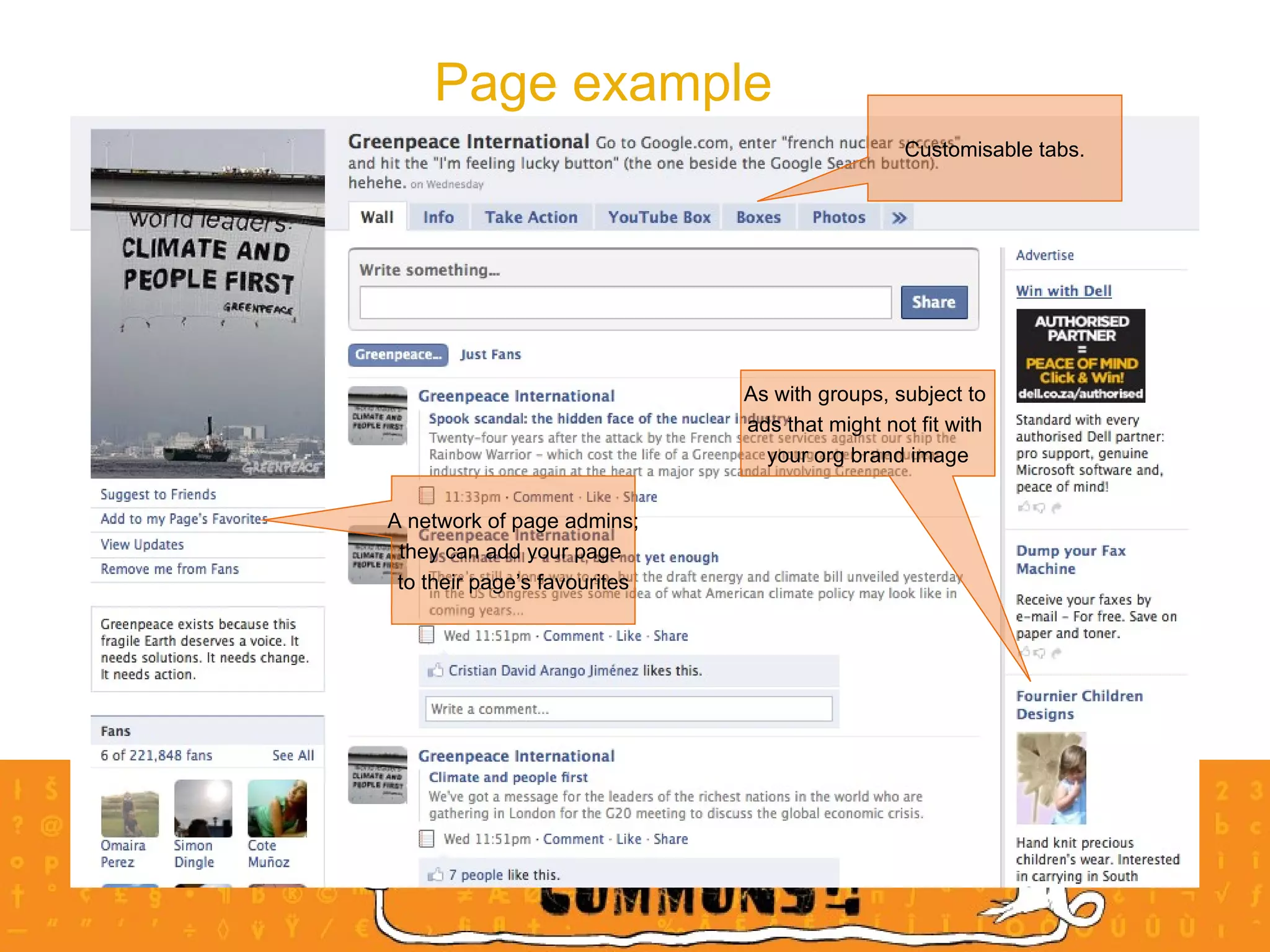
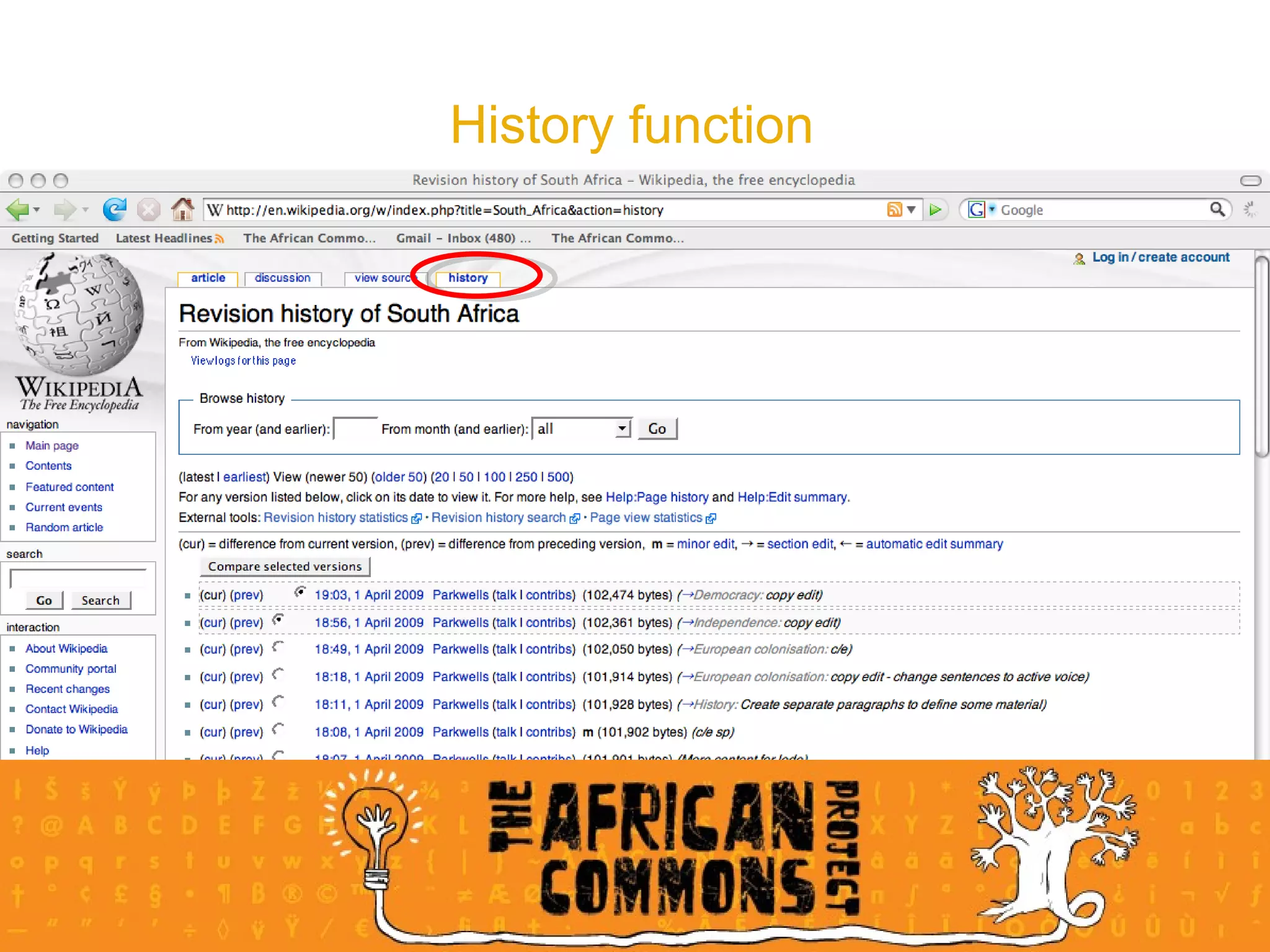
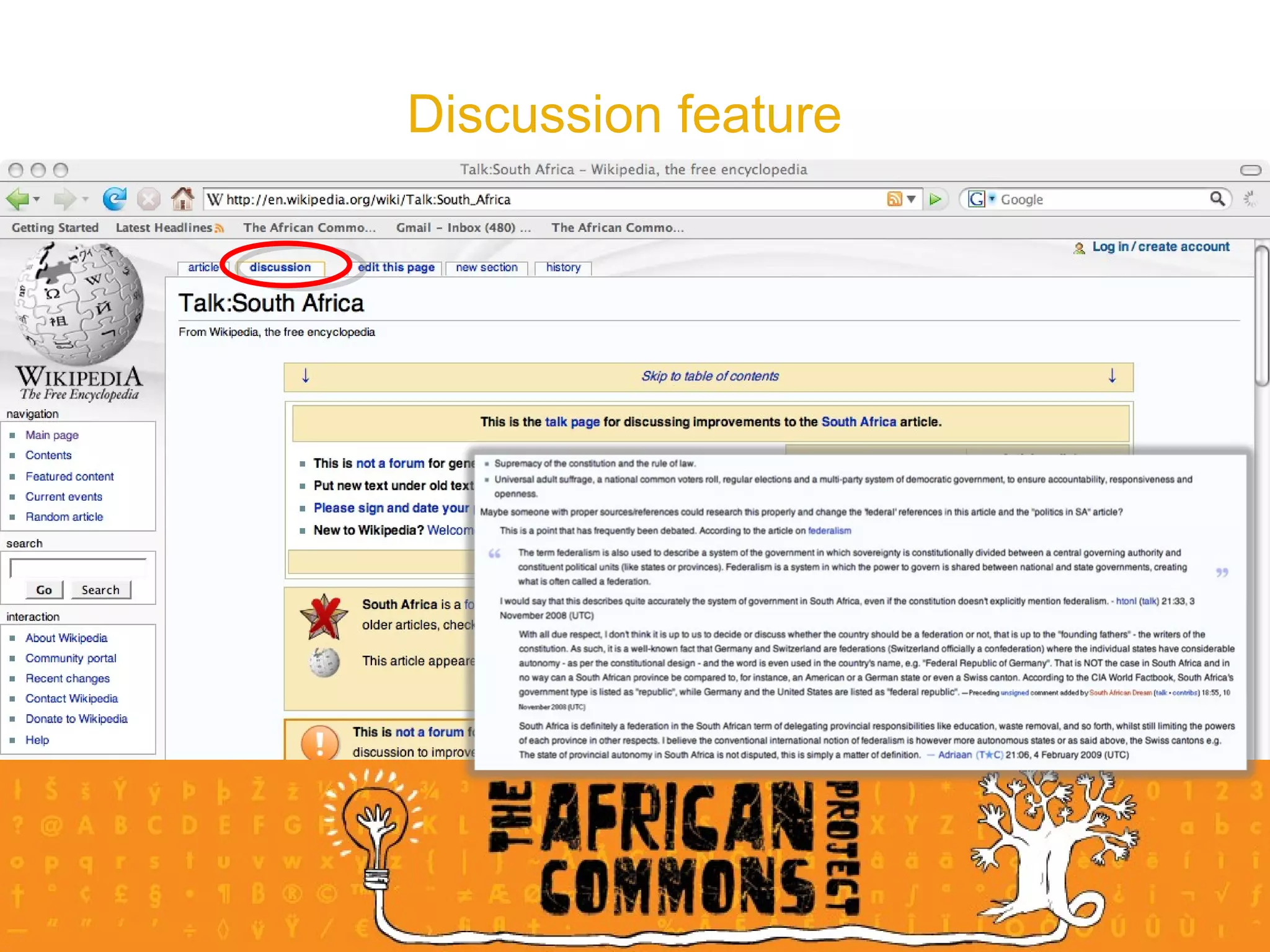
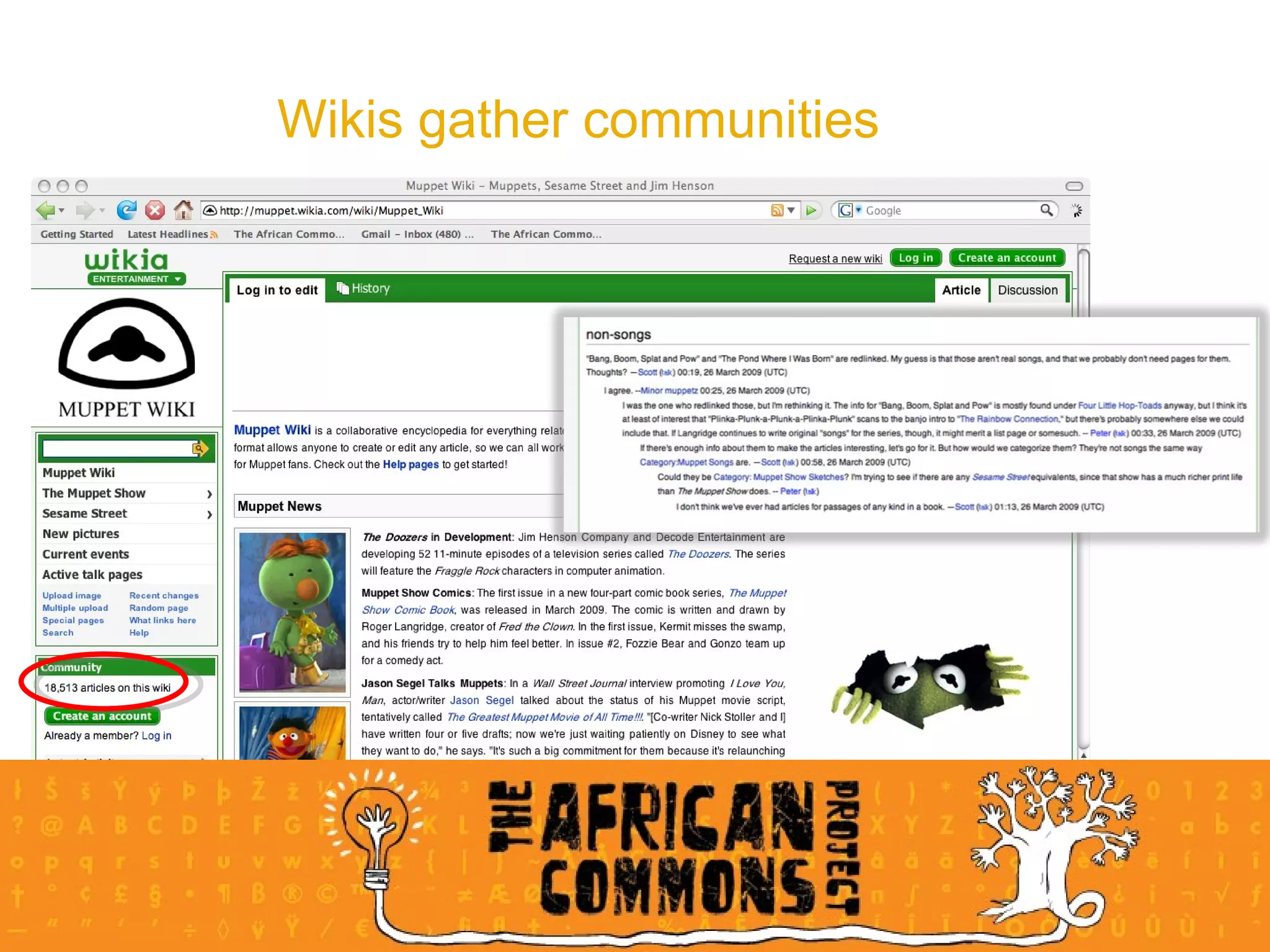
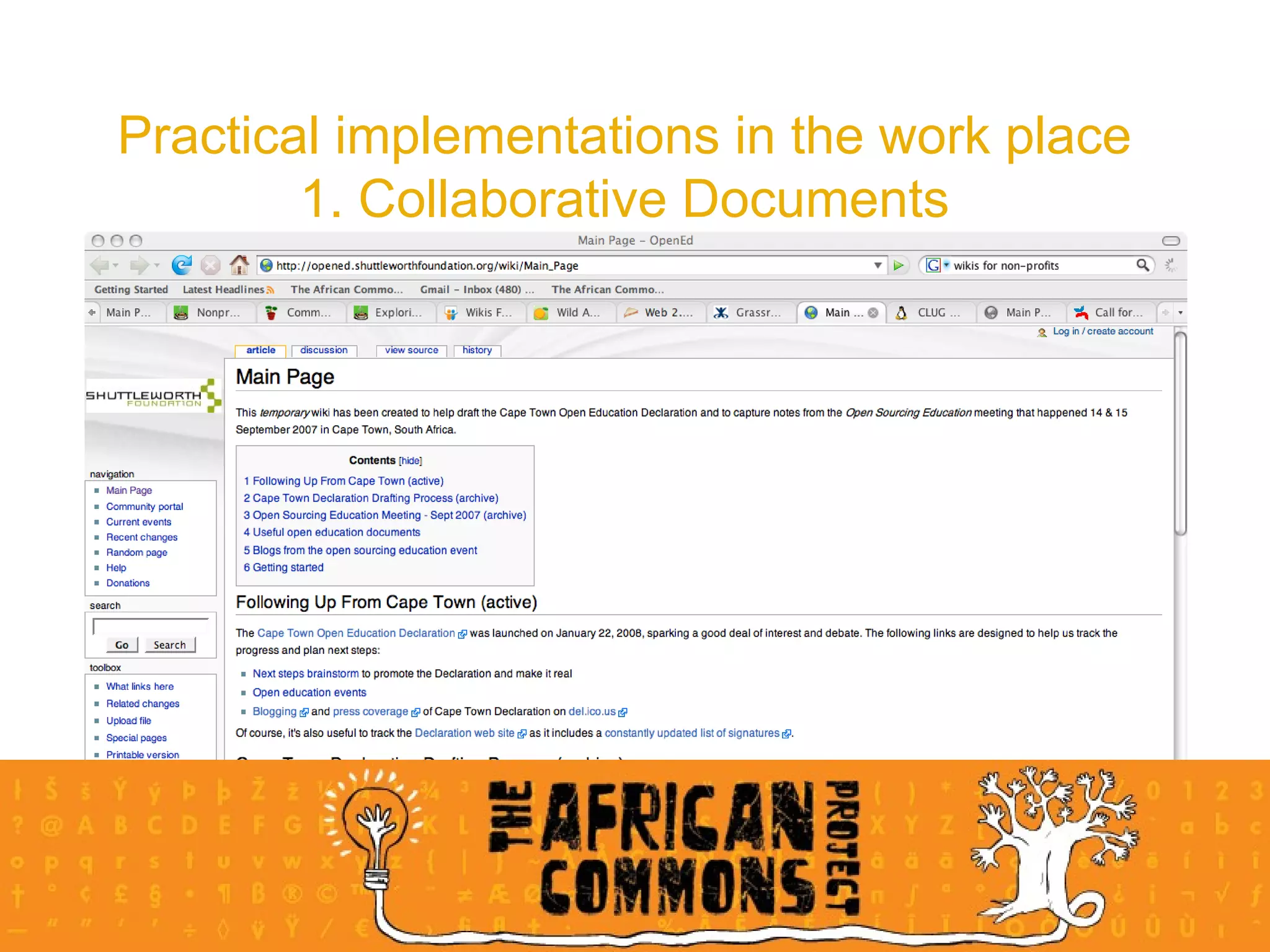
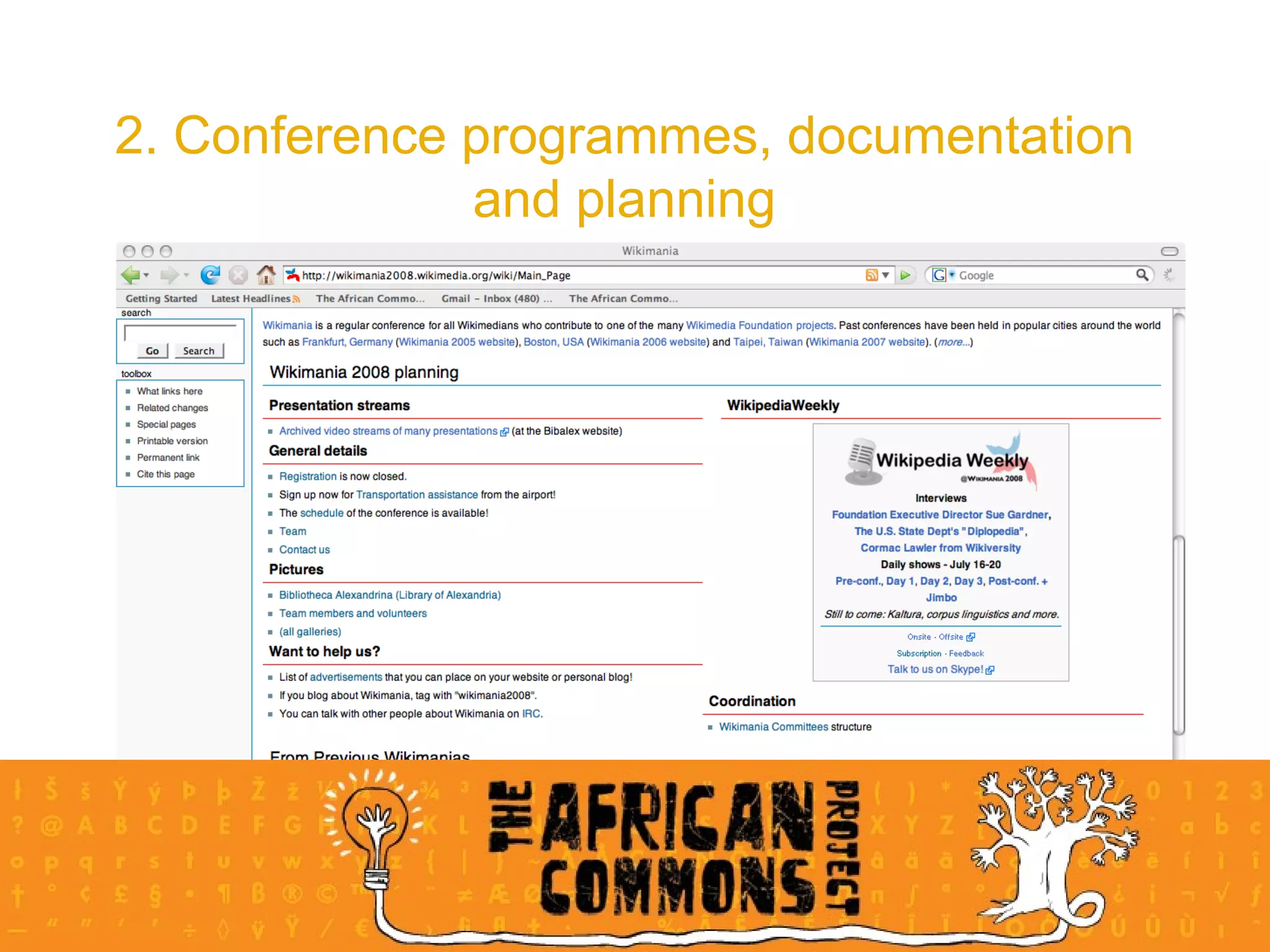
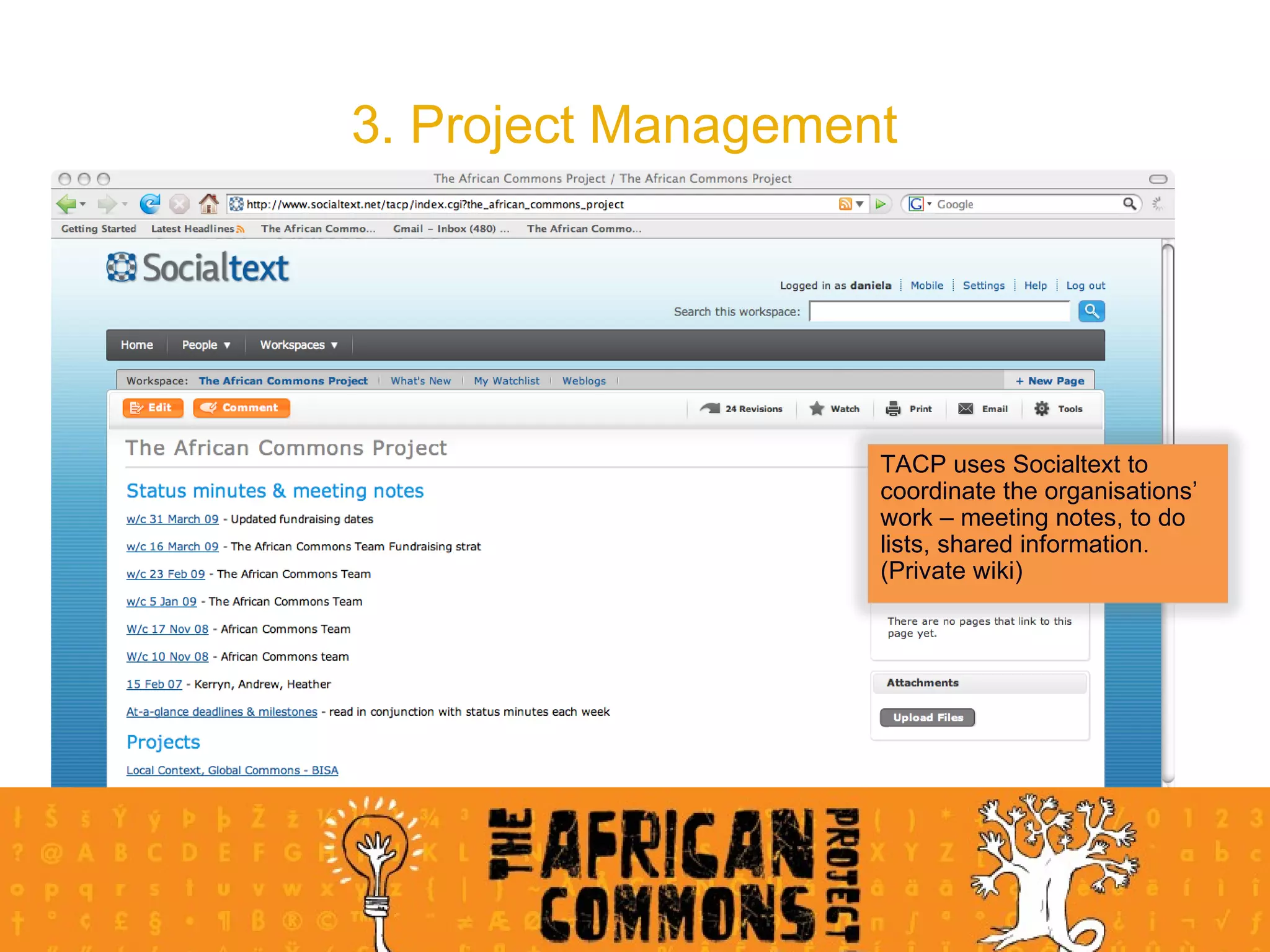
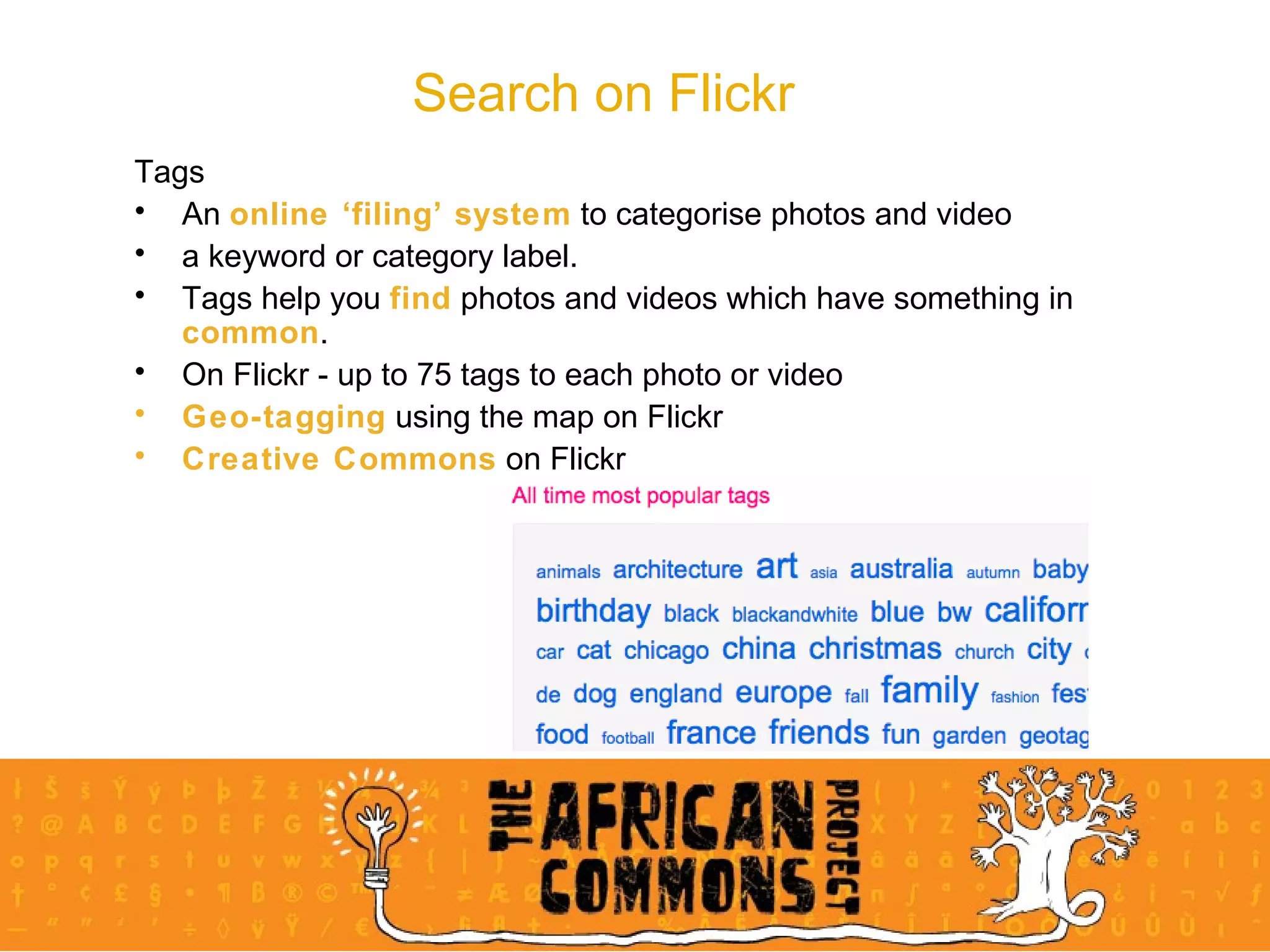
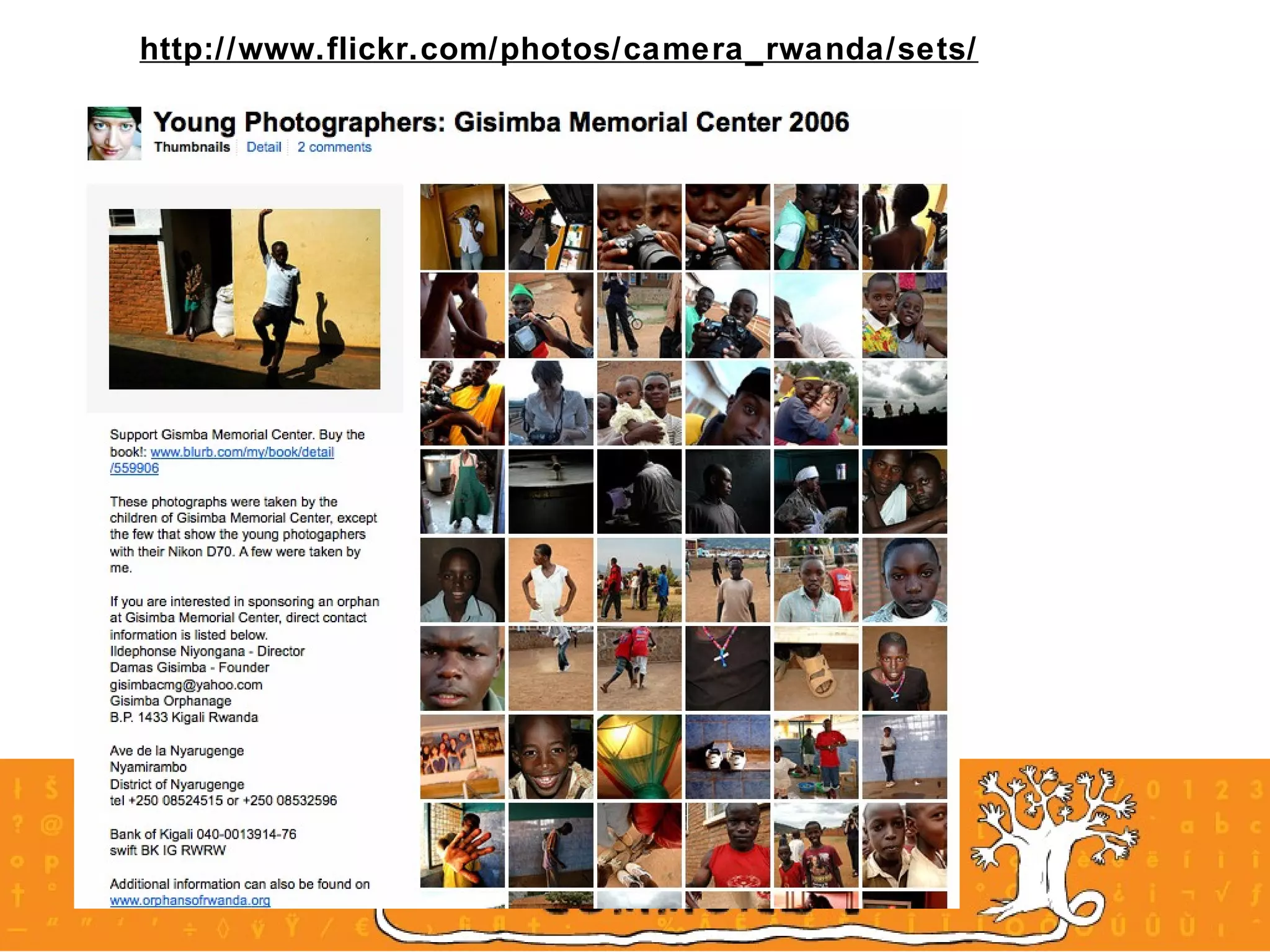
The document provides an overview of a social media course for NGOs, covering topics such as blogging, microblogging, social networking sites, wikis, and multimedia sites. It includes introductions and examples for each topic, as well as exercises for participants to practice using different social media platforms like blogs, Twitter, Facebook, wikis and Flickr.