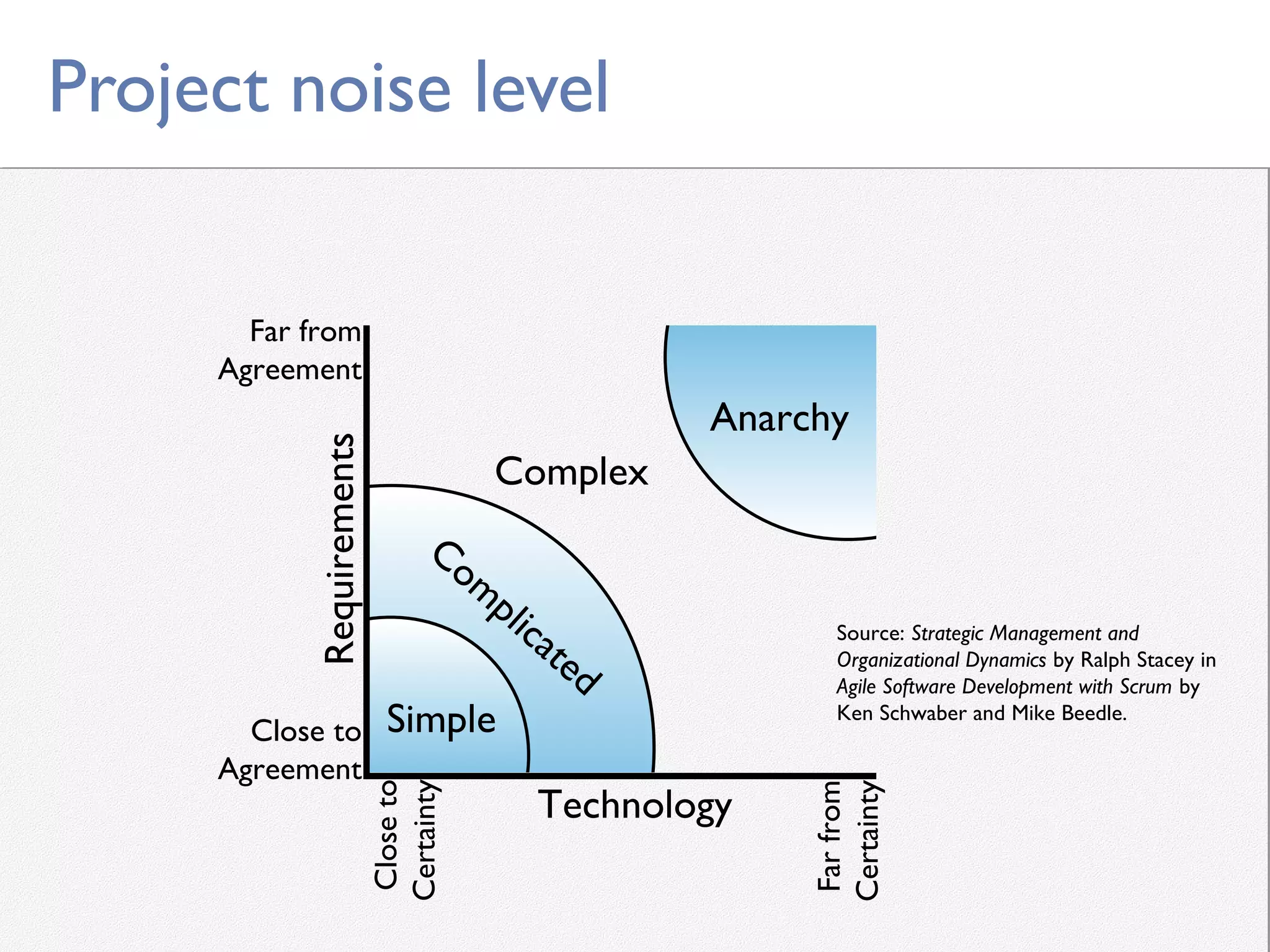
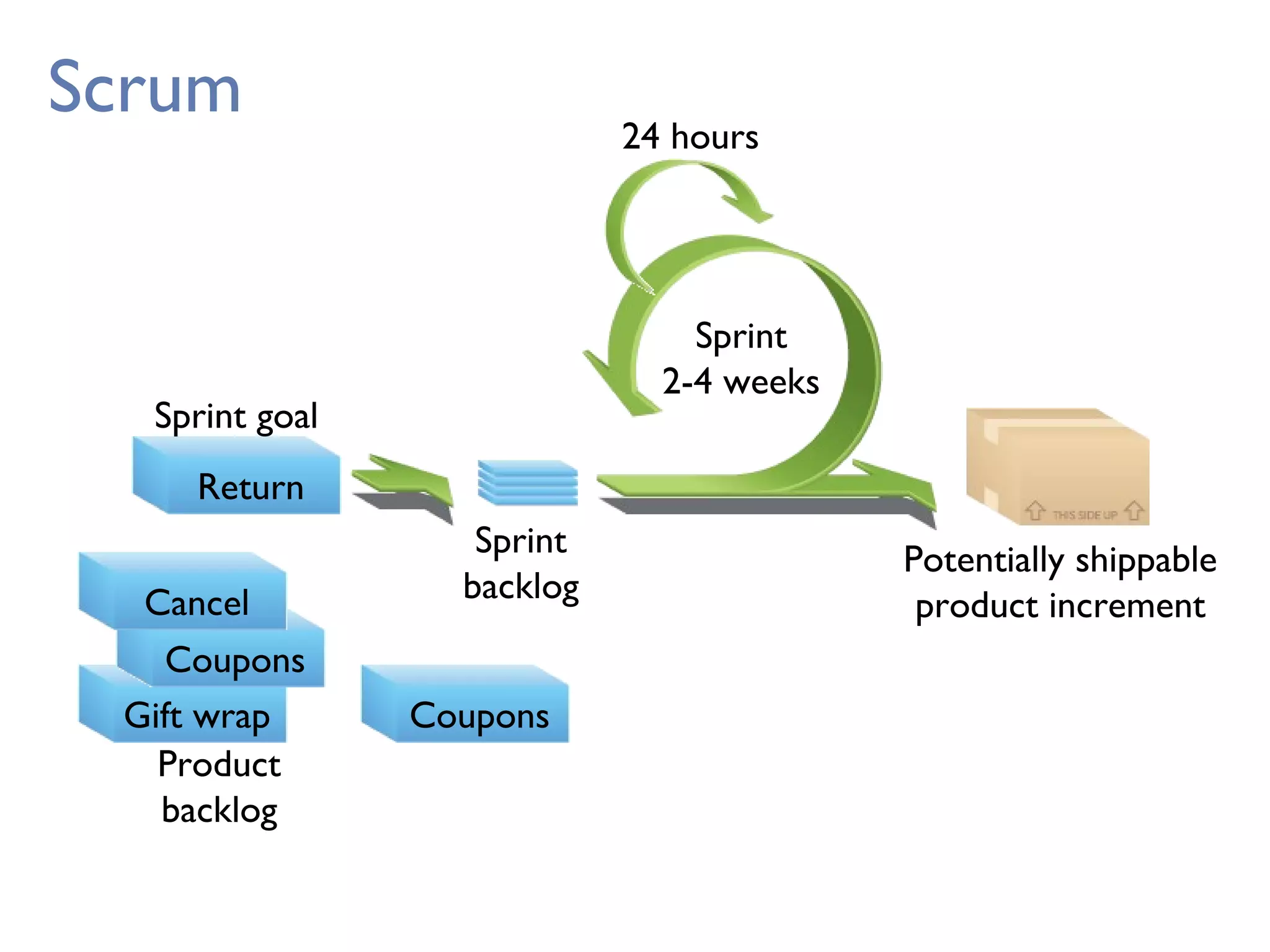
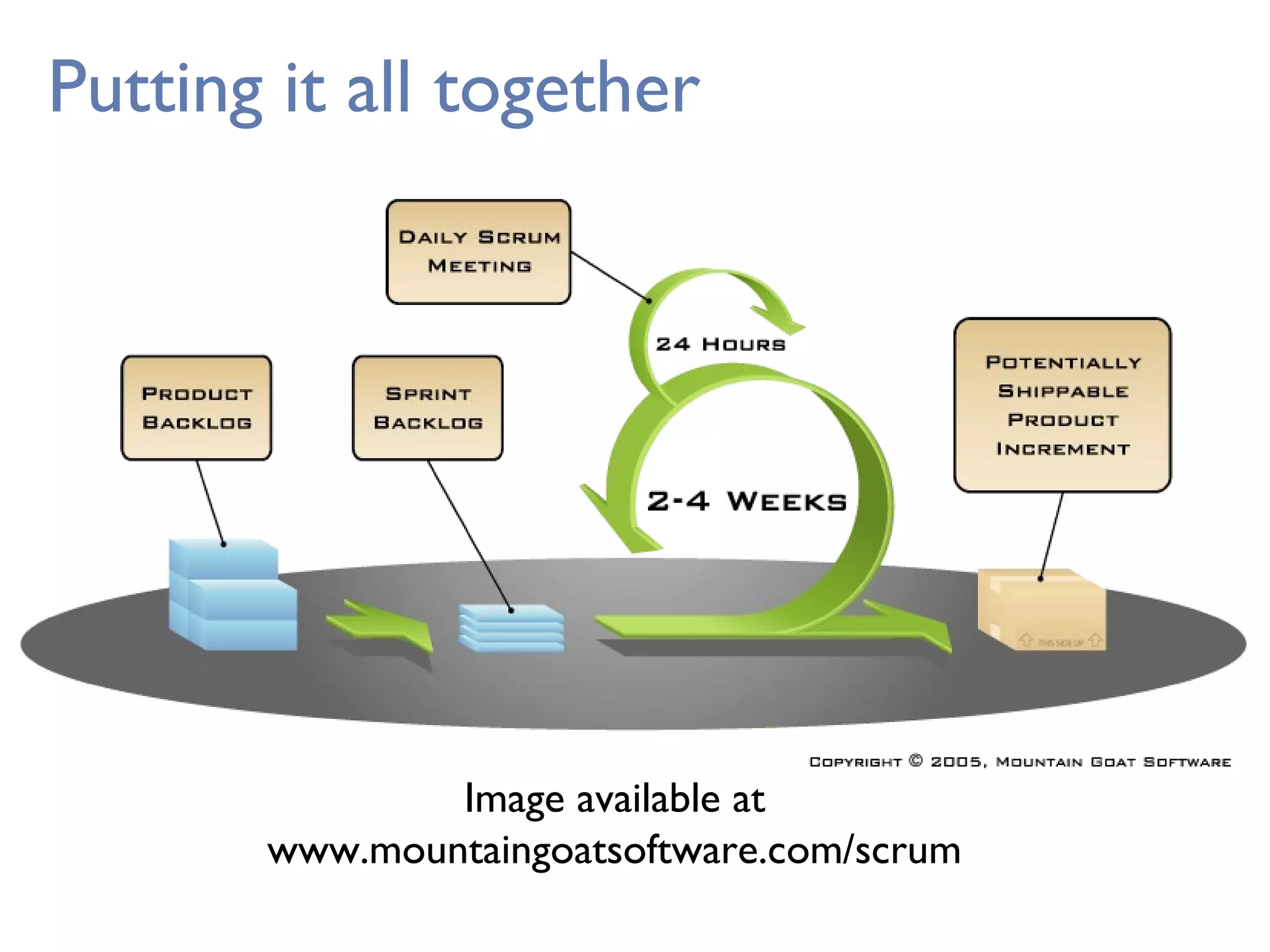
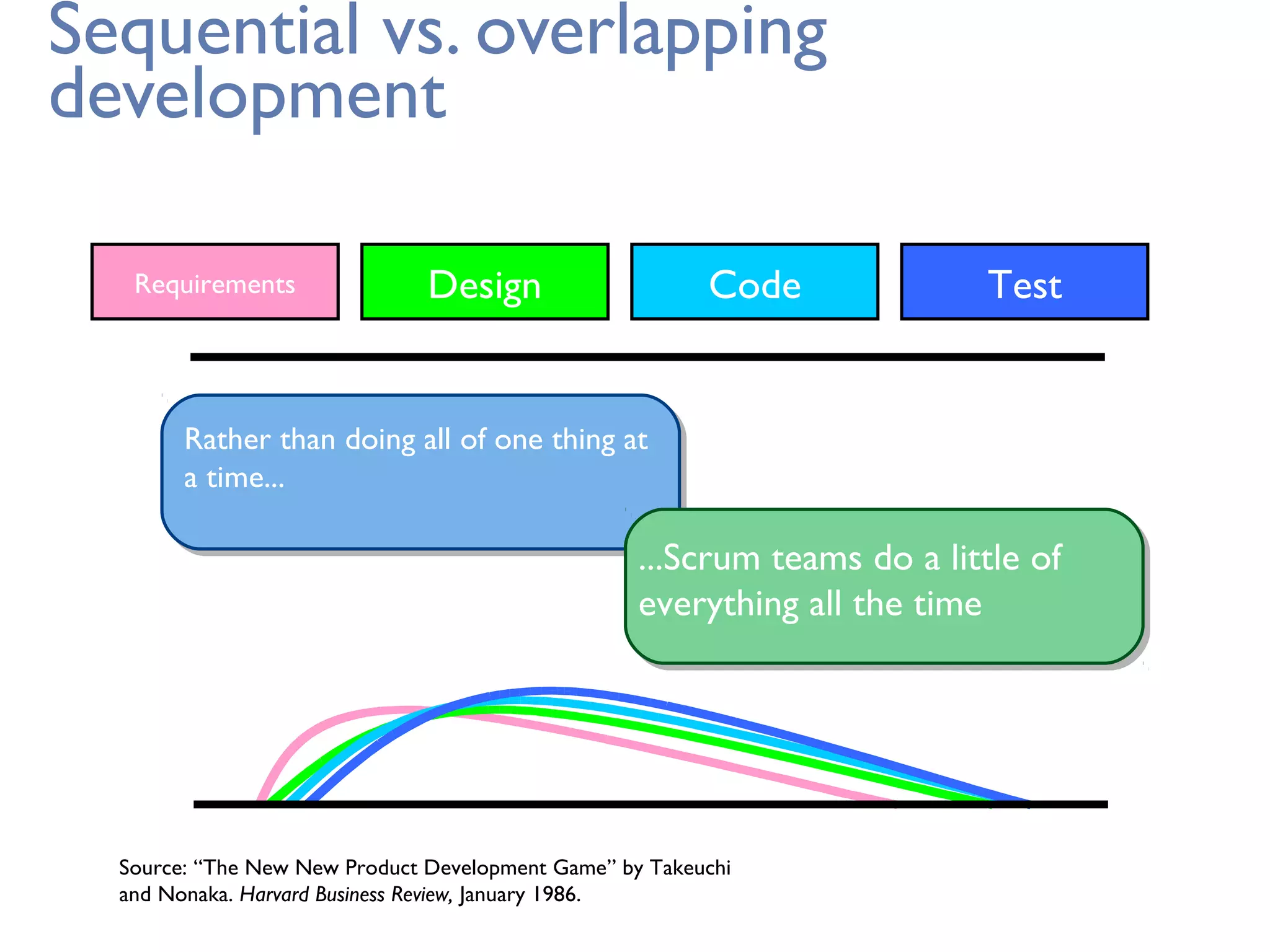
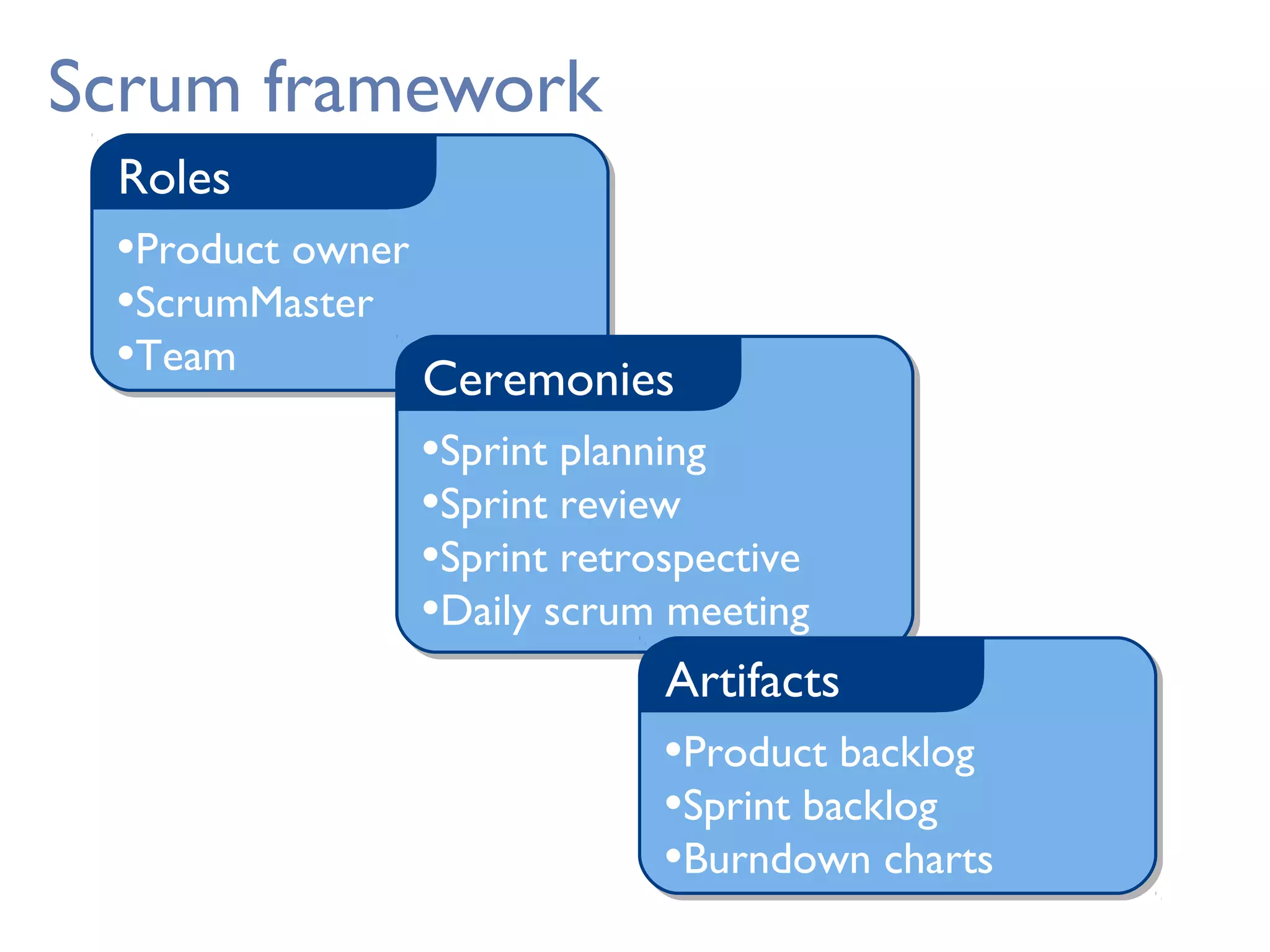
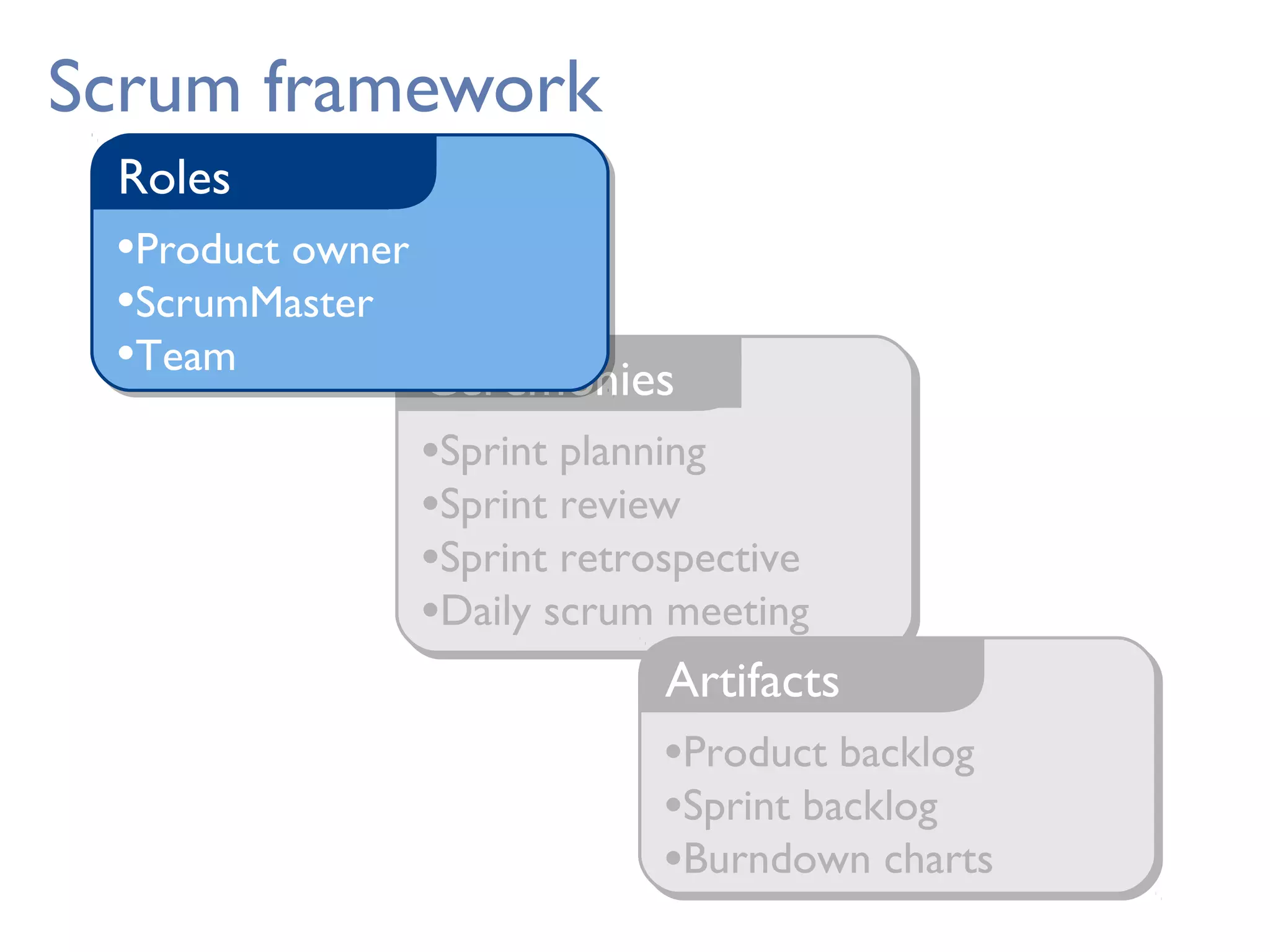
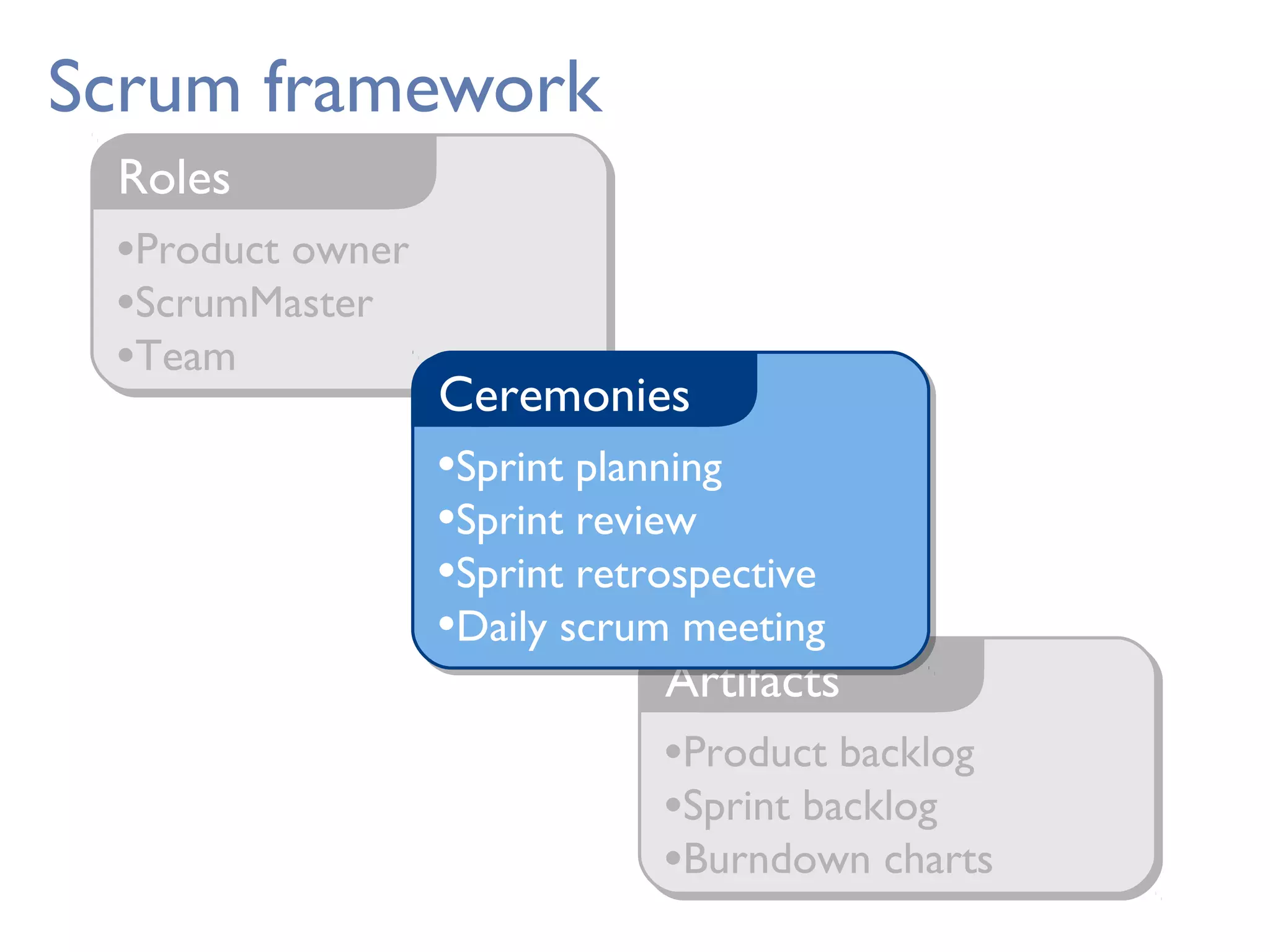
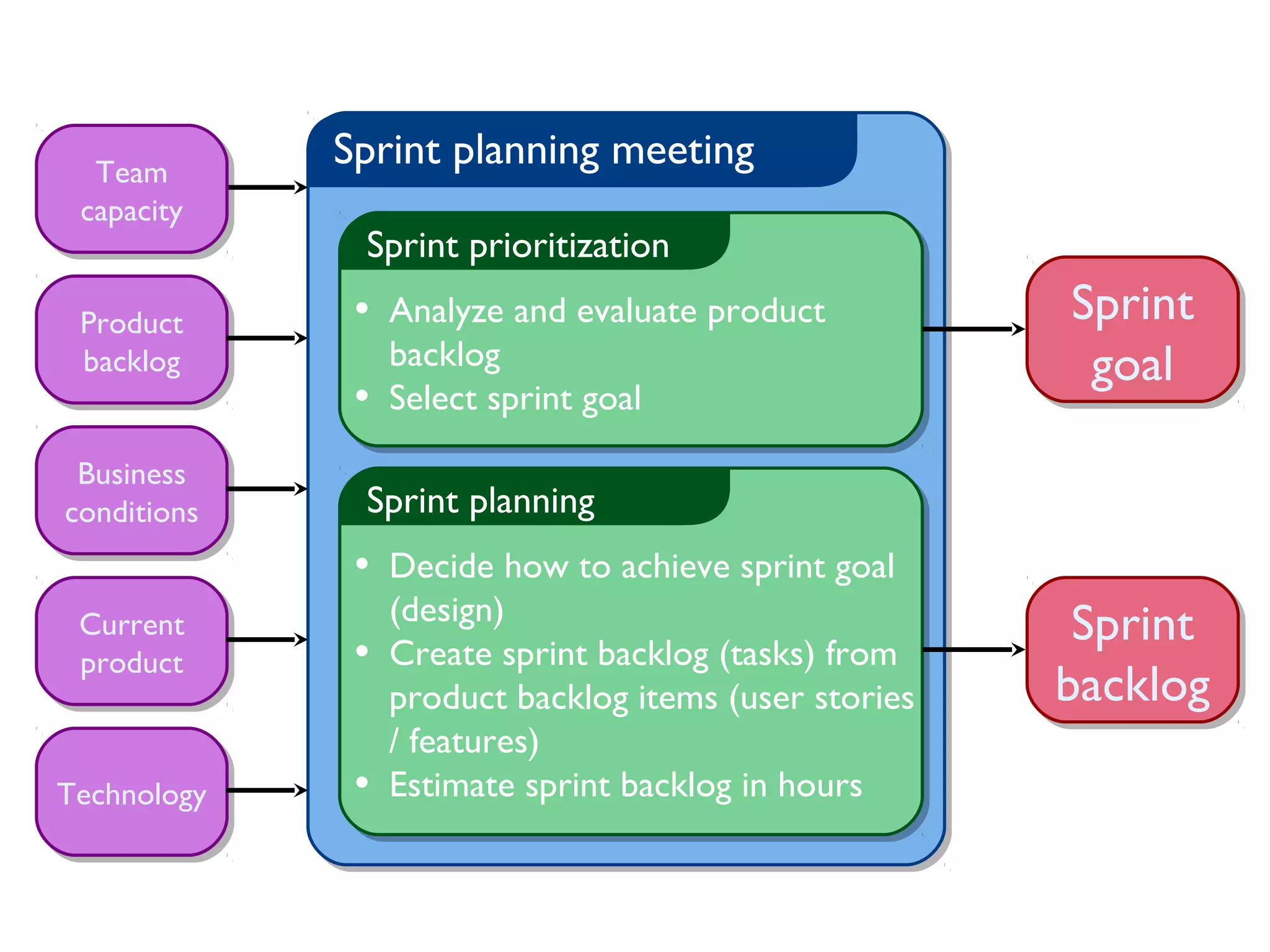
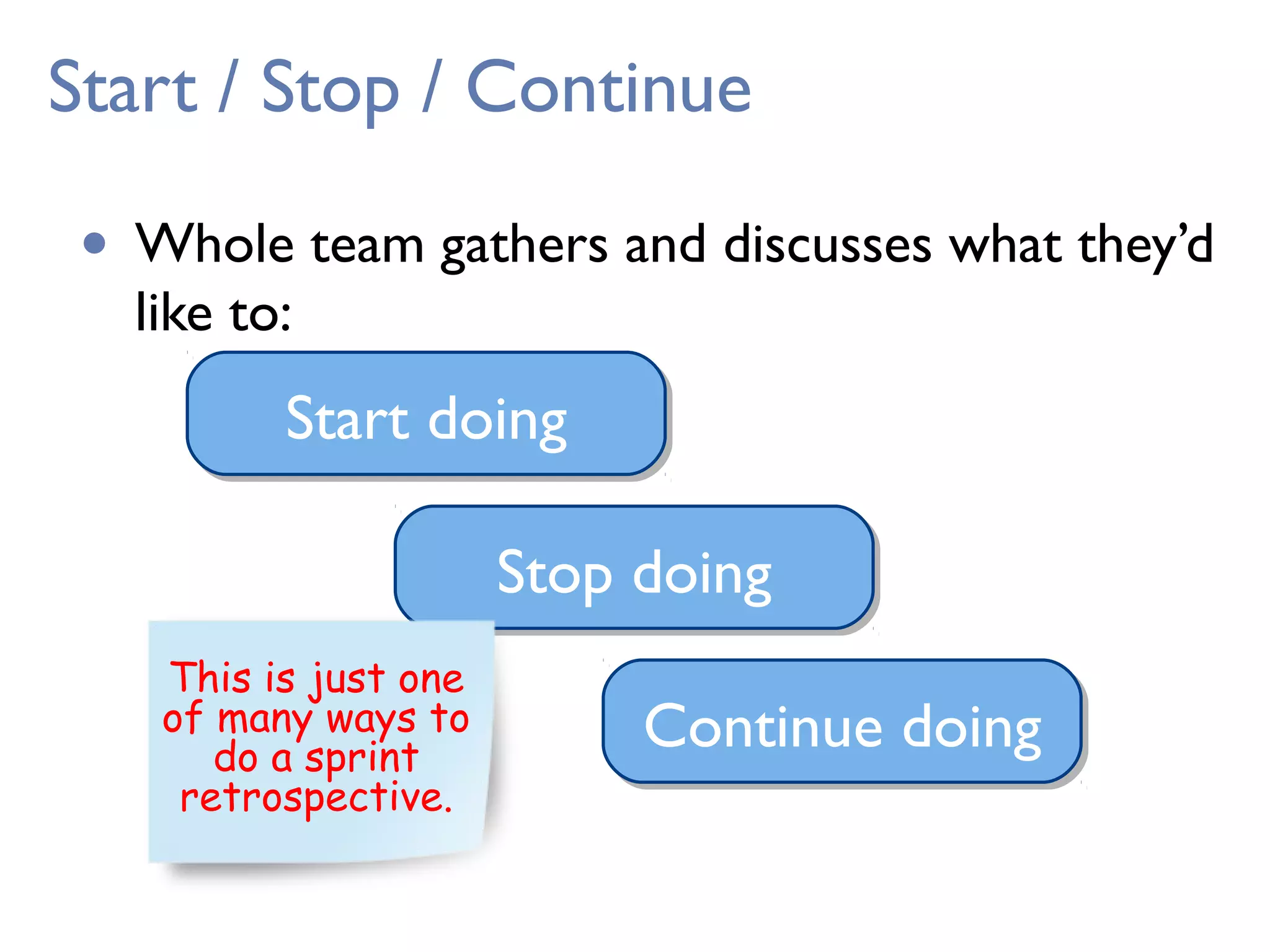
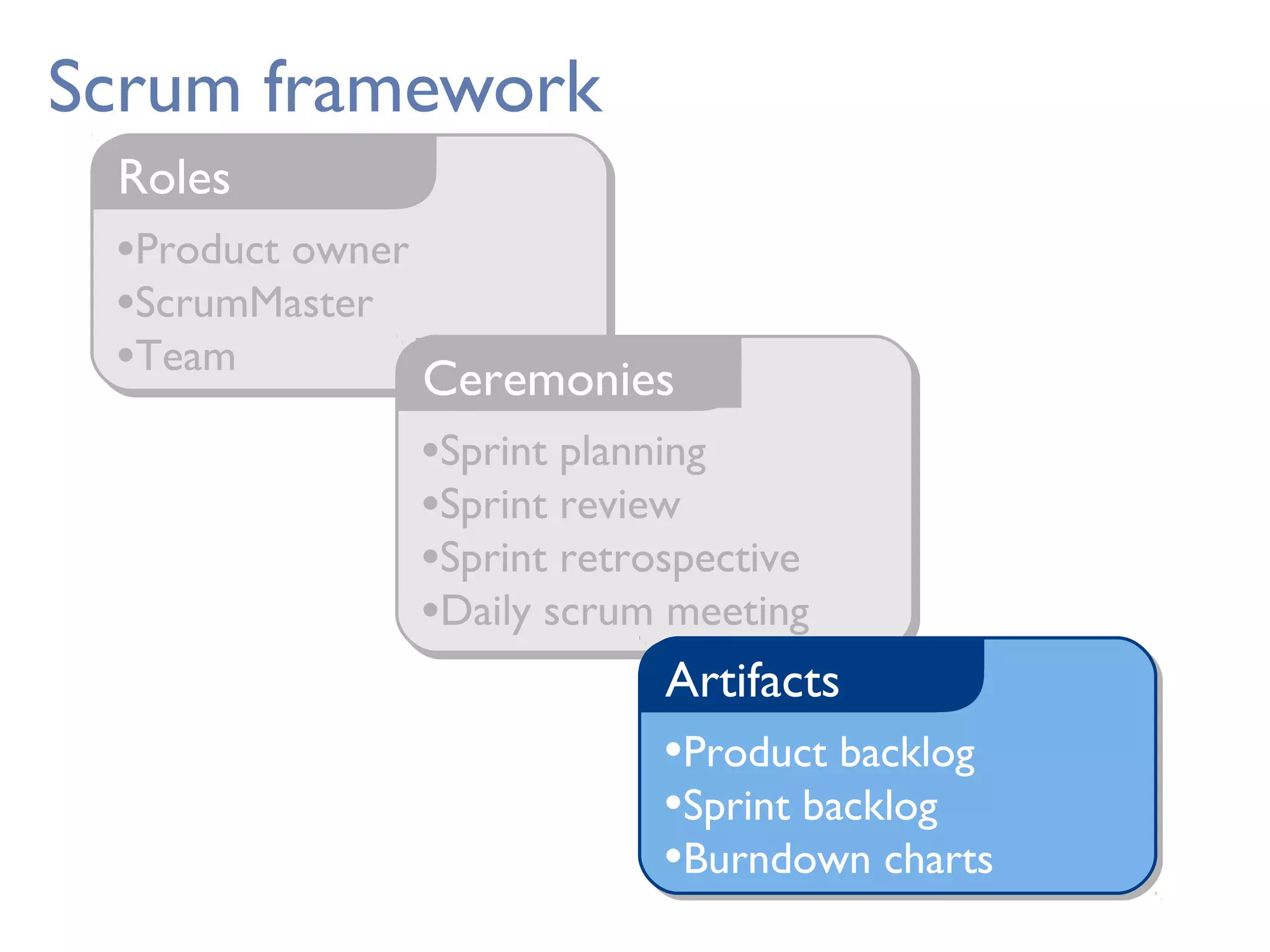
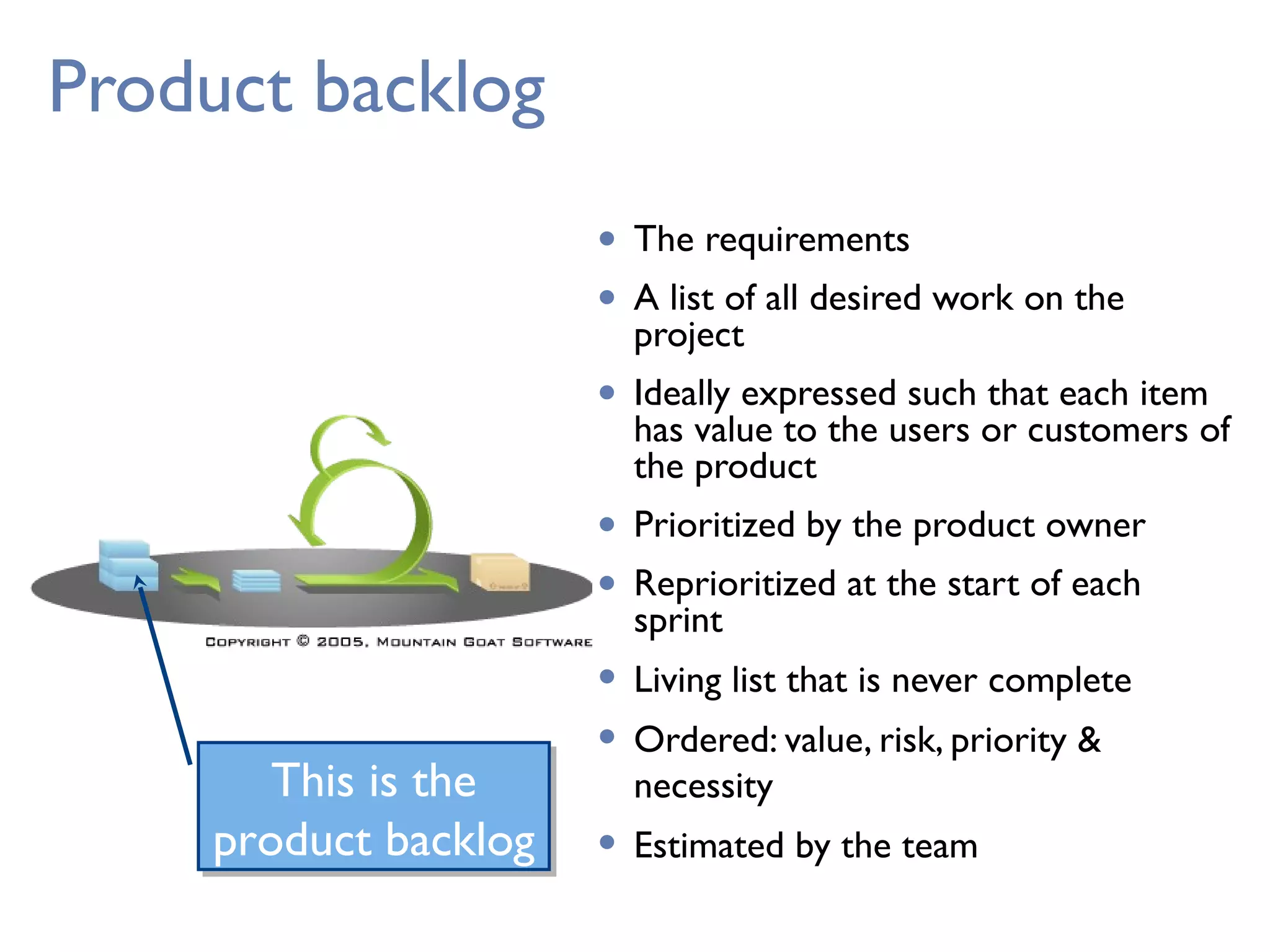
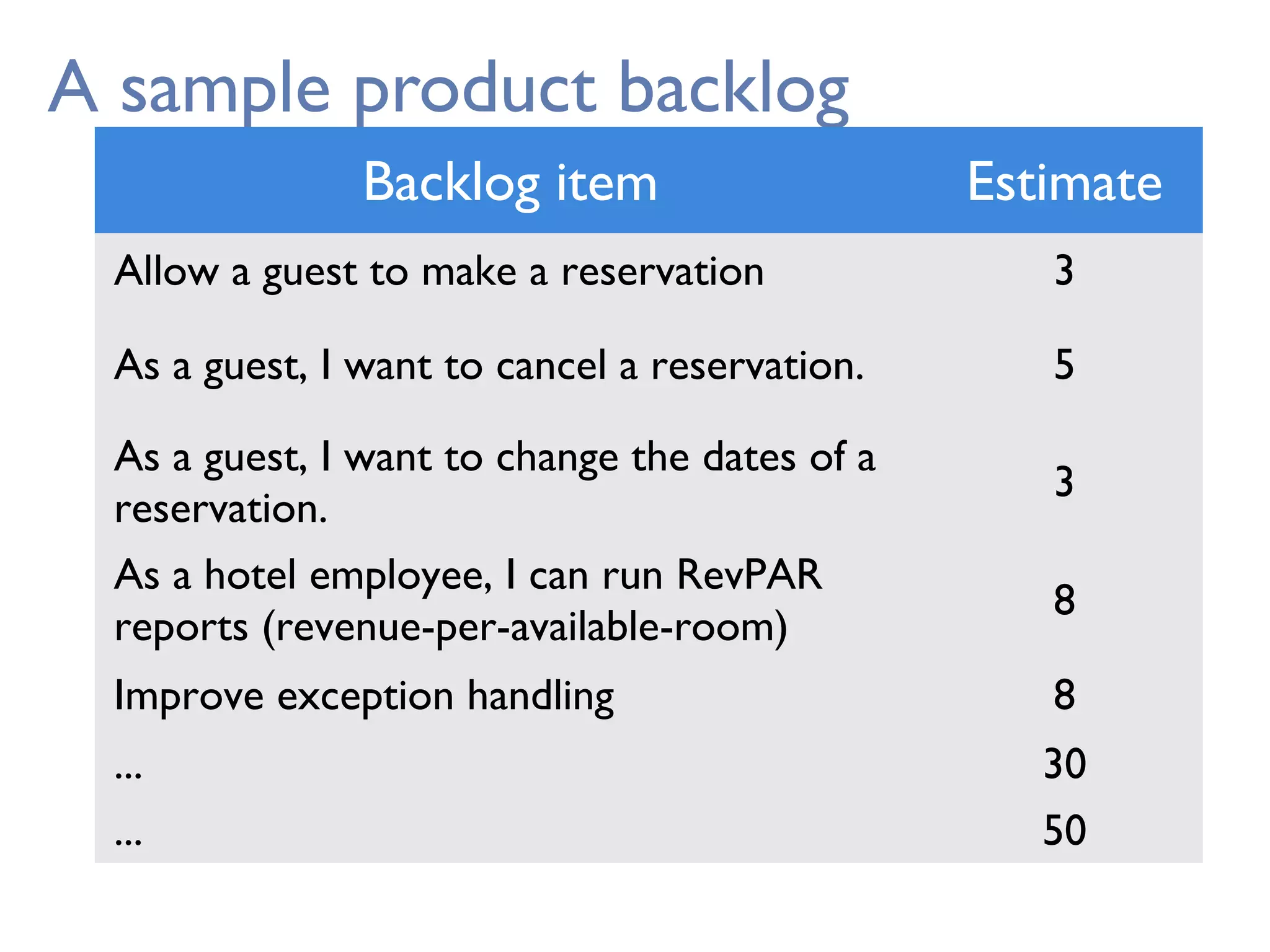
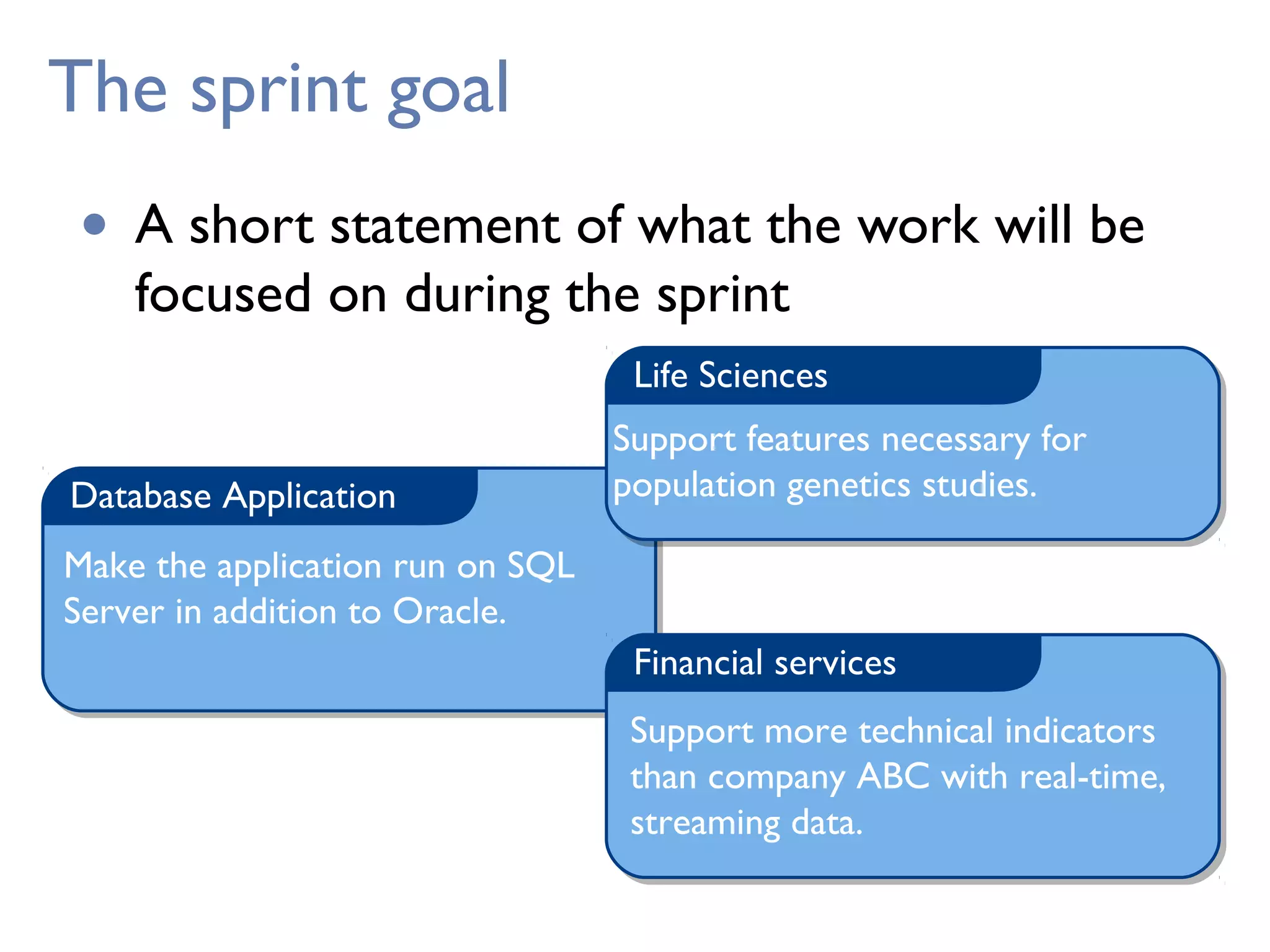
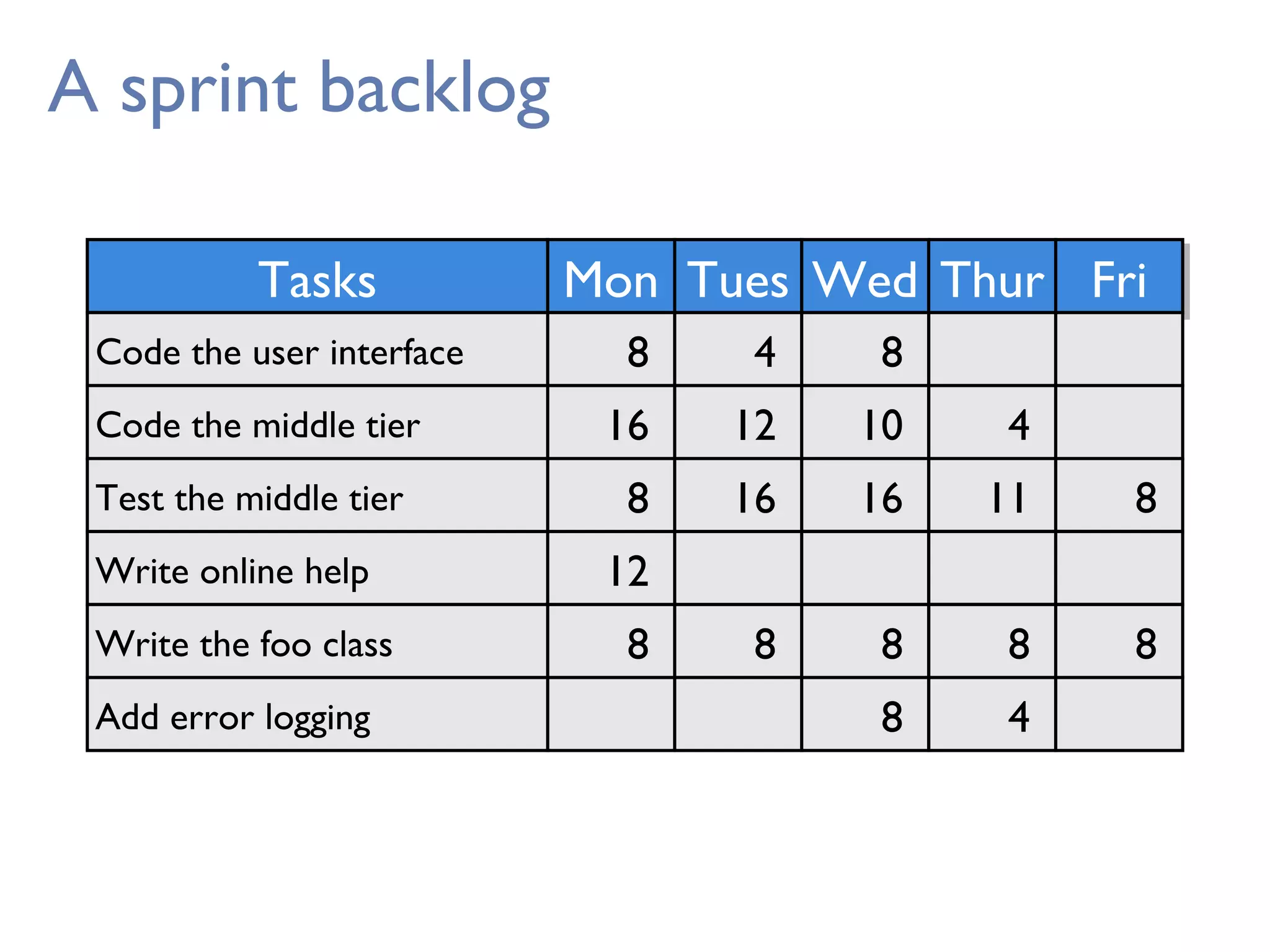
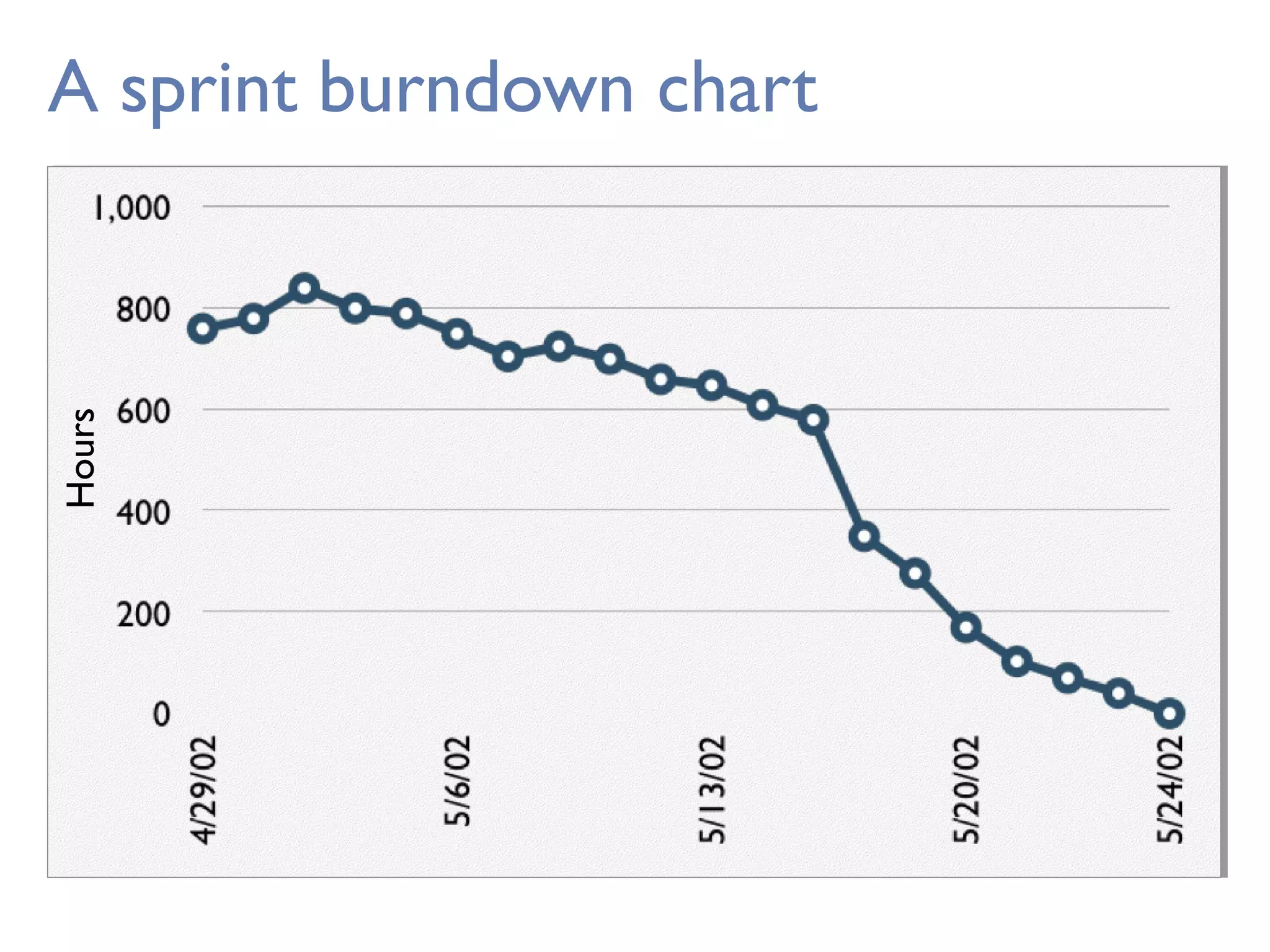
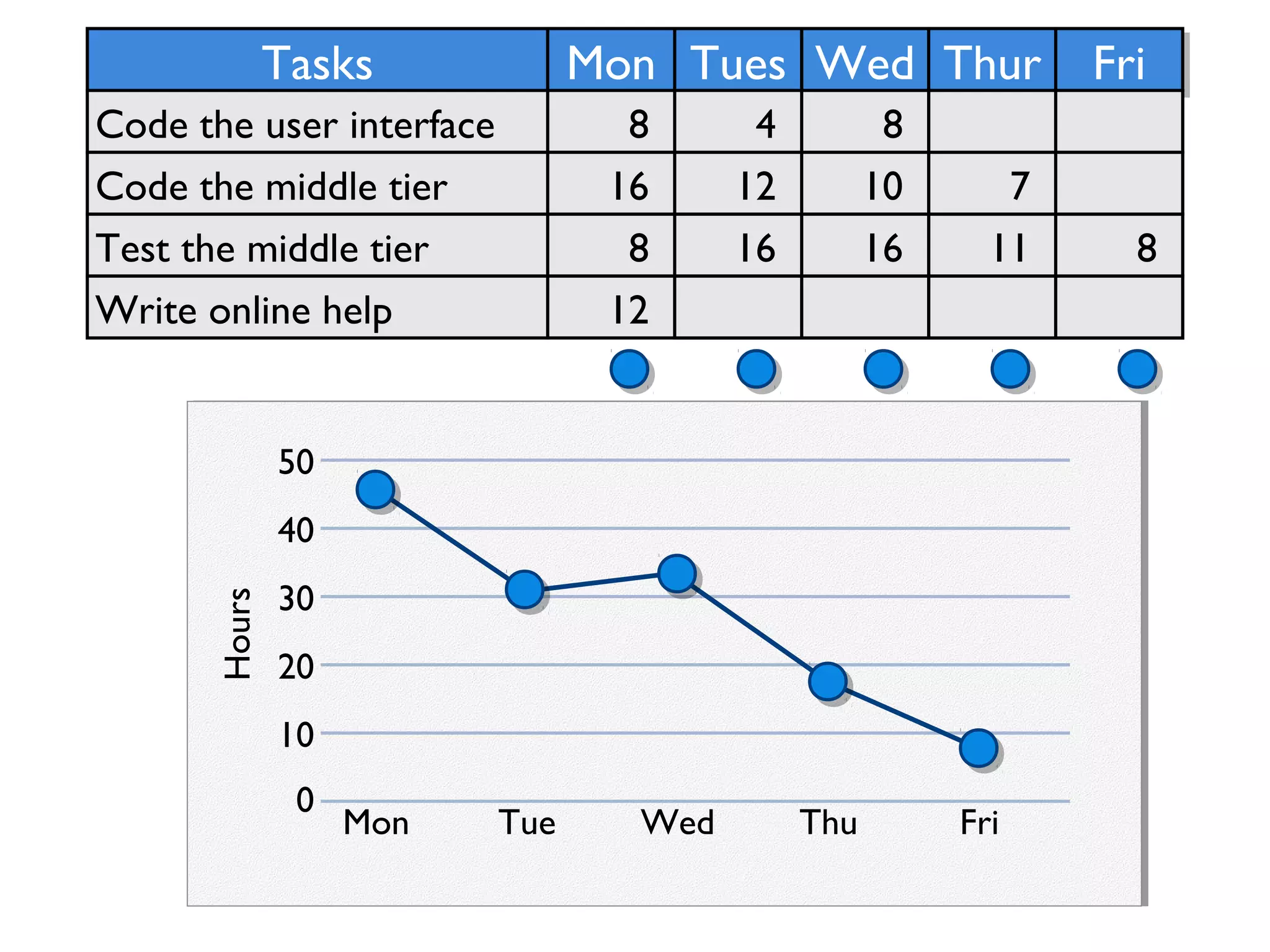
This document provides an overview of Scrum, an agile framework for project management. It describes key Scrum roles like the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and self-organizing team. It outlines common Scrum events like sprint planning, daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives. It also explains main Scrum artifacts like the product backlog, sprint backlog, and burn down charts that are used to track work. The document aims to explain the basic concepts, roles, events, and artifacts that make up the Scrum framework.