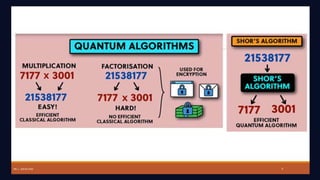
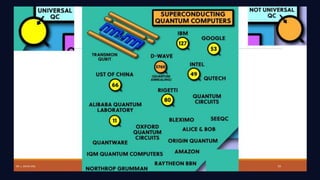
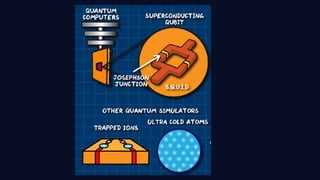
Quantum computing leverages quantum mechanics to perform computations far surpassing classical computers, utilizing qubits that can exist in superposition and exhibit entanglement. Key applications include advancements in cryptography, drug discovery, optimization, and sensing, with ongoing developments driving commercialization and the potential for quantum supremacy. The document encourages further exploration and engagement with quantum computing advancements in both technical and practical contexts.