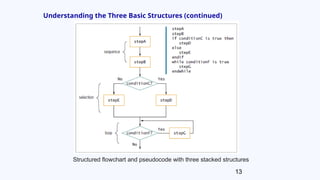
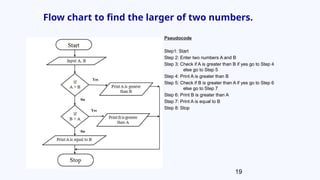
The document provides an overview of basic programming structures, specifically focusing on sequence, selection, and loop. It describes how each structure operates, including examples of flowcharts and pseudocode to illustrate their implementation. Additionally, it discusses the concept of nesting structures and the characteristics of structured programs.