The document discusses several key topics in computer science and programming:
1. It defines programming languages as sets of instructions used to communicate with computers and develop applications. It distinguishes between low-level languages like machine code and assembly, and high-level languages like Python, Java, and C++.
2. It also covers markup languages like HTML and XML used to structure documents, and scripting languages like Python, Ruby, and Perl used to integrate systems.
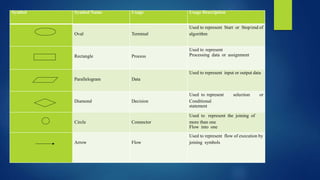
3. The document outlines the program development process of understanding problems, designing solutions, writing code, and testing programs. It introduces flowcharts, pseudocode, and algorithms used in the design process.
4. Finally, it provides an overview