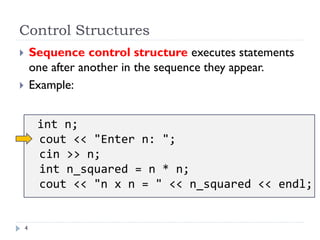
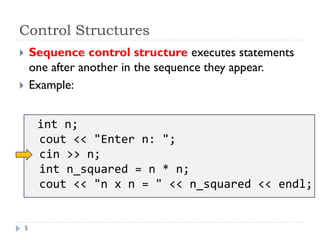
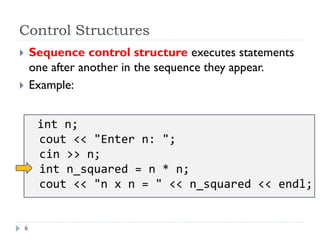
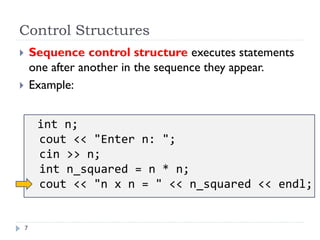
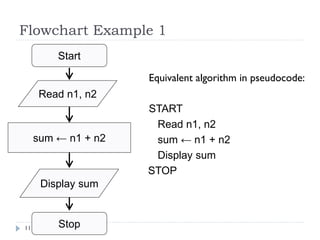
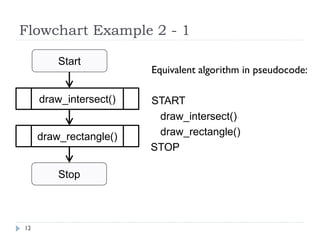
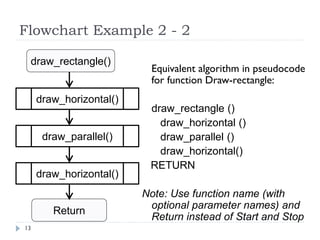
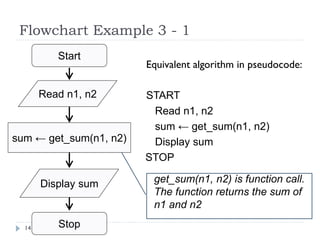
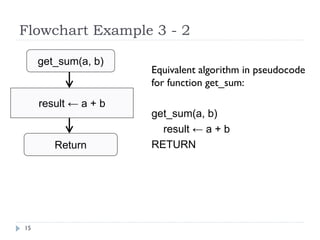
The document discusses control structures and flowcharts. There are three types of control structures: sequence, selection, and repetition. Sequence executes statements in order. Selection chooses between alternatives using conditional statements. Repetition repeats a block of code. Flowcharts use graphic symbols to represent program logic and flow. Common symbols include terminals, flow lines, and connectors. Flowcharts are similar to pseudocode and can model algorithms to solve problems.