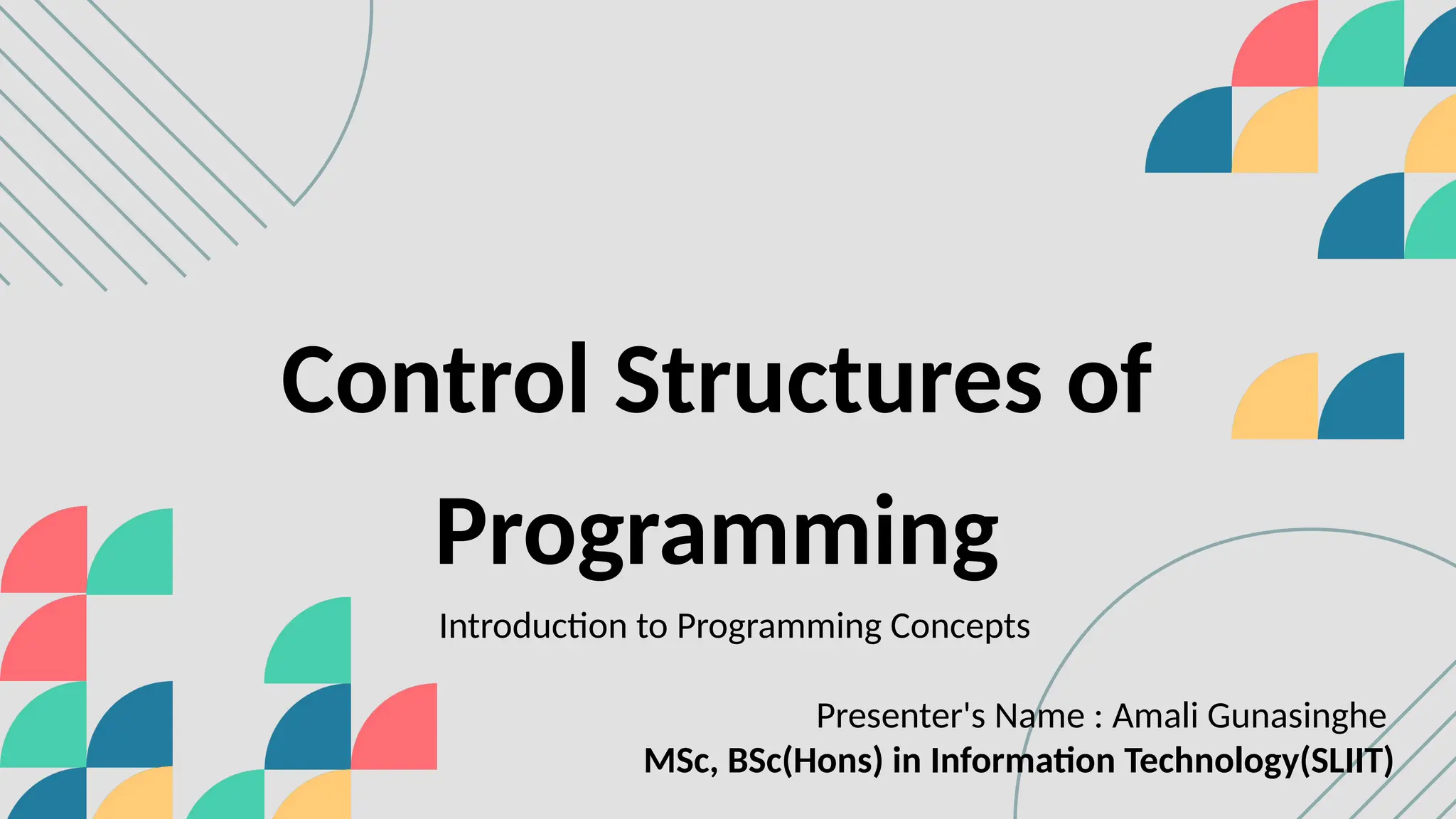
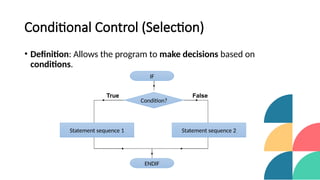
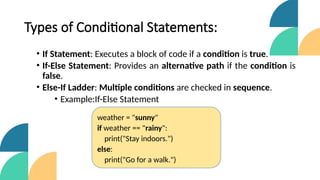
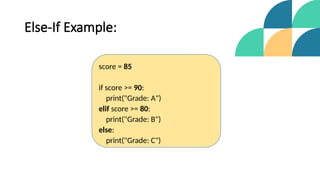
The document introduces control structures in programming, emphasizing their importance in managing program flow through sequential, conditional, iterative, and branching methods. It provides definitions, examples, and types for each control structure, illustrating their practical applications in programming. The lecture aims to equip students with the ability to implement these structures effectively in their coding practices.








![References
1) B. W. Kernighan and D. M. Ritchie, The C Programming Language, 2nd ed. Upper Saddle River,
NJ, USA: Prentice Hall, 1988.
2) S. G. Kochan, Programming in C, 4th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA: Addison-Wesley
Professional, 2014.
3) M. Sipser, Introduction to the Theory of Computation, 3rd ed. Boston, MA, USA: Cengage
Learning, 2012.
4) GeeksforGeeks, "Control Structures in C," [Online]. Available: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org.
[Accessed: 27-Aug-2024].
5) TutorialsPoint, "Control Structures," [Online]. Available: https://www.tutorialspoint.com.
[Accessed: 27-Aug-2024].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlstructuresofprogramming-240908141332-e92916cb/85/Control-Structures-of-Programming-Introduction-to-Programming-Concepts-14-320.jpg)
