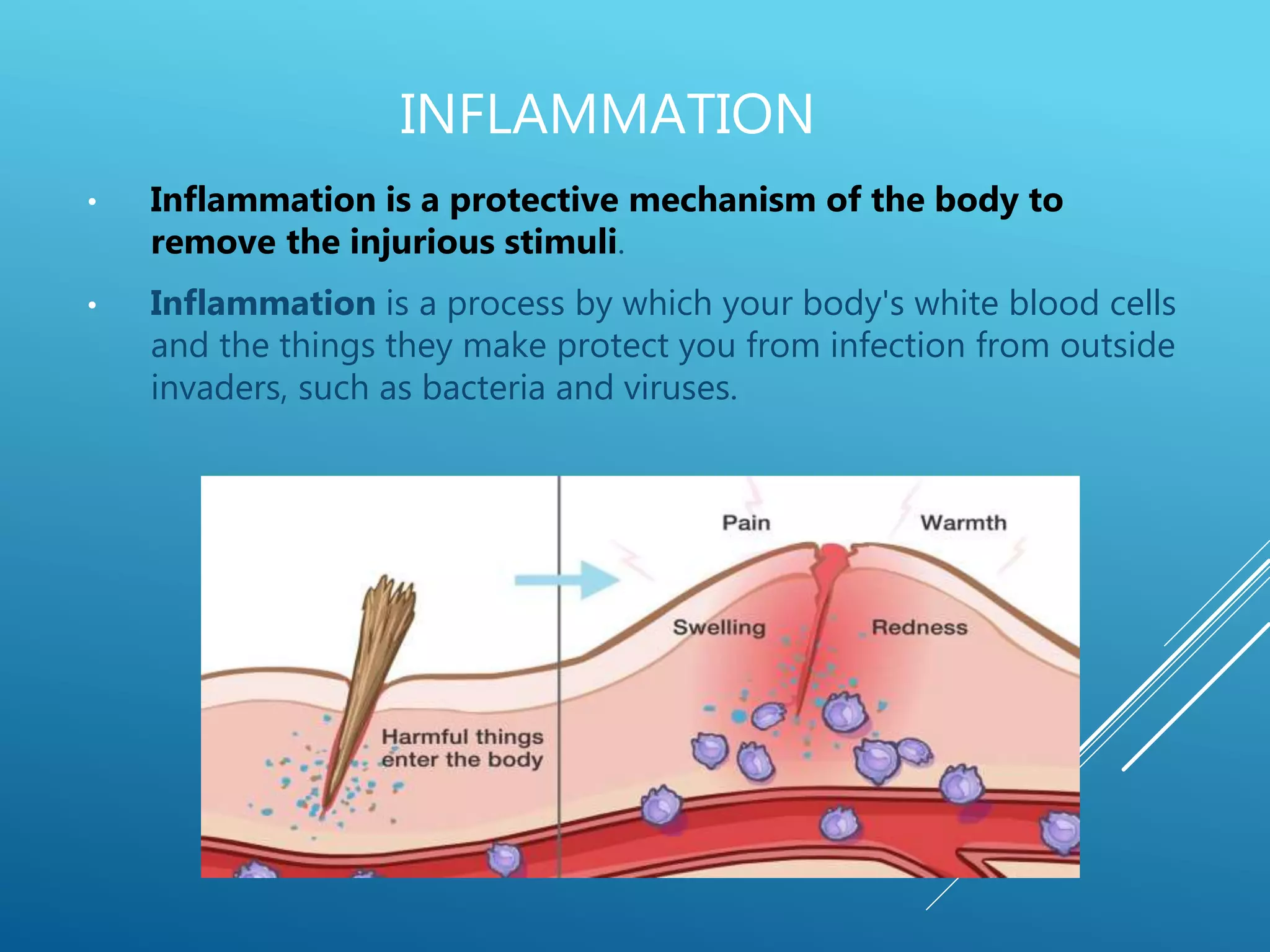
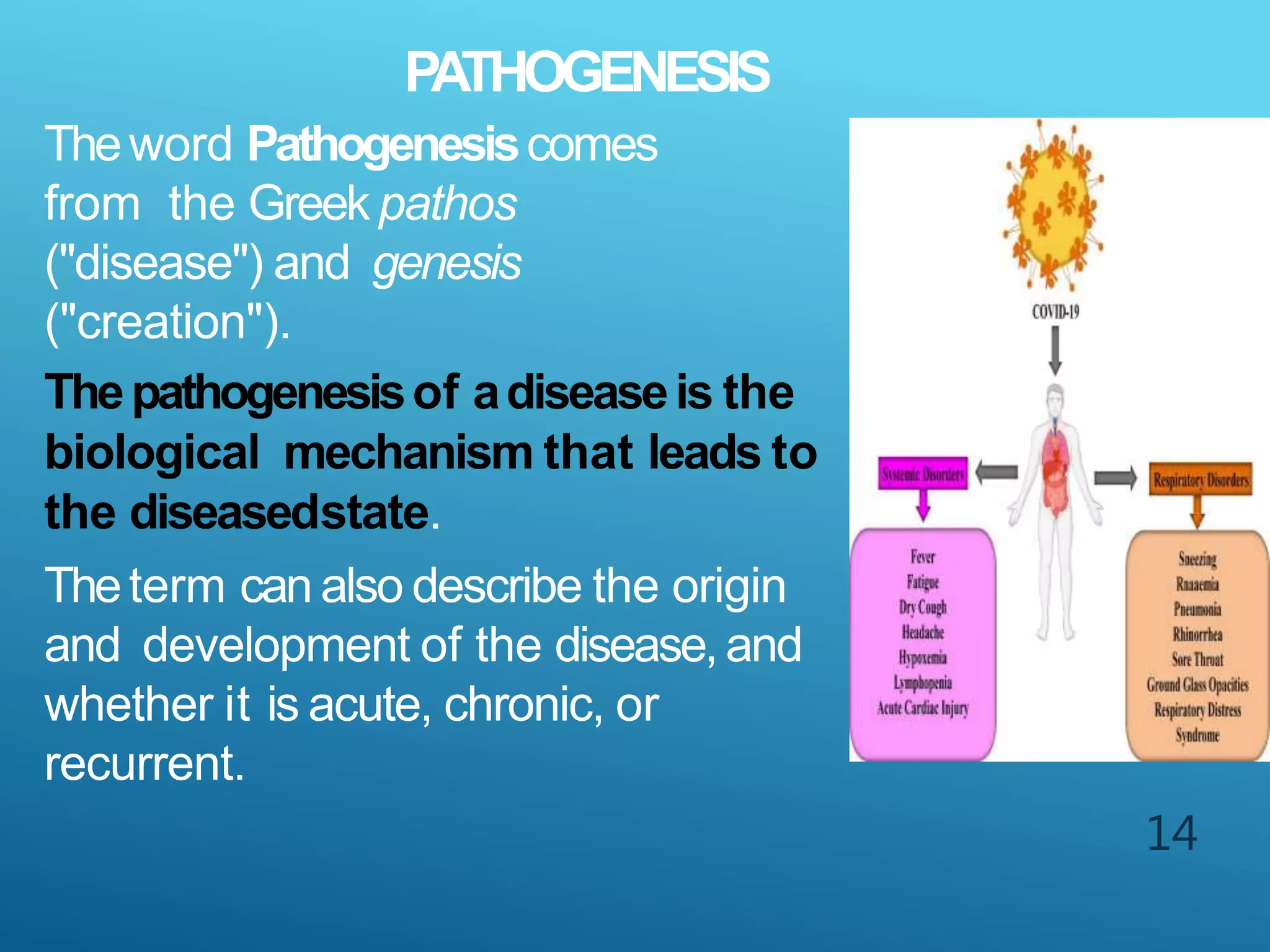
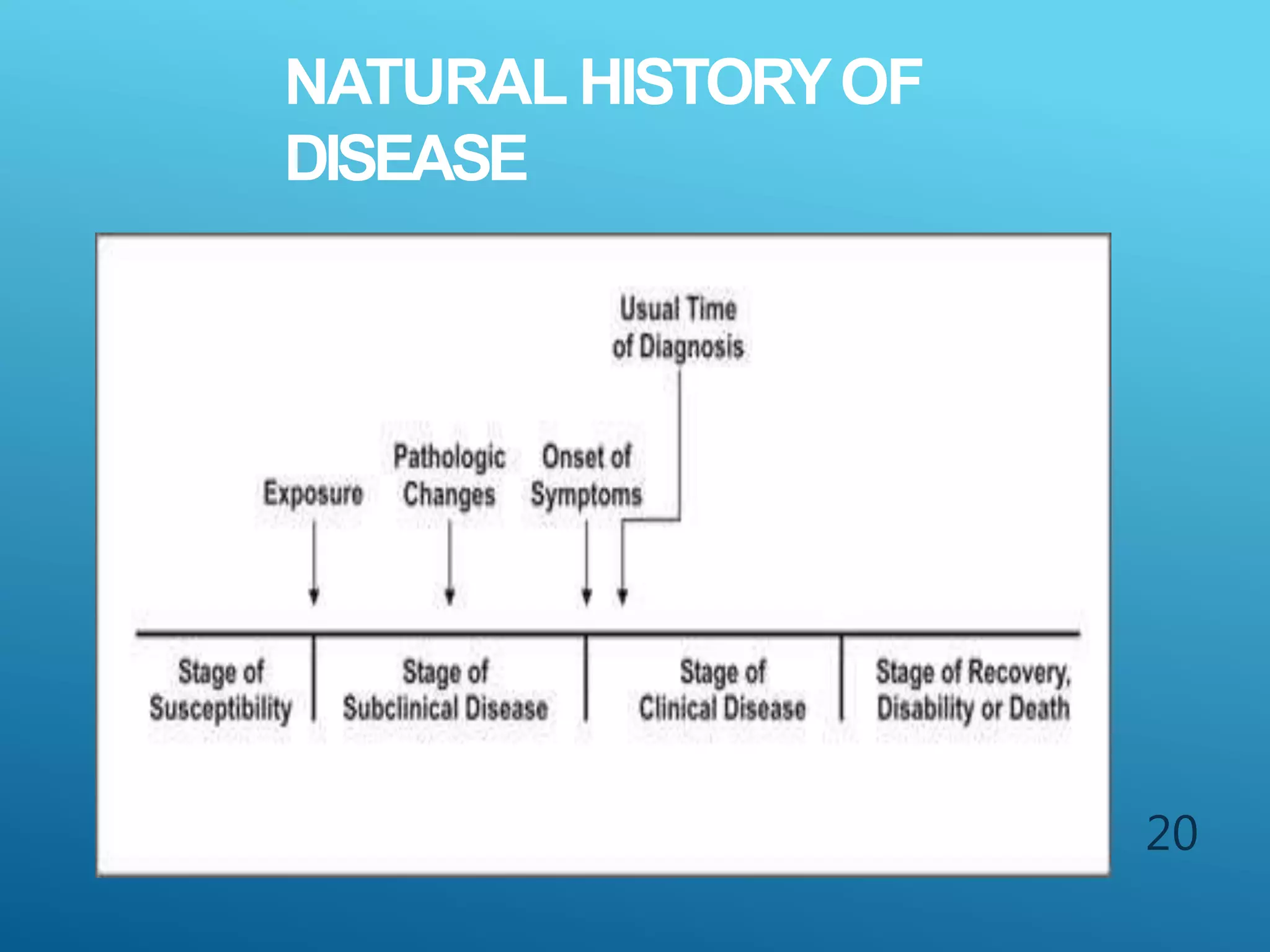
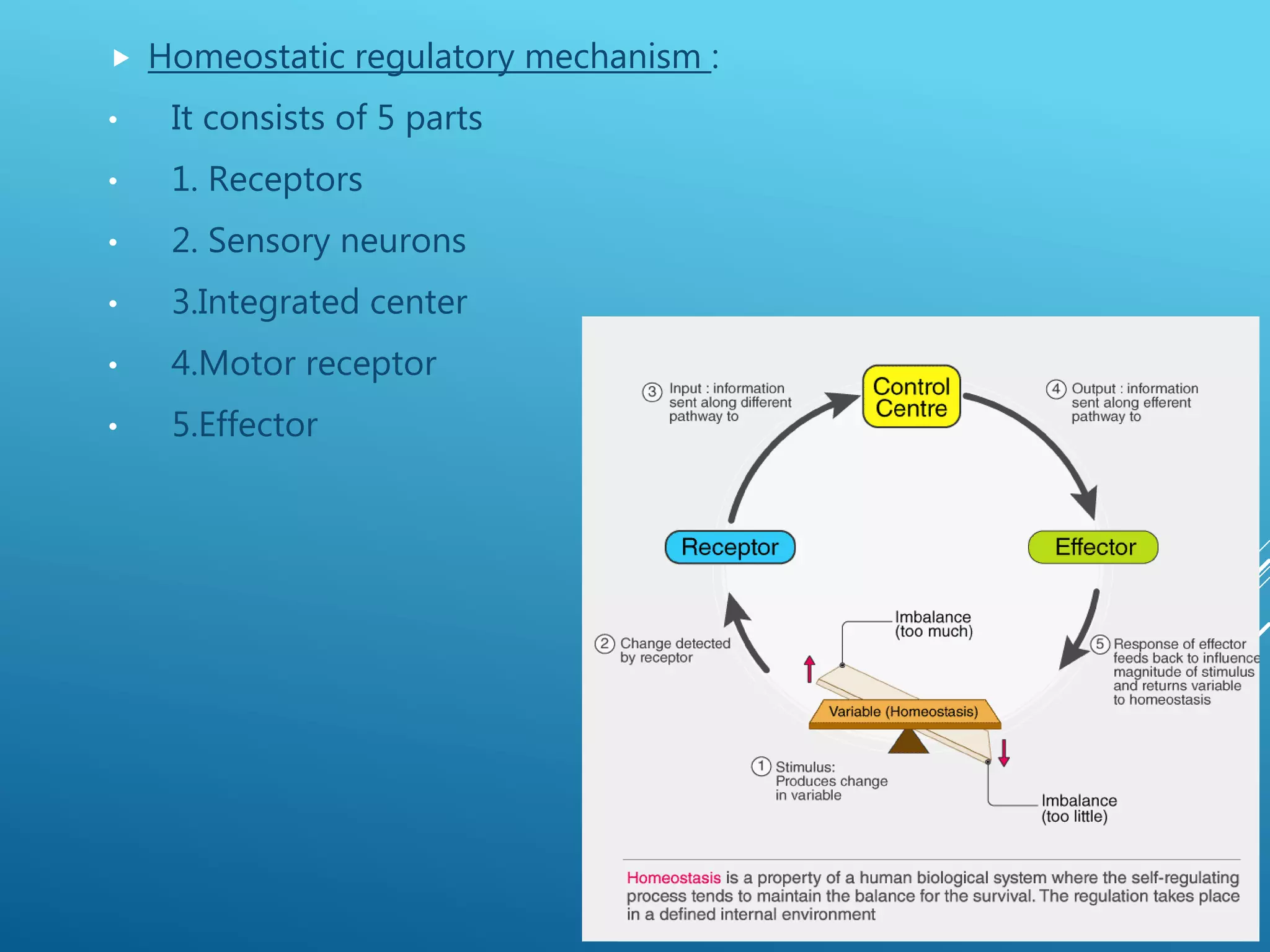
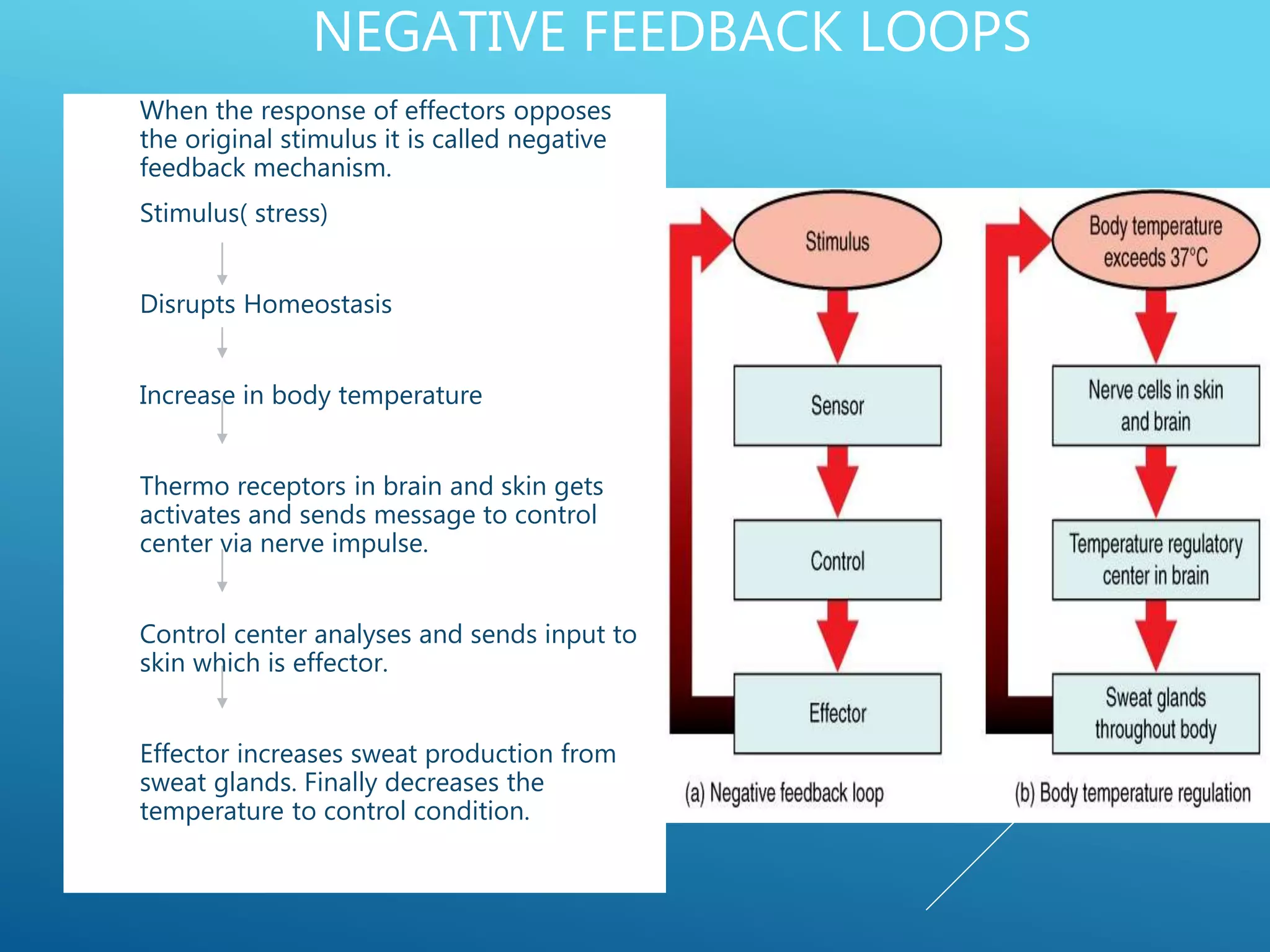
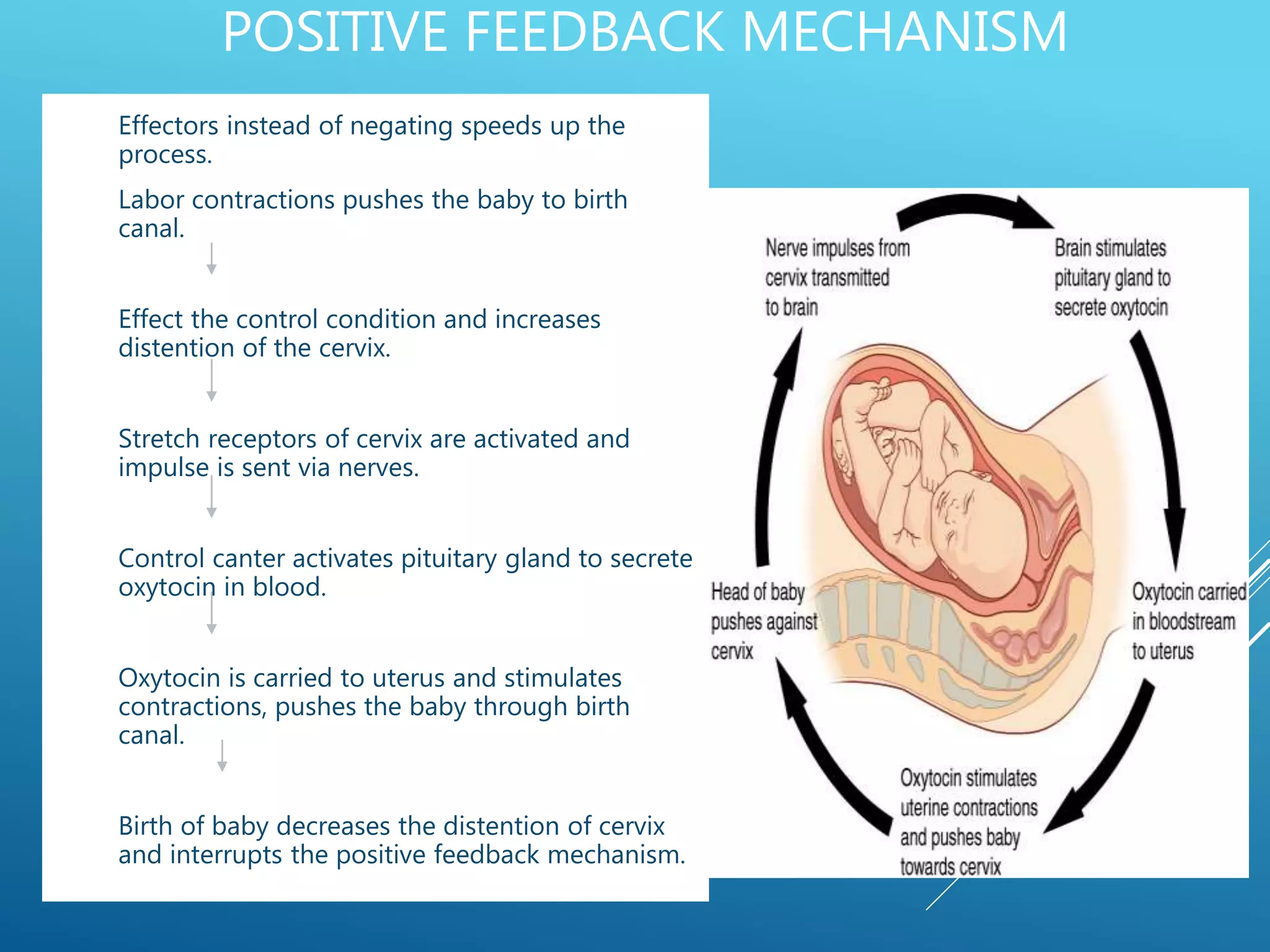
The document discusses the fields of pathology and pathophysiology, emphasizing their importance in understanding disease mechanisms and mechanisms of the body’s response to injuries. It covers various branches including clinical pathology, clinical biochemistry, microbiology, hematology, and immunology, detailing their roles in disease diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, it outlines the concepts of disease, disorder, inflammation, infection, and homeostasis, and explains the significance of studying pathophysiology for healthcare professionals.