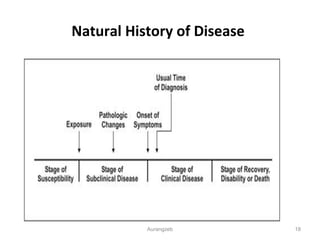
This document provides an introduction to pathophysiology. It defines pathology and pathophysiology, and differentiates them from other biomedical sciences. The document discusses the basic concepts of disease development, including the five components of the disease process: prevalence, etiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestation, and outcomes. It also provides overview definitions and examples of key topics in pathology, including clinical pathology, clinical biochemistry, clinical microbiology, hematology, clinical immunology, and molecular pathology.