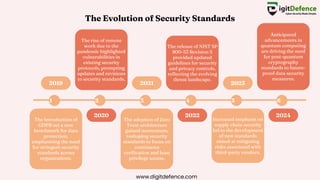
The document outlines the importance of network security protocols as foundational elements for protecting data integrity, confidentiality, and authentication in digital communications. It discusses key protocols such as SSL and TLS, as well as other security frameworks and standards, emphasizing the evolving landscape of cybersecurity and emerging technologies like blockchain and AI. Recent advancements and trends, such as the impact of GDPR and the rise of zero trust architecture, highlight ongoing developments in security standards to combat modern threats.