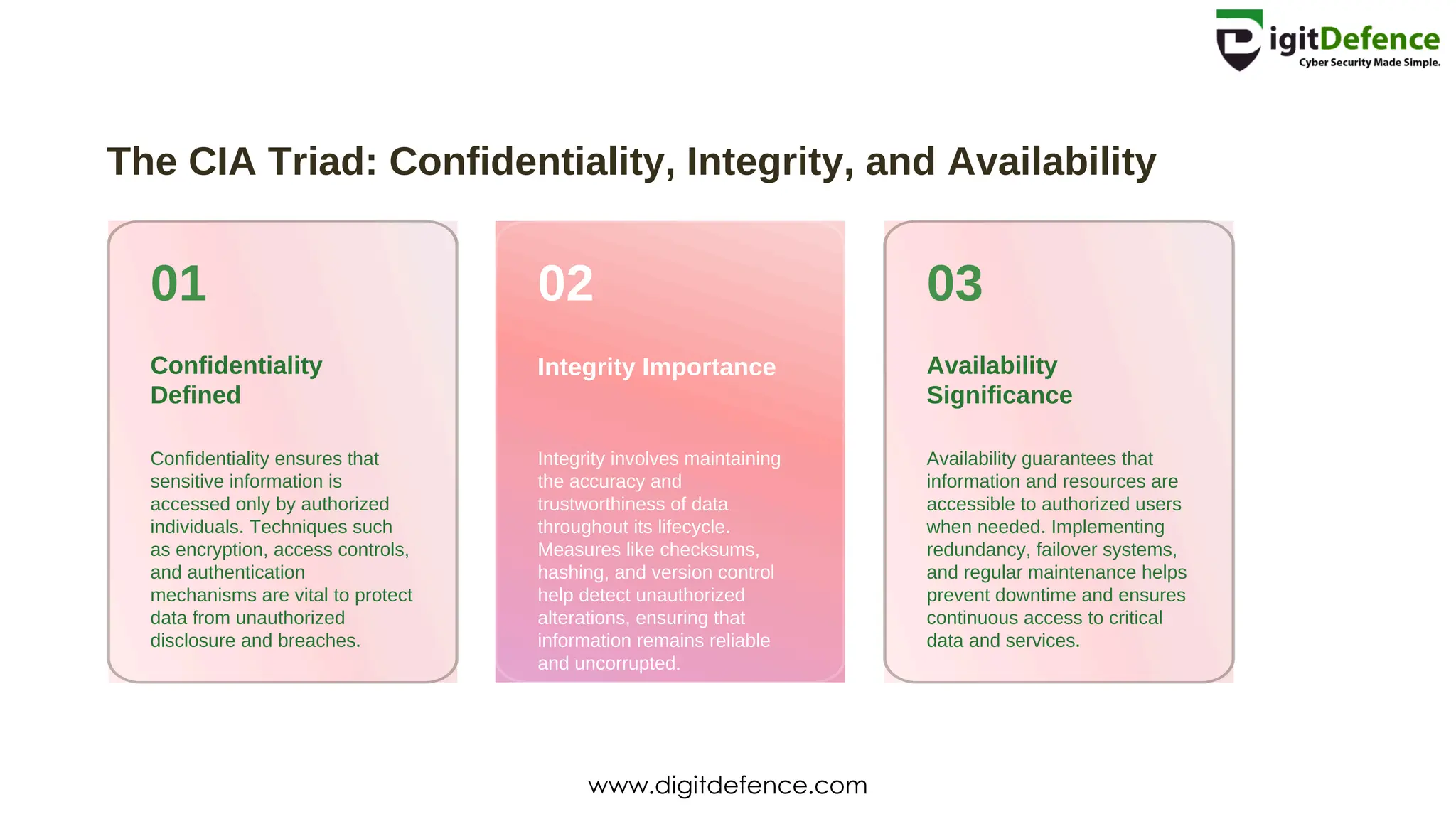
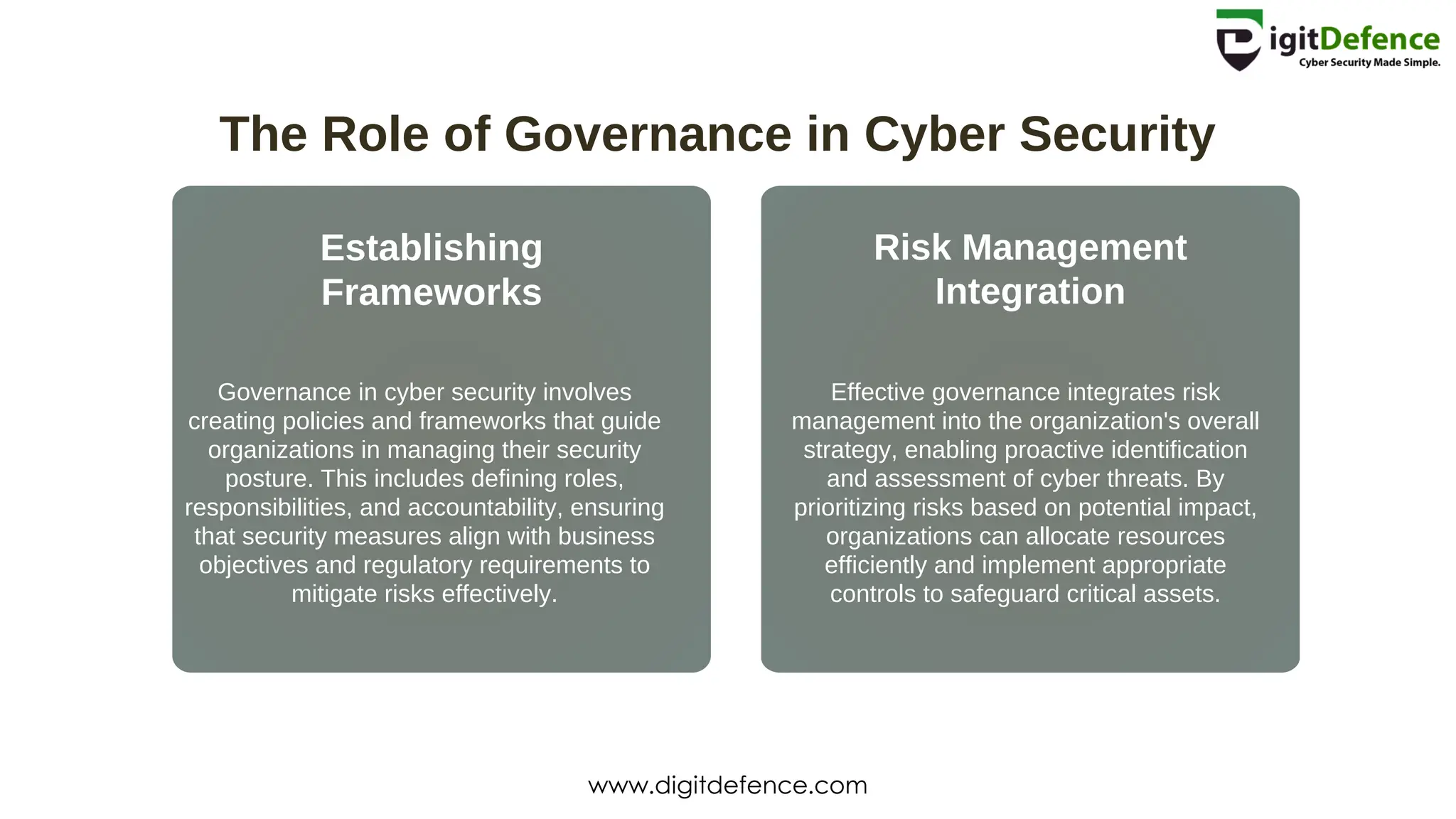
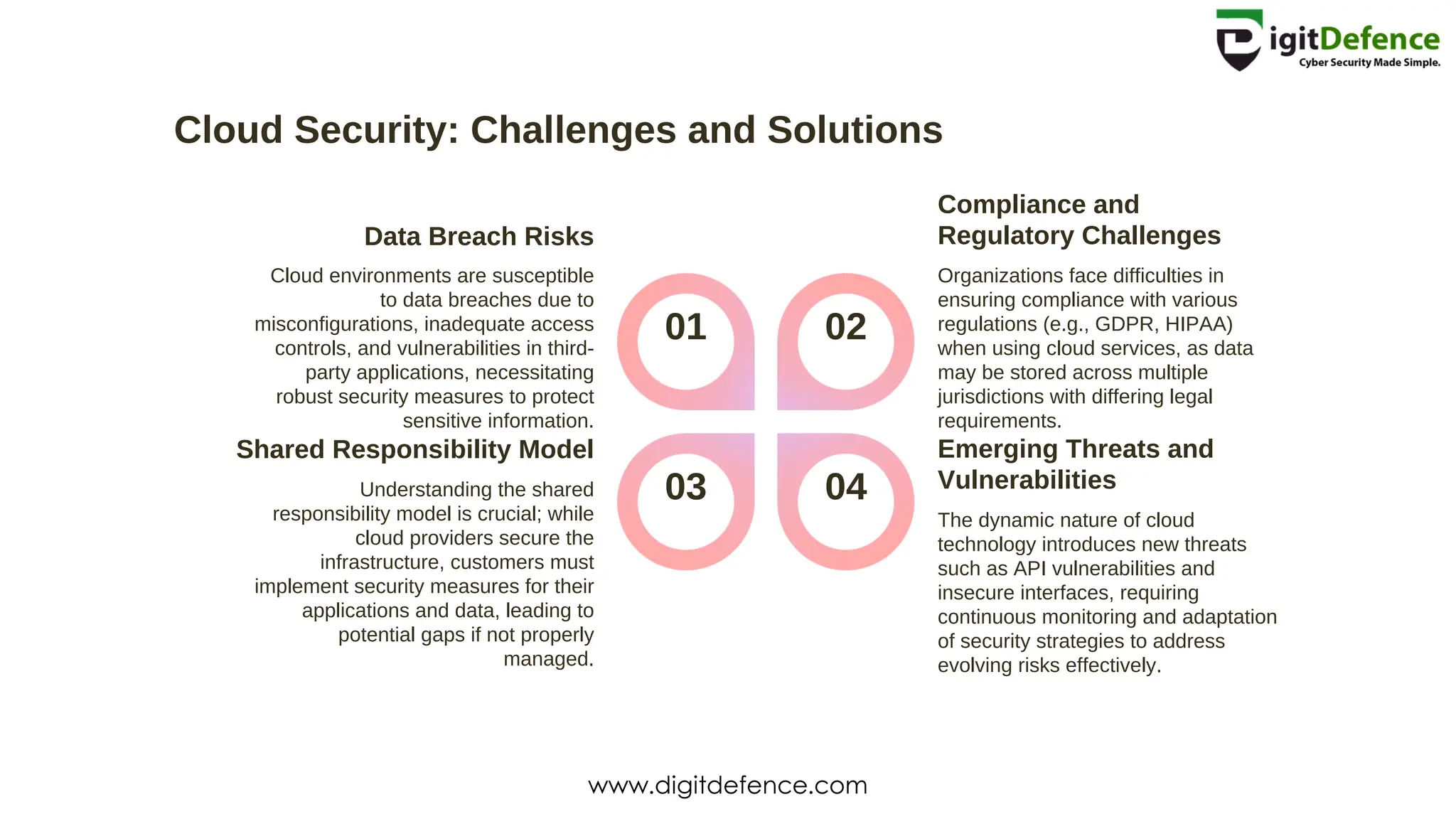
The document outlines the critical components of cyber security, including its definition, importance, and the CIA triad: confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It highlights key threats such as malware, phishing, and insider threats, and emphasizes the role of governance, security awareness, and continuous monitoring in managing cyber risks. Additionally, it addresses the challenges of cloud security and the implications of IoT on data privacy and security vulnerabilities.