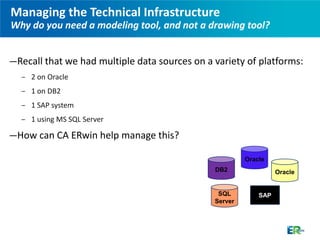
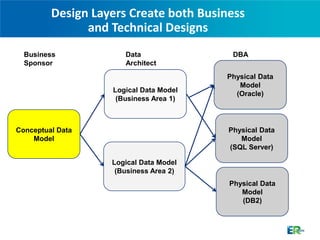
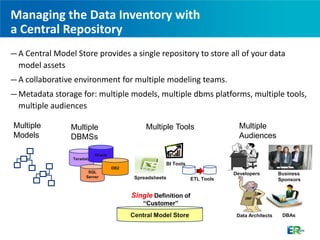
The document discusses CA ERwin, a data modeling tool that can be used to visualize data across different platforms through conceptual, logical, and physical data models in order to effectively manage increasingly complex data environments with multiple databases and applications. CA ERwin provides a centralized repository for storing metadata from multiple data sources and supports communication between business and technical stakeholders through intuitive reports and high-level conceptual models.