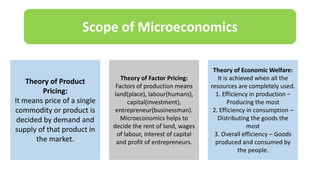
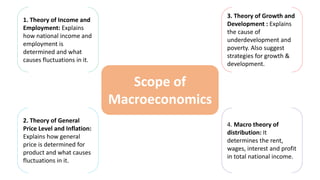
1. Microeconomics studies individual components of the economy such as consumers, producers, and prices of individual goods, while macroeconomics looks at aggregates for the entire economy such as total output, employment, and income.
2. Microeconomics focuses on partial equilibrium analysis and determining prices through supply and demand, while macroeconomics uses general equilibrium analysis and considers the interdependence between economic variables.
3. Both microeconomics and macroeconomics are important for understanding economic decisions, developing policies, and analyzing fluctuations and growth at different levels of the economy.