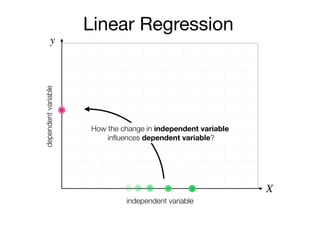
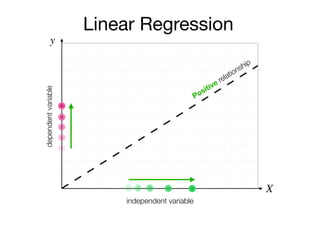
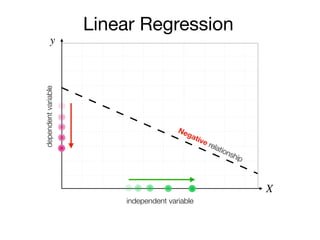
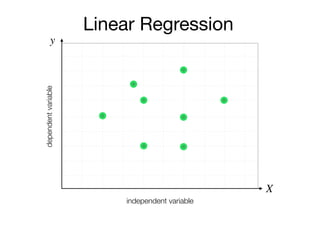
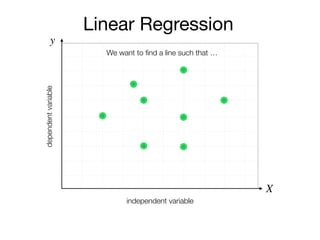
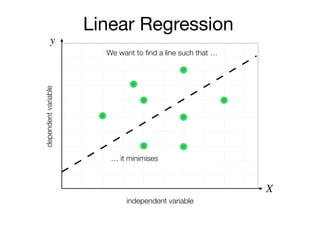
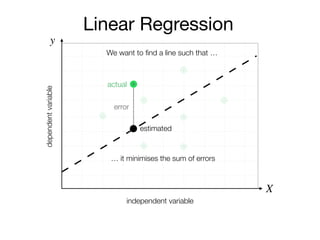
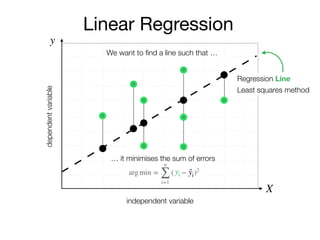
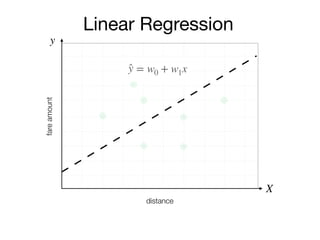
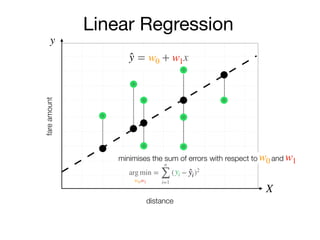
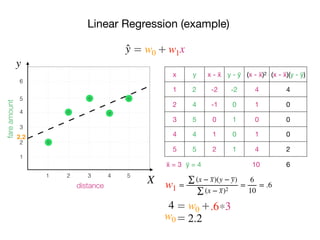
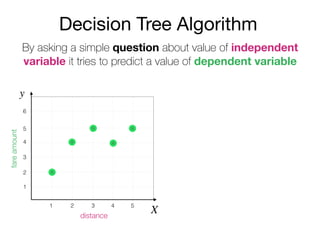
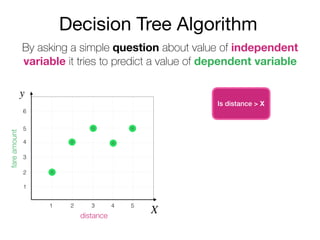
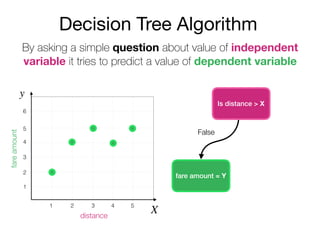
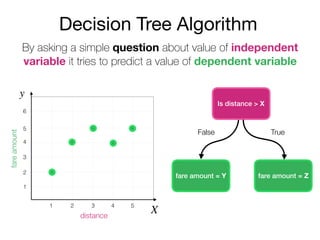
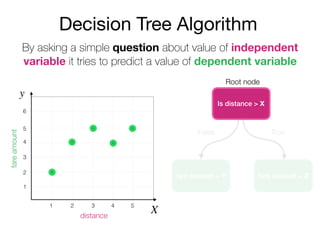
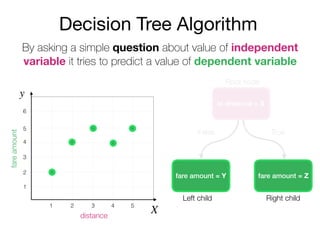
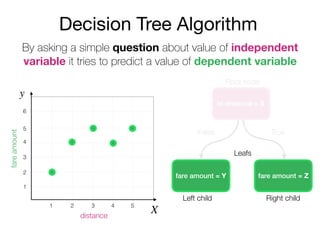
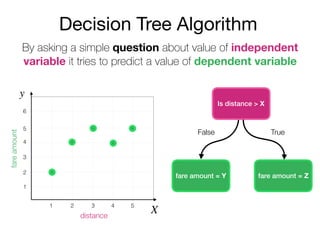
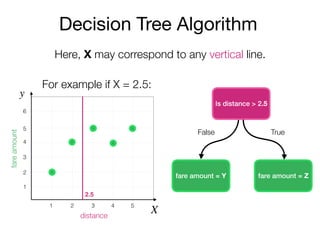
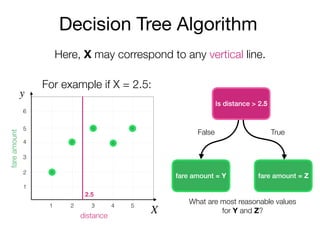
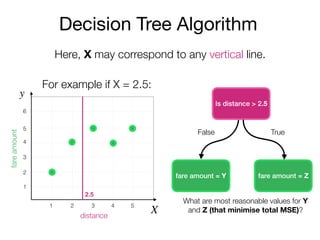
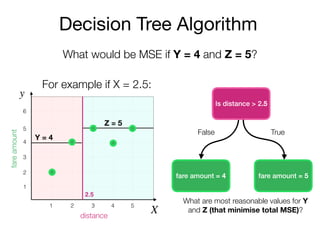
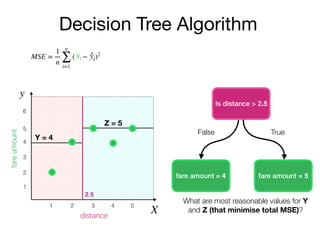
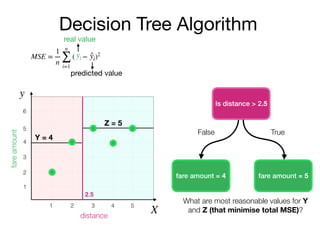
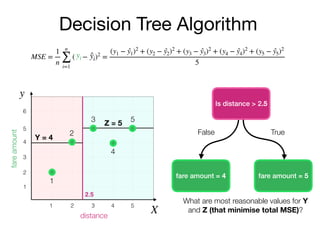
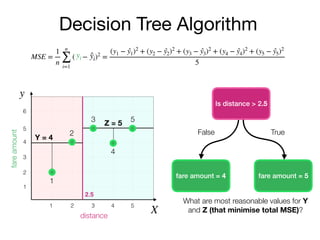
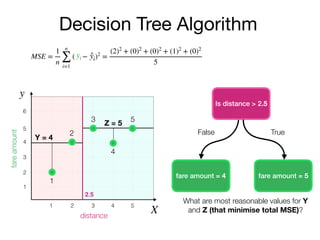
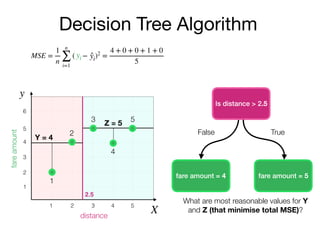
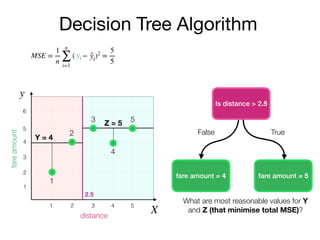
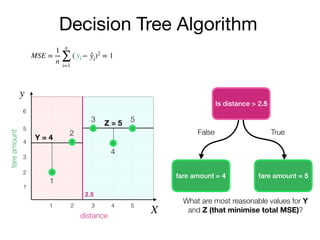
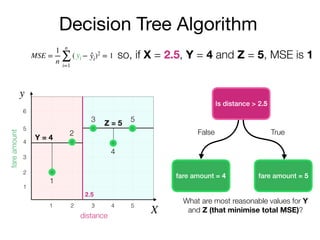
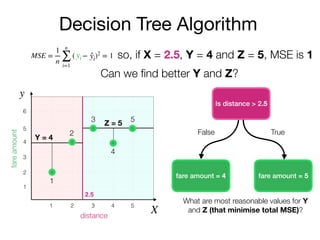
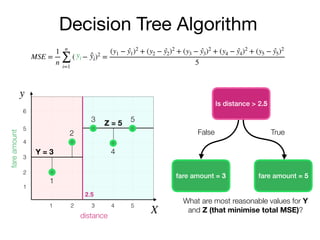
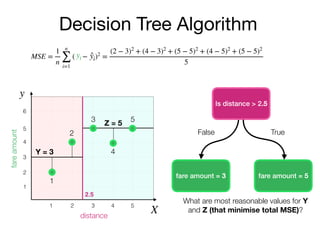
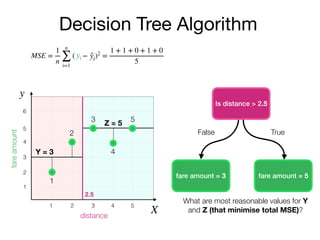
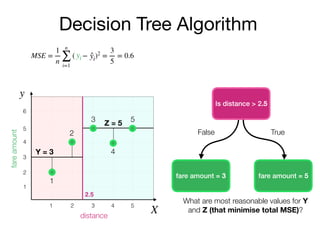
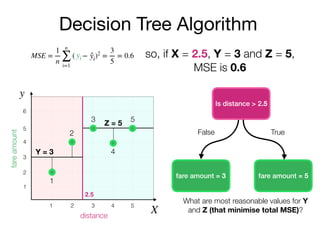
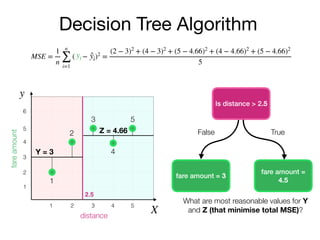
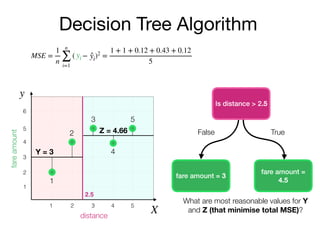
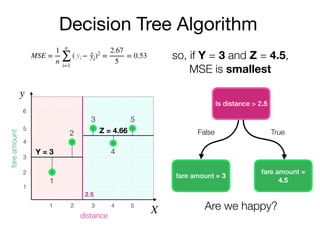
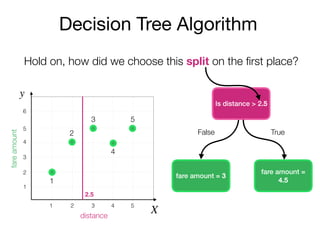
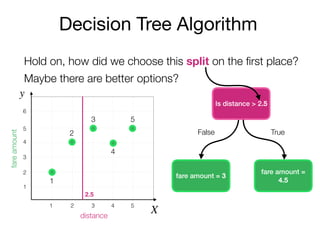
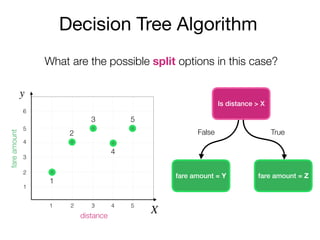
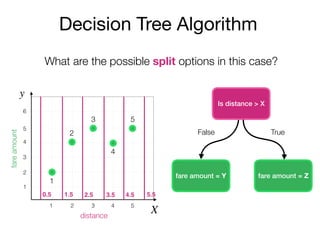
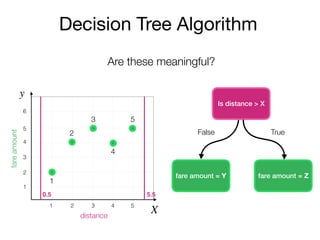
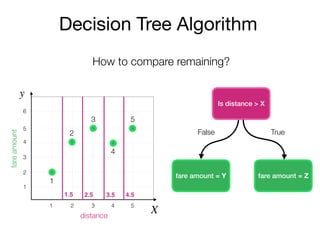
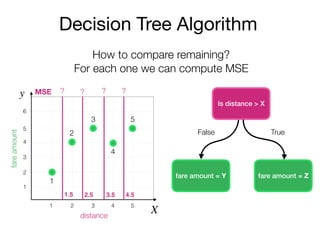
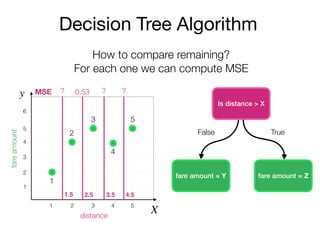
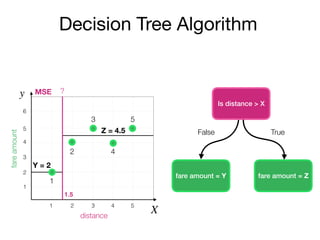
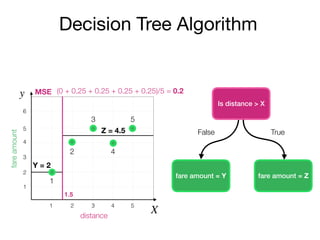
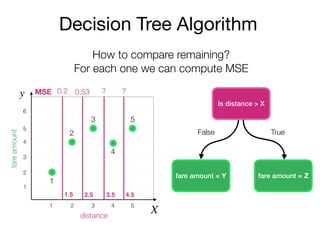
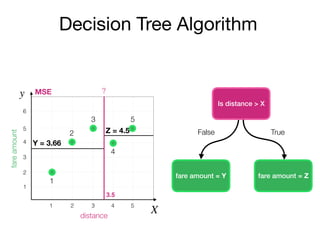
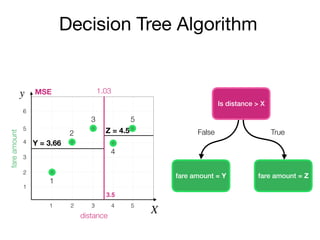
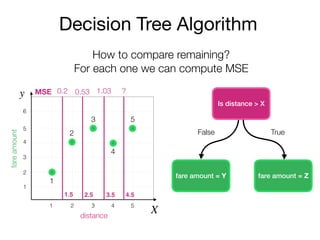
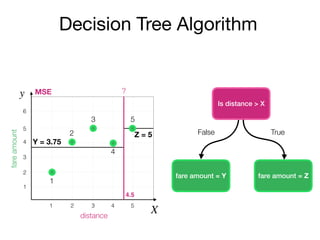
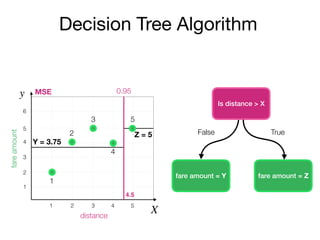
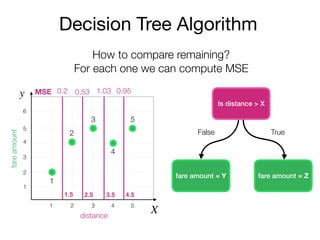
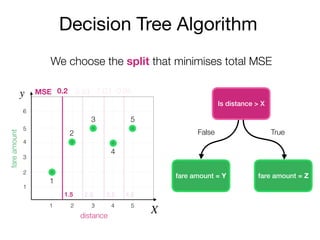
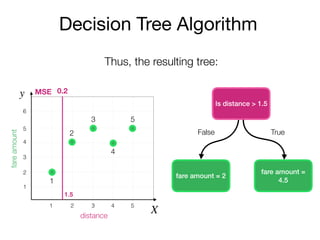
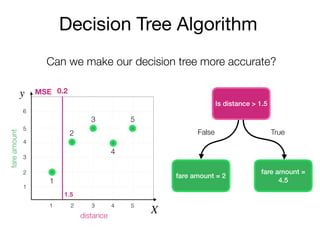
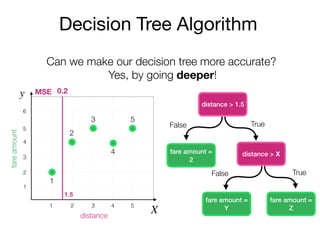
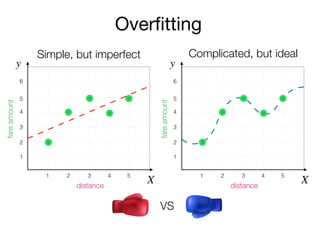
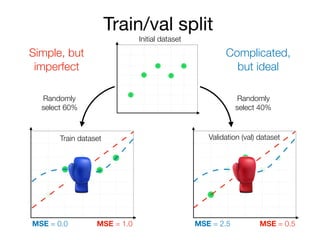
The document outlines a lecture on machine learning focused on predicting New York City taxi fares using linear regression and decision trees. It discusses the importance of independent and dependent variables and the minimization of errors using methods like least squares. Additionally, it explains the functioning of decision tree algorithms and how they can be applied to regression problems in predicting fare amounts based on distance.