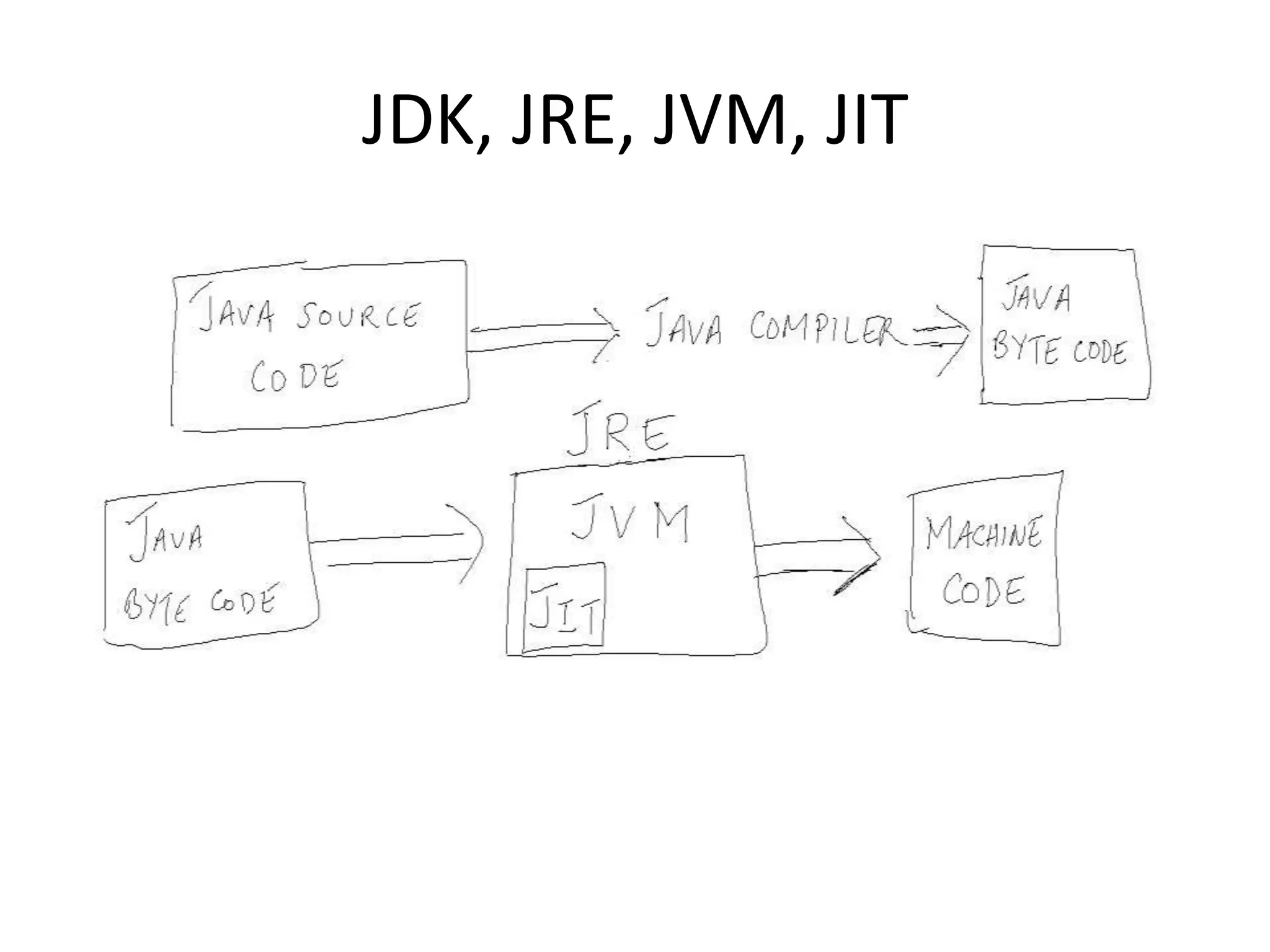
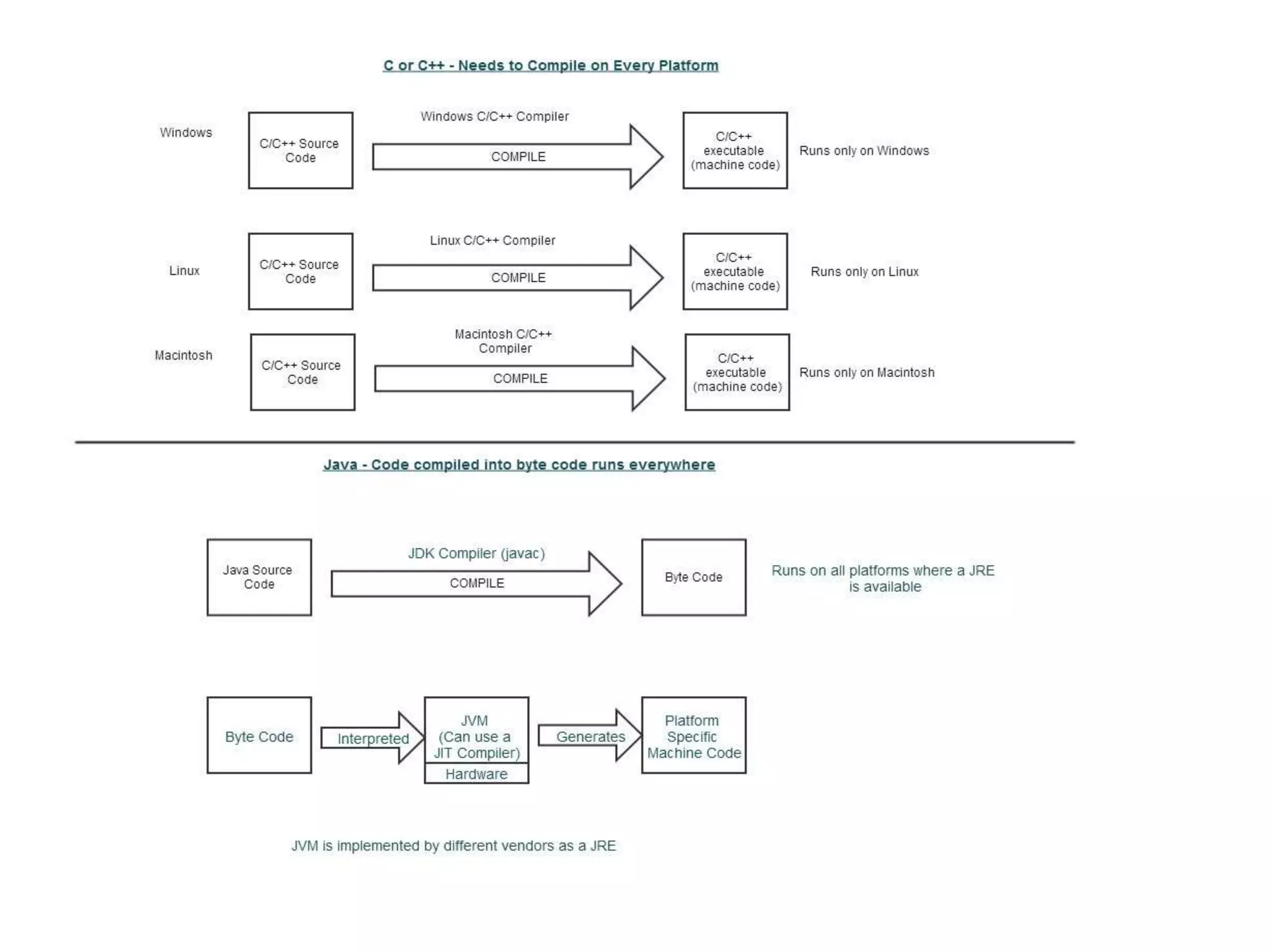
This document provides an introduction to Java, including descriptions of the Java ecosystem, the Java Development Kit (JDK), Java Runtime Environment (JRE), and key features of Java such as portability, object orientation, and security. The JDK contains development tools like compilers and debuggers as well as the JRE, which runs Java programs. The JRE includes the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and class libraries. The JVM interprets bytecode into machine code and includes a just-in-time (JIT) compiler to improve performance. Java's portability comes from writing bytecode rather than platform-specific machine code.