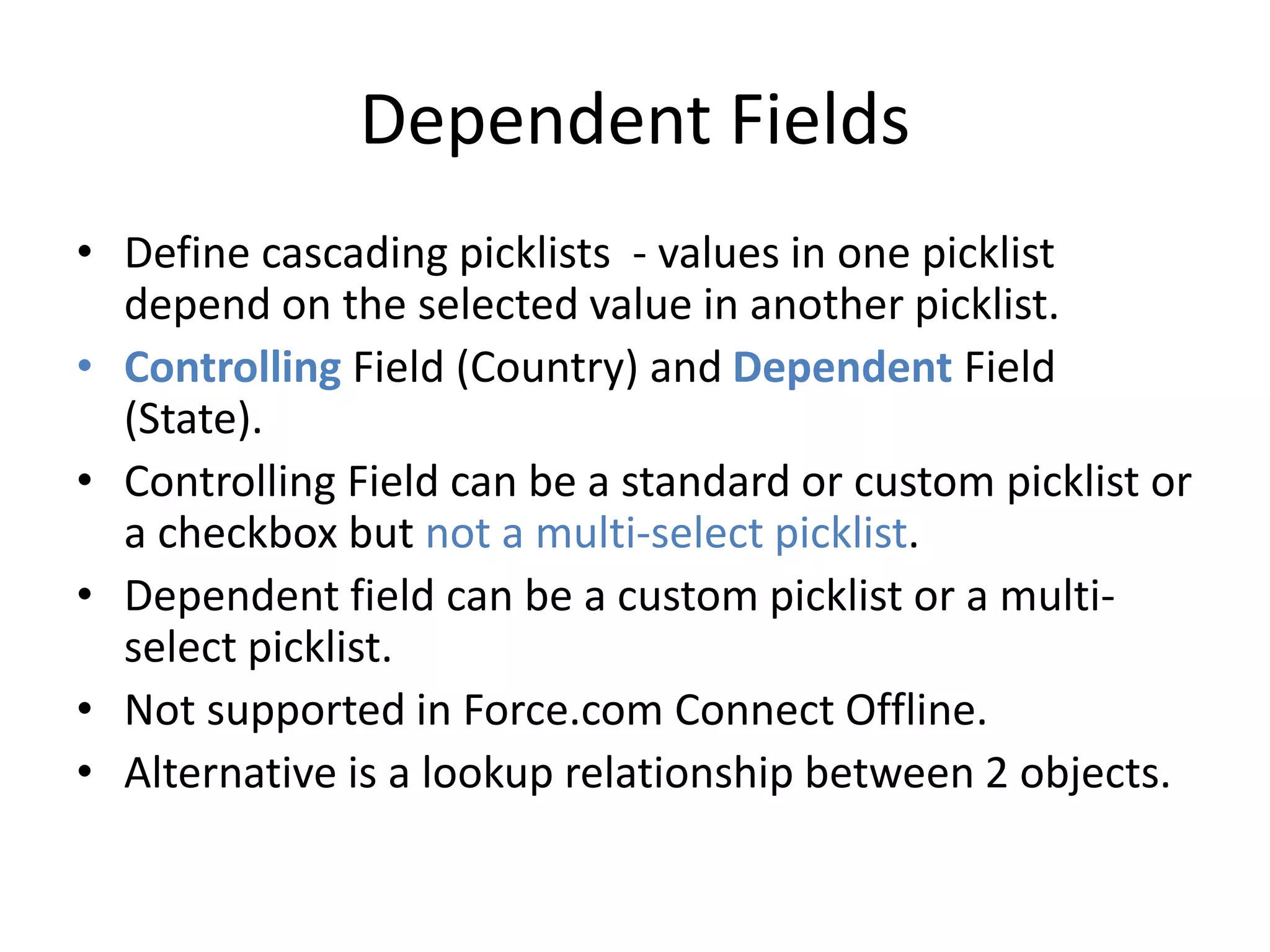
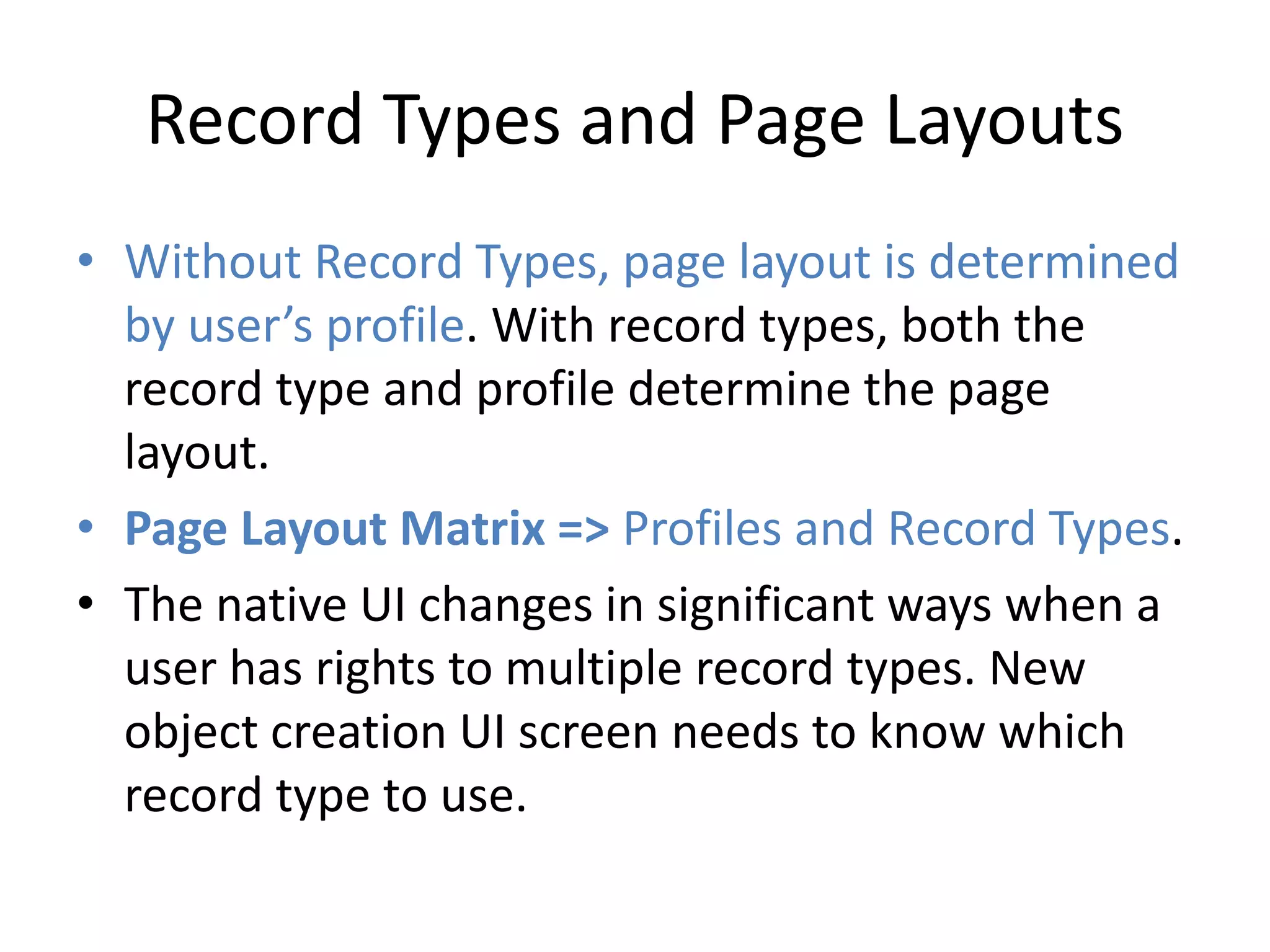
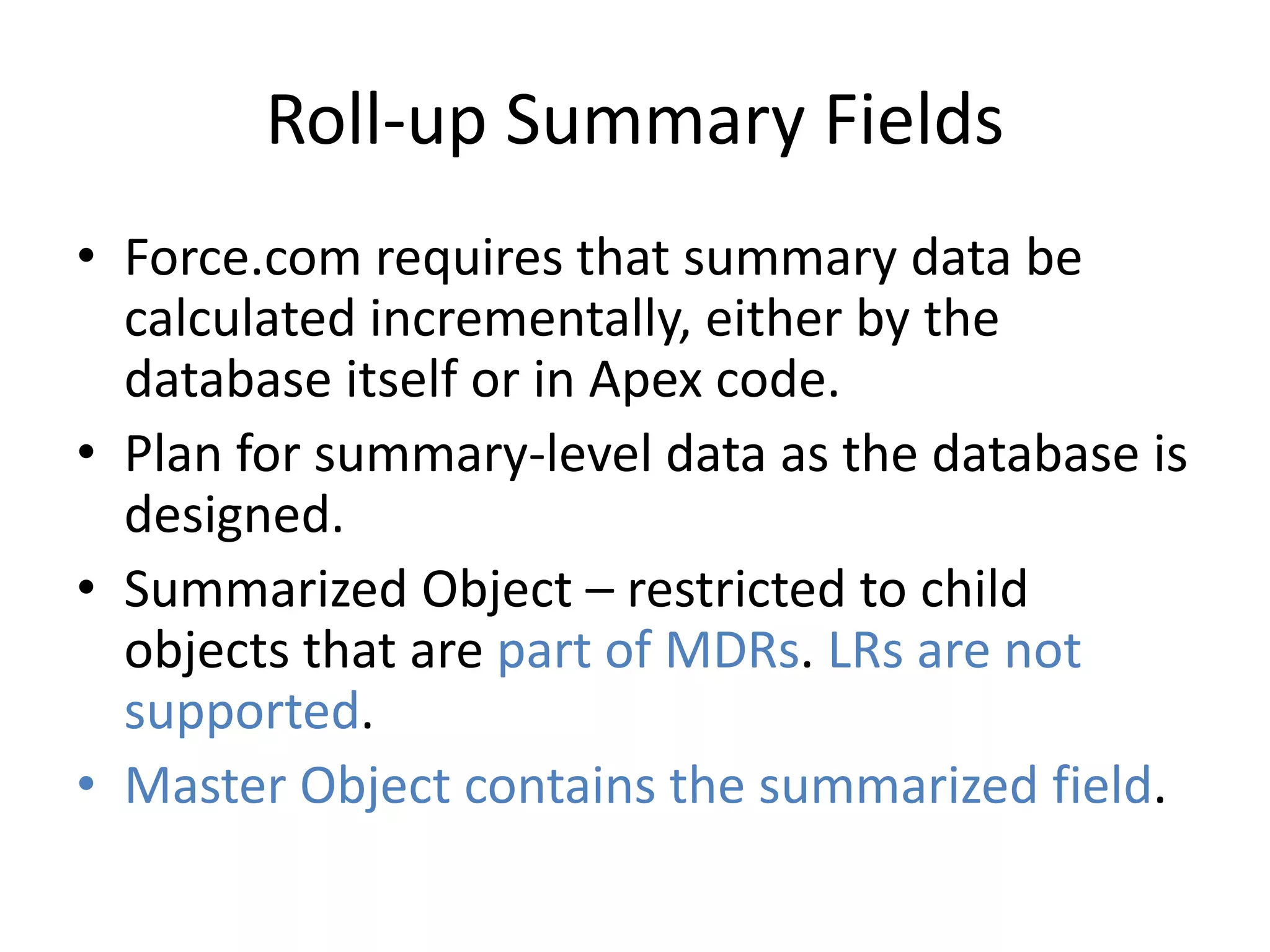
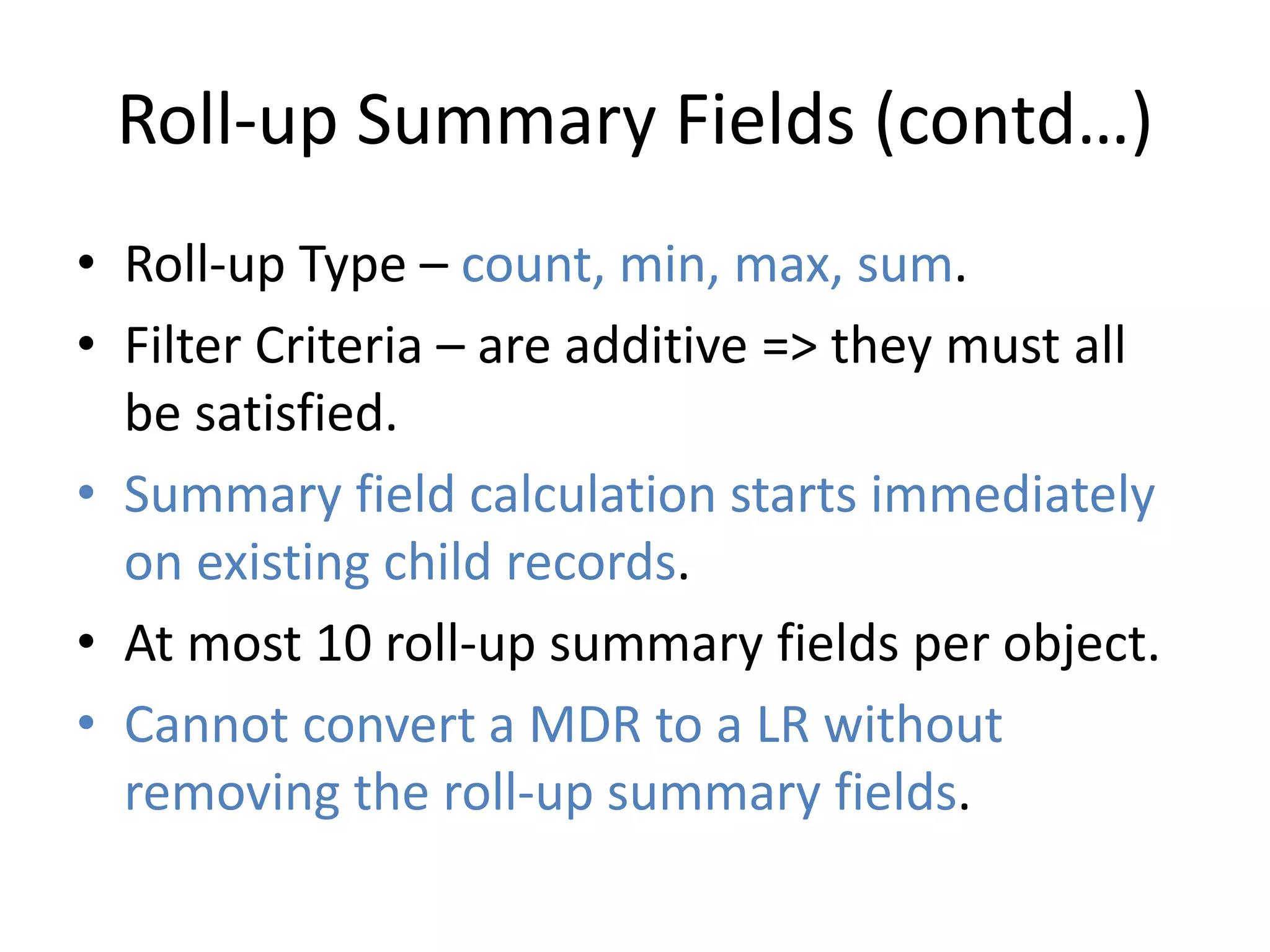
This document summarizes several additional database features in Force.com including dependent fields, record types and security, roll-up summary fields, field history tracking, tags, and connect offline. Dependent fields allow picklist values to depend on other values. Record types customize picklists and user interfaces for different record variations. Roll-up summary fields incrementally calculate summaries on child objects. Field history tracking provides an audit trail for certain fields. Tags and connect offline improve record search and offline data access.