The document provides an introduction to Java programming, highlighting its platform-independent nature and key concepts such as variables, data types, classes, control flow statements, and object-oriented programming principles. It includes example Java programs for tasks like printing 'hello, world!', checking for prime numbers, and reversing strings, as well as discussing Java IDEs and arrays. Additionally, it explains array operations, including declaration, initialization, accessing elements, and finding the longest name in an array.



![TASK-01:
Create a simple "Hello World" program written in Java:
Program:
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, world!");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javainetrnship1-240429174435-e2e41b70/85/JAVA-INETRNSHIP1-made-with-simple-topics-ppt-pptx-4-320.jpg)

![public class PrimeChecker {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 7;
boolean isPrime = true;
if (number <= 1) {
isPrime = false;
} else {
for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(number); i++) {
if (number % i == 0) {
isPrime = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (isPrime) {
System.out.println(number + " is a prime number.");
} else {
System.out.println(number + " is not a prime number.");
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javainetrnship1-240429174435-e2e41b70/85/JAVA-INETRNSHIP1-made-with-simple-topics-ppt-pptx-6-320.jpg)
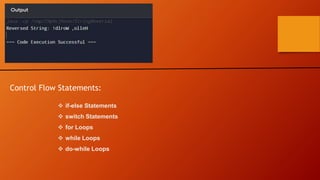
![Task-03:
To create a Reverse a String:
Program:
public class StringReversal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "Hello, World!";
StringBuilder reversed = new StringBuilder(str).reverse();
System.out.println("Reversed String: " + reversed);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javainetrnship1-240429174435-e2e41b70/85/JAVA-INETRNSHIP1-made-with-simple-topics-ppt-pptx-7-320.jpg)



![1.Declaration and Initialization:
To declare an array variable in Java, you specify the element
type followed by square brackets (“[]”).
SYNTAX:
dataType[] arrayName; // Array declaration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javainetrnship1-240429174435-e2e41b70/85/JAVA-INETRNSHIP1-made-with-simple-topics-ppt-pptx-12-320.jpg)
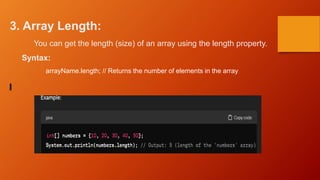
![2. Accessing Array Elements:
Array elements are accessed using an index, which starts
from 0 for the first element.
Syntax:
arrayName[index]; // Accessing the element at the specified index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javainetrnship1-240429174435-e2e41b70/85/JAVA-INETRNSHIP1-made-with-simple-topics-ppt-pptx-13-320.jpg)
![5. Multidimensional Arrays:
Java also supports multidimensional arrays, which are arrays of arrays.
Syntax:
dataType[][] arrayName; // Declaration of a 2D array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javainetrnship1-240429174435-e2e41b70/85/JAVA-INETRNSHIP1-made-with-simple-topics-ppt-pptx-15-320.jpg)
![public class ArrayOperationsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initialize an array of strings (names)
String[] names = {"Alice", "Bob", "Charlie", "David", "Emma"};
// Display all names in the array
System.out.println("All names in the array:");
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
// Find the longest name in the array
String longestName = findLongestName(names);
System.out.println("nThe longest name in the array is: " + longestName);
// Display all names in uppercase
System.out.println("nAll names in uppercase:");
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name.toUpperCase());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javainetrnship1-240429174435-e2e41b70/85/JAVA-INETRNSHIP1-made-with-simple-topics-ppt-pptx-16-320.jpg)
![// Method to find the longest name in an array of strings
public static String findLongestName(String[] names) {
String longestName = "";
for (String name : names) {
if (name.length() > longestName.length()) {
longestName = name;
}
}
return longestName;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javainetrnship1-240429174435-e2e41b70/85/JAVA-INETRNSHIP1-made-with-simple-topics-ppt-pptx-17-320.jpg)
