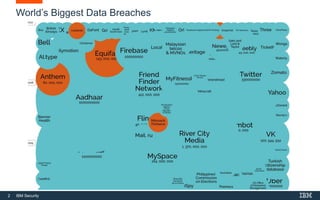
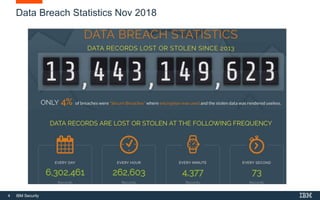
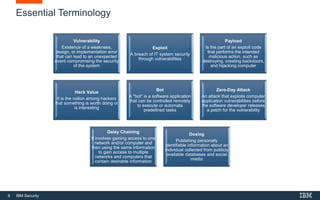
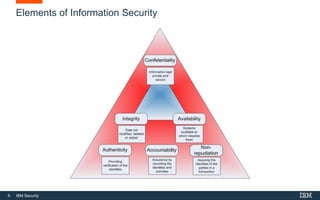
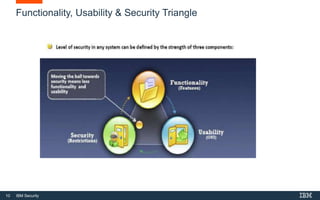
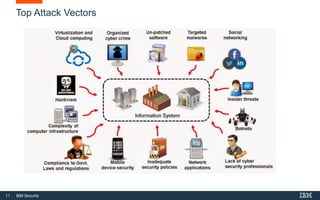
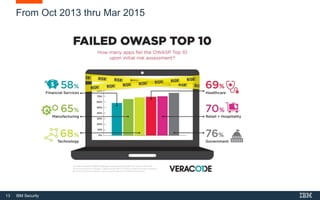
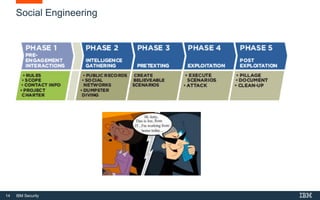
This document provides an overview of hacking fundamentals, including definitions of key terminology, different types of hackers, common attack vectors, and data security laws and regulations. It discusses the history of hacking and different hacking methods. The document also lists free online training resources and recommended videos for learning more about hacking techniques and cybersecurity.