1) Greatest common factors (GCF) and least common multiples (LCM) are important concepts in mathematics. The GCF is the largest integer that divides two or more numbers, while the LCM is the smallest integer that is a multiple of two or more numbers.
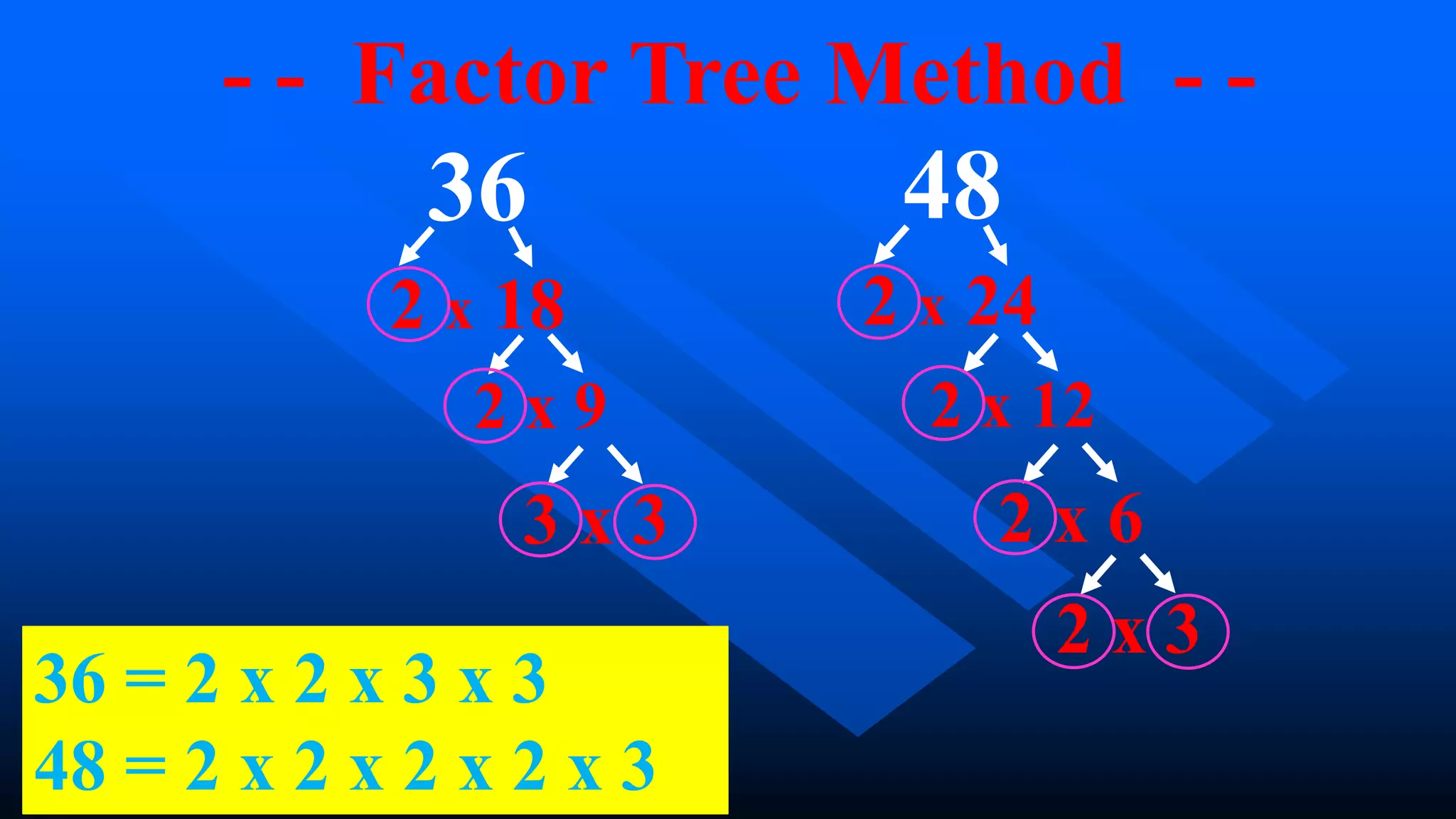
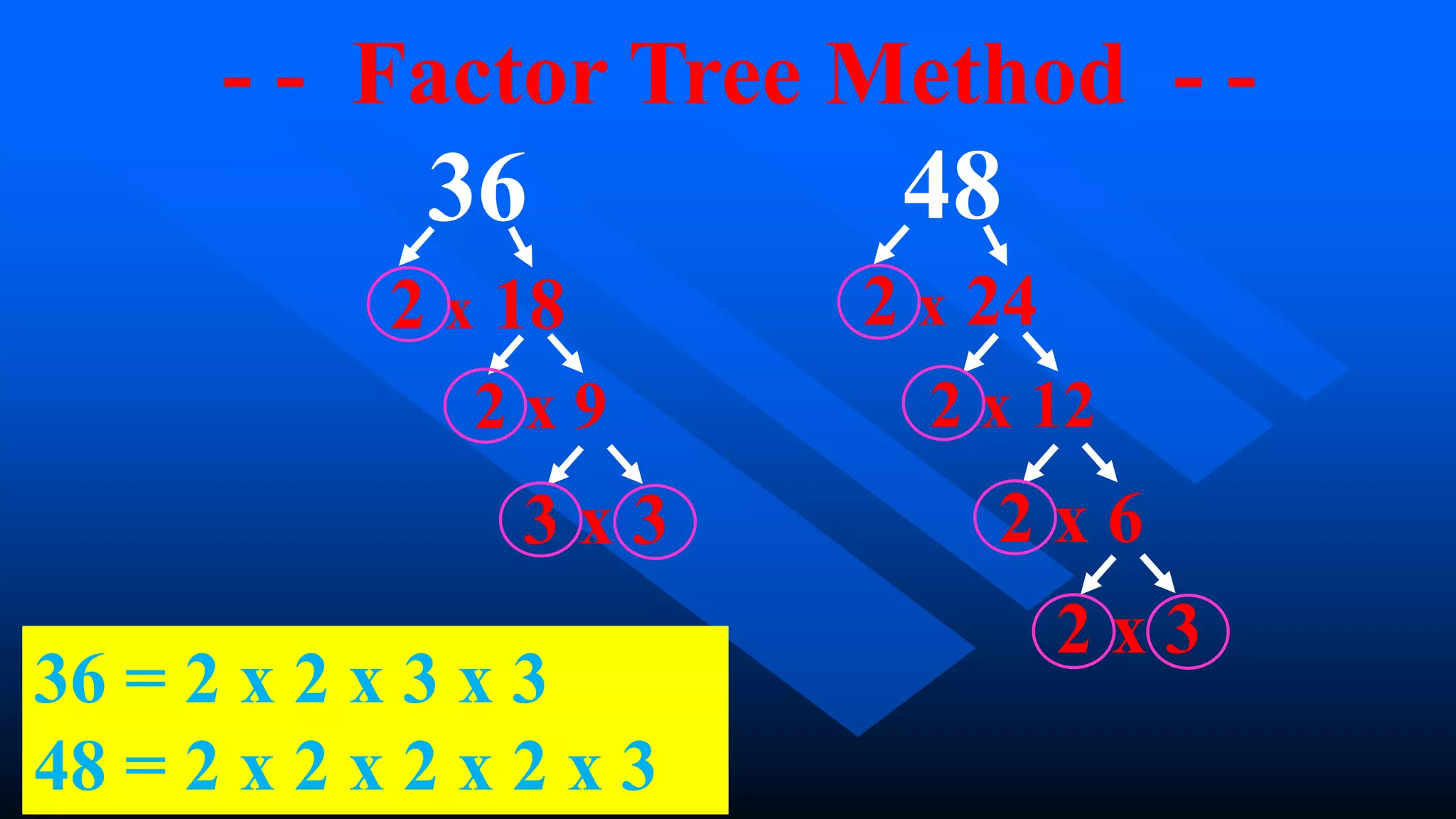
2) There are several methods to find the GCF and LCM, including listing factors, using a factor tree, and continuous division. These methods involve breaking numbers down into their prime factors to identify common factors or multiples.
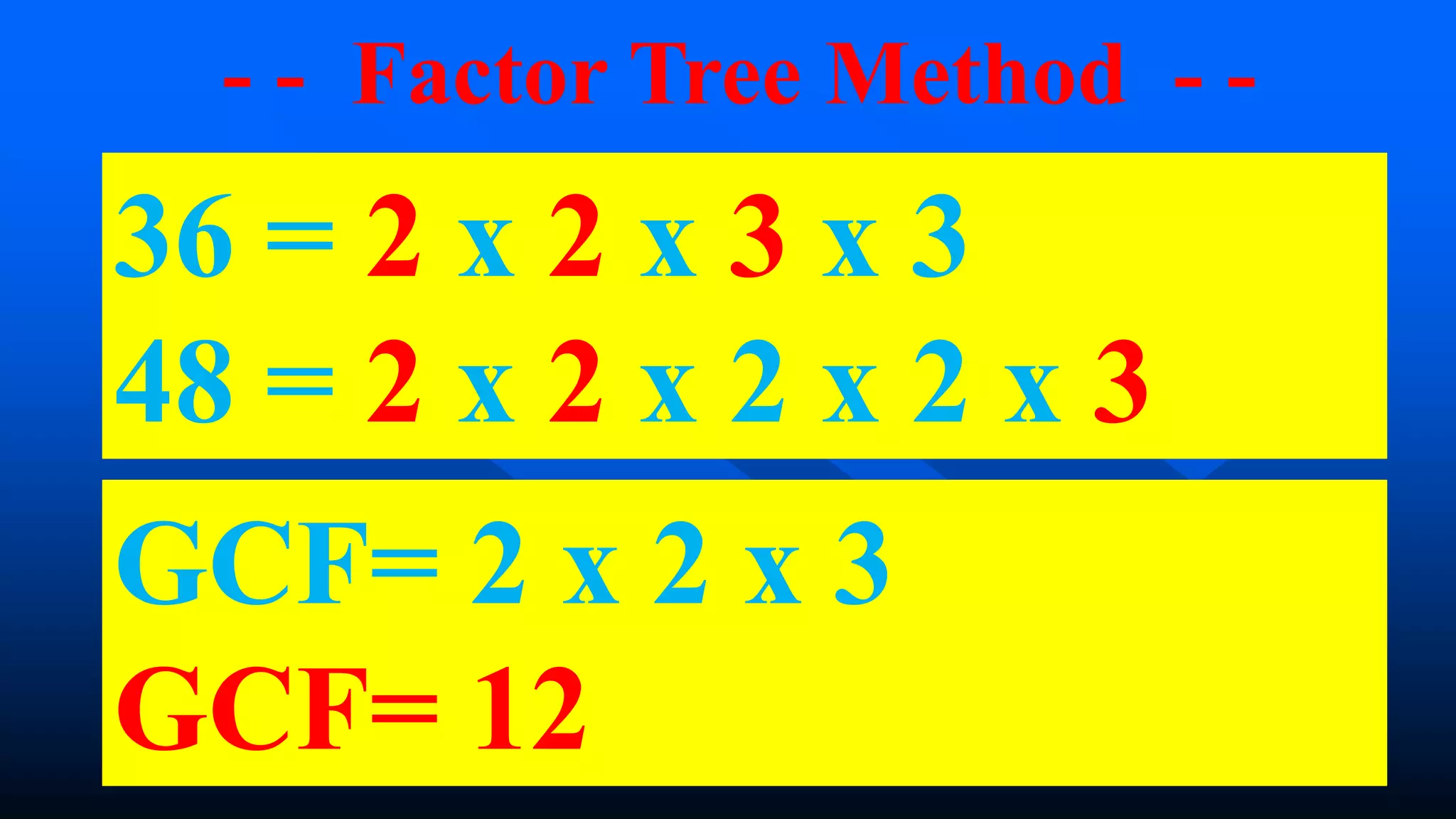
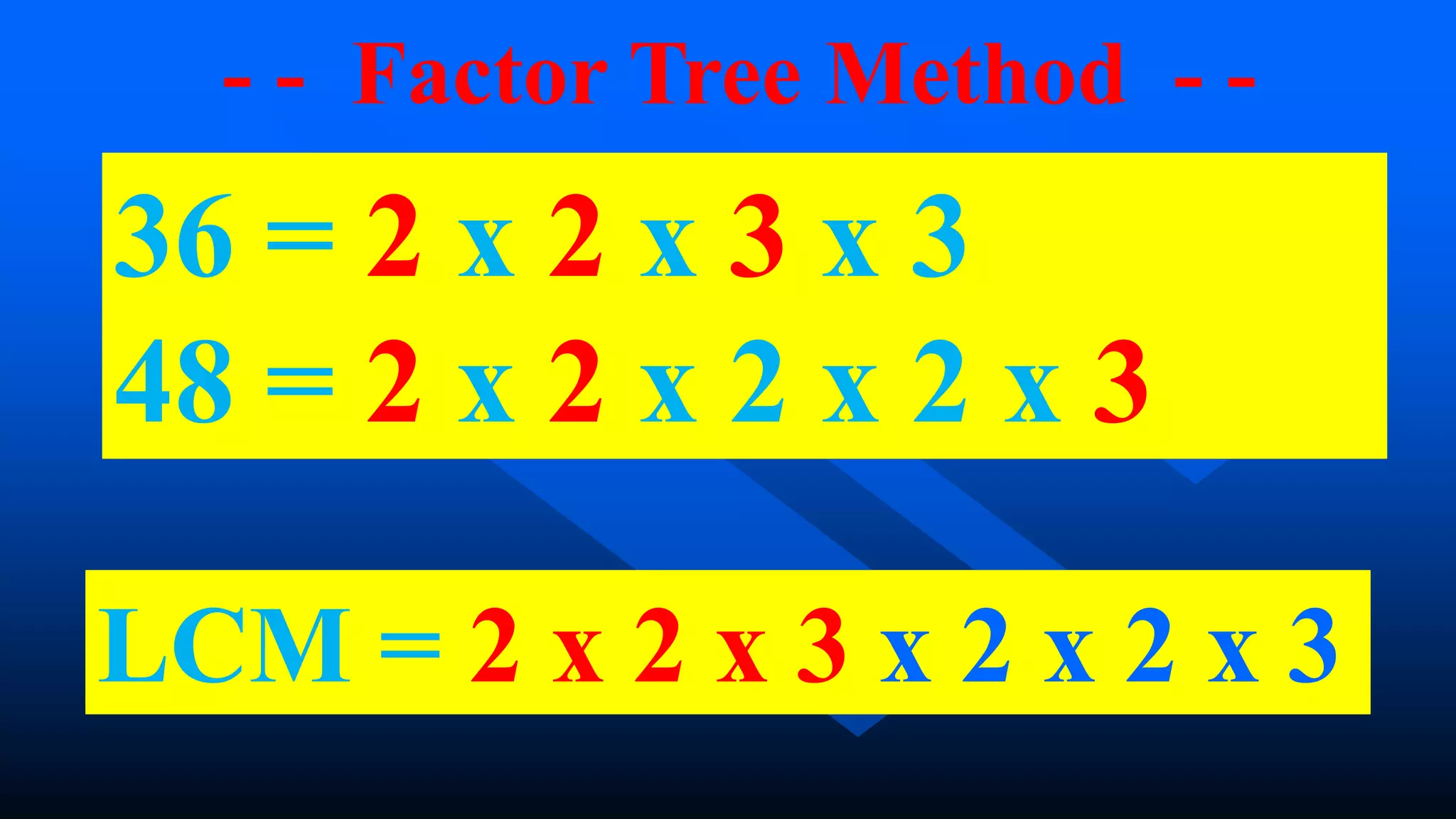
3) For the example of finding the GCF and LCM of 36 and 48, the GCF is 12 and the LCM is 144 using either the factor tree or continuous division methods.