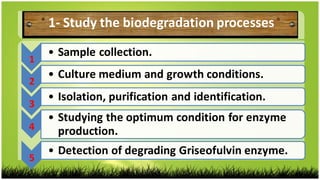
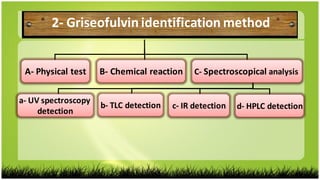
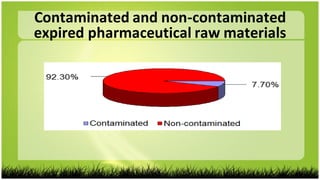
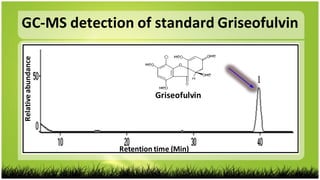
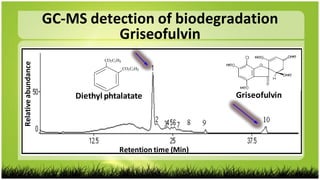
This study investigated the biodegradation of the antifungal drug griseofulvin by Bacillus subtilis isolated from expired pharmaceutical raw materials. Key findings include:
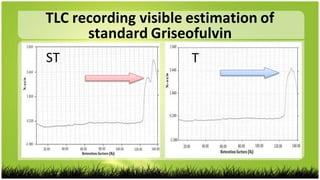
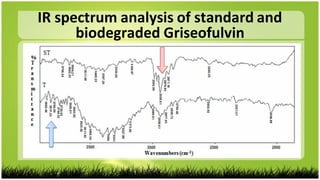
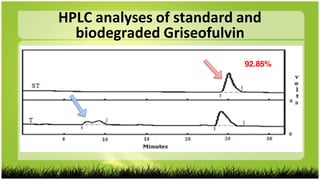
1) B. subtilis was able to degrade griseofulvin as detected by TLC, IR and HPLC analysis of degradation products but not physical/chemical tests.
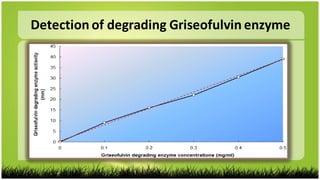
2) The degradation enzyme was purified using column chromatography and identified to have a molecular weight of 5.3439 kDa.
3) Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry identified diethyl phthalate and carbon dioxide as biodegradation products, indicating B. subtilis' ability to metabolize griseofulvin.
4