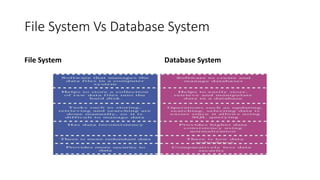
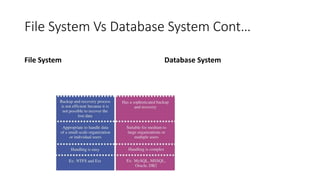
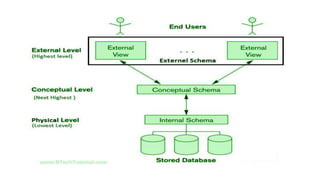
The document provides an overview of database management systems (DBMS), discussing the types of data, differences between file systems and database systems, and the functions of DBMS. It explains data independence, outlining physical and logical data independence along with levels of databases. The document emphasizes the importance of data organization and efficient management for applications in various fields.