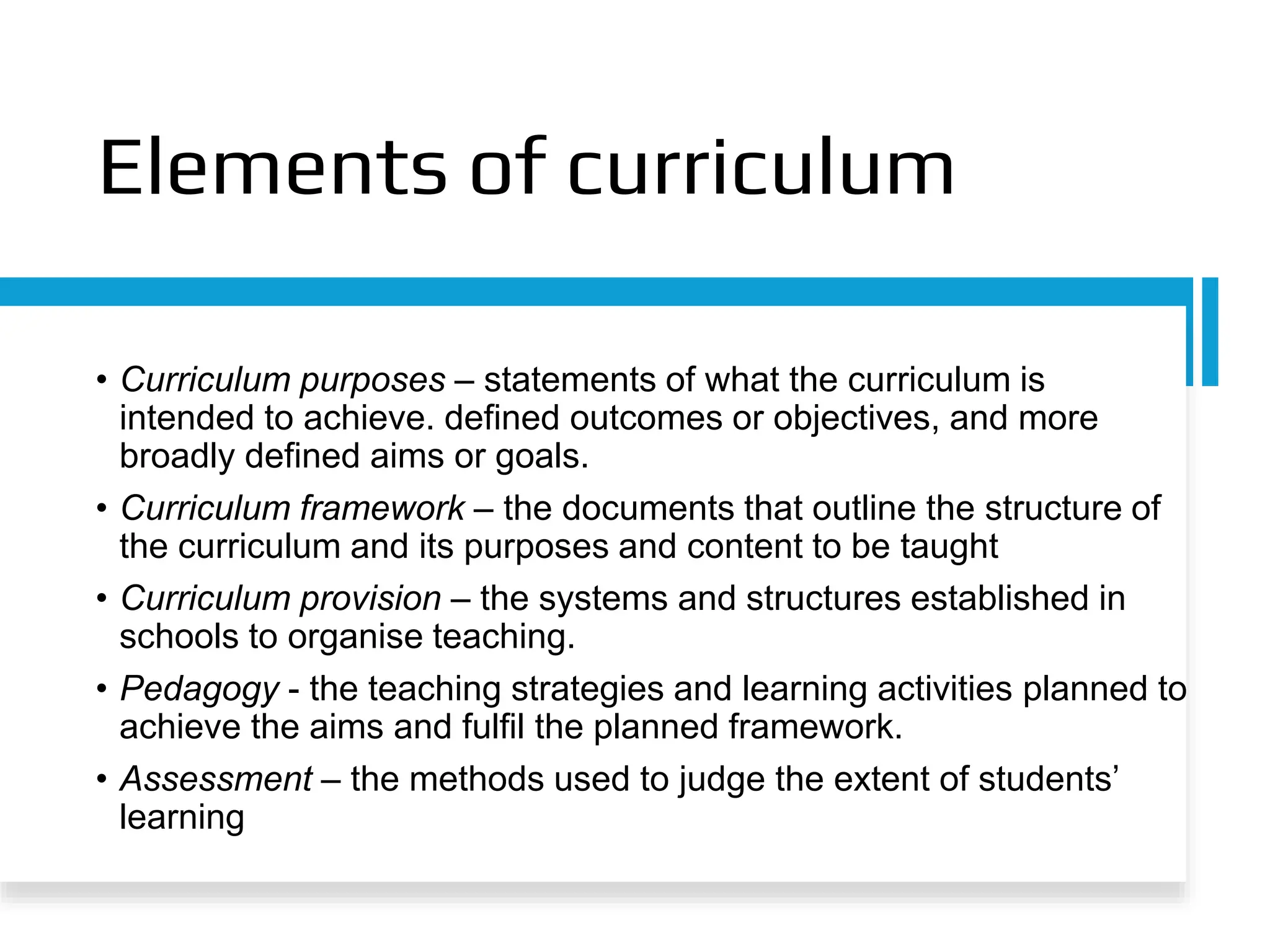
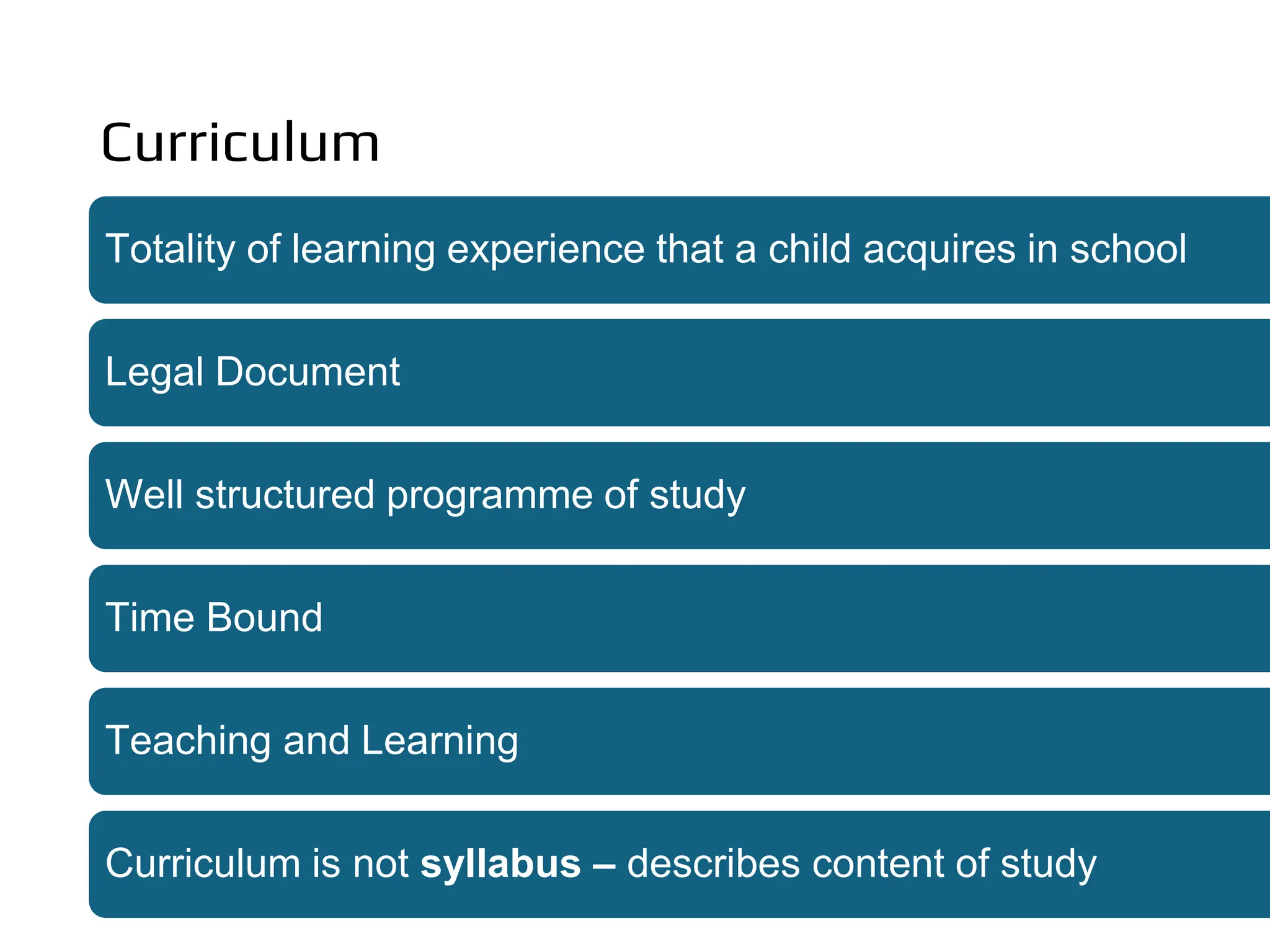
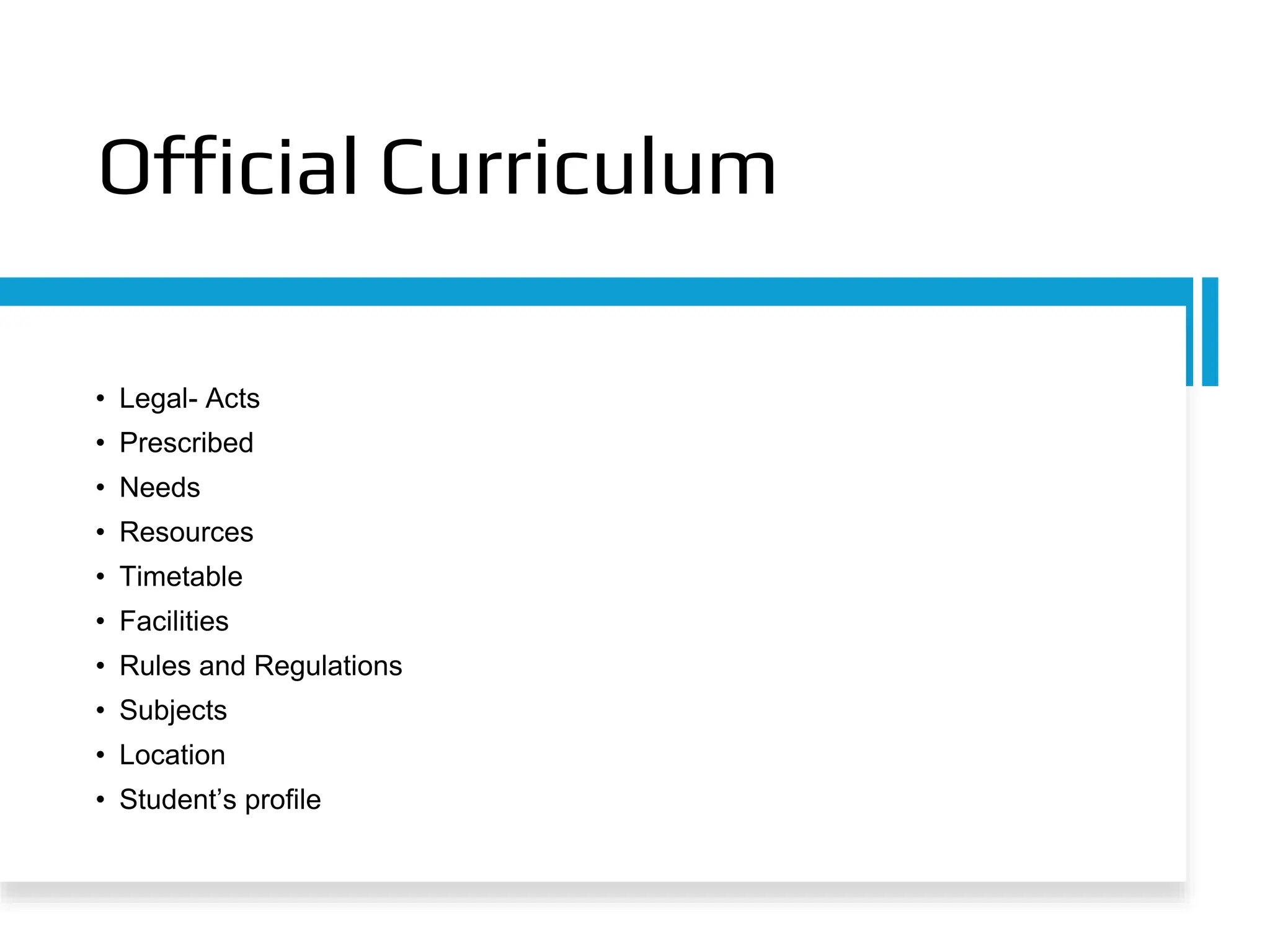
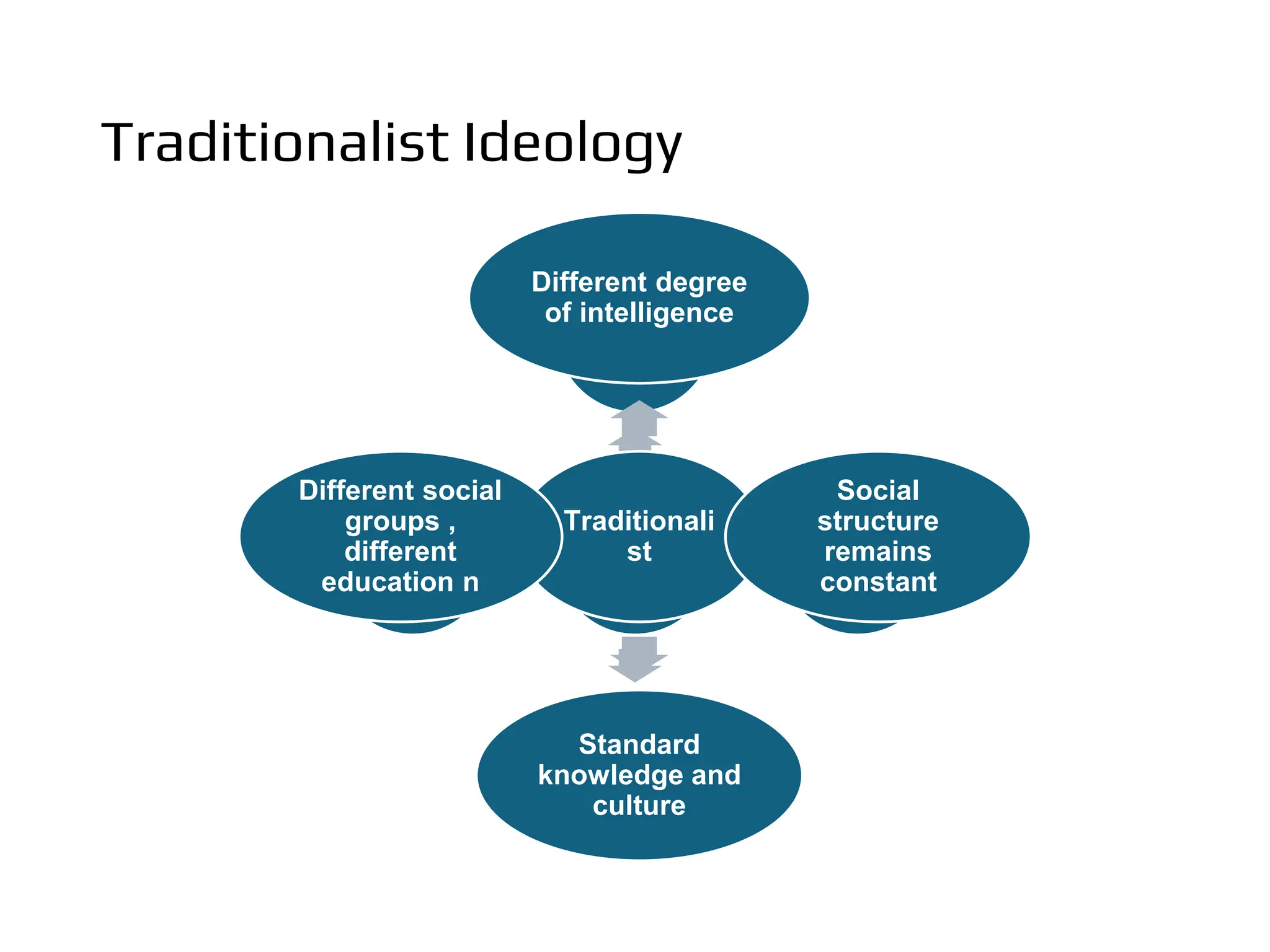
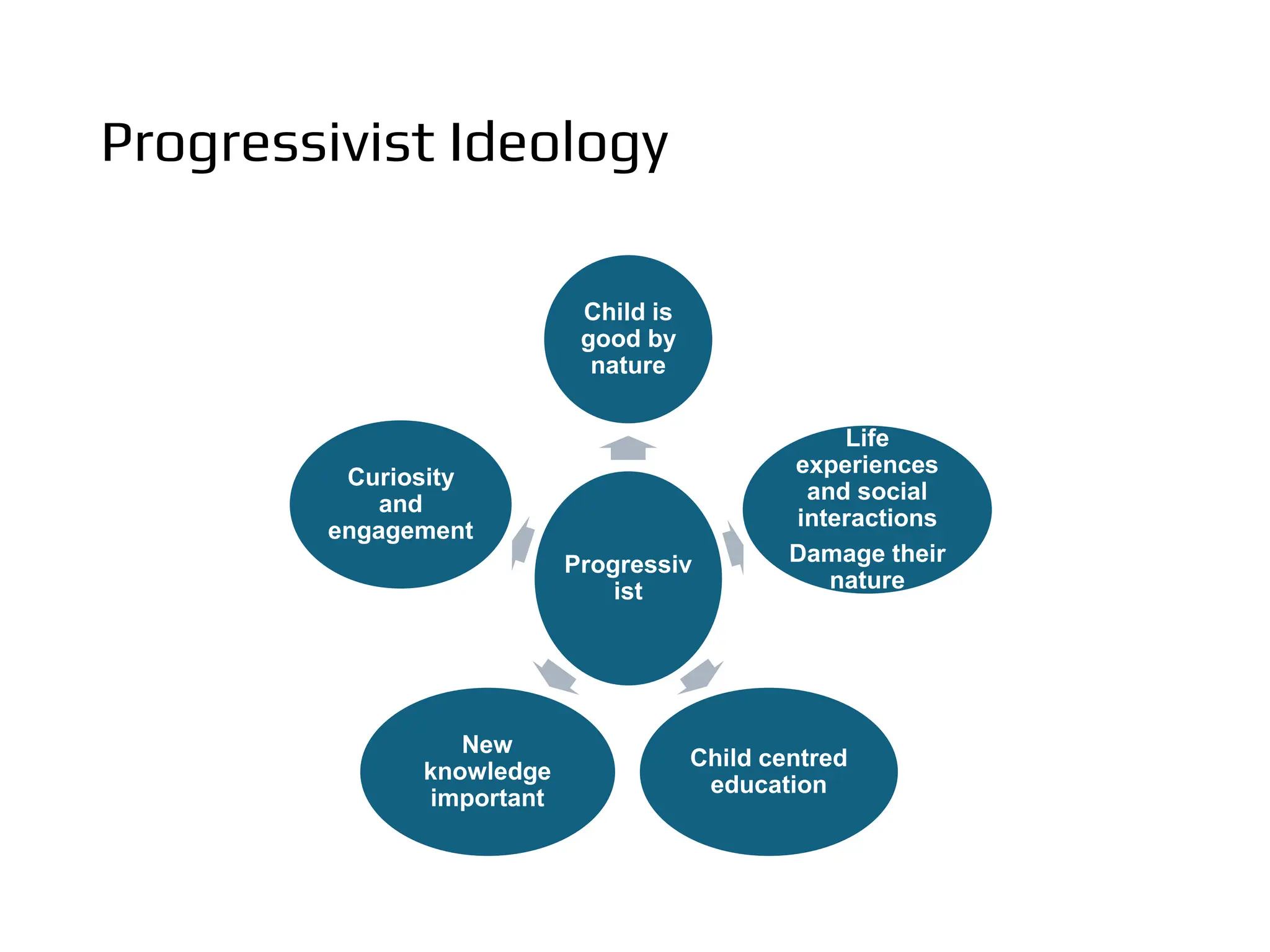
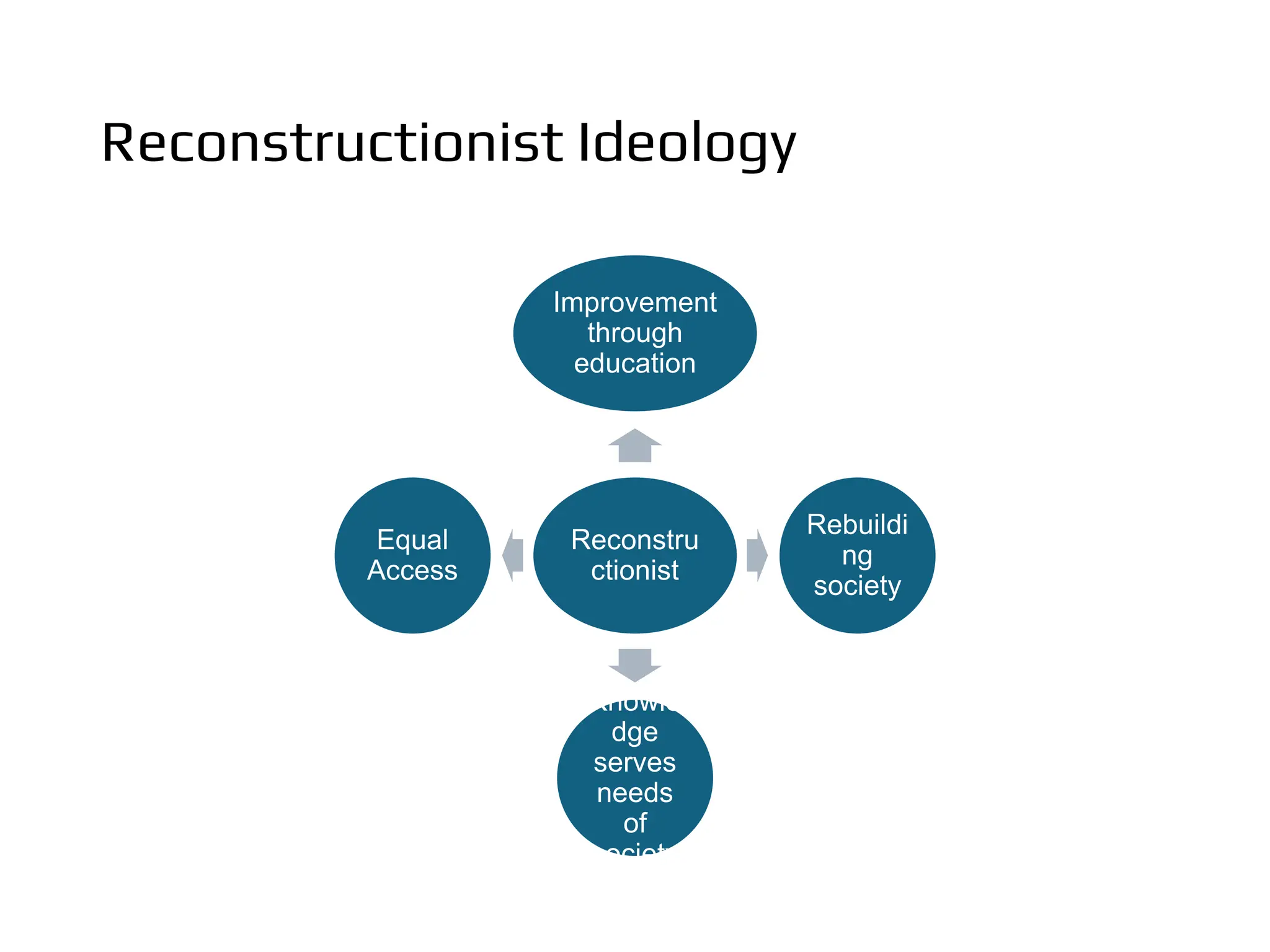
The document discusses the concept of curriculum, defining it as the total structure of ideas and activities designed to meet educational aims and the learning needs of students. It outlines key elements of curriculum, including purposes, framework, provision, pedagogy, and assessment, while also differentiating between the official, taught, hidden, and null curricula. Additionally, it explores various factors influencing curriculum, such as environmental, economic, political, social, pedagogical, philosophical, psychological, and sociological factors.