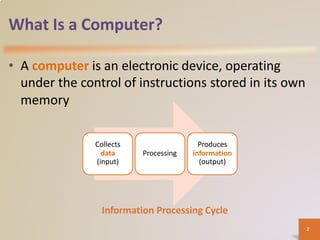
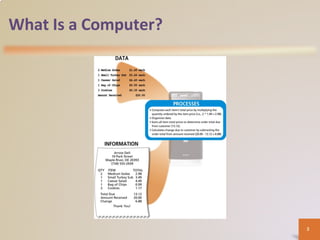
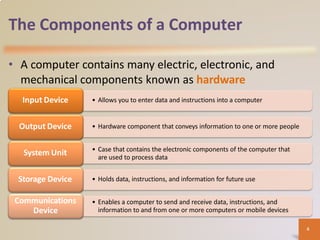
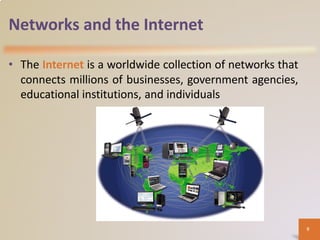
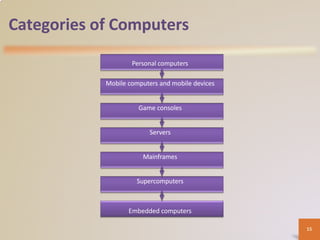
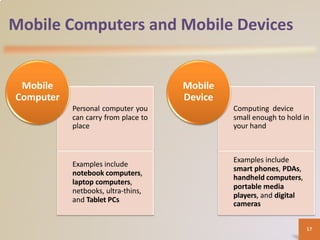
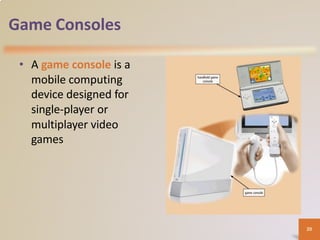
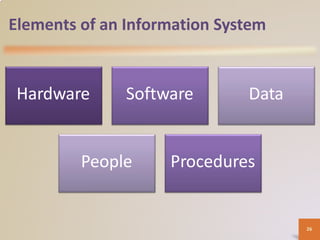
A computer is an electronic device that processes data according to stored instructions. It has hardware components like an input device, output device, system unit, storage device, and communications device. There are advantages like speed and reliability, but also disadvantages such as health risks and environmental impact. Computers connect to networks and the internet for communication, research, and entertainment. Different types of computers include personal computers, mobile devices, servers, mainframes, and embedded computers used in various applications to benefit society.