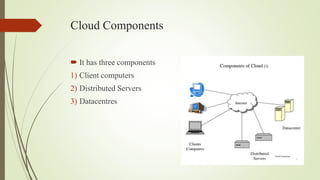
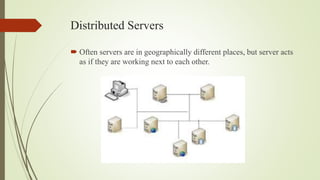
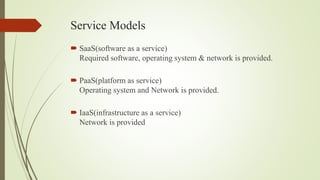
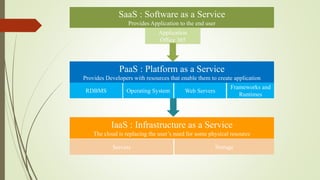
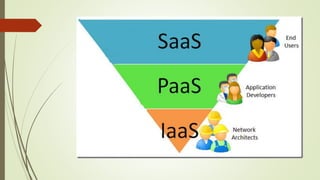
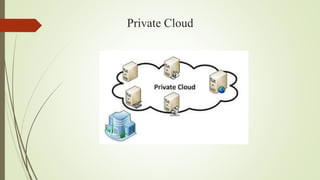
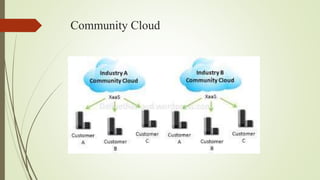
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, explaining it as using the internet to access software and hardware located in data centers, along with its advantages such as cost savings, scalability, and security improvements. It also discusses potential disadvantages, including downtime, security risks, vendor lock-in, and reduced control over infrastructure. Various cloud service models and implementation types, such as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, are outlined, along with the distinctions between public, private, community, and hybrid clouds.