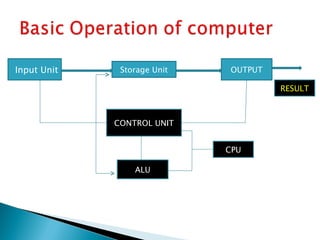
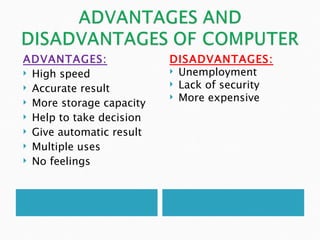
Charles Babbage designed the Analytical Engine in the 19th century, laying the foundations for modern computers. A computer is an electronic device that processes data according to a set of instructions in order to calculate or acquire, process, and store data and information. Key components include the hardware, software, central processing unit, arithmetic logic unit, control unit, input and output units, and storage. Computers have evolved through five generations from vacuum tubes to integrated circuits and microprocessors. They are now widely used for banking, education, entertainment, transportation and more due to their speed, accuracy, storage capacity and ability to make decisions.