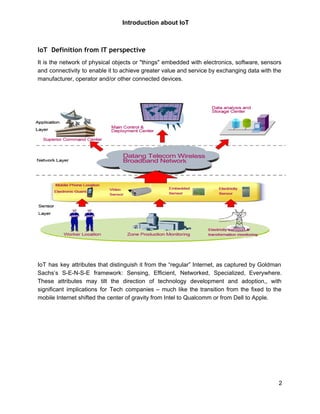
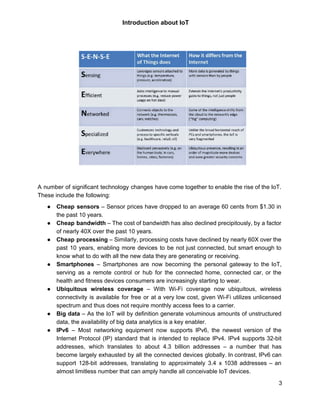
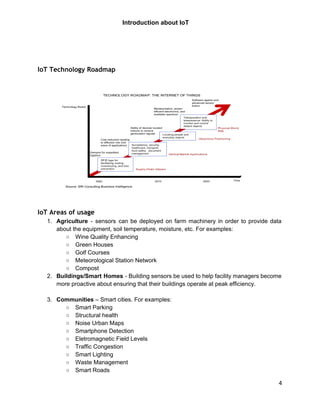
The document provides an introduction to the Internet of Things (IoT). It defines IoT as connecting physical objects via sensors to the internet, allowing data exchange without human interaction. Key enablers of IoT include cheap sensors, bandwidth, processing power, smartphones, and wireless coverage. Common applications areas are agriculture, smart homes, cities, manufacturing, and healthcare. The document outlines an IoT technology roadmap and lists resources for IoT products, services, companies and labs.