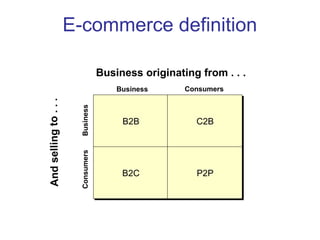
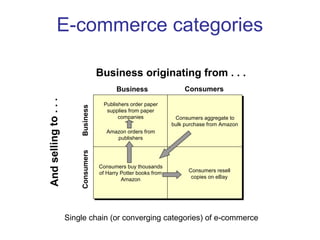
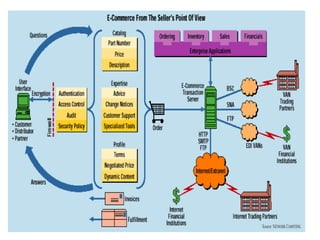
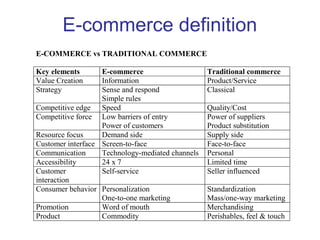
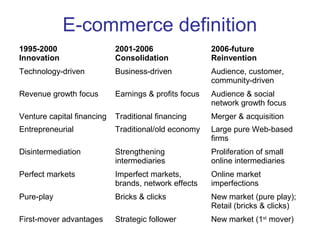
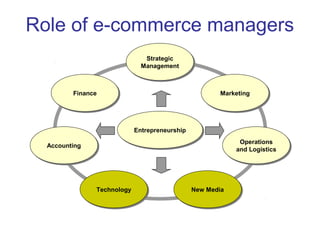
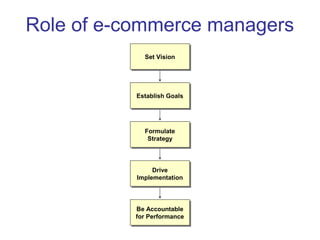
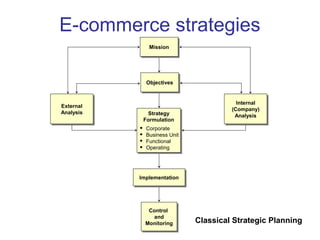
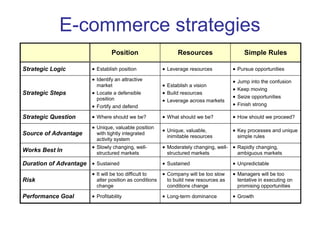
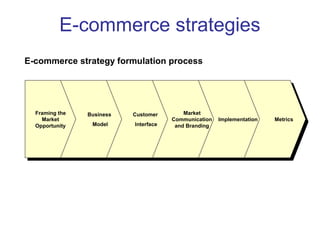
The document discusses e-commerce strategies. It defines e-commerce as technology-enabled transactions and technology-mediated exchanges between parties. It discusses different types of e-commerce like B2B, B2C, etc. It outlines the objectives of understanding what e-commerce is, the challenges of e-commerce, and strategies for e-commerce. It then discusses different strategies like positioning, leveraging resources, and using simple rules. It provides examples of how companies implement different strategic approaches and the goals of each approach.